C语言中内存四区的本质分析
素材来源 | 抖点料er
1.1数据类型本质分析
1.1.1数据类型的概念
1.1.2数据类型的本质
1.2变量的本质分析
1.2.1变量的概念
1.2.2变量的本质
1.3程序的内存四区模型
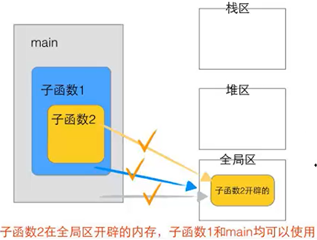
1.4函数调用模型

1.5函数调用变量传递分析
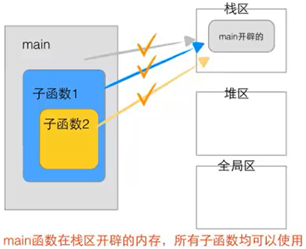
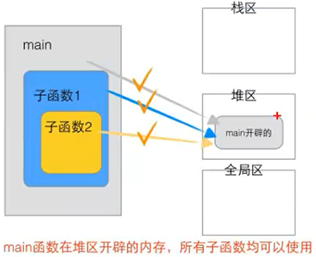
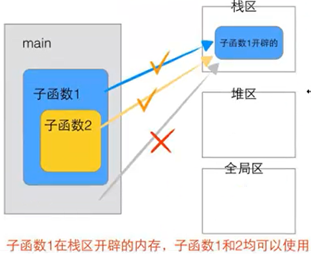
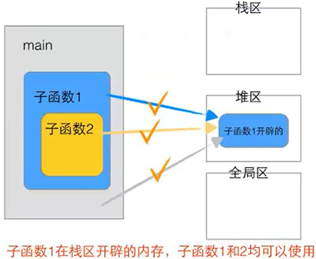
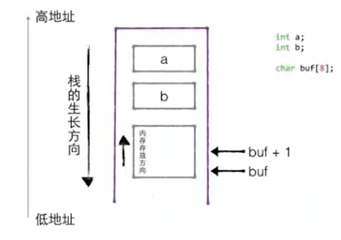
1.5栈的生长方向和内存存放方向
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a;//告诉编译器,分配4个字节
int b[10];//告诉编译器,分配4*10个字节
/*
类型本质:固定内存块大小别名
可以通过sizeof()测试
*/
printf("sizeof(a)=%d,sizeof(b)=%d\n", sizeof(a), sizeof(b));
//打印地址
//数组名称,数组首元素地址,数组首地址
printf("b:%d,&b:%d\n",b,&b);//地址相同
//b,&b数组类型不同
//b,数组首地址元素 一个元素4字节,+1 地址+4
//&b,整个数组首地址 一个数组4*10=40字节, +1 地址+40
printf("b+1:%d,&b+1:%d\n", b + 1, &b + 1);//不同
//指针类型长度,32位机器32位系统下长度是 4字节
// 64 64 8
char********* p = NULL;
int* q = NULL;
printf("%d,%d\n", sizeof(p), sizeof(q));//4 , 4
return 0;
}#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include
#include
#include
typedef unsigned int u32;
//typedef 和结构体结合使用
struct Mystruct
{
int a;
int b;
};
typedef struct Mystruct2
{
int a;
int b;
}TMP;
/*
void 无类型
1.函数参数为空,定义函数时用void修饰 int fun(void)
2.函数没有返回值:使用void void fun (void)
3.不能定义void类型的普通变量:void a;//err 无法确定是什么类型
4.可以定义 void* 变量 void* p;//ok 32位系统下永远是4字节
5.数据类型本质:固定内存块大小别名
6.void *p万能指针,函数返回值,函数参数
*/
int main()
{
u32 t;//unsigned int
//定义结构体变量,一定要加上struct 关键字
struct Mystruct m1;
//Mystruct m2;//err
TMP m3;//typedef配合结构体使用
struct Mystruct2 m4;
printf("\n");
return 0;
}04_变量的赋值.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
//变量本质:一段连续内存空间别名
//变量相当于门牌号,内存相当于房间
int a;
int* p;
//直接赋值
a = 10;
printf("a=%d\n", a);
//间接赋值
printf("&a:%d\n", &a);
p = &a;
printf("p=%d\n", p);
*p = 22;
printf("*p=%d,a=%d\n", *p, a);
return 0;
}
05_全局区分析.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
//变量本质:一段连续内存空间别名
//变量相当于门牌号,内存相当于房间
int a;
int* p;
//直接赋值
a = 10;
printf("a=%d\n", a);
//间接赋值
printf("&a:%d\n", &a);
p = &a;
printf("p=%d\n", p);
*p = 22;
printf("*p=%d,a=%d\n", *p, a);
return 0;
}
06_堆栈区分析.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include
#include
#include
char* get_str()
{
char str[] = "abcdef";//内容分配在栈区,函数运行完毕后内存释放
printf("%s\n", str);
return str;
}
char* get_str2()
{
char* temp = (char*)malloc(100);
if (temp == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
strcpy(temp, "abcdefg");
return temp;
}
int main()
{
char buf[128] = { 0 };
//strcpy(buf,get_str());
//printf("buf = %s\n", buf);//乱码,不确定内容
char* p = NULL;
p = get_str2();
if (p != NULL)
{
printf("p=%s\n", p);
free(p);
p = NULL;
}
return 0;
}07_静态局部变量.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include
#include
#include
int* getA()
{
static int a = 10;//在静态区,静态区在全局区
return &a;
}
int main()
{
int* p = getA();
*p = 5;
printf("%d\n",);
return 0;
}
08_栈的生长方向.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include
#include
#include
int* getA()
{
static int a = 10;//在静态区,静态区在全局区
return &a;
}
int main()
{
int* p = getA();
*p = 5;
printf("%d\n",);
return 0;
}版权申明:内容来源网络,版权归原创者所有。除非无法确认,我们都会标明作者及出处,如有侵权烦请告知,我们会立即删除并表示歉意。谢谢!
评论
