NeurIPS 2019杰出论文深度解读:窥视机器学习的核心问题

新智元推荐
来源:学术头条(ID:SciTouTiao)
作者:AMiner编辑部
【新智元导读】在NeurIPS 2019一千多篇入选论文中,有那么1篇杰出论文值得长时间、深入、反复学习。这篇杰出论文的出彩之处在哪里呢?我们又能从中学到什么呢?现在戳右边链接上新智元小程序 了解更多!
该论文的作者是:Ilias Diakonikolas(威斯康辛大学麦迪逊分校)、Themis Gouleakis(马克斯普朗克计算机科学研究所)、Christos Tzamos(威斯康辛大学麦迪逊分校)。

论文地址:https://papers.nips.cc/paper/8722-distribution-independent-pac-learning-of- halfspaces-with-massart-noise
前言
本文将对NeurIPS 2019杰出论文《Distribution-Independent PAC Learning of Halfspaces with Massart Noise》进行解读,该论文在半空间学习上取得了显著进展。作者研究了存在Massart噪声的半空间(halfspaces)分布独立的PAC学习问题。具体而言,给定从R^d+1上的分布D中提取的一组有标签样本(x, y),使无标记点x上的边缘分布是任意的,且标签y由未知半空间生成,该空间被噪声率为η<1/2的Massart噪声破坏。最终目标是找到一个分类器h,使错误分类误差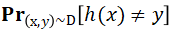 最小。对于具有错误分类误差η+ε的问题,作者给出了一个poly(d, 1/ε)时间算法。作者还证明了对算法的误差保证进行改进可能很难实现。在此工作之前,即使是析取类,在这个模型中也没有有效的弱学习方法(分布独立)。
最小。对于具有错误分类误差η+ε的问题,作者给出了一个poly(d, 1/ε)时间算法。作者还证明了对算法的误差保证进行改进可能很难实现。在此工作之前,即使是析取类,在这个模型中也没有有效的弱学习方法(分布独立)。
研究现状
Massart 噪声与RCN
随机分类噪声(Random Classification Noise ,RCN)【1】是Massart噪声的特殊情况,其每个标签的翻转概率恰好为η<1/2。似乎Massart噪声比RCN更易于处理。但实际上,Massart对抗需要选择是否扰动给定的标签,如扰动,以何种概率进行,因此,在该模型中设计有效的算法具有很大挑战性。尤其是,RCN学习与统计查询(Statistical Query,SQ)模型【2】【3】之间的联系不再成立,即,作为SQ算法的性质已不能自动满足用Massart噪声进行噪声容忍学习(noise-tolerant learning)的需要。而【4】【5】中正是利用了RCN与SQ模型的关系,得到了用RCN学习半空间的多项式时间算法。
相关工作介绍
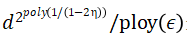 采样和时间算法。
采样和时间算法。方法
相关基础

带Massart噪声的半空间学习算法


学习大边界半空间

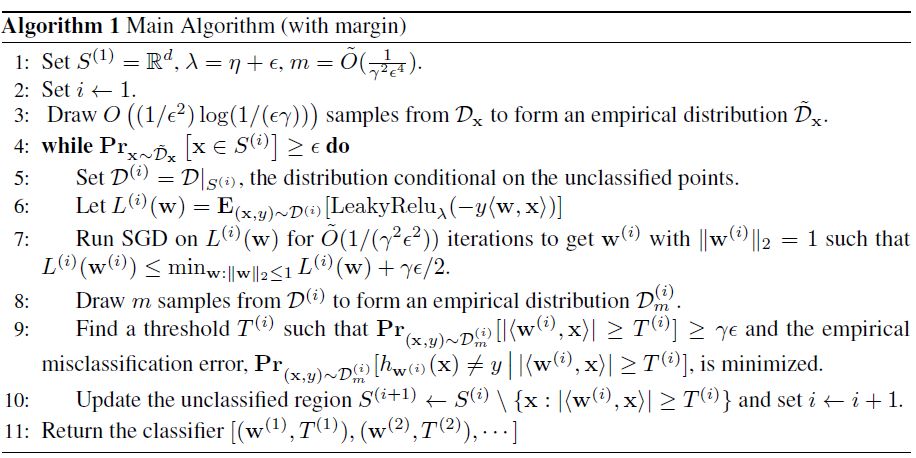



一般情况

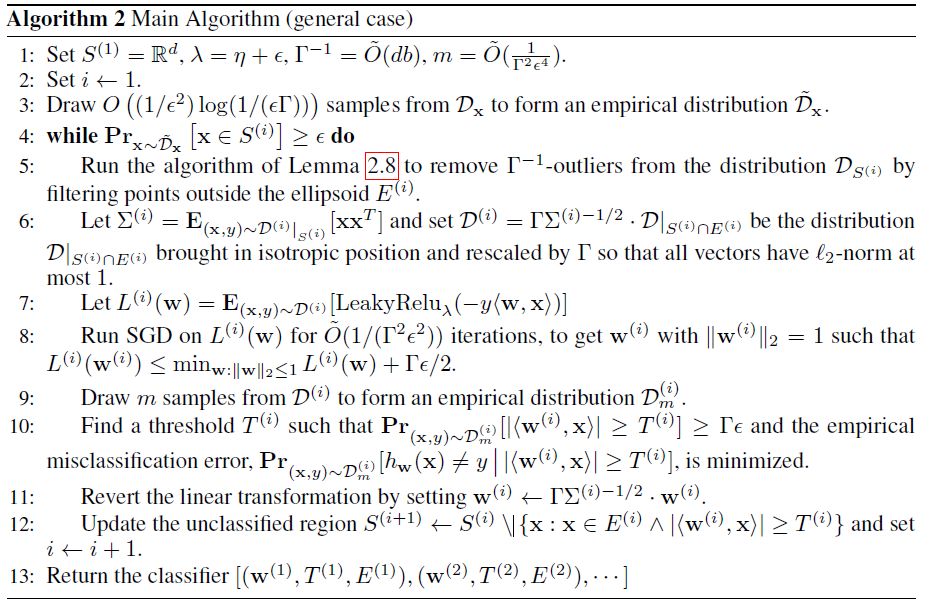
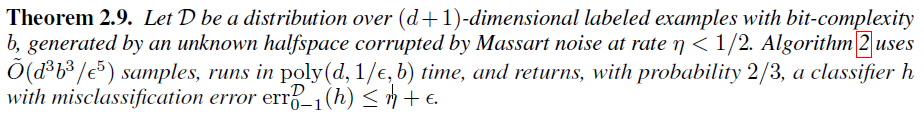
令D为(d + 1)维度的带标签样本在b-bit复杂度上的分布,由一个未知的半空间所产生,该空间被噪声率为η<1/2的Massart噪声破坏。算法2使用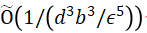 个样本,运行时间为poly(d, 1/ε, b),最终以2/3的概率返回一个分类器h,且其误分类误差
个样本,运行时间为poly(d, 1/ε, b),最终以2/3的概率返回一个分类器h,且其误分类误差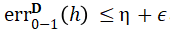 。
。
【1】D. Angluin and P. Laird. Learning from noisy examples. Mach. Learn., 2(4):343–370,1988.【2】M. J. Kearns. Efficient noise-tolerant learning from statistical queries. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, pages 392–401,1993.【3】M. J. Kearns. Efficient noise-tolerant learning from statistical queries. Journal of the ACM, 45(6):983–1006, 1998.【4】A. Blum, A. M. Frieze, R. Kannan, and S. Vempala. A polynomial-time algorithm for learning noisy linear threshold functions. In 37th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, FOCS ’96, pages 330–338, 1996.【5】A. Blum, A. Frieze, R. Kannan, and S. Vempala. A polynomial time algorithm for learning noisy linear threshold functions. Algorithmica, 22(1/2):35–52, 1997.【6】T. Bylander. Learning linear threshold functions in the presence of classification noise.In Proceedings of the Seventh Annual ACM Conference on Computational Learning Theory, COLT 1994, pages 340–347, 1994.【7】A. Blum, A. M. Frieze, R. Kannan, and S. Vempala. A polynomial-time algorithm for learning noisy linear threshold functions. In 37th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, FOCS ’96, pages 330–338, 1996.【8】E. Cohen. Learning noisy perceptrons by a perceptron in polynomial time. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Eighth Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, pages 514–521,1997.【9】J. Dunagan and S. Vempala. A simple polynomial-time rescaling algorithm for solving linear programs. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, pages 315–320, 2004【10】P. Awasthi, M. F. Balcan, N. Haghtalab, and R. Urner. Efficient learning of linear separators under bounded noise. In Proceedings of The 28th Conference on Learning Theory, COLT 2015, pages 167–190, 2015.【11】Y. Zhang, P. Liang, and M. Charikar. A hitting time analysis of stochastic gradient langevin dynamics. In Proceedings of the 30th Conference on Learning Theory, COLT 2017, pages 1980–2022, 2017.【12】Y. Zhang, P. Liang, and M. Charikar. A hitting time analysis of stochastic gradient langevin dynamics. In Proceedings of the 30th Conference on Learning Theory, COLT 2017, pages 1980–2022, 2017.【13】P. Awasthi, M. F. Balcan, N. Haghtalab, and H. Zhang. Learning and 1-bit compressed sensing under asymmetric noise. In Proceedings of the 29th Conference on Learning Theory, COLT 2016, pages 152–192, 2016.【14】A. Dvoretzky, J. Kiefer, and J. Wolfowitz. Asymptotic minimax character of the sample distribution function and of the classical multinomial estimator. Ann. Mathematical Statistics, 27(3):642–669, 1956.【15】J. Dunagan and S. Vempala. Optimal outlier removal in high-dimensional spaces. J.Computer & System Sciences, 68(2):335–373, 2004.
本文经授权转载自:学术头条

