在面试中,被反复提及的 OpenGL NV21 图像渲染
YUV 渲染原理
前面文章一文掌握 YUV 图像的基本处理介绍了 YUV 常用的基本格式,本文以实现 NV21/NV12 的渲染为例。
前文提到,YUV 图不能直接用于显示,需要转换为 RGB 格式,而 YUV 转 RGB 是一个逐像素处理的耗时操作,在 CPU 端进行转换效率过低,这时正好可以利用 GPU 强大的并行处理能力来实现 YUV 到 RGB 的转换。
YUV 与 RGB 之间的转换公式。
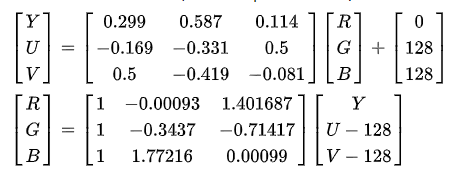

需要注意的是 OpenGLES 的内置矩阵实际上是一列一列地构建的,比如 YUV 和 RGB 的转换矩阵的构建是:
mat3 convertMat = mat3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, //第一列
0.0,-0.338,1.732, //第二列
1.371,-0.698, 0.0);//第三列
OpenGLES 实现 YUV 渲染需要用到 GL_LUMINANCE 和 GL_LUMINANCE_ALPHA 格式的纹理,其中 GL_LUMINANCE 纹理用来加载 NV21 Y Plane 的数据,GL_LUMINANCE_ALPHA 纹理用来加载 UV Plane 的数据。
OpenGLES 常用纹理的格式类型。
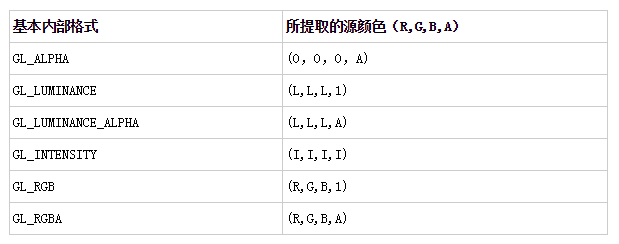
GL_LUMINANCE 纹理在着色器中采样的纹理像素格式是(L,L,L,1),L 表示亮度。GL_LUMINANCE_ALPHA 纹理在着色器中采样的纹理像素格式是(L,L,L,A),A 表示透明度。
YUV 渲染实现
YUV 渲染步骤:
生成 2 个纹理,编译链接着色器程序;
确定纹理坐标及对应的顶点坐标;
分别加载 NV21 的两个 Plane 数据到 2 个纹理,加载纹理坐标和顶点坐标数据到着色器程序;
绘制。
片段着色器脚本。
#version 300 es
precision mediump float;
in vec2 v_texCoord;
layout(location = 0) out vec4 outColor;
uniform sampler2D y_texture;
uniform sampler2D uv_texture;
void main()
{
vec3 yuv;
yuv.x = texture(y_texture, v_texCoord).r;
yuv.y = texture(uv_texture, v_texCoord).a-0.5;
yuv.z = texture(uv_texture, v_texCoord).r-0.5;
vec3 rgb =mat3( 1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
0.0, -0.344, 1.770,
1.403, -0.714, 0.0) * yuv;
outColor = vec4(rgb, 1);
}
y_texture 和 uv_texture 分别是 NV21 Y Plane 和 UV Plane 纹理的采样器,对两个纹理采样之后组成一个(y,u,v)三维向量,之后左乘变换矩阵转换为(r,g,b)三维向量。
Java 层 Load NV21 数据。
private void LoadNV21Image() {
InputStream is = null;
try {
is = getAssets().open("YUV_Image_840x1074.NV21");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
int lenght = 0;
try {
lenght = is.available();
byte[] buffer = new byte[lenght];
is.read(buffer);
mGLSurfaceView.getNativeRender().native_SetImageData(IMAGE_FORMAT_NV21, 840, 1074, buffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try
{
is.close();
}
catch(IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Native 层转换为 NativeImage。
void MyGLRenderContext::SetImageData(int format, int width, int height, uint8_t *pData)
{
LOGCATE("MyGLRenderContext::SetImageData format=%d, width=%d, height=%d, pData=%p", format, width, height, pData);
NativeImage nativeImage;
nativeImage.format = format;
nativeImage.width = width;
nativeImage.height = height;
nativeImage.ppPlane[0] = pData;
switch (format)
{
case IMAGE_FORMAT_NV12:
case IMAGE_FORMAT_NV21:
nativeImage.ppPlane[1] = nativeImage.ppPlane[0] + width * height;
break;
case IMAGE_FORMAT_I420:
nativeImage.ppPlane[1] = nativeImage.ppPlane[0] + width * height;
nativeImage.ppPlane[2] = nativeImage.ppPlane[1] + width * height / 4;
break;
default:
break;
}
if (m_Sample)
{
m_Sample->LoadImage(&nativeImage);
}
}
//copy 到 sample
void NV21TextureMapSample::LoadImage(NativeImage *pImage)
{
LOGCATE("NV21TextureMapSample::LoadImage pImage = %p", pImage->ppPlane[0]);
if (pImage)
{
m_RenderImage.width = pImage->width;
m_RenderImage.height = pImage->height;
m_RenderImage.format = pImage->format;
NativeImageUtil::CopyNativeImage(pImage, &m_RenderImage);
}
}
加载 NV21 的 2 个 Plane 数据到纹理,ppPlane[0] 表示 Y Plane 的指针,ppPlane[1] 表示 UV Plane 的指针,注意 2 个纹理的格式和宽高。
//upload Y plane data
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, m_yTextureId);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_LUMINANCE, m_RenderImage.width, m_RenderImage.height, 0, GL_LUMINANCE, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, m_RenderImage.ppPlane[0]);
glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_NONE);
//update UV plane data
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, m_uvTextureId);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_LUMINANCE_ALPHA, m_RenderImage.width >> 1, m_RenderImage.height >> 1, 0, GL_LUMINANCE_ALPHA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, m_RenderImage.ppPlane[1]);
glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_NONE);
简单代码实现。
// 编译链接着色器程序,生成 2 个纹理
void NV21TextureMapSample::Init()
{
char vShaderStr[] =
"#version 300 es \n"
"layout(location = 0) in vec4 a_position; \n"
"layout(location = 1) in vec2 a_texCoord; \n"
"out vec2 v_texCoord; \n"
"void main() \n"
"{ \n"
" gl_Position = a_position; \n"
" v_texCoord = a_texCoord; \n"
"} \n";
char fShaderStr[] =
"#version 300 es \n"
"precision mediump float; \n"
"in vec2 v_texCoord; \n"
"layout(location = 0) out vec4 outColor; \n"
"uniform sampler2D y_texture; \n"
"uniform sampler2D uv_texture; \n"
"void main() \n"
"{ \n"
" vec3 yuv; \n"
" yuv.x = texture(y_texture, v_texCoord).r; \n"
" yuv.y = texture(uv_texture, v_texCoord).a-0.5; \n"
" yuv.z = texture(uv_texture, v_texCoord).r-0.5; \n"
" highp vec3 rgb = mat3( 1, 1, 1, \n"
" 0, -0.344, 1.770, \n"
" 1.403, -0.714, 0) * yuv; \n"
" outColor = vec4(rgb, 1); \n"
"} \n";
// Load the shaders and get a linked program object
m_ProgramObj= GLUtils::CreateProgram(vShaderStr, fShaderStr, m_VertexShader, m_FragmentShader);
// Get the sampler location
m_ySamplerLoc = glGetUniformLocation (m_ProgramObj, "y_texture" );
m_uvSamplerLoc = glGetUniformLocation(m_ProgramObj, "uv_texture");
//create textures
GLuint textureIds[2] = {0};
glGenTextures(2, textureIds);
m_yTextureId = textureIds[0];
m_uvTextureId = textureIds[1];
}
// 加载 NV21 图像数据到纹理,加载纹理坐标和顶点坐标数据到着色器程序,绘制实现 YUV 渲染
void NV21TextureMapSample::Draw(int screenW, int screenH)
{
LOGCATE("NV21TextureMapSample::Draw()");
if(m_ProgramObj == GL_NONE || m_yTextureId == GL_NONE || m_uvTextureId == GL_NONE) return;
//upload Y plane data
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, m_yTextureId);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_LUMINANCE, m_RenderImage.width, m_RenderImage.height, 0, GL_LUMINANCE, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, m_RenderImage.ppPlane[0]);
glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_NONE);
//update UV plane data
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, m_uvTextureId);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_LUMINANCE_ALPHA, m_RenderImage.width >> 1, m_RenderImage.height >> 1, 0, GL_LUMINANCE_ALPHA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, m_RenderImage.ppPlane[1]);
glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_NONE);
//glViewport(0, 0, m_RenderImage.width, m_RenderImage.height);
GLfloat verticesCoords[] = {
-1.0f, 0.78f, 0.0f, // Position 0
-1.0f, -0.78f, 0.0f, // Position 1
1.0f, -0.78f, 0.0f, // Position 2
1.0f, 0.78f, 0.0f, // Position 3
};
GLfloat textureCoords[] = {
0.0f, 0.0f, // TexCoord 0
0.0f, 1.0f, // TexCoord 1
1.0f, 1.0f, // TexCoord 2
1.0f, 0.0f // TexCoord 3
};
GLushort indices[] = { 0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3 };
// Use the program object
glUseProgram (m_ProgramObj);
// Load the vertex position
glVertexAttribPointer (0, 3, GL_FLOAT,
GL_FALSE, 3 * sizeof (GLfloat), verticesCoords);
// Load the texture coordinate
glVertexAttribPointer (1, 2, GL_FLOAT,
GL_FALSE, 2 * sizeof (GLfloat), textureCoords);
glEnableVertexAttribArray (0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray (1);
// Bind the Y plane map
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, m_yTextureId);
// Set the Y plane sampler to texture unit to 0
glUniform1i(m_ySamplerLoc, 0);
// Bind the UV plane map
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, m_uvTextureId);
// Set the UV plane sampler to texture unit to 1
glUniform1i(m_uvSamplerLoc, 1);
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, 6, GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT, indices);
}
-- END --
推荐:
全网最全的 Android 音视频和 OpenGL ES 干货,都在这了
