.NET6中全局异常处理
微信公众号:趣编程ACE
关注可了解每日一更的.NET日常实战开发技巧,欢迎公众号留言开发 获取源码;
.NET6中全局异常处理
异常处理是我们在程序开发中不可或缺的一环,下文我将会结合程序Sample讲解如何在.NET6中有效处理异常。
Try-Ctach 块包裹
自定义异常中间件
Try-Catch 块
Try-Catch 是最基本的异常处理方法,下面我们看下例子。
创建一个基于.net6的Asp.Net Core Web Api项目
1using ExceptionHandling.Services;
2using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
3namespace ExceptionHandling.Controllers;
4
5[ApiController]
6[Route("api/[controller]")]
7public class UserController : Controller
8{
9 private readonly IUserService _userService;
10 private readonly ILogger _logger;
11
12 ///
13 /// 依赖注入 IUserService ILogger
14 ///
15 ///
16 ///
17 public UserController(IUserService userService, ILogger logger )
18 {
19 _userService = userService;
20 _logger = logger;
21 }
22
23 [HttpGet]
24 public IActionResult GetUsers()
25 {
26
27 try
28 {
29 _logger.LogInformation("Get User Details");
30
31 var result = _userService.GetUsers();
32 if(result.Count==0)
33 throw new ApplicationException("Get User failed"); // 此处抛出一个获取用户出错异常
34
35 return Ok(result);
36 }
37 catch (System.Exception e)
38 {
39 _logger.LogError(e.Message);
40 return BadRequest("获取失败"); // 返回给前端
41 }
42 }
43}
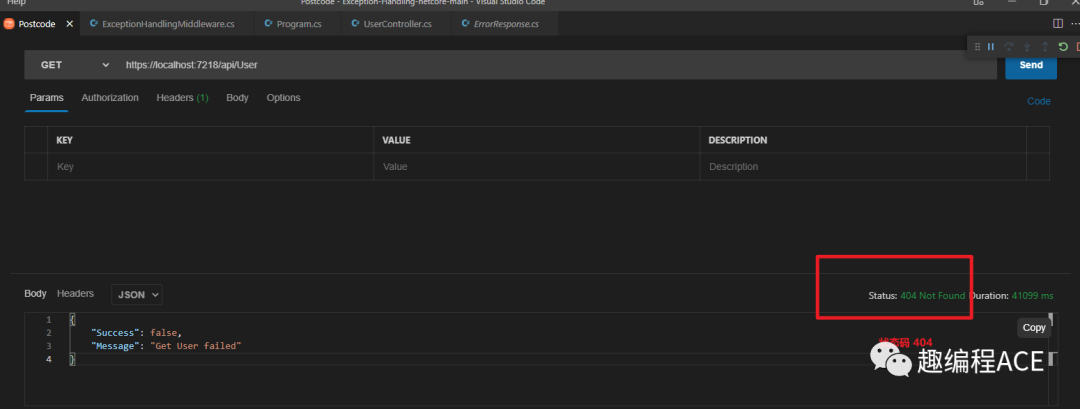
我们在VsCode里面按照一个Postman插件PostCode 调用上面接口https://localhost:7218/api/User
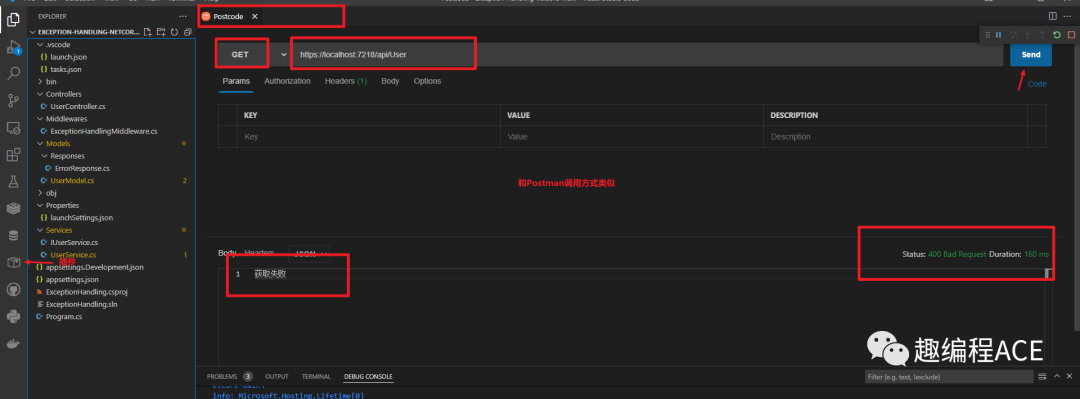
通过结果可知,当我们没有获取到用户的时候,代码将会抛出一个Get User failed的异常(见上图)。对于初学者来说,这是最常见最基础的方法,但是这个方法对于大项目来说也有一个缺点。
如果项目中有许多控制器和动作方法,然后我们需要对每一个动作方法都使用try-catch,那么在这种情况下,用try-catch就很累赘,也会增加代码行数。此时就需要自定义一个处理全局异常的中间件啦!
使用这个方法的好处就是我们可以在一个地方捕获未处理的异常,而不需要在每个动作方法中使用try-catch。
自定义中间件处理异常
在根目录下创建一个Middlewares文件夹,新建一个名为ExceptionHandlingMiddleware.cs类
1using System.Net;
2using System.Text.Json;
3using ExceptionHandling.Models.Responses;
4
5namespace ExceptionHandling.Middlewares;
6
7public class ExceptionHandlingMiddleware
8{
9 private readonly RequestDelegate _next; // 用来处理上下文请求
10 private readonly ILogger _logger;
11 public ExceptionHandlingMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, ILogger logger )
12 {
13 _next = next;
14 _logger = logger;
15 }
16
17 public async Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext httpContext)
18 {
19 try
20 {
21 await _next(httpContext); //要么在中间件中处理,要么被传递到下一个中间件中去
22 }
23 catch (Exception ex)
24 {
25 await HandleExceptionAsync(httpContext, ex); // 捕获异常了 在HandleExceptionAsync中处理
26 }
27 }
28 private async Task HandleExceptionAsync(HttpContext context, Exception exception)
29 {
30 context.Response.ContentType = "application/json"; // 返回json 类型
31 var response = context.Response;
32
33 var errorResponse = new ErrorResponse
34 {
35 Success = false
36 }; // 自定义的异常错误信息类型
37 switch (exception)
38 {
39 case ApplicationException ex:
40 if (ex.Message.Contains("Invalid token"))
41 {
42 response.StatusCode = (int) HttpStatusCode.Forbidden;
43 errorResponse.Message = ex.Message;
44 break;
45 }
46 response.StatusCode = (int) HttpStatusCode.BadRequest;
47 errorResponse.Message = ex.Message;
48 break;
49 case KeyNotFoundException ex:
50 response.StatusCode = (int) HttpStatusCode.NotFound;
51 errorResponse.Message = ex.Message;
52 break;
53 default:
54 response.StatusCode = (int) HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError;
55 errorResponse.Message = "Internal Server errors. Check Logs!";
56 break;
57 }
58 _logger.LogError(exception.Message);
59 var result = JsonSerializer.Serialize(errorResponse);
60 await context.Response.WriteAsync(result);
61 }
62}
这就是我们自定义的中间件,在ExceptionHandlingMiddleware中,我们首先通过依赖注入ILogger和RequestDelegate服务。委托类型_next用来处理上下文请求,要么将上下文放在中间件中处理,要么传递到下个中间链里的下一个中间件中去。
如果我们的请求发生异常,那么就会执行HandleExceptionAsync这个方法。这个方法里面会根据异常类型来返回不同的状态码并且记录到日志中去,不需要返回给调用的客户端,然后我们就可以通过检查日志来发现异常信息。
我们在Program.cs中添加自定义异常
1 app.UseMiddleware<ExceptionHandlingMiddleware>();
接着我们修改下控制器里GetUsers()这个方法,去掉try-catch,直接抛出异常
1[HttpGet]
2 public IActionResult GetUsers()
3 {
4
5 _logger.LogInformation("Get User Details");
6
7 var result = _userService.GetUsers();
8 if(result.Count==0)
9 throw new KeyNotFoundException("Get User failed"); // 此处抛出一个KeyNotFoundException异常
10
11 return Ok(result);
12 }
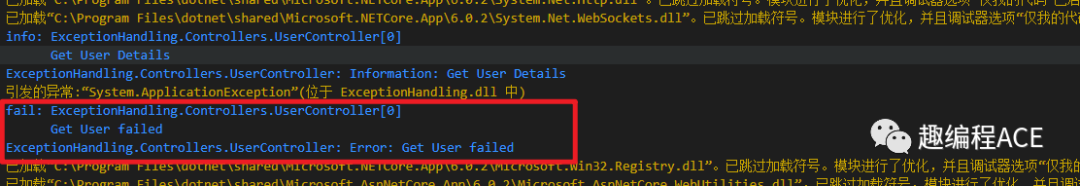
通过调试我们可以发现,当发生异常的时候,程序将会执行到HandleExceptionAsync()方法中去,接着根据类型KeyNotFoundException 返回404的状态码和异常信息。