【JS】1034- Event Loop :你知道它们的打印顺序吗?

前言
在 《浏览器知识点整理(十三)不同的回调执行时机:宏任务和微任务》[1] 这篇文章的后面有几道打印面试题,觉得不够过瘾,于是又找了一些对应的面试题来,还在不同的 Node.js 版本上面跑了跑,希望你也能过过瘾。
先来回顾一下浏览器 Event Loop 的过程:
先执行 当前调用栈中的同步代码(一个宏任务); 调用栈为空后去检查是否有异步任务(微任务)需要执行; 如果有则 执行完当前异步代码(当前宏任务中微任务队列里的所有微任务), 再之后就是 从消息队列中取出下一个宏任务 去执行(重新维护一个调用栈),然后开始新一轮的 Event Lopp。
然后不同版本的 Node.js 的一个 Event Loop 区别:
如果是 Node 10 及其之前版本:宏任务队列当中有几个宏任务,是要等到宏任务队列当中的所有宏任务全部执行完毕才会去执行微队列当中的微任务。 如果是 Node 11 及之后版本:一旦执行一个阶段里对应宏队列当中的一个宏任务( setTimeout,setInterval和setImmediate三者其中之一,不包括 I/O)就立刻执行微任务队列,执行完微队列当中的所有微任务再回到刚才的宏队列执行下一个宏任务。这就 跟浏览器端运行一致 了。
为了过这个瘾,我意用 nvm (nvm install 10.13.0)安装了 10.13.0 版本的 Node.js
参赛选手主要是宏任务代表 setTimeout 和微任务扛把子 Promise 及新贵 async/awiat 。
基础版本
首先是单个任务的版本:
setTimeout:
console.log('script start');
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout1')
}, 100)
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout2')
}, 50)
console.log('script end');
复制代码
在 Chrome 中有一个 ProcessDelayTask 函数,该函数会根据发起时间和延迟时间计算出到期的任务,然后依次执行这些到期的任务。执行顺序如下:

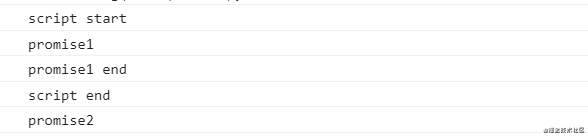
Promise:
console.log('script start');
new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log('promise1');
resolve();
console.log('promise1 end');
}).then(() => {
console.log('promise2');
})
console.log('script end');
复制代码
在 Promise 内部是 同步执行 的,所以会有以下打印顺序:
async/awiat:
async function async1() {
console.log('async1 start')
await async2();
console.log('async1 end')
}
async function async2() {
console.log('async2')
}
console.log('script start')
async1();
console.log('script end')
复制代码
执行顺序如下,这里需要注意的是 async2 函数也是同步执行的。

以上的基础版本就是同步和异步的区别了,因为是单个任务,也没有其它复杂的场景,在 Node.js 中的表现和浏览器是一样的。
组合版本一(setTimeout 和 Promise)
console.log('script start');
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setimeout');
}, 0)
new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log('promise1');
resolve();
console.log('promise1 end');
}).then(() => {
console.log('promise2');
})
console.log('script end');
复制代码
在 Chrome 中的执行顺序:
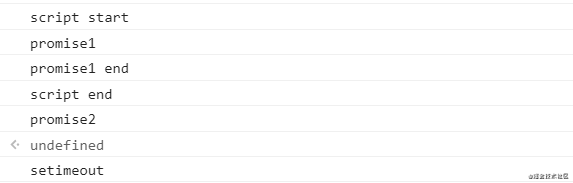
这个版本就是简单的宏任务 setTimeout 和微任务 Promise 的组合了,因为也就一个宏任务和一个微任务,它在不同版本中的 Node.js 里面表现也是和在浏览器一样的。
组合版本二(setTimeout 和 Promise、async/await)
console.log('script start')
async function async1() {
console.log('async1 start')
await async2()
console.log('async1 end')
}
async function async2() {
console.log('async2')
}
async1()
new Promise(resolve => {
console.log('promise1 start')
resolve()
console.log('promise1 end')
}).then(() => {
console.log('promise2')
})
console.log('script end')
复制代码
在 Chrome 中的执行顺序:
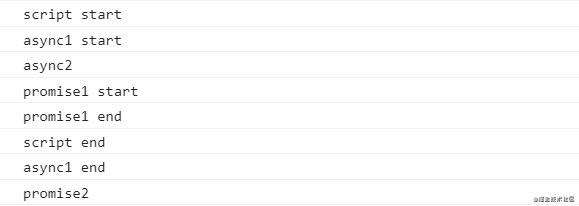
在 Node.js 10.13.0 中的执行顺序:
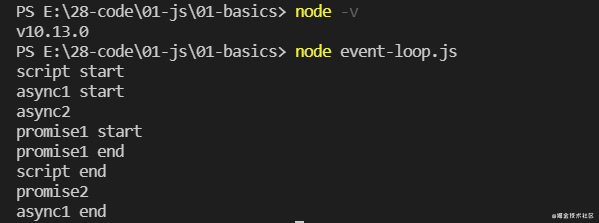
在 Node.js 12.18.3 中的执行顺序:
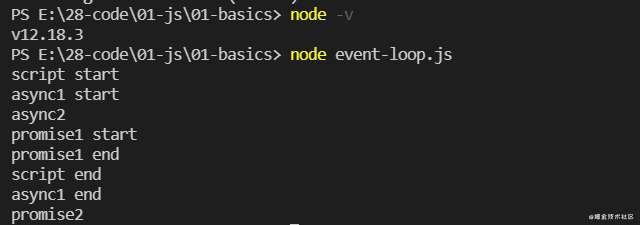
惊不惊喜!意不意外!Chrome(91版本)和 Node.js 12.18.3 的版本表现是一致的,在 Node.js 10.13.0 版本中有些差异,主要是 promise2 和 async1 end 打印顺序的不同,也就是说 async/await 在不同版本的 Node.js 处理是不一样的(Chrome 70 后和 Chrome 70 前的处理也不一样)。
想要搞清楚其中的区别,可以去 promise, async, await, execution order[2] 一探究竟。
混合版本一(setTimeout 和 Promise)
console.log('script start')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout1')
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('promise1')
})
}, 0)
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout2')
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('promise2')
})
}, 0)
console.log('script end')
复制代码
在 Chrome 中的执行顺序:
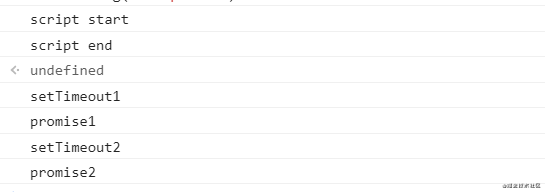
在 Node.js 10.13.0 中的执行顺序:
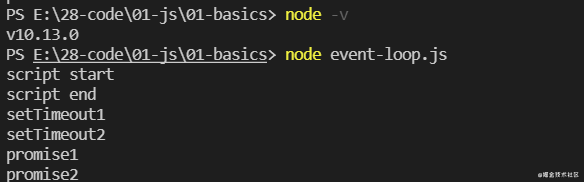
在 Node.js 12.18.3 中的执行顺序:
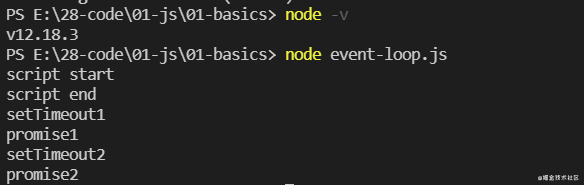
这个混合版本主要是看 Node.js 版本 10 前后 Event Loop 的差别。
混合版本二(setTimeout 和 Promise)
setTimeout 和 Promise:
console.log('script start')
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('promise1')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout1')
}, 0)
})
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout2')
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('promise2')
})
}, 0)
console.log('script end')
复制代码
在 Chrome 中的执行顺序:
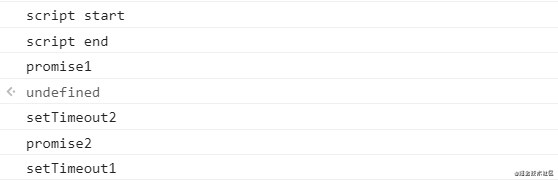
在 Node.js 10.13.0 中的执行顺序:
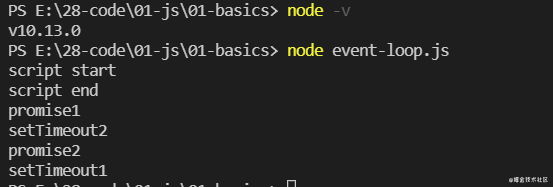
在 Node.js 12.18.3 中的执行顺序:
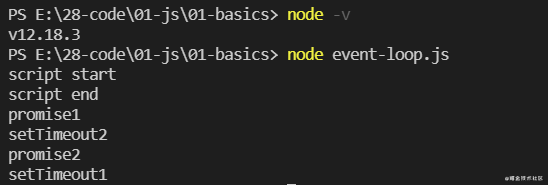
这个版本是执行完同步代码(script end)后,这时候第一个 Promise(promise1) 在微任务队列里面,第二个 setTimeout 已经加到消息队列(延迟队列)尾部了;这时候去执行微任务,即打印 promise1,然后把第一个 setTimeout 加到消息队列(延迟队列)尾部,所以会是先打印 setTimeout2、promise2 之后再打印 setTimeout1。
混合版本三(Promise)
宏任务和微任务的组合混合都差不多了,那来看看微任务之间的混合吧!
async function async1() {
console.log('async1 start');
Promise.resolve(async2()).then(() => {
console.log('async1 end');
})
}
async function async2() {
console.log('async2');
Promise.resolve(async3()).then(() => {
console.log('async2 end');
})
}
async function async3() {
console.log('async3');
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('async3 end');
})
}
console.log('script start');
async1();
new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log('promise1');
resolve();
}).then(() => {
console.log('promise2');
});
console.log('script end');
复制代码
在 Chrome 中的执行顺序:
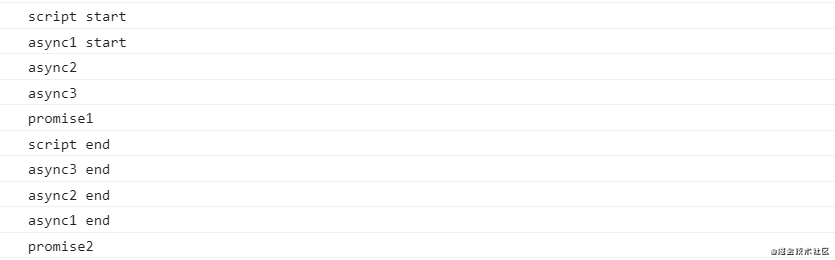
在 Node.js 10.13.0 中的执行顺序:
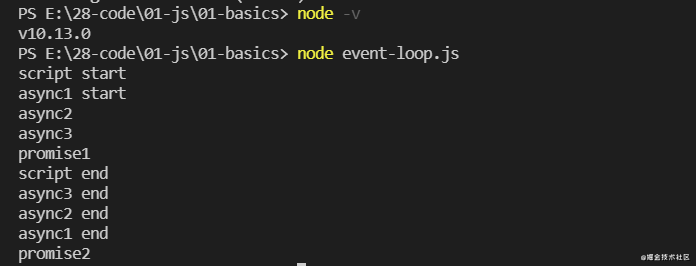
这个也容易理解,按照调用栈的出入栈顺序,先执行的是同步代码,执行到 async3 的时候才把 async3 end 加入微任务队列,之后 async3() 函数出栈,回到 async2,把 async2 end 加入微任务队列,后面的同理,于是就有了这个打印顺序。
混合版本四(Promise 和 async/await)
async function async1() {
console.log('async1 start');
await async2();
console.log('async1 end');
}
async function async2() {
console.log('async2');
await async3()
console.log('async2 end')
}
async function async3() {
await console.log('async3');
console.log('async3 end')
}
console.log('script start');
async1();
new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log('promise1');
resolve();
}).then(() => {
console.log('promise2');
});
console.log('script end');
复制代码
在 Chrome 中的执行顺序:
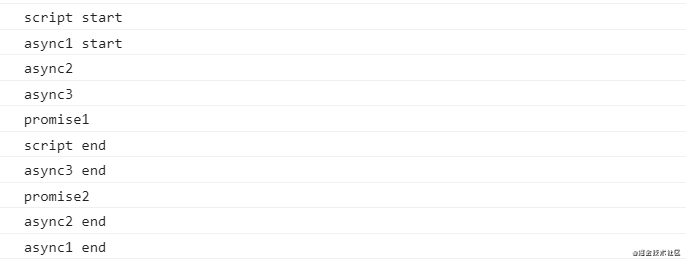
在 Node.js 10.13.0 中的执行顺序:
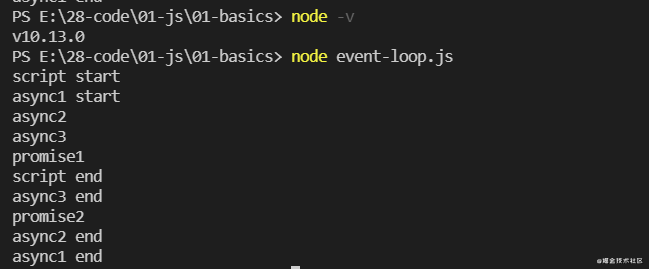
版本四和版本三的区别是将 async 函数里面的 Promise 换成了 await,而且版本三中的 async 函数里面没有 await,都可以把 function 前面的 async 标记拿掉的,不要被迷惑了哦。
在同步代码执行到 script end 之前我想都没什么问题,async 里面都是有 await 的,所以在后面的代码可以理解为如下形式:
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('async3 end');
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('async2 end');
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('async1 end');
})
})
})
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('promise2');
})
复制代码
混合版本五(Promise 和 async/await)
function async1() {
console.log('async1 start');
Promise.resolve(async2()).then(() => {
console.log('async1 end');
})
}
function async2() {
console.log('async2');
Promise.resolve(async3()).then(() => {
console.log('async2 end');
})
}
async function async3() {
await console.log('async3');
console.log('async3 end');
}
console.log('script start');
async1();
new Promise(function (resolve) {
console.log('promise1');
resolve();
}).then(function () {
console.log('promise2');
});
console.log('script end');
复制代码
在 Chrome 中的执行顺序:
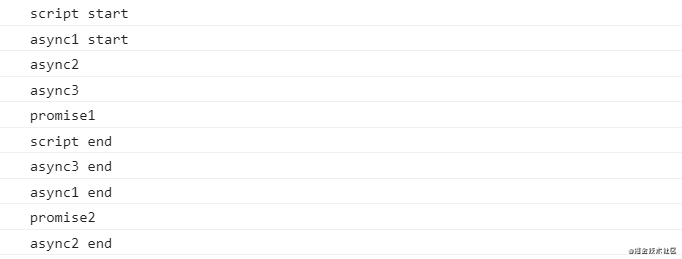
在 Node.js 10.13.0 中的执行顺序:
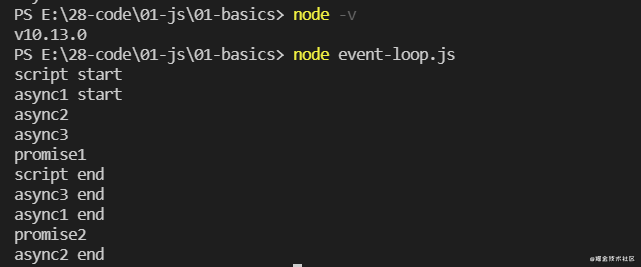
通过前面版本四的考验,这里应该也难不倒你,这里只有 async3 里面有一个 await,执行到 script end 之前都一样,到了 async3 end 后面的代码可以转化为以下形式思考:
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('async3 end');
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('async2 end');
})
})
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('async1 end');
})
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('promise2');
})
复制代码
总结
纸上得来终觉浅,绝知此事要躬行。
关于本文
来源:起风了Q
https://juejin.cn/post/6979244116199047204

回复“加群”与大佬们一起交流学习~
点击“阅读原文”查看 120+ 篇原创文章
