太强了,终于彻底搞懂 Nginx 的五大应用场景~
阅读本文大概需要 10 分钟。
来自:https://blog.csdn.net/vbirdbest/article/details/80913319
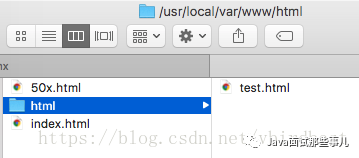
user mengday staff;http {server {listen 80;server_name localhost;client_max_body_size 1024M;# 默认locationlocation / {root /usr/local/var/www/html;index index.html index.htm;}}}
http://localhost/ 指向/usr/local/var/www/index.html, index.html是安装nginx自带的html http://localhost/test.html 指向/usr/local/var/www/html/test.html
注意:如果访问图片出现403 Forbidden错误,可能是因为nginx.conf 的第一行user配置不对,默认是#user nobody;是注释的,linux下改成user root; macos下改成user 用户名 所在组; 然后重新加载配置文件或者重启,再试一下就可以了, 用户名可以通过who am i 命令来查看。
server : 用于定义服务,http中可以有多个server块 listen : 指定服务器侦听请求的IP地址和端口,如果省略地址,服务器将侦听所有地址,如果省略端口,则使用标准端口 server_name : 服务名称,用于配置域名 location : 用于配置映射路径uri对应的配置,一个server中可以有多个location, location后面跟一个uri,可以是一个正则表达式, / 表示匹配任意路径, 当客户端访问的路径满足这个uri时就会执行location块里面的代码 root : 根路径,当访问http://localhost/test.html,“/test.html”会匹配到”/”uri, 找到root为/usr/local/var/www/html,用户访问的资源物理地址=root + uri = /usr/local/var/www/html + /test.html=/usr/local/var/www/html/test.html index : 设置首页,当只访问server_name时后面不跟任何路径是不走root直接走index指令的;如果访问路径中没有指定具体的文件,则返回index设置的资源,如果访问http://localhost/html/ 则默认返回index.html
. :匹配除换行符以外的任意字符 ? :重复0次或1次 + :重复1次或更多次 * :重复0次或更多次 \d :匹配数字 ^ :匹配字符串的开始 $ :匹配字符串的结束 {n} :重复n次 {n,} :重复n次或更多次 [c] :匹配单个字符c [a-z] :匹配a-z小写字母的任意一个 (a|b|c) : 属线表示匹配任意一种情况,每种情况使用竖线分隔,一般使用小括号括括住,匹配符合a字符 或是b字符 或是c字符的字符串 \ 反斜杠:用于转义特殊字符
# 静态服务器

http {server {listen 80;server_name localhost;set $doc_root /usr/local/var/www;# 默认locationlocation / {root /usr/local/var/www/html;index index.html index.htm;}location ^~ /images/ {root $doc_root;}location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|ico|swf|css|js)$ {root $doc_root/img;}}}
使用路径,如 /images/ 一般图片都会放在某个图片目录下, 使用后缀,如 .jpg、.png 等后缀匹配模式
= 进行普通字符精确匹配。也就是完全匹配。 ^~ 前缀匹配。如果匹配成功,则不再匹配其他location。 ~ 表示执行一个正则匹配,区分大小写 ~* 表示执行一个正则匹配,不区分大小写 /xxx/ 常规字符串路径匹配 / 通用匹配,任何请求都会匹配到
location优先级
等号类型(=)的优先级最高。一旦匹配成功,则不再查找其他匹配项,停止搜索。 ^~类型表达式,不属于正则表达式。一旦匹配成功,则不再查找其他匹配项,停止搜索。 正则表达式类型(~ ~*)的优先级次之。如果有多个location的正则能匹配的话,则使用正则表达式最长的那个。 常规字符串匹配类型。按前缀匹配。 / 通用匹配,如果没有匹配到,就匹配通用的
等号类型、^~类型:一旦匹配上就停止搜索了,不会再匹配其他location了 正则表达式类型(~ ~*),常规字符串匹配类型/xxx/ : 匹配到之后,还会继续搜索其他其它location,直到找到优先级最高的,或者找到第一种情况而停止搜索
location = / {# 精确匹配/,主机名后面不能带任何字符串 /[ configuration A ]}location / {# 匹配所有以 / 开头的请求。# 但是如果有更长的同类型的表达式,则选择更长的表达式。# 如果有正则表达式可以匹配,则优先匹配正则表达式。[ configuration B ]}location /documents/ {# 匹配所有以 /documents/ 开头的请求,匹配符合以后,还要继续往下搜索。# 但是如果有更长的同类型的表达式,则选择更长的表达式。# 如果有正则表达式可以匹配,则优先匹配正则表达式。[ configuration C ]}location ^~ /images/ {# 匹配所有以 /images/ 开头的表达式,如果匹配成功,则停止匹配查找,停止搜索。# 所以,即便有符合的正则表达式location,也不会被使用[ configuration D ]}location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {# 匹配所有以 gif jpg jpeg结尾的请求。# 但是 以 /images/开头的请求,将使用 Configuration D,D具有更高的优先级[ configuration E ]}location /images/ {# 字符匹配到 /images/,还会继续往下搜索[ configuration F ]}location = /test.htm {root /usr/local/var/www/htm;index index.htm;}
# 反向代理
server {listen 80;server_name localhost;location / {proxy_pass http://localhost:8081;proxy_set_header Host $host:$server_port;# 设置用户ip地址proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;# 当请求服务器出错去寻找其他服务器proxy_next_upstream error timeout invalid_header http_500 http_502 http_503;}}
# 负载均衡
1. RR(round robin :轮询 默认)
upstream web_servers {server localhost:8081;server localhost:8082;}server {listen 80;server_name localhost;#access_log logs/host.access.log main;location / {proxy_pass http://web_servers;# 必须指定Header Hostproxy_set_header Host $host:$server_port;}}
2. 权重
upstream test {server localhost:8081 weight=1;server localhost:8082 weight=3;server localhost:8083 weight=4 backup;}
3. ip_hash
upstream test {ip_hash;server localhost:8080;server localhost:8081;}
4. fair(第三方)
upstream backend {fair;server localhost:8080;server localhost:8081;}
5. url_hash(第三方)
upstream backend {hash $request_uri;hash_method crc32;server localhost:8080;server localhost:8081;}
# 动静分离
upstream web_servers {server localhost:8081;server localhost:8082;}server {listen 80;server_name localhost;set $doc_root /usr/local/var/www;location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|ico|swf|css|js)$ {root $doc_root/img;}location / {proxy_pass http://web_servers;# 必须指定Header Hostproxy_set_header Host $host:$server_port;}error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;location = /50x.html {root $doc_root;}}
# 其他
1.return指令
location /permanently/moved/url {return 301 http://www.example.com/moved/here;}
2. rewrite指令
location /users/ {rewrite ^/users/(.*)$ /show?user=$1 break;}
3. error_page指令
error_page 404 /404.html;
4. 日志
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ''$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ''"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';access_log /usr/local/etc/nginx/logs/host.access.log main;gzip on;
5. deny 指令
# 禁止访问某个目录location ~* \.(txt|doc)${root $doc_root;deny all;}
6. 内置变量
$args :#这个变量等于请求行中的参数,同$query_string $content_length :请求头中的Content-length字段。 $content_type :请求头中的Content-Type字段。 $document_root :当前请求在root指令中指定的值。 $host :请求主机头字段,否则为服务器名称。 $http_user_agent :客户端agent信息 $http_cookie :客户端cookie信息 $limit_rate :这个变量可以限制连接速率。 $request_method :客户端请求的动作,通常为GET或POST。 $remote_addr :客户端的IP地址。 $remote_port :客户端的端口。 $remote_user :已经经过Auth Basic Module验证的用户名。 $request_filename :当前请求的文件路径,由root或alias指令与URI请求生成。 $scheme :HTTP方法(如http,https)。 $server_protocol :请求使用的协议,通常是HTTP/1.0或HTTP/1.1。 $server_addr :服务器地址,在完成一次系统调用后可以确定这个值。 $server_name :服务器名称。 $server_port :请求到达服务器的端口号。 $request_uri :包含请求参数的原始URI,不包含主机名,如:”/foo/bar.php?arg=baz”。 $uri :不带请求参数的当前URI,$uri不包含主机名,如”/foo/bar.html”。 $document_uri :与$uri相同
推荐阅读:
基于SpringBoot+WebMagic实现一个的爬虫框架
最近面试BAT,整理一份面试资料《Java面试BATJ通关手册》,覆盖了Java核心技术、JVM、Java并发、SSM、微服务、数据库、数据结构等等。
朕已阅 
评论

