Android使用svg构造交互式中国地图
1. 概念
什么是svg
SVG的W3C的解释:
什么是矢量图像,什么是位图图像?
1、矢量图像:SVG是W3C 推出的一种开放标准的文本式矢量图形描述语言,他是基于XML的、专门为网络而设计的图像格式,
SVG是一种采用XML来描述二维图形的语言,所以它可以直接打开xml文件来修改和编辑。
2、位图图像:位图图像的存储单位是图像上每一点的像素值,因而文件会比较大,像GIF、JPEG、PNG等都是位图图像格式。
Vector
可以说Vector就是Android中的SVG实现
补充:Vector图像刚发布的时候,是只支持Android 5.0+的,自从AppCompat 23.2之后,Vector可以使用于Android 2.1以上的所有系统,只需要引用com.android.support:appcompat-v7:23.2.0以上的版本就可以了。(所谓的兼容也是个坑爹的兼容,即低版本非真实使用SVG,而是生成PNG图片)
Vector Drawable
Vector Drawable相对于普通的Drawable来说,有以下几个好处:
(1)Vector图像可以自动进行适配,不需要通过分辨率来设置不同的图片。
(2)Vector图像可以大幅减少图像的体积,同样一张图,用Vector来实现,可能只有PNG的几十分之一。
(3)使用简单,很多设计工具,都可以直接导出SVG图像,从而转换成Vector图像 功能强大。
(4)不用写很多代码就可以实现非常复杂的动画 成熟、稳定,前端已经非常广泛的进行使用了。
1) Vector 语法简介通过使用它的Path标签,几乎可以实现SVG中的其它所有标签,虽然可能会复杂一点,但这些东西都是可以通过工具来完成的,所以,不用担心写起来会很复杂。(1)Path指令解析如下所示:M = moveto(M X,Y) :将画笔移动到指定的坐标位置,相当于 android Path 里的moveTo()L = lineto(L X,Y) :画直线到指定的坐标位置,相当于 android Path 里的lineTo()H = horizontal lineto(H X):画水平线到指定的X坐标位置V = vertical lineto(V Y):画垂直线到指定的Y坐标位置C = curveto(C X1,Y1,X2,Y2,ENDX,ENDY):三次贝赛曲线S = smooth curveto(S X2,Y2,ENDX,ENDY) 同样三次贝塞尔曲线,更平滑Q = quadratic Belzier curve(Q X,Y,ENDX,ENDY):二次贝赛曲线T = smooth quadratic Belzier curveto(T ENDX,ENDY):映射 同样二次贝塞尔曲线,更平滑A = elliptical Arc(A RX,RY,XROTATION,FLAG1,FLAG2,X,Y):弧线 ,相当于arcTo()Z = closepath():关闭路径(会自动绘制链接起点和终点)注意,’M’处理时,只是移动了画笔, 没有画任何东西。注意:1.关于这些语法,开发者不需要全部精通,而是能够看懂即可,这些path标签及数据生成都可以交给工具来实现。(一般美工来帮你搞定!PS、Illustrator等等都支持导出SVG图片)2.程序员:没必要去学习使用这些设计工具,开发者可以利用一些工具,自己转换一些比较基础的图像,如:http://inloop.github.io/svg2android/3.还可以使用SVG的编辑器来进行SVG图像的编写,例如:http://editor.method.ac/(绝配!可以先用http://editor.method.ac/ 生成SVG图片,然后用http://inloop.github.io/svg2android/ 生成 VectorDrawable xml代码)4.使用AndroidStudio插件完成SVG添加(Vector Asset Studio)详细:http://www.jianshu.com/p/d6c39f2dd5e7AS会自动生成兼容性图片(高版本会生成xxx.xml的SVG图片;低版本会自动生成xxx.png图片)5.有些网站可以找到SVG资源SVG下载地址:http://www.shejidaren.com/8000-flat-icons.htmlhttp://www.flaticon.com/http://www.iconfont.cn/plus --- 阿里巴巴图片转成SVG https://vectormagic.com/
1、使用Android Studio 2.2以上的版本,gradle版本在2.0以上,准备步骤1.1、添加defaultConfig {vectorDrawables.useSupportLibrary = true}1.2、添加compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:25.3.1' //需要是23.2 版本以上的1.3、Activity需要继承与AppCompatActivity1.4、布局文件当中添加xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"2、使用在Actvity前面添加一个flag设置static {AppCompatDelegate.setCompatVectorFromResourcesEnabled(true);}2.1 ImageView/ImageButtonXML app:srcCompat代码里面使用无区别2.2 Button 不支持app:srcCompatXml 使用在Button的selector2.3 RadioButton 直接使用2.4 textview的drawable 直接使用2.5 使用的动态Vector Drawable主要是不能直接修改 pathData不能使用自定义interpolator
SVG使用
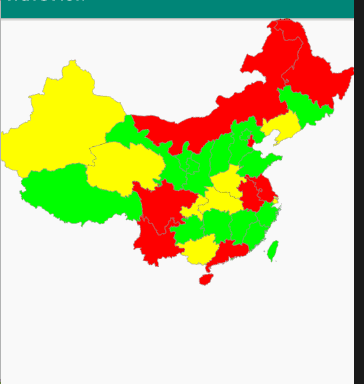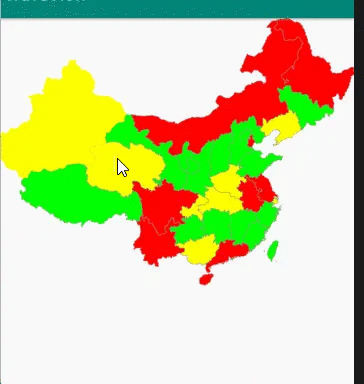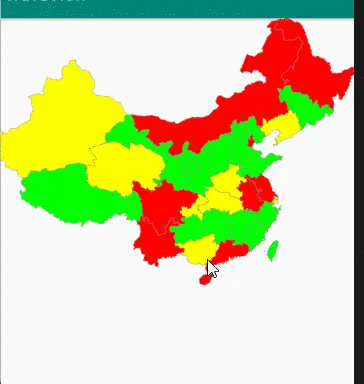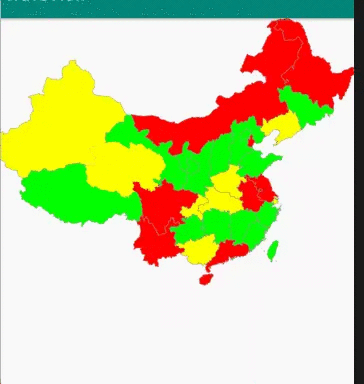
第一步 下载含有中国地图的 SVG
第二步 使用 网站:
http://inloop.github.io/svg2android/第三步 利用Xml解析SVG的代码 封装成javaBean 最重要的得到Path
第四步 重写OnDraw方法 利用Path绘制中国地图
第五步 重写OnTouchEvent方法,记录手指触摸位置,判断这个位置是否坐落在某个省份上。
public class MyMapView extends View {private Paint mPaint;private Context context;private int[] colors = new int[]{Color.RED, Color.GREEN, Color.YELLOW, Color.GREEN};private ArrayList<ProvinceBean> itemList = new ArrayList<>();private ProvinceBean selectItem;private GestureDetectorCompat gestureDetectorCompat;public MyMapView(Context context) {this(context, null);}public MyMapView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {super(context, attrs);init(context);}private void init(Context context) {//准备画笔mPaint = new Paint();mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);this.context = context;thread.start();//手势处理类gestureDetectorCompat = new GestureDetectorCompat(context, new GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener() {public boolean onDown(MotionEvent e) {Log.d("event ", e.getAction() + "");handlerTouch(e.getX(), e.getY());return true;}});}private void handlerTouch(float x, float y) {if (itemList != null) {for (ProvinceBean item : itemList) {if (item.isTouch((int) (x / 1.4), (int) (y / 1.4))) {selectItem = item;postInvalidate();break;}}}}public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {return gestureDetectorCompat.onTouchEvent(event);}protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {super.onDraw(canvas);canvas.save();canvas.scale(1.4f, 1.4f);for (int i = 0; i < itemList.size(); i++) {if (selectItem != itemList.get(i)) {itemList.get(i).draw(mPaint, canvas, false);}}if (selectItem != null) {selectItem.draw(mPaint, canvas, true);}canvas.restore();}Handler handler = new Handler() {public void handleMessage(Message msg) {super.handleMessage(msg);if (msg != null) {postInvalidate();}}};Thread thread = new Thread() {public void run() {//dom解析xmlInputStream inputStream = context.getResources().openRawResource(R.raw.chinahigh);DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();DocumentBuilder builder = null;try {builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();Document document = builder.parse(inputStream);//解析输入流Element rootElement = document.getDocumentElement();NodeList items = rootElement.getElementsByTagName("path");Log.d("MyMapView:", "集合大小=" + items.getLength());for (int i = 0; i < items.getLength(); i++) {int colorsIndex = i % 4;Element element = (Element) items.item(i);String pathData = element.getAttribute("android:pathData");Path path = PathParser.createPathFromPathData(pathData);ProvinceBean provinceBean = new ProvinceBean(path);provinceBean.setColor(colors[colorsIndex]);itemList.add(provinceBean);}handler.sendEmptyMessage(1);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}};}public class ProvinceBean {private Path path;private int color;public ProvinceBean(Path path) {this.path = path;}public int getColor() {return color;}public void setColor(int color) {this.color = color;}/*** 绘制省份** @param paint* @param canvas* @param isSelected 是否被选中*/public void draw(Paint paint, Canvas canvas, boolean isSelected) {if (isSelected){//绘制点击后的背景paint.setStrokeWidth(2);paint.setColor(color);paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);//添加阴影paint.setShadowLayer(8,0,0,Color.BLACK);canvas.drawPath(path,paint);//绘制背景paint.clearShadowLayer();paint.setStrokeWidth(2);paint.setColor(color);paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);canvas.drawPath(path,paint);}else{//绘制背景paint.setStrokeWidth(2);paint.clearShadowLayer();paint.setColor(color);paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);canvas.drawPath(path,paint);//绘制边界线paint.setStrokeWidth(1);paint.setColor(Color.GRAY);paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);canvas.drawPath(path,paint);}}//触摸点是否在这个省的path内public boolean isTouch(int x, int y) {//构造一个矩形对象RectF rectF=new RectF();//返回路径控制点的计算边界保存到rectFpath.computeBounds(rectF,true);//构造一个区域对象Region region=new Region();//给区赋值region.setPath(path,new Region((int)rectF.left,(int)rectF.top,(int)rectF.right,(int)rectF.bottom));return region.contains(x,y);}
评论
