5. Python代码和项目文档
为什么需要记录Python代码?项目文档应该包括什么?如何编写和生成文档?
文档是软件开发的重要组成部分。如果没有适当的文档,内部和外部利益相关者可能很难或不可能使用或维护我们的代码。这也使得新加入的开发人员变得更加困难。甚至自己也看不懂自己写下的代码。
1 注释 vs 文档
文档是一个独立的资源,可以帮助其他人使用我们的API、程序包、库或框架等,而无需阅读源代码。而注释是供阅读源代码的开发人员使用的。文档应该告诉其他人:
- 什么时候用
- 怎么用
而注释应该告诉其他人:
- 这是啥?
- 这个函数做了什么?
- 为什么这样做?等。
2 Docstrings
Python的docstring是一种特殊的字符串,它作为模块、函数、类或方法定义中的第一条语句出现,形成给定对象的__doc__属性。它使您可以将文档直接嵌入到源代码中:
"""
The temperature module: Manipulate your temperature easily
Easily calculate daily average temperature
"""
from typing import List
class HighTemperature:
"""Class representing very high temperatures"""
def __init__(self, value: float):
"""
:param value: value of temperature
"""
self.value = value
def daily_average(temperatures: List[float]) -> float:
"""
Get average daily temperature
Calculate average temperature from multiple measurements
:param temperatures: list of temperatures
:return: average temperature
"""
return sum(temperatures) / len(temperatures)
我们可以看到daily_average的__doc__属性:
>>> from temperature import daily_average
>>>
>>> print(daily_average.__doc__)
Get average daily temperature
:param temperatures: list of temperatures
:return: average temperature
我们可以用内置的help查看更详细的信息:
>>> import temperature
>>>
>>> help(temperature)
我们可以通过docstrings指定:
- 函数参数
- 函数返回
- 类属性
- 异常
- 边界或限制
- 示例代码等
比较流行的文档风格:
- Google[1]
- reStructuredText[2]
- Numpy[3]
- Epytext[4]
选择一种适合自己的文档风格,或者自定义一种属于自己的风格,使我们的项目更清晰。
3 Sphinx
将docstrings添加到代码中是很棒的,但是仍然需要将它呈现给用户。
这时就是Sphinx,Epydoc和MKDocs等工具发挥作用的时候了,这些工具会将项目的文档字符串转换为HTML和CSS。
Sphinx是迄今为止最受欢迎的。它被用于为许多开源项目生成文档(例如Python和Flask)。它也是Read the Docs支持的文档工具之一,仅举几例,它被数千个开源项目使用(如Requests,Flake8和pytest等)。
没安装的可以使用pip安装,一起看看怎么用:
$ sphinx-quickstart --version
sphinx-quickstart 3.5.4
在我们项目文件夹下新建一个temperature.py,添加上文提到的代码,然后运行:
$ sphinx-quickstart docs
> Separate source and build directories (y/n) [n]: n
> Project name: Temperature
> Author name(s): JKL
> Project release []: 1.0.0
> Project language [en]: en
这将会生成docs文件夹以及文件夹下面的一些文件。
更改docs/source/conf.py,将以下代码:
# import os
# import sys
# sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath('.'))
改为:
import os
import sys
sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath('../..'))
在extensions列表添加:
extensions = [
'sphinx.ext.autodoc',
]
修改docs/source/index.rst:
.. Temperature documentation master file, created by
sphinx-quickstart on Sat Apr 24 14:11:59 2021.
You can adapt this file completely to your liking, but it should at least
contain the root `toctree` directive.
Welcome to Temperature's documentation!
=======================================
.. toctree::
:maxdepth: 2
:caption: Contents:
.. automodule:: temperature
:members:
Indices and tables
==================
* :ref:`genindex`
* :ref:`modindex`
* :ref:`search`
进入docs文件夹下执行:
$ make html
html文档就创建成功了。浏览器打开docs/build/html/index.html我们将会看到:
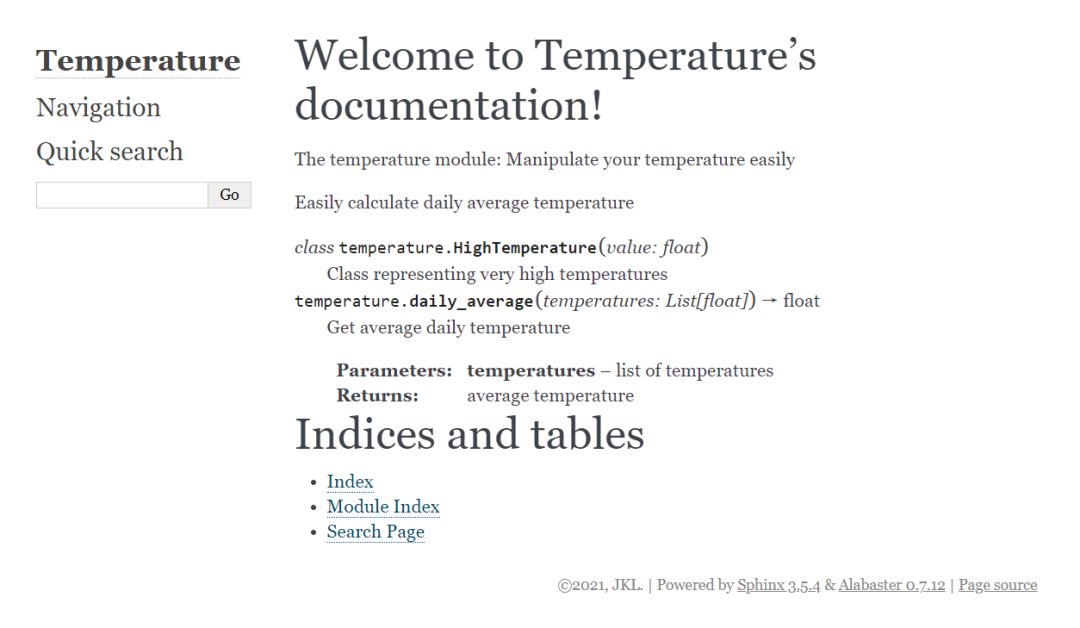
然后我们就可以更进一步,将我们的文档上传到类似Read the Docs[5]的网站了。
4 API文档
API文档有URL、URL参数、查询参数、状态码、请求主体和响应主体等。即使是简单的API,也可能具有许多难以记住的参数。
OpenAPI给我们提供了一个好看而且使用的文档。我们可以通过yaml或者json文件指定我们的api,OpenAPI会为我们自动生成好看的文档。
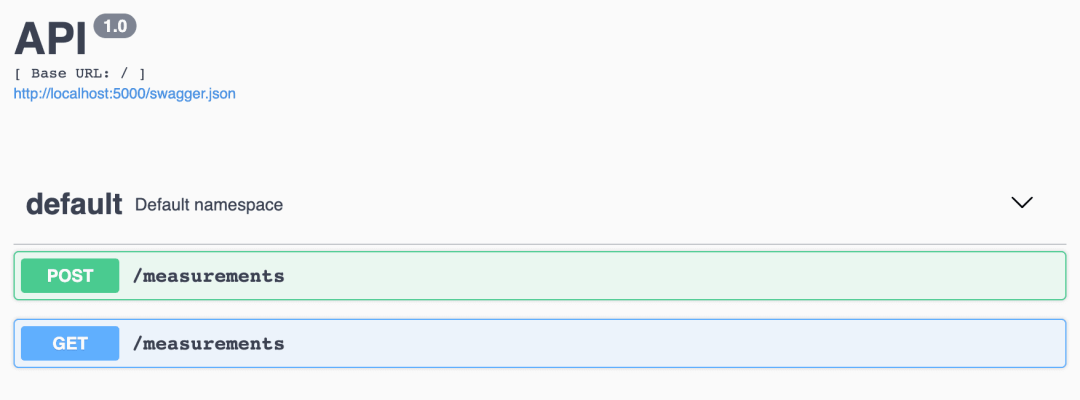
FastAPI[6]就是一个很好的示例。
5 总结
本篇介绍了注释与文档的区别,使用sphinx生成文档,简单介绍了OpenAPI生成api文档。为了使我们的项目让别人(甚至自己)轻松理解和使用,开始动手写文档吧。
更多文档请参考 www.testdriven.io[7]
参考资料
[1]Google: https://github.com/google/styleguide/blob/gh-pages/pyguide.md#38-comments-and-docstrings
[2]reStructuredText: https://docutils.sourceforge.io/rst.html
[3]Numpy: https://numpydoc.readthedocs.io/en/latest/format.html
[4]Epytext: http://epydoc.sourceforge.net/epytext.html
[5]Read the Docs: https://readthedocs.org/
[6]FastAPI: https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/
[7]更多文档: https://testdriven.io/blog/documenting-python/
