自己写了个 RPC ,真牛逼!
点击上方蓝色字体,选择“标星公众号”
优质文章,第一时间送达
RPC(remote procedure call)远程过程调用
RPC是为了在分布式应用中,两台主机的Java进程进行通信,当A主机调用B主机的方法时,过程简洁,就像是调用自己进程里的方法一样。
RPC框架的职责就是,封装好底层调用的细节,客户端只要调用方法,就能够获取服务提供者的响应,方便开发者编写代码。
RPC底层使用的是TCP协议,服务端和客户端和点对点通信。
作用
在RPC的应用场景中,客户端调用服务端的代码
客户端需要有相应的api接口,将方法名、方法参数类型、具体参数等等都发送给服务端
服务端需要有方法的具体实现,在接收到客户端的请求后,根据信息调用对应的方法,并返回响应给客户端

流程图演示
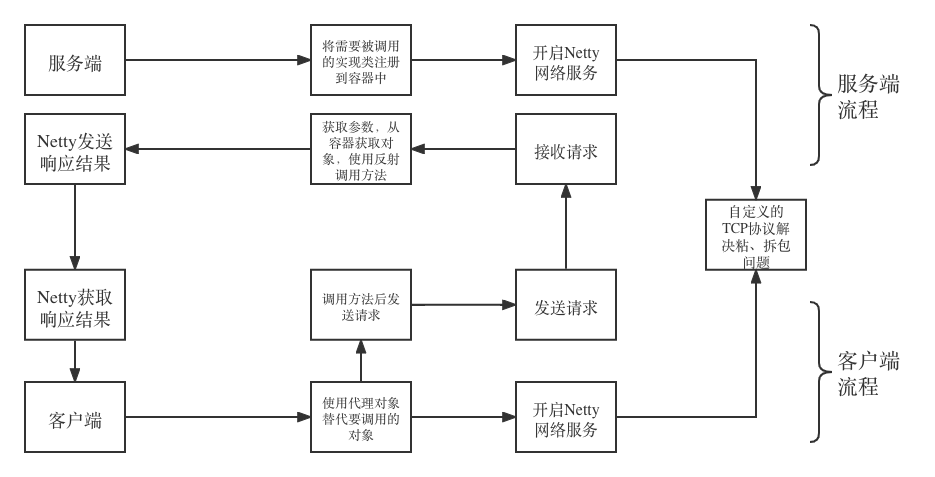
代码实现
首先客户端要知道服务端的接口,然后封装一个请求对象,发送给服务端
要调用一个方法需要有:方法名、方法参数类型、具体参数、执行方法的类名
@Data
public class RpcRequest {
private String methodName;
private String className;
private Class[] paramType;
private Object[] args;
}
由服务端返回给客户端的响应(方法调用结果)也使用一个对象进行封装
@Data
public class RpcResponse {
private int code;
private Object result;
}
如果是在多线程调用中,需要具体把每个响应返回给对应的请求,可以加一个ID进行标识
将对象通过网络传输,需要先进行序列化操作,这里使用的是jackson工具
com.fasterxml.jackson.core
jackson-databind
2.11.4
public class JsonSerialization {
private static ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
static {
objectMapper.setSerializationInclusion(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL);
objectMapper.disable(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATE_KEYS_AS_TIMESTAMPS);
objectMapper.disable(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS);
objectMapper.setDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
objectMapper.disable(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES);
}
public static byte[] serialize(Object output) throws JsonProcessingException {
byte[] bytes = objectMapper.writeValueAsBytes(output);
return bytes;
}
public static Object deserialize(byte[] input,Class clazz) throws IOException {
Object parse = objectMapper.readValue(input,clazz);
return parse;
}
}在反序列化过程中,需要指定要转化的类型,而服务端接收request,客户端接收response,二者类型是不一样的,所以在后续传输时指定类型
有了需要传输的数据后,使用Netty开启网络服务进行传输
服务端
绑定端口号,开启连接
public class ServerNetty {
public static void connect(int port) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.group(bossGroup,workGroup)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
/**
* 加入自定义协议的数据处理器,指定接收到的数据类型
* 加入服务端处理器
*/
ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyProtocolHandler(RpcRequest.class));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
});
bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
}
}
Netty中绑定了两个数据处理器
一个是数据处理器,服务端接收到请求->调用方法->返回响应,这些过程都在数据处理器中执行
public class ServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
RpcRequest rpcRequest = (RpcRequest)msg;
// 获取使用反射需要的各个参数
String methodName = rpcRequest.getMethodName();
Class[] paramTypes = rpcRequest.getParamType();
Object[] args = rpcRequest.getArgs();
String className = rpcRequest.getClassName();
//从注册中心容器中获取对象
Object object = Server.hashMap.get(className);
Method method = object.getClass().getMethod(methodName,paramTypes);
//反射调用方法
String result = (String) method.invoke(object,args);
// 将响应结果封装好后发送回去
RpcResponse rpcResponse = new RpcResponse();
rpcResponse.setCode(200);
rpcResponse.setResult(result);
ctx.writeAndFlush(rpcResponse);
}
}
这里从hash表中获取对象,有一个预先进行的操作:将有可能被远程调用的对象放入容器中,等待使用
一个是自定义的TCP协议处理器,为了解决TCP的常见问题:因为客户端发送的数据包和服务端接收数据缓冲区之间,大小不匹配导致的粘包、拆包问题。
/**
* 网络传输的自定义TCP协议
* 发送时:为传输的字节流添加两个魔数作为头部,再计算数据的长度,将数据长度也添加到头部,最后才是数据
* 接收时:识别出两个魔数后,下一个就是首部,最后使用长度对应的字节数组接收数据
*/
public class NettyProtocolHandler extends ChannelDuplexHandler {
private static final byte[] MAGIC = new byte[]{0x15,0x66};
private Class decodeType;
public NettyProtocolHandler() {
}
public NettyProtocolHandler(Class decodeType){
this.decodeType = decodeType;
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf in = (ByteBuf) msg;
//接收响应对象
Object dstObject;
byte[] header = new byte[2];
in.readBytes(header);
byte[] lenByte = new byte[4];
in.readBytes(lenByte);
int len = ByteUtils.Bytes2Int_BE(lenByte);
byte[] object = new byte[len];
in.readBytes(object);
dstObject = JsonSerialization.deserialize(object, decodeType);
//交给下一个数据处理器
ctx.fireChannelRead(dstObject);
}
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.buffer();
//写入魔数
byteBuf.writeBytes(MAGIC);
byte[] object = JsonSerialization.serialize(msg);
//数据长度转化为字节数组并写入
int len = object.length;
byte[] bodyLen = ByteUtils.int2bytes(len);
byteBuf.writeBytes(bodyLen);
//写入对象
byteBuf.writeBytes(object);
ctx.writeAndFlush(byteBuf);
}
}
这个数据处理器是服务端和客户端都要使用的,就相当于是一个双方定好传输数据要遵守的协议
在这里进行了对象的序列化和反序列化,所以反序列化类型在这个处理器中指定
这里面要将数据的长度发送,需一个将整数类型转化为字节类型的工具
转化数据工具类
public class ByteUtils {
/** short2\u5B57\u8282\u6570\u7EC4 */
public static byte[] short2bytes(short v) {
byte[] b = new byte[4];
b[1] = (byte) v;
b[0] = (byte) (v >>> 8);
return b;
}
/** int4\u5B57\u8282\u6570\u7EC4 */
public static byte[] int2bytes(int v) {
byte[] b = new byte[4];
b[3] = (byte) v;
b[2] = (byte) (v >>> 8);
b[1] = (byte) (v >>> 16);
b[0] = (byte) (v >>> 24);
return b;
}
/** long8\u5B57\u8282\u6570\u7EC4 */
public static byte[] long2bytes(long v) {
byte[] b = new byte[8];
b[7] = (byte) v;
b[6] = (byte) (v >>> 8);
b[5] = (byte) (v >>> 16);
b[4] = (byte) (v >>> 24);
b[3] = (byte) (v >>> 32);
b[2] = (byte) (v >>> 40);
b[1] = (byte) (v >>> 48);
b[0] = (byte) (v >>> 56);
return b;
}
/** \u5B57\u8282\u6570\u7EC4\u8F6C\u5B57\u7B26\u4E32 */
public static String bytesToHexString(byte[] bs) {
if (bs == null || bs.length == 0) {
return null;
}
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
String tmp = null;
for (byte b : bs) {
tmp = Integer.toHexString(Byte.toUnsignedInt(b));
if (tmp.length() < 2) {
sb.append(0);
}
sb.append(tmp);
}
return sb.toString();
}
/**
* @return
*/
public static int Bytes2Int_BE(byte[] bytes) {
if(bytes.length < 4){
return -1;
}
int iRst = (bytes[0] << 24) & 0xFF;
iRst |= (bytes[1] << 16) & 0xFF;
iRst |= (bytes[2] << 8) & 0xFF;
iRst |= bytes[3] & 0xFF;
return iRst;
}
/**
* long\u8F6C8\u5B57\u8282\u6570\u7EC4
*/
public static long bytes2long(byte[] b) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(8);
buffer.put(b, 0, b.length);
buffer.flip();// need flip
return buffer.getLong();
}
}
客户端
将Netty的操作封装了起来,最后返回一个Channle类型,由它进行发送数据的操作
public class ClientNetty {
public static Channel connect(String host,int port) throws InterruptedException {
InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(host,port);
EventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.group(workGroup)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//自定义协议handler(客户端接收的是response)
ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyProtocolHandler(RpcResponse.class));
//处理数据handler
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ClientHandler());
}
});
Channel channel = bootstrap.connect(address).sync().channel();
return channel;
}
}
数据处理器负责接收response,并将响应结果放入在future中,future的使用在后续的动态代理中
public class ClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
RpcResponse rpcResponse = (RpcResponse) msg;
//服务端正常情况返回码为200
if(rpcResponse.getCode() != 200){
throw new Exception();
}
//将结果放到future里
RPCInvocationHandler.future.complete(rpcResponse.getResult());
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
super.exceptionCaught(ctx, cause);
}
}
要让客户端在调用远程方法时像调用本地方法一样,就需要一个代理对象,供客户端调用,让代理对象去调用服务端的实现。
代理对象构造
public class ProxyFactory {
public static Object getProxy(Class[] interfaces){
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(ProxyFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new RPCInvocationHandler());
}
}
客户端代理对象的方法执行
将request发送给服务端后,一直阻塞,等到future里面有了结果为止。
public class RPCInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
static public CompletableFuture future;
static Channel channel;
static {
future = new CompletableFuture();
//开启netty网络服务
try {
channel = ClientNetty.connect("127.0.0.1",8989);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
RpcRequest rpcRequest = new RpcRequest();
rpcRequest.setArgs(args);
rpcRequest.setMethodName(method.getName());
rpcRequest.setParamType(method.getParameterTypes());
rpcRequest.setClassName(method.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName());
channel.writeAndFlush(rpcRequest);
//一个阻塞操作,等待网络传输的结果
String result = (String) future.get();
return result;
}
}
这里用static修饰future和channle,没有考虑到客户端去连接多个服务端和多次远程调用
可以使用一个hash表,存储与不同服务端对应的channle,每次调用时从hash表中获取即可
用hash表存储与不同request对应的future,每个响应的结果与之对应
客户端
要进行远程调用需要拥有的接口
public interface OrderService {
public String buy();
}预先的操作和测试代码
public class Client {
static OrderService orderService;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//创建一个代理对象给进行远程调用的类
orderService = (OrderService) ProxyFactory.getProxy(new Class[]{OrderService.class});
String result = orderService.buy();
System.out.println(result);
}
}
服务端
要接受远程调用需要拥有的具体实现类
public class OrderImpl implements OrderService {
public OrderImpl() {
}
@Override
public String buy() {
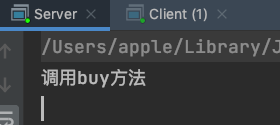
System.out.println("调用buy方法");
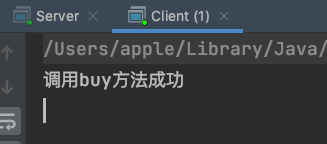
return "调用buy方法成功";
}
}
预先操作和测试代码
public class Server {
public static HashMap hashMap = new HashMap<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//开启netty网络服务
ServerNetty.connect(8989);
//提前将需要开放的服务注册到hash表中
hashMap.put("OrderService",new OrderImpl());
}
}
执行结果
作者 | 划水的鱼dm
来源 | cnblogs.com/davidFB/p/15481823.html

