知识蒸馏综述:代码整理
点击上方“小白学视觉”,选择加"星标"或“置顶”
重磅干货,第一时间送达
编者荐语
收集自RepDistiller中的蒸馏方法,尽可能简单解释蒸馏用到的策略,并提供了实现源码。
全称:Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network
链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1503.02531.pd3f
发表:NIPS14
最经典的,也是明确提出知识蒸馏概念的工作,通过使用带温度的softmax函数来软化教师网络的逻辑层输出作为学生网络的监督信息,
使用KL divergence来衡量学生网络与教师网络的差异,具体流程如下图所示(来自Knowledge Distillation A Survey)
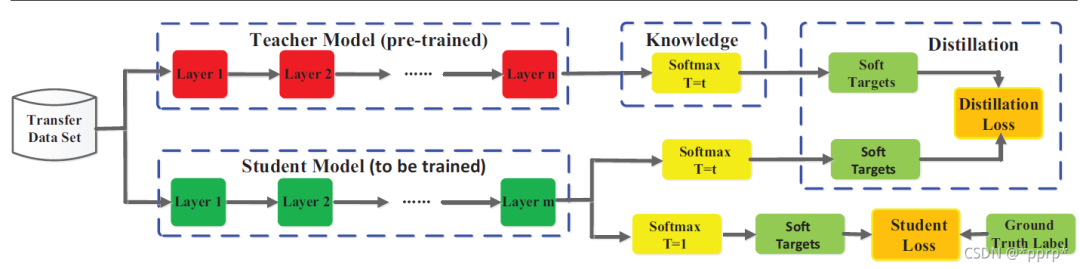
对学生网络来说,一部分监督信息来自hard label标签,另一部分来自教师网络提供的soft label。
代码实现:
class DistillKL(nn.Module):
"""Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network"""
def __init__(self, T):
super(DistillKL, self).__init__()
self.T = T
def forward(self, y_s, y_t):
p_s = F.log_softmax(y_s/self.T, dim=1)
p_t = F.softmax(y_t/self.T, dim=1)
loss = F.kl_div(p_s, p_t, size_average=False) * (self.T**2) / y_s.shape[0]
return loss
核心就是一个kl_div函数,用于计算学生网络和教师网络的分布差异。
2. FitNet: Hints for thin deep nets
全称:Fitnets: hints for thin deep nets
链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6550.pdf
发表:ICLR 15 Poster
对中间层进行蒸馏的开山之作,通过将学生网络的feature map扩展到与教师网络的feature map相同尺寸以后,使用均方误差MSE Loss来衡量两者差异。
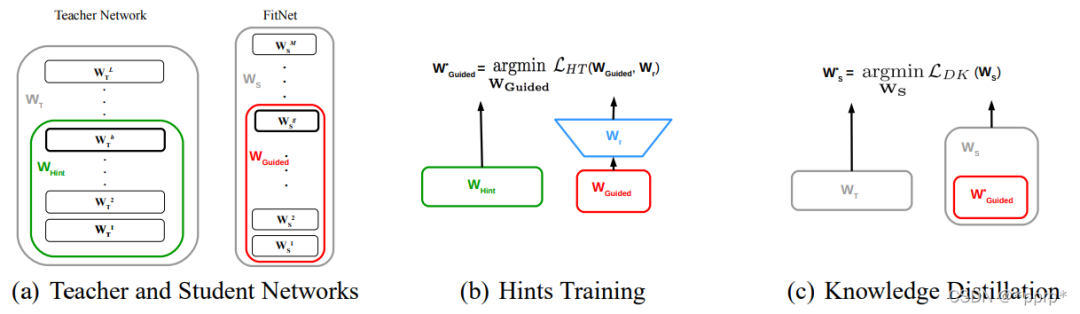
实现如下:
class HintLoss(nn.Module):
"""Fitnets: hints for thin deep nets, ICLR 2015"""
def __init__(self):
super(HintLoss, self).__init__()
self.crit = nn.MSELoss()
def forward(self, f_s, f_t):
loss = self.crit(f_s, f_t)
return loss
实现核心就是MSELoss
3. AT: Attention Transfer
全称:Paying More Attention to Attention: Improving the Performance of Convolutional Neural Networks via Attention Transfer
链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1612.03928.pdf
发表:ICLR16
为了提升学生模型性能提出使用注意力作为知识载体进行迁移,文中提到了两种注意力,一种是activation-based attention transfer,另一种是gradient-based attention transfer。实验发现第一种方法既简单效果又好。
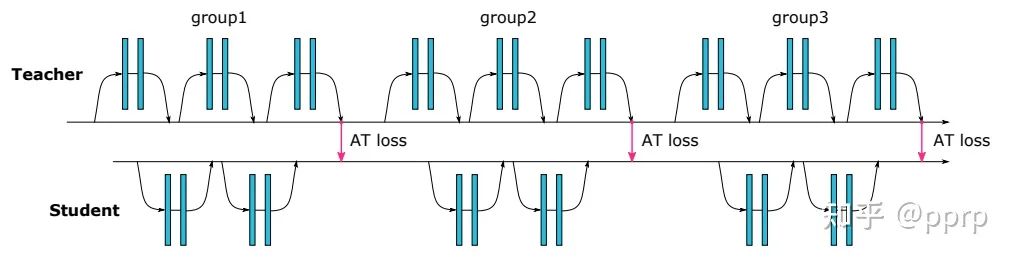
实现如下:
class Attention(nn.Module):
"""Paying More Attention to Attention: Improving the Performance of Convolutional Neural Networks
via Attention Transfer
code: https://github.com/szagoruyko/attention-transfer"""
def __init__(self, p=2):
super(Attention, self).__init__()
self.p = p
def forward(self, g_s, g_t):
return [self.at_loss(f_s, f_t) for f_s, f_t in zip(g_s, g_t)]
def at_loss(self, f_s, f_t):
s_H, t_H = f_s.shape[2], f_t.shape[2]
if s_H > t_H:
f_s = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(f_s, (t_H, t_H))
elif s_H < t_H:
f_t = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(f_t, (s_H, s_H))
else:
pass
return (self.at(f_s) - self.at(f_t)).pow(2).mean()
def at(self, f):
return F.normalize(f.pow(self.p).mean(1).view(f.size(0), -1))
首先使用avgpool将尺寸调整一致,然后使用MSE Loss来衡量两者差距。
4. SP: Similarity-Preserving
全称:Similarity-Preserving Knowledge Distillation
链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1907.09682.pdf
发表:ICCV19
SP归属于基于关系的知识蒸馏方法。文章思想是提出相似性保留的知识,使得教师网络和学生网络会对相同的样本产生相似的激活。可以从下图看出处理流程,教师网络和学生网络对应feature map通过计算内积,得到bsxbs的相似度矩阵,然后使用均方误差来衡量两个相似度矩阵。
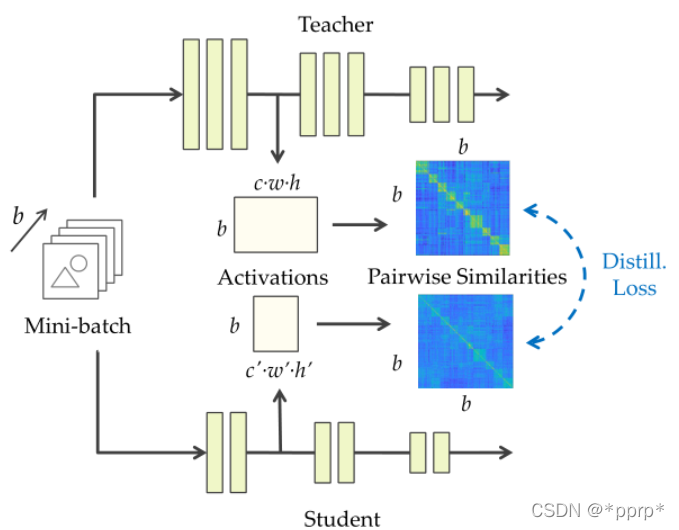
最终Loss为:
G代表的就是bsxbs的矩阵。
实现如下:
class Similarity(nn.Module):
"""Similarity-Preserving Knowledge Distillation, ICCV2019, verified by original author"""
def __init__(self):
super(Similarity, self).__init__()
def forward(self, g_s, g_t):
return [self.similarity_loss(f_s, f_t) for f_s, f_t in zip(g_s, g_t)]
def similarity_loss(self, f_s, f_t):
bsz = f_s.shape[0]
f_s = f_s.view(bsz, -1)
f_t = f_t.view(bsz, -1)
G_s = torch.mm(f_s, torch.t(f_s))
# G_s = G_s / G_s.norm(2)
G_s = torch.nn.functional.normalize(G_s)
G_t = torch.mm(f_t, torch.t(f_t))
# G_t = G_t / G_t.norm(2)
G_t = torch.nn.functional.normalize(G_t)
G_diff = G_t - G_s
loss = (G_diff * G_diff).view(-1, 1).sum(0) / (bsz * bsz)
return loss
5. CC: Correlation Congruence
全称:Correlation Congruence for Knowledge Distillation
链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.01802.pdf
发表:ICCV19
CC也归属于基于关系的知识蒸馏方法。不应该仅仅引导教师网络和学生网络单个样本向量之间的差异,还应该学习两个样本之间的相关性,而这个相关性使用的是Correlation Congruence 教师网络雨学生网络相关性之间的欧氏距离。
整体Loss如下:
实现如下:
class Correlation(nn.Module):
"""Similarity-preserving loss. My origianl own reimplementation
based on the paper before emailing the original authors."""
def __init__(self):
super(Correlation, self).__init__()
def forward(self, f_s, f_t):
return self.similarity_loss(f_s, f_t)
def similarity_loss(self, f_s, f_t):
bsz = f_s.shape[0]
f_s = f_s.view(bsz, -1)
f_t = f_t.view(bsz, -1)
G_s = torch.mm(f_s, torch.t(f_s))
G_s = G_s / G_s.norm(2)
G_t = torch.mm(f_t, torch.t(f_t))
G_t = G_t / G_t.norm(2)
G_diff = G_t - G_s
loss = (G_diff * G_diff).view(-1, 1).sum(0) / (bsz * bsz)
return loss
6. VID: Variational Information Distillation
全称:Variational Information Distillation for Knowledge Transfer
链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.05835.pdf
发表:CVPR19
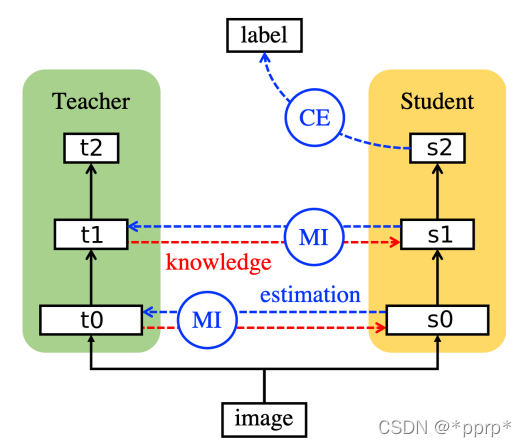
利用互信息(Mutual Information)来衡量学生网络和教师网络差异。互信息可以表示出两个变量的互相依赖程度,其值越大,表示变量之间的依赖程度越高。互信息计算如下:
互信息是教师模型的熵减去在已知学生模型条件下教师模型的熵。目标是最大化互信息,因为互信息越大说明H(t|s)越小,即学生网络确定的情况下,教师网络的熵会变小,证明学生网络已经学习的比较充分。
整体loss如下:
由于p(t|s)很难计算,可以使用变分分布q(t|s)去接近真实分布。
其中q(t|s)是使用方差可学习的高斯分布模拟(公式中的log_scale):
实现如下:
class VIDLoss(nn.Module):
"""Variational Information Distillation for Knowledge Transfer (CVPR 2019),
code from author: https://github.com/ssahn0215/variational-information-distillation"""
def __init__(self,
num_input_channels,
num_mid_channel,
num_target_channels,
init_pred_var=5.0,
eps=1e-5):
super(VIDLoss, self).__init__()
def conv1x1(in_channels, out_channels, stride=1):
return nn.Conv2d(
in_channels, out_channels,
kernel_size=1, padding=0,
bias=False, stride=stride)
self.regressor = nn.Sequential(
conv1x1(num_input_channels, num_mid_channel),
nn.ReLU(),
conv1x1(num_mid_channel, num_mid_channel),
nn.ReLU(),
conv1x1(num_mid_channel, num_target_channels),
)
self.log_scale = torch.nn.Parameter(
np.log(np.exp(init_pred_var-eps)-1.0) * torch.ones(num_target_channels)
)
self.eps = eps
def forward(self, input, target):
# pool for dimentsion match
s_H, t_H = input.shape[2], target.shape[2]
if s_H > t_H:
input = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(input, (t_H, t_H))
elif s_H < t_H:
target = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(target, (s_H, s_H))
else:
pass
pred_mean = self.regressor(input)
pred_var = torch.log(1.0+torch.exp(self.log_scale))+self.eps
pred_var = pred_var.view(1, -1, 1, 1)
neg_log_prob = 0.5*(
(pred_mean-target)**2/pred_var+torch.log(pred_var)
)
loss = torch.mean(neg_log_prob)
return loss
7. RKD: Relation Knowledge Distillation
全称:Relational Knowledge Disitllation
链接:http://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.05068
发表:CVPR19
RKD也是基于关系的知识蒸馏方法,RKD提出了两种损失函数,二阶的距离损失和三阶的角度损失。
Distance-wise Loss
Angle-wise Loss
实现如下:
class RKDLoss(nn.Module):
"""Relational Knowledge Disitllation, CVPR2019"""
def __init__(self, w_d=25, w_a=50):
super(RKDLoss, self).__init__()
self.w_d = w_d
self.w_a = w_a
def forward(self, f_s, f_t):
student = f_s.view(f_s.shape[0], -1)
teacher = f_t.view(f_t.shape[0], -1)
# RKD distance loss
with torch.no_grad():
t_d = self.pdist(teacher, squared=False)
mean_td = t_d[t_d > 0].mean()
t_d = t_d / mean_td
d = self.pdist(student, squared=False)
mean_d = d[d > 0].mean()
d = d / mean_d
loss_d = F.smooth_l1_loss(d, t_d)
# RKD Angle loss
with torch.no_grad():
td = (teacher.unsqueeze(0) - teacher.unsqueeze(1))
norm_td = F.normalize(td, p=2, dim=2)
t_angle = torch.bmm(norm_td, norm_td.transpose(1, 2)).view(-1)
sd = (student.unsqueeze(0) - student.unsqueeze(1))
norm_sd = F.normalize(sd, p=2, dim=2)
s_angle = torch.bmm(norm_sd, norm_sd.transpose(1, 2)).view(-1)
loss_a = F.smooth_l1_loss(s_angle, t_angle)
loss = self.w_d * loss_d + self.w_a * loss_a
return loss
@staticmethod
def pdist(e, squared=False, eps=1e-12):
e_square = e.pow(2).sum(dim=1)
prod = e @ e.t()
res = (e_square.unsqueeze(1) + e_square.unsqueeze(0) - 2 * prod).clamp(min=eps)
if not squared:
res = res.sqrt()
res = res.clone()
res[range(len(e)), range(len(e))] = 0
return res
8. PKT:Probabilistic Knowledge Transfer
全称:Probabilistic Knowledge Transfer for deep representation learning
链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.10837
发表:CoRR18
提出一种概率知识转移方法,引入了互信息来进行建模。该方法具有可跨模态知识转移、无需考虑任务类型、可将手工特征融入网络等有点。
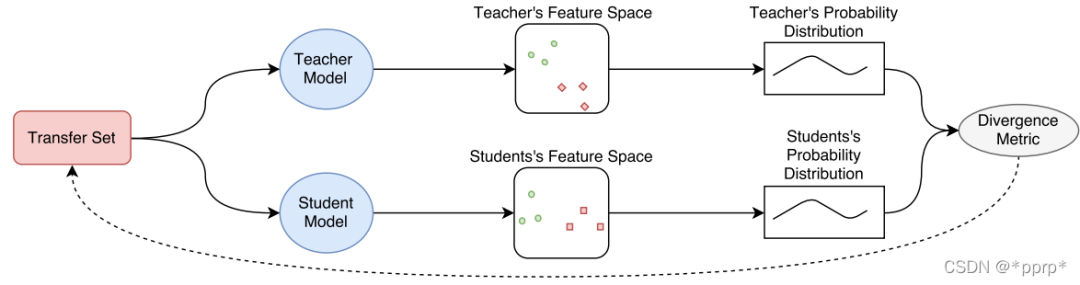
实现如下:
class PKT(nn.Module):
"""Probabilistic Knowledge Transfer for deep representation learning
Code from author: https://github.com/passalis/probabilistic_kt"""
def __init__(self):
super(PKT, self).__init__()
def forward(self, f_s, f_t):
return self.cosine_similarity_loss(f_s, f_t)
@staticmethod
def cosine_similarity_loss(output_net, target_net, eps=0.0000001):
# Normalize each vector by its norm
output_net_norm = torch.sqrt(torch.sum(output_net ** 2, dim=1, keepdim=True))
output_net = output_net / (output_net_norm + eps)
output_net[output_net != output_net] = 0
target_net_norm = torch.sqrt(torch.sum(target_net ** 2, dim=1, keepdim=True))
target_net = target_net / (target_net_norm + eps)
target_net[target_net != target_net] = 0
# Calculate the cosine similarity
model_similarity = torch.mm(output_net, output_net.transpose(0, 1))
target_similarity = torch.mm(target_net, target_net.transpose(0, 1))
# Scale cosine similarity to 0..1
model_similarity = (model_similarity + 1.0) / 2.0
target_similarity = (target_similarity + 1.0) / 2.0
# Transform them into probabilities
model_similarity = model_similarity / torch.sum(model_similarity, dim=1, keepdim=True)
target_similarity = target_similarity / torch.sum(target_similarity, dim=1, keepdim=True)
# Calculate the KL-divergence
loss = torch.mean(target_similarity * torch.log((target_similarity + eps) / (model_similarity + eps)))
return loss
9. AB: Activation Boundaries
全称:Knowledge Transfer via Distillation of Activation Boundaries Formed by Hidden Neurons
链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1811.03233.pdf
发表:AAAI18
目标:让教师网络层的神经元的激活边界尽量和学生网络的一样。所谓的激活边界指的是分离超平面(针对的是RELU这种激活函数),其决定了神经元的激活与失活。AB提出的激活转移损失,让教师网络与学生网络之间的分离边界尽可能一致。
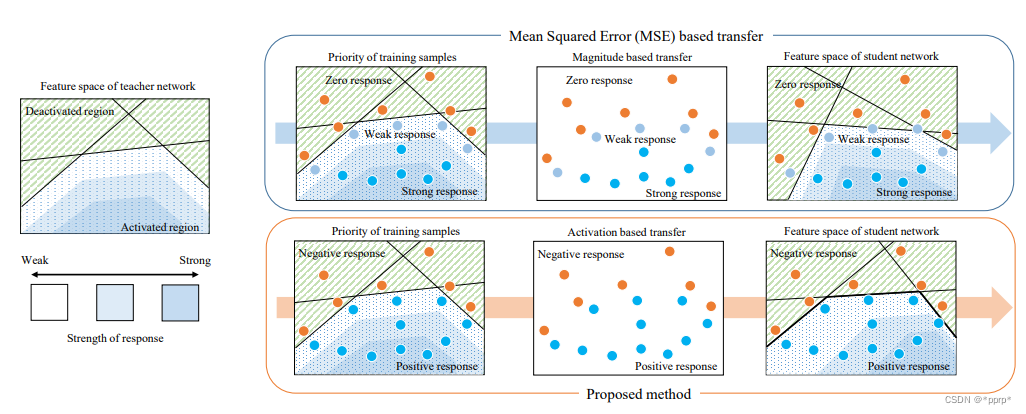
实现如下:
class ABLoss(nn.Module):
"""Knowledge Transfer via Distillation of Activation Boundaries Formed by Hidden Neurons
code: https://github.com/bhheo/AB_distillation
"""
def __init__(self, feat_num, margin=1.0):
super(ABLoss, self).__init__()
self.w = [2**(i-feat_num+1) for i in range(feat_num)]
self.margin = margin
def forward(self, g_s, g_t):
bsz = g_s[0].shape[0]
losses = [self.criterion_alternative_l2(s, t) for s, t in zip(g_s, g_t)]
losses = [w * l for w, l in zip(self.w, losses)]
# loss = sum(losses) / bsz
# loss = loss / 1000 * 3
losses = [l / bsz for l in losses]
losses = [l / 1000 * 3 for l in losses]
return losses
def criterion_alternative_l2(self, source, target):
loss = ((source + self.margin) ** 2 * ((source > -self.margin) & (target <= 0)).float() +
(source - self.margin) ** 2 * ((source <= self.margin) & (target > 0)).float())
return torch.abs(loss).sum()
10. FT: Factor Transfer
全称:Paraphrasing Complex Network: Network Compression via Factor Transfer
链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1802.04977.pdf
发表:NIPS18
提出的是factor transfer的方法。所谓的factor,其实是对模型最后的数据结果进行一个编解码的过程,提取出的一个factor矩阵,用教师网络的factor来指导学生网络的factor。
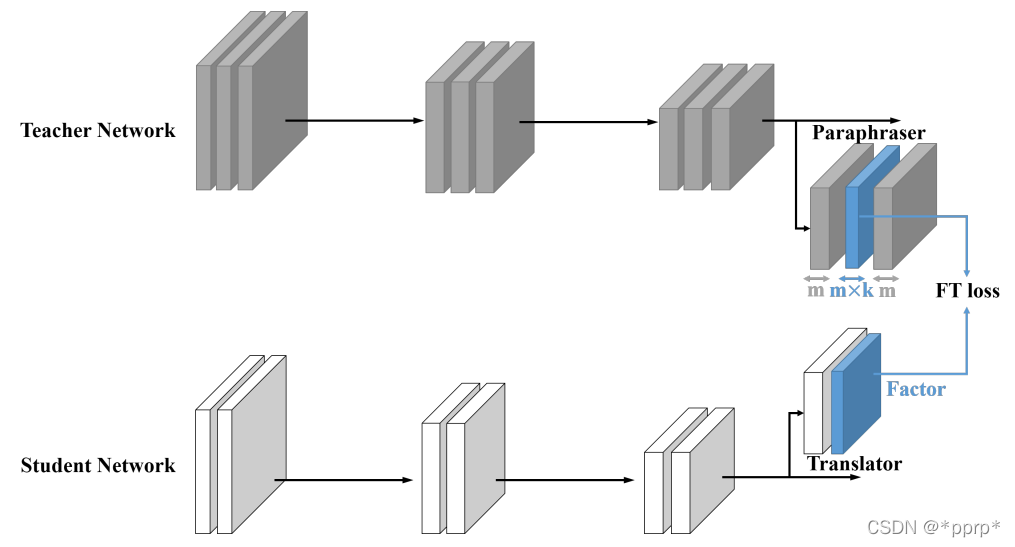
FT计算公式为:
实现如下:
class FactorTransfer(nn.Module):
"""Paraphrasing Complex Network: Network Compression via Factor Transfer, NeurIPS 2018"""
def __init__(self, p1=2, p2=1):
super(FactorTransfer, self).__init__()
self.p1 = p1
self.p2 = p2
def forward(self, f_s, f_t):
return self.factor_loss(f_s, f_t)
def factor_loss(self, f_s, f_t):
s_H, t_H = f_s.shape[2], f_t.shape[2]
if s_H > t_H:
f_s = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(f_s, (t_H, t_H))
elif s_H < t_H:
f_t = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(f_t, (s_H, s_H))
else:
pass
if self.p2 == 1:
return (self.factor(f_s) - self.factor(f_t)).abs().mean()
else:
return (self.factor(f_s) - self.factor(f_t)).pow(self.p2).mean()
def factor(self, f):
return F.normalize(f.pow(self.p1).mean(1).view(f.size(0), -1))
11. FSP: Flow of Solution Procedure
全称:A Gift from Knowledge Distillation: Fast Optimization, Network Minimization and Transfer Learning
链接:https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2017/papers/Yim_A_Gift_From_CVPR_2017_paper.pdf
发表:CVPR17
FSP认为教学生网络不同层输出的feature之间的关系比教学生网络结果好
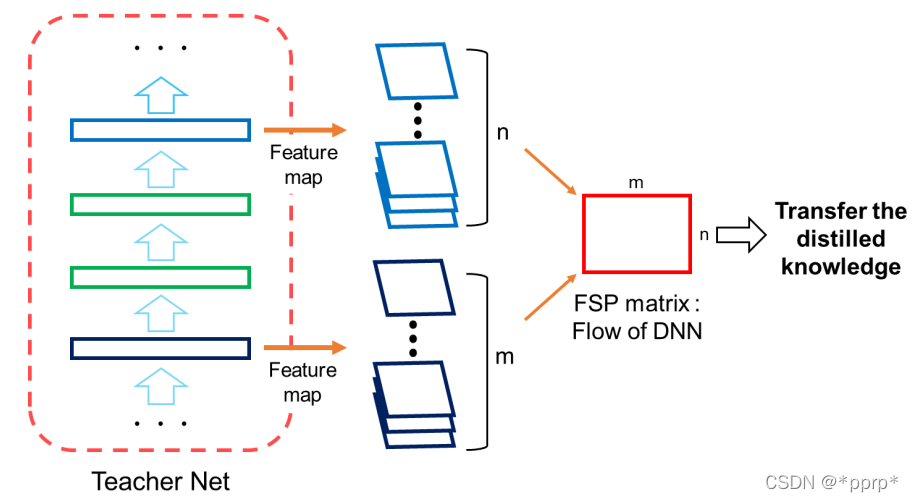
定义了FSP矩阵来定义网络内部特征层之间的关系,是一个Gram矩阵反映老师教学生的过程。
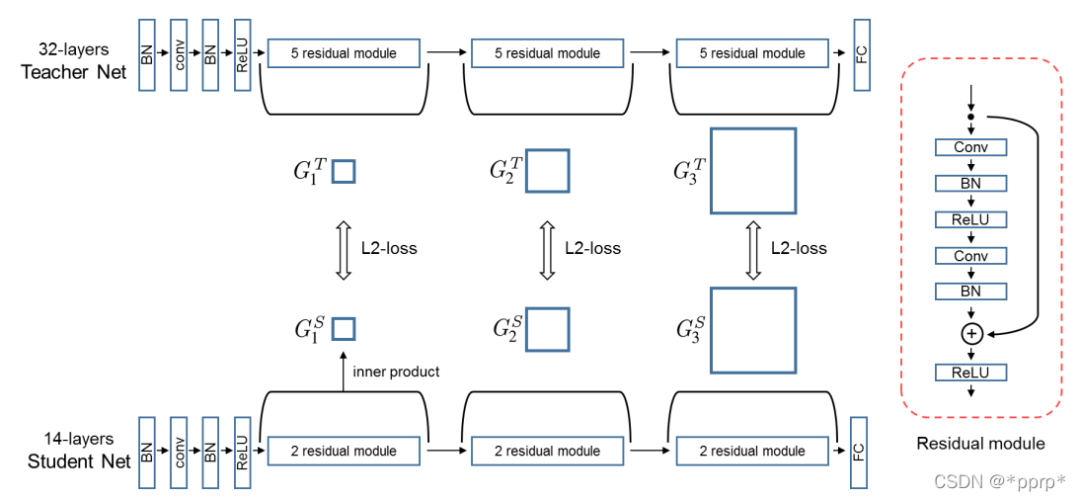
使用的是L2 Loss进行约束FSP矩阵。
实现如下:
class FSP(nn.Module):
"""A Gift from Knowledge Distillation:
Fast Optimization, Network Minimization and Transfer Learning"""
def __init__(self, s_shapes, t_shapes):
super(FSP, self).__init__()
assert len(s_shapes) == len(t_shapes), 'unequal length of feat list'
s_c = [s[1] for s in s_shapes]
t_c = [t[1] for t in t_shapes]
if np.any(np.asarray(s_c) != np.asarray(t_c)):
raise ValueError('num of channels not equal (error in FSP)')
def forward(self, g_s, g_t):
s_fsp = self.compute_fsp(g_s)
t_fsp = self.compute_fsp(g_t)
loss_group = [self.compute_loss(s, t) for s, t in zip(s_fsp, t_fsp)]
return loss_group
@staticmethod
def compute_loss(s, t):
return (s - t).pow(2).mean()
@staticmethod
def compute_fsp(g):
fsp_list = []
for i in range(len(g) - 1):
bot, top = g[i], g[i + 1]
b_H, t_H = bot.shape[2], top.shape[2]
if b_H > t_H:
bot = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(bot, (t_H, t_H))
elif b_H < t_H:
top = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(top, (b_H, b_H))
else:
pass
bot = bot.unsqueeze(1)
top = top.unsqueeze(2)
bot = bot.view(bot.shape[0], bot.shape[1], bot.shape[2], -1)
top = top.view(top.shape[0], top.shape[1], top.shape[2], -1)
fsp = (bot * top).mean(-1)
fsp_list.append(fsp)
return fsp_list
12. NST: Neuron Selectivity Transfer
全称:Like what you like: knowledge distill via neuron selectivity transfer
链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.01219.pdf
发表:CoRR17
使用新的损失函数最小化教师网络与学生网络之间的Maximum Mean Discrepancy(MMD), 文中选择的是对其教师网络与学生网络之间神经元选择样式的分布。
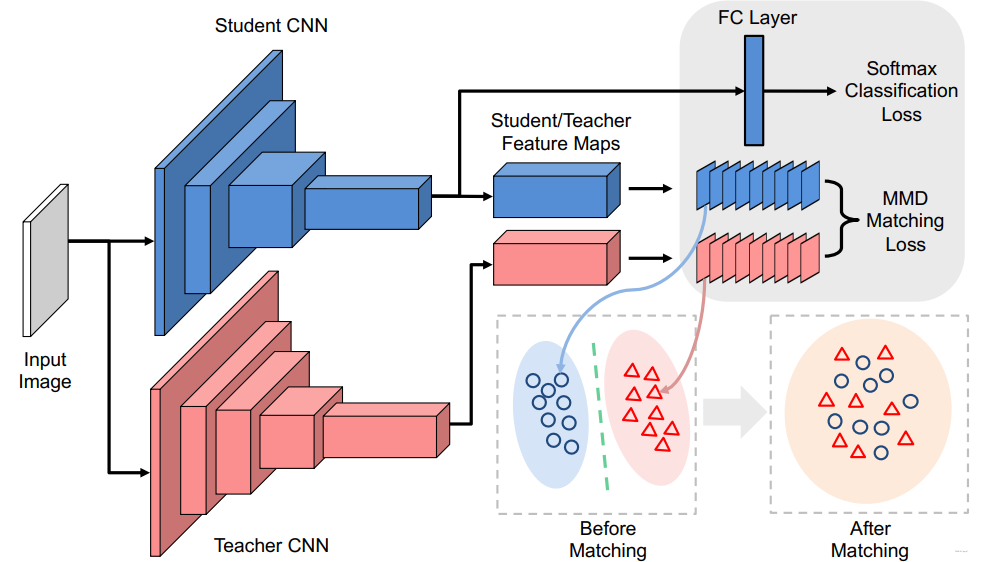
使用核技巧(对应下面poly kernel)并进一步展开以后可得:
实际上提供了Linear Kernel、Poly Kernel、Gaussian Kernel三种,这里实现只给了Poly这种,这是因为Poly这种方法可以与KD进行互补,这样整体效果会非常好。
实现如下:
class NSTLoss(nn.Module):
"""like what you like: knowledge distill via neuron selectivity transfer"""
def __init__(self):
super(NSTLoss, self).__init__()
pass
def forward(self, g_s, g_t):
return [self.nst_loss(f_s, f_t) for f_s, f_t in zip(g_s, g_t)]
def nst_loss(self, f_s, f_t):
s_H, t_H = f_s.shape[2], f_t.shape[2]
if s_H > t_H:
f_s = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(f_s, (t_H, t_H))
elif s_H < t_H:
f_t = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(f_t, (s_H, s_H))
else:
pass
f_s = f_s.view(f_s.shape[0], f_s.shape[1], -1)
f_s = F.normalize(f_s, dim=2)
f_t = f_t.view(f_t.shape[0], f_t.shape[1], -1)
f_t = F.normalize(f_t, dim=2)
# set full_loss as False to avoid unnecessary computation
full_loss = True
if full_loss:
return (self.poly_kernel(f_t, f_t).mean().detach() + self.poly_kernel(f_s, f_s).mean()
- 2 * self.poly_kernel(f_s, f_t).mean())
else:
return self.poly_kernel(f_s, f_s).mean() - 2 * self.poly_kernel(f_s, f_t).mean()
def poly_kernel(self, a, b):
a = a.unsqueeze(1)
b = b.unsqueeze(2)
res = (a * b).sum(-1).pow(2)
return res
13. CRD: Contrastive Representation Distillation
全称:Contrastive Representation Distillation
链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.10699v2
发表:ICLR20
将对比学习引入知识蒸馏中,其目标修正为:学习一个表征,让正样本对的教师网络与学生网络尽可能接近,负样本对教师网络与学生网络尽可能远离。
构建的对比学习问题表示如下:
整体的蒸馏Loss表示如下:
实现如下:https://github.com/HobbitLong/RepDistiller
class ContrastLoss(nn.Module):
"""
contrastive loss, corresponding to Eq (18)
"""
def __init__(self, n_data):
super(ContrastLoss, self).__init__()
self.n_data = n_data
def forward(self, x):
bsz = x.shape[0]
m = x.size(1) - 1
# noise distribution
Pn = 1 / float(self.n_data)
# loss for positive pair
P_pos = x.select(1, 0)
log_D1 = torch.div(P_pos, P_pos.add(m * Pn + eps)).log_()
# loss for K negative pair
P_neg = x.narrow(1, 1, m)
log_D0 = torch.div(P_neg.clone().fill_(m * Pn), P_neg.add(m * Pn + eps)).log_()
loss = - (log_D1.sum(0) + log_D0.view(-1, 1).sum(0)) / bsz
return loss
class CRDLoss(nn.Module):
"""CRD Loss function
includes two symmetric parts:
(a) using teacher as anchor, choose positive and negatives over the student side
(b) using student as anchor, choose positive and negatives over the teacher side
Args:
opt.s_dim: the dimension of student's feature
opt.t_dim: the dimension of teacher's feature
opt.feat_dim: the dimension of the projection space
opt.nce_k: number of negatives paired with each positive
opt.nce_t: the temperature
opt.nce_m: the momentum for updating the memory buffer
opt.n_data: the number of samples in the training set, therefor the memory buffer is: opt.n_data x opt.feat_dim
"""
def __init__(self, opt):
super(CRDLoss, self).__init__()
self.embed_s = Embed(opt.s_dim, opt.feat_dim)
self.embed_t = Embed(opt.t_dim, opt.feat_dim)
self.contrast = ContrastMemory(opt.feat_dim, opt.n_data, opt.nce_k, opt.nce_t, opt.nce_m)
self.criterion_t = ContrastLoss(opt.n_data)
self.criterion_s = ContrastLoss(opt.n_data)
def forward(self, f_s, f_t, idx, contrast_idx=None):
"""
Args:
f_s: the feature of student network, size [batch_size, s_dim]
f_t: the feature of teacher network, size [batch_size, t_dim]
idx: the indices of these positive samples in the dataset, size [batch_size]
contrast_idx: the indices of negative samples, size [batch_size, nce_k]
Returns:
The contrastive loss
"""
f_s = self.embed_s(f_s)
f_t = self.embed_t(f_t)
out_s, out_t = self.contrast(f_s, f_t, idx, contrast_idx)
s_loss = self.criterion_s(out_s)
t_loss = self.criterion_t(out_t)
loss = s_loss + t_loss
return loss
14. Overhaul
全称:A Comprehensive Overhaul of Feature Distillation
链接:http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ICCV_2019/papers/
发表:CVPR19
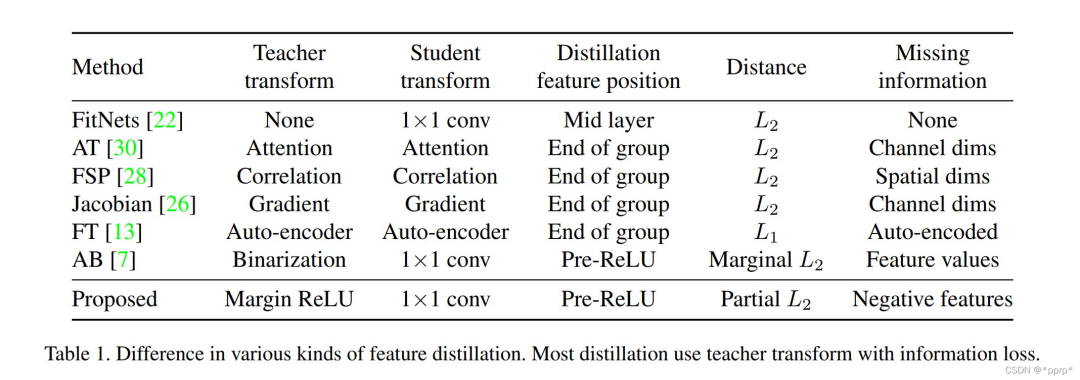
teacher transform中提出使用margin RELU激活函数。
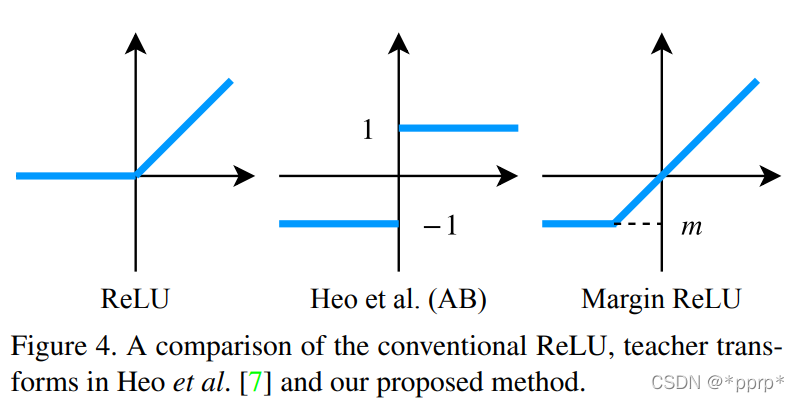
student transform中提出使用1x1卷积。
distillation feature postion选择Pre-ReLU。
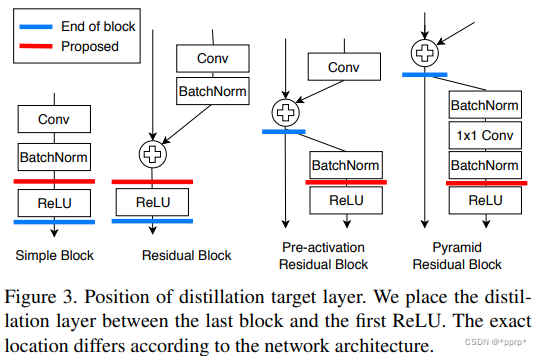
distance function部分提出了Partial L2 损失函数。
部分实现如下:
class OFD(nn.Module):
'''
A Comprehensive Overhaul of Feature Distillation
http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ICCV_2019/papers/
Heo_A_Comprehensive_Overhaul_of_Feature_Distillation_ICCV_2019_paper.pdf
'''
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(OFD, self).__init__()
self.connector = nn.Sequential(*[
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
])
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward(self, fm_s, fm_t):
margin = self.get_margin(fm_t)
fm_t = torch.max(fm_t, margin)
fm_s = self.connector(fm_s)
mask = 1.0 - ((fm_s <= fm_t) & (fm_t <= 0.0)).float()
loss = torch.mean((fm_s - fm_t)**2 * mask)
return loss
def get_margin(self, fm, eps=1e-6):
mask = (fm < 0.0).float()
masked_fm = fm * mask
margin = masked_fm.sum(dim=(0,2,3), keepdim=True) / (mask.sum(dim=(0,2,3), keepdim=True)+eps)
return margin
参考文献
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44579633/article/details/119350631
https://blog.csdn.net/winycg/article/details/105297089
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46239293/article/details/120289163
https://blog.csdn.net/DD_PP_JJ/article/details/121578722
https://blog.csdn.net/DD_PP_JJ/article/details/121714957
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/344881975
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44633882/article/details/108927033
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46239293/article/details/120266111
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43402775/article/details/109011296
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37665984/article/details/103288582
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37665984/article/details/103269740
好消息!
小白学视觉知识星球
开始面向外开放啦👇👇👇
下载1:OpenCV-Contrib扩展模块中文版教程 在「小白学视觉」公众号后台回复:扩展模块中文教程,即可下载全网第一份OpenCV扩展模块教程中文版,涵盖扩展模块安装、SFM算法、立体视觉、目标跟踪、生物视觉、超分辨率处理等二十多章内容。 下载2:Python视觉实战项目52讲 在「小白学视觉」公众号后台回复:Python视觉实战项目,即可下载包括图像分割、口罩检测、车道线检测、车辆计数、添加眼线、车牌识别、字符识别、情绪检测、文本内容提取、面部识别等31个视觉实战项目,助力快速学校计算机视觉。 下载3:OpenCV实战项目20讲 在「小白学视觉」公众号后台回复:OpenCV实战项目20讲,即可下载含有20个基于OpenCV实现20个实战项目,实现OpenCV学习进阶。 交流群
欢迎加入公众号读者群一起和同行交流,目前有SLAM、三维视觉、传感器、自动驾驶、计算摄影、检测、分割、识别、医学影像、GAN、算法竞赛等微信群(以后会逐渐细分),请扫描下面微信号加群,备注:”昵称+学校/公司+研究方向“,例如:”张三 + 上海交大 + 视觉SLAM“。请按照格式备注,否则不予通过。添加成功后会根据研究方向邀请进入相关微信群。请勿在群内发送广告,否则会请出群,谢谢理解~

