Tomcat session的实现:线程安全与管理
本文所说的session是单机版本的session, 事实上在当前的互联网实践中已经不太存在这种定义了。我们主要讨论的是其安全共享的实现,只从理论上来讨论,不必太过在意实用性问题。
1:session 的意义简说
大概就是一个会话的的定义,客户端有cookie记录,服务端session定义。用于确定你就是你的一个东西。
每个用户在一定范围内共享某个session信息,以实现登录状态,操作的鉴权保持等。
我们将会借助tomcat的实现,剖析session管理的一些实现原理。
2. tomcat 中 session 什么时候创建?
session 信息会在两个地方调用,一是每次请求进来时,框架会尝试去加载原有对应的session信息(不会新建)。二是应用自己调用getSession()时,此时如果不存在session信息,则创建一个新的session对象,代表应用后续会使用此功能。即框架不会自动支持session相关功能,只是在你需要的时候进行辅助操作。
// case1. 框架自行调用session信息,不会主动创建session// org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager#retrieveFlashMaps/*** Retrieves saved FlashMap instances from the HTTP session, if any.*/@Override@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")protected List<FlashMap> retrieveFlashMaps(HttpServletRequest request) {HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);return (session != null ? (List<FlashMap>) session.getAttribute(FLASH_MAPS_SESSION_ATTRIBUTE) : null);}// case2. 应用主动调用session信息,不存在时会创建新的session, 以满足业务连续性需要@GetMapping("sessionTest")public Object sessionTest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {// 主动获取session信息HttpSession session = request.getSession();String sid = session.getId();System.out.println("sessionId:" + sid);return ResponseInfoBuilderUtil.success(sid);}
在tomcat中,HttpServletRequest的实际类都是 RequestFacade, 所以获取session信息也是以其为入口进行。
// org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade#getSession()@Overridepublic HttpSession getSession() {if (request == null) {throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString("requestFacade.nullRequest"));}// 如果不存在session则创建一个// session 的实现有两种:一是基于内存的实现,二是基于文件的实现。return getSession(true);}@Overridepublic HttpSession getSession(boolean create) {if (request == null) {throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString("requestFacade.nullRequest"));}if (SecurityUtil.isPackageProtectionEnabled()){return AccessController.doPrivileged(new GetSessionPrivilegedAction(create));} else {// RequestFacade 是个外观模式实现,核心请求还是会传递给 Request处理的// org.apache.catalina.connector.Requestreturn request.getSession(create);}}// org.apache.catalina.connector.Request#getSession(boolean)/*** @return the session associated with this Request, creating one* if necessary and requested.** @param create Create a new session if one does not exist*/@Overridepublic HttpSession getSession(boolean create) {// 由 create 字段决定是否需要创建新的session, 如果不存在的话。// Session 是tomcat的一个会话实现类,并非对接规范接口类,其会包装一个HttpSession,以便统一交互// 因为只有 HttpSession 才是 Servlet 的接口规范,在tomcat中会以 StandardSessionFacade 实现接口,其也是一个外观模式的实现,具体工作由 StandardSession 处理。Session session = doGetSession(create);if (session == null) {return null;}// 包装 Session 为 HttpSession 规范返回return session.getSession();}// org.apache.catalina.connector.Request#doGetSessionprotected Session doGetSession(boolean create) {// There cannot be a session if no context has been assigned yet// mappingData.context;Context context = getContext();if (context == null) {return (null);}// Return the current session if it exists and is valid// 此处检查session有效性时,也会做部分清理工作if ((session != null) && !session.isValid()) {session = null;}if (session != null) {return (session);}// Return the requested session if it exists and is valid// 获取manager 实例,即真正进行 Session 管理的类,其实主要分两种:1. 基于内存;2. 基于文件的持久化;Manager manager = context.getManager();if (manager == null) {return (null); // Sessions are not supported}if (requestedSessionId != null) {try {// 如果不是第一次请求,则会带上服务返回的 sessionId, 就会主动查找原来的session// 从 sessions 中查找即可session = manager.findSession(requestedSessionId);} catch (IOException e) {session = null;}if ((session != null) && !session.isValid()) {session = null;}// 后续请求,每次请求都会更新有效时间if (session != null) {session.access();return (session);}}// Create a new session if requested and the response is not committed// 主动请求session时,才会继续后续逻辑if (!create) {return (null);}if (response != null&& context.getServletContext().getEffectiveSessionTrackingModes().contains(SessionTrackingMode.COOKIE)&& response.getResponse().isCommitted()) {throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString("coyoteRequest.sessionCreateCommitted"));}// Re-use session IDs provided by the client in very limited// circumstances.String sessionId = getRequestedSessionId();if (requestedSessionSSL) {// If the session ID has been obtained from the SSL handshake then// use it.} else if (("/".equals(context.getSessionCookiePath())&& isRequestedSessionIdFromCookie())) {/* This is the common(ish) use case: using the same session ID with* multiple web applications on the same host. Typically this is* used by Portlet implementations. It only works if sessions are* tracked via cookies. The cookie must have a path of "/" else it* won't be provided for requests to all web applications.** Any session ID provided by the client should be for a session* that already exists somewhere on the host. Check if the context* is configured for this to be confirmed.*/if (context.getValidateClientProvidedNewSessionId()) {boolean found = false;for (Container container : getHost().findChildren()) {Manager m = ((Context) container).getManager();if (m != null) {try {if (m.findSession(sessionId) != null) {found = true;break;}} catch (IOException e) {// Ignore. Problems with this manager will be// handled elsewhere.}}}if (!found) {sessionId = null;}}} else {// 当session无效时,需要将原来的seesionId置空,删除并新创建一个使用sessionId = null;}// 创建session, StandardManager -> ManagerBasesession = manager.createSession(sessionId);// Creating a new session cookie based on that sessionif (session != null&& context.getServletContext().getEffectiveSessionTrackingModes().contains(SessionTrackingMode.COOKIE)) {// 创建cookie信息,与session对应Cookie cookie =ApplicationSessionCookieConfig.createSessionCookie(context, session.getIdInternal(), isSecure());// 添加到response中,在响应结果一起返回给客户端response.addSessionCookieInternal(cookie);}if (session == null) {return null;}// 每次请求session时,必然刷新激活时间,以便判定会话是否超时session.access();return session;}
从上面我们可以看到,session的流程大概是这样的:
1. 先查找是否有session信息存在,如果有则判断是否失效;
2. 如果不存在session或已失效,则使用一个新的sessionId(非必须)创建一个session实例;
3. session创建成功,则将sessionId写入到cookie信息中,以便客户端后续使用;
4. 每次请求完session,必定刷新下访问时间以续期;
session的管理主要有两种实现方式,类图如下:
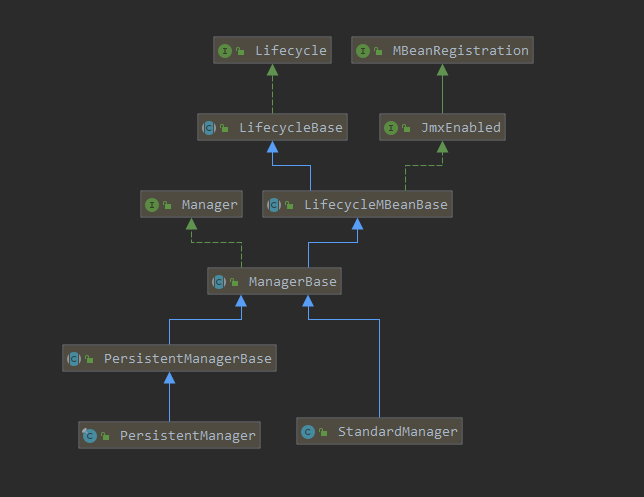
我们先主要以基于内存的实现来理解下session的管理过程。实际上StandardManager基本就依托于 ManagerBase 就实现了Session管理功能,下面我们来看一下其创建session如何?
// org.apache.catalina.session.ManagerBase#createSession@Overridepublic Session createSession(String sessionId) {// 首先来个安全限制,允许同时存在多少会话// 这个会话实际上代表的是一段时间的有效性,并非真正的用户有效使用在线,所以该值一般要求比预计的数量大些才好if ((maxActiveSessions >= 0) &&(getActiveSessions() >= maxActiveSessions)) {rejectedSessions++;throw new TooManyActiveSessionsException(sm.getString("managerBase.createSession.ise"),maxActiveSessions);}// Recycle or create a Session instance// 创建空的session 容器 return new StandardSession(this);Session session = createEmptySession();// Initialize the properties of the new session and return it// 默认30分钟有效期session.setNew(true);session.setValid(true);session.setCreationTime(System.currentTimeMillis());session.setMaxInactiveInterval(getContext().getSessionTimeout() * 60);String id = sessionId;if (id == null) {// sessionId 为空时,生成一个,随机idid = generateSessionId();}// 设置sessionId, 注意此处不仅仅是set这么简单,其同时会将自身session注册到全局session管理器中.如下文session.setId(id);sessionCounter++;SessionTiming timing = new SessionTiming(session.getCreationTime(), 0);synchronized (sessionCreationTiming) {// LinkedList, 添加一个,删除一个?sessionCreationTiming.add(timing);sessionCreationTiming.poll();}return (session);}// org.apache.catalina.session.StandardSession#setId/*** Set the session identifier for this session.** @param id The new session identifier*/@Overridepublic void setId(String id) {setId(id, true);}@Overridepublic void setId(String id, boolean notify) {// 如果原来的id不为空,则先删除原有的if ((this.id != null) && (manager != null))manager.remove(this);this.id = id;// 再将自身会话注册到 manager 中,即 sessions 中if (manager != null)manager.add(this);// 通知监听者,这是框架该做好的事(扩展点),不过不是本文的方向,忽略if (notify) {tellNew();}}// org.apache.catalina.session.ManagerBase#add@Overridepublic void add(Session session) {// 取出 sessionId, 添加到 sessions 容器,统一管理sessions.put(session.getIdInternal(), session);int size = getActiveSessions();// 刷新最大活跃数,使用双重锁优化更新该值if( size > maxActive ) {synchronized(maxActiveUpdateLock) {if( size > maxActive ) {maxActive = size;}}}}// 查找session也是异常简单,只管从 ConcurrentHashMap 中查找即可// org.apache.catalina.session.ManagerBase#findSession@Overridepublic Session findSession(String id) throws IOException {if (id == null) {return null;}return sessions.get(id);}
有兴趣的同学可以看一下sessionId的生成算法:主要保证两点:1. 随机性;2.不可重复性;
// org.apache.catalina.session.ManagerBase#generateSessionId/*** Generate and return a new session identifier.* @return a new session id*/protected String generateSessionId() {String result = null;do {if (result != null) {// Not thread-safe but if one of multiple increments is lost// that is not a big deal since the fact that there was any// duplicate is a much bigger issue.duplicates++;}// 使用 sessionIdGenerator 生成sessionIdresult = sessionIdGenerator.generateSessionId();// 如果已经存在该sessionId, 则重新生成一个// session 是一个 ConcurrentHashMap 结构数据} while (sessions.containsKey(result));return result;}// org.apache.catalina.util.SessionIdGeneratorBase#generateSessionId/*** Generate and return a new session identifier.*/@Overridepublic String generateSessionId() {return generateSessionId(jvmRoute);}// org.apache.catalina.util.StandardSessionIdGenerator#generateSessionId@Overridepublic String generateSessionId(String route) {byte random[] = new byte[16];// 默认16int sessionIdLength = getSessionIdLength();// Render the result as a String of hexadecimal digits// Start with enough space for sessionIdLength and medium route size// 创建双倍大小的stringBuilder, 容纳sessionIdStringBuilder buffer = new StringBuilder(2 * sessionIdLength + 20);int resultLenBytes = 0;//while (resultLenBytes < sessionIdLength) {getRandomBytes(random);for (int j = 0;j < random.length && resultLenBytes < sessionIdLength;j++) {// 转换为16进制byte b1 = (byte) ((random[j] & 0xf0) >> 4);byte b2 = (byte) (random[j] & 0x0f);if (b1 < 10)buffer.append((char) ('0' + b1));elsebuffer.append((char) ('A' + (b1 - 10)));if (b2 < 10)buffer.append((char) ('0' + b2));elsebuffer.append((char) ('A' + (b2 - 10)));resultLenBytes++;}}if (route != null && route.length() > 0) {buffer.append('.').append(route);} else {String jvmRoute = getJvmRoute();if (jvmRoute != null && jvmRoute.length() > 0) {buffer.append('.').append(jvmRoute);}}return buffer.toString();}// org.apache.catalina.util.SessionIdGeneratorBase#getRandomBytesprotected void getRandomBytes(byte bytes[]) {// 使用 random.nextBytes(), 预生成 randomSecureRandom random = randoms.poll();if (random == null) {random = createSecureRandom();}random.nextBytes(bytes);// 添加到 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 队列中,事实上该 random 将会被反复循环使用, poll->addrandoms.add(random);}
创建好session后,需要进行随时的维护:我们看下tomcat是如何刷新访问时间的?可能比预想的简单,其仅是更新一个访问时间字段,再无其他。
// org.apache.catalina.session.StandardSession#access/*** Update the accessed time information for this session. This method* should be called by the context when a request comes in for a particular* session, even if the application does not reference it.*/@Overridepublic void access() {// 更新访问时间this.thisAccessedTime = System.currentTimeMillis();// 访问次数统计,默认不启用if (ACTIVITY_CHECK) {accessCount.incrementAndGet();}}
最后,还需要看下 HttpSession 是如何被包装返回的?
// org.apache.catalina.session.StandardSession#getSession/*** Return the <code>HttpSession</code> for which this object* is the facade.*/@Overridepublic HttpSession getSession() {if (facade == null){if (SecurityUtil.isPackageProtectionEnabled()){final StandardSession fsession = this;facade = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<StandardSessionFacade>(){@Overridepublic StandardSessionFacade run(){return new StandardSessionFacade(fsession);}});} else {// 直接使用 StandardSessionFacade 包装即可facade = new StandardSessionFacade(this);}}return (facade);}
再最后,要说明的是,整个sessions的管理使用一个 ConcurrentHashMap 来存放全局会话信息,sessionId->session实例。
对于同一次http请求中,该session会被存储在当前的Request栈org.apache.catalina.connector.Request#session字段中,从而无需每次深入获取。每个请求进来后,会将session保存在当前的request信息中。
3. 过期session清理?
会话不可能不过期,不过期的也不叫会话了。
会话过期的触发时机主要有三个:1. 每次进行会话调用时,会主动有效性isValid()验证,此时如果发现过期可以主动清理:2. 后台定时任务触发清理;3. 启动或停止应用的时候清理;(这对于非内存式的存储会更有用些)
// case1. 请求时验证,如前面所述// org.apache.catalina.connector.Request#doGetSessionprotected Session doGetSession(boolean create) {...// Return the current session if it exists and is validif ((session != null) && !session.isValid()) {session = null;}if (session != null) {return (session);}...}// case2. 后台定时任务清理// org.apache.catalina.session.ManagerBase#backgroundProcess@Overridepublic void backgroundProcess() {// 并非每次定时任务到达时都会进行清理,而是要根据其清理频率设置来运行// 默认是 6count = (count + 1) % processExpiresFrequency;if (count == 0)processExpires();}/*** Invalidate all sessions that have expired.*/public void processExpires() {long timeNow = System.currentTimeMillis();// 找出所有的sessions, 转化为数组遍历Session sessions[] = findSessions();int expireHere = 0 ;if(log.isDebugEnabled())log.debug("Start expire sessions " + getName() + " at " + timeNow + " sessioncount " + sessions.length);for (int i = 0; i < sessions.length; i++) {// 事实上后台任务也是调用 isValid() 方法 进行过期任务清理的if (sessions[i]!=null && !sessions[i].isValid()) {expireHere++;}}long timeEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();if(log.isDebugEnabled())log.debug("End expire sessions " + getName() + " processingTime " + (timeEnd - timeNow) + " expired sessions: " + expireHere);processingTime += ( timeEnd - timeNow );}//case3. start/stop 时触发过期清理(生命周期事件)// org.apache.catalina.session.StandardManager#startInternal/*** Start this component and implement the requirements* of {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.** @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error* that prevents this component from being used*/@Overrideprotected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {super.startInternal();// Load unloaded sessions, if anytry {// doLoad() 调用load();} catch (Throwable t) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);log.error(sm.getString("standardManager.managerLoad"), t);}setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);}/*** Load any currently active sessions that were previously unloaded* to the appropriate persistence mechanism, if any. If persistence is not* supported, this method returns without doing anything.** @exception ClassNotFoundException if a serialized class cannot be* found during the reload* @exception IOException if an input/output error occurs*/protected void doLoad() throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Start: Loading persisted sessions");}// Initialize our internal data structuressessions.clear();// Open an input stream to the specified pathname, if anyFile file = file();if (file == null) {return;}if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug(sm.getString("standardManager.loading", pathname));}Loader loader = null;ClassLoader classLoader = null;Log logger = null;try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file.getAbsolutePath());BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis)) {Context c = getContext();loader = c.getLoader();logger = c.getLogger();if (loader != null) {classLoader = loader.getClassLoader();}if (classLoader == null) {classLoader = getClass().getClassLoader();}// Load the previously unloaded active sessionssynchronized (sessions) {try (ObjectInputStream ois = new CustomObjectInputStream(bis, classLoader, logger,getSessionAttributeValueClassNamePattern(),getWarnOnSessionAttributeFilterFailure())) {Integer count = (Integer) ois.readObject();int n = count.intValue();if (log.isDebugEnabled())log.debug("Loading " + n + " persisted sessions");for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {StandardSession session = getNewSession();session.readObjectData(ois);session.setManager(this);sessions.put(session.getIdInternal(), session);session.activate();if (!session.isValidInternal()) {// If session is already invalid,// expire session to prevent memory leak.// 主动调用 expiresession.setValid(true);session.expire();}sessionCounter++;}} finally {// Delete the persistent storage fileif (file.exists()) {file.delete();}}}} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("No persisted data file found");}return;}if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Finish: Loading persisted sessions");}}// stopInternal() 事件到达时清理 sessions/*** Save any currently active sessions in the appropriate persistence* mechanism, if any. If persistence is not supported, this method* returns without doing anything.** @exception IOException if an input/output error occurs*/protected void doUnload() throws IOException {if (log.isDebugEnabled())log.debug(sm.getString("standardManager.unloading.debug"));if (sessions.isEmpty()) {log.debug(sm.getString("standardManager.unloading.nosessions"));return; // nothing to do}// Open an output stream to the specified pathname, if anyFile file = file();if (file == null) {return;}if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug(sm.getString("standardManager.unloading", pathname));}// Keep a note of sessions that are expiredArrayList<StandardSession> list = new ArrayList<>();try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file.getAbsolutePath());BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos)) {synchronized (sessions) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Unloading " + sessions.size() + " sessions");}// Write the number of active sessions, followed by the detailsoos.writeObject(Integer.valueOf(sessions.size()));for (Session s : sessions.values()) {StandardSession session = (StandardSession) s;list.add(session);session.passivate();session.writeObjectData(oos);}}}// Expire all the sessions we just wrote// 将所有session失效,实际上应用即将关闭,失不失效的应该也无所谓了if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Expiring " + list.size() + " persisted sessions");}for (StandardSession session : list) {try {session.expire(false);} catch (Throwable t) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);} finally {session.recycle();}}if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Unloading complete");}}
接下来我们看下具体如何清理过期的会话?实际应该就是一个remove的事。
// org.apache.catalina.session.StandardSession#isValid/*** Return the <code>isValid</code> flag for this session.*/@Overridepublic boolean isValid() {if (!this.isValid) {return false;}if (this.expiring) {return true;}if (ACTIVITY_CHECK && accessCount.get() > 0) {return true;}// 超过有效期,主动触发清理if (maxInactiveInterval > 0) {int timeIdle = (int) (getIdleTimeInternal() / 1000L);if (timeIdle >= maxInactiveInterval) {expire(true);}}return this.isValid;}// org.apache.catalina.session.StandardSession#expire(boolean)/*** Perform the internal processing required to invalidate this session,* without triggering an exception if the session has already expired.** @param notify Should we notify listeners about the demise of* this session?*/public void expire(boolean notify) {// Check to see if session has already been invalidated.// Do not check expiring at this point as expire should not return until// isValid is falseif (!isValid)return;// 上锁保证线程安全synchronized (this) {// Check again, now we are inside the sync so this code only runs once// Double check locking - isValid needs to be volatile// The check of expiring is to ensure that an infinite loop is not// entered as per bug 56339if (expiring || !isValid)return;if (manager == null)return;// Mark this session as "being expired"expiring = true;// Notify interested application event listeners// FIXME - Assumes we call listeners in reverse orderContext context = manager.getContext();// The call to expire() may not have been triggered by the webapp.// Make sure the webapp's class loader is set when calling the// listenersif (notify) {ClassLoader oldContextClassLoader = null;try {oldContextClassLoader = context.bind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, null);Object listeners[] = context.getApplicationLifecycleListeners();if (listeners != null && listeners.length > 0) {HttpSessionEvent event =new HttpSessionEvent(getSession());for (int i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++) {int j = (listeners.length - 1) - i;if (!(listeners[j] instanceof HttpSessionListener))continue;HttpSessionListener listener =(HttpSessionListener) listeners[j];try {context.fireContainerEvent("beforeSessionDestroyed",listener);listener.sessionDestroyed(event);context.fireContainerEvent("afterSessionDestroyed",listener);} catch (Throwable t) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);try {context.fireContainerEvent("afterSessionDestroyed", listener);} catch (Exception e) {// Ignore}manager.getContext().getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardSession.sessionEvent"), t);}}}} finally {context.unbind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, oldContextClassLoader);}}if (ACTIVITY_CHECK) {accessCount.set(0);}// Remove this session from our manager's active sessions// 从ManagerBase 中删除manager.remove(this, true);// Notify interested session event listenersif (notify) {fireSessionEvent(Session.SESSION_DESTROYED_EVENT, null);}// Call the logout methodif (principal instanceof TomcatPrincipal) {TomcatPrincipal gp = (TomcatPrincipal) principal;try {gp.logout();} catch (Exception e) {manager.getContext().getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardSession.logoutfail"),e);}}// We have completed expire of this sessionsetValid(false);expiring = false;// Unbind any objects associated with this sessionString keys[] = keys();ClassLoader oldContextClassLoader = null;try {oldContextClassLoader = context.bind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, null);for (int i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {removeAttributeInternal(keys[i], notify);}} finally {context.unbind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, oldContextClassLoader);}}}// org.apache.catalina.session.ManagerBase#remove(org.apache.catalina.Session, boolean)@Overridepublic void remove(Session session, boolean update) {// If the session has expired - as opposed to just being removed from// the manager because it is being persisted - update the expired statsif (update) {long timeNow = System.currentTimeMillis();int timeAlive =(int) (timeNow - session.getCreationTimeInternal())/1000;updateSessionMaxAliveTime(timeAlive);expiredSessions.incrementAndGet();SessionTiming timing = new SessionTiming(timeNow, timeAlive);synchronized (sessionExpirationTiming) {sessionExpirationTiming.add(timing);sessionExpirationTiming.poll();}}// 从sessions中移除sessionif (session.getIdInternal() != null) {sessions.remove(session.getIdInternal());}}
清理工作的核心任务没猜错,还是进行remove对应的session, 但作为框架必然会设置很多的扩展点,为各监听器接入的机会。这些点的设计,直接关系到整个功能的好坏了。
4. session如何保证线程安全?
实际是废话,前面已经明显看出,其使用一个 ConcurrentHashMap 作为session的管理容器,而ConcurrentHashMap本身就是线程安全的,自然也就保证了线程安全了。
不过需要注意的是,上面的线程安全是指的不同客户端间的数据是互不影响的。然而对于同一个客户端的重复请求,以上实现并未处理,即可能会生成一次session,也可能生成n次session,不过实际影响不大,因为客户端的状态与服务端的状态都是一致的。
5. 使用持久化方案的session管理实现
默认情况使用内存作为session管理工具,一是方便,二是速度相当快。但是最大的缺点是,其无法实现持久化,即可能停机后信息就丢失了(虽然上面有在停机时做了持久化操作,但仍然是不可靠的)。
所以就有了与之相对的存储方案了:Persistent,它有一个基类 PersistentManagerBase 继承了 ManagerBase,做了些特别的实现:
// 1. session的添加// 复用 ManagerBase// 2. session的查找// org.apache.catalina.session.PersistentManagerBase#findSession/*** {@inheritDoc}* <p>* This method checks the persistence store if persistence is enabled,* otherwise just uses the functionality from ManagerBase.*/@Overridepublic Session findSession(String id) throws IOException {// 复用ManagerBase, 获取Session实例Session session = super.findSession(id);// OK, at this point, we're not sure if another thread is trying to// remove the session or not so the only way around this is to lock it// (or attempt to) and then try to get it by this session id again. If// the other code ran swapOut, then we should get a null back during// this run, and if not, we lock it out so we can access the session// safely.if(session != null) {synchronized(session){session = super.findSession(session.getIdInternal());if(session != null){// To keep any external calling code from messing up the// concurrency.session.access();session.endAccess();}}}if (session != null)return session;// See if the Session is in the Store// 如果内存中找不到会话信息,从存储中查找,这是主要的区别session = swapIn(id);return session;}// org.apache.catalina.session.PersistentManagerBase#swapIn/*** Look for a session in the Store and, if found, restore* it in the Manager's list of active sessions if appropriate.* The session will be removed from the Store after swapping* in, but will not be added to the active session list if it* is invalid or past its expiration.** @param id The id of the session that should be swapped in* @return restored session, or {@code null}, if none is found* @throws IOException an IO error occurred*/protected Session swapIn(String id) throws IOException {if (store == null)return null;Object swapInLock = null;/** The purpose of this sync and these locks is to make sure that a* session is only loaded once. It doesn't matter if the lock is removed* and then another thread enters this method and tries to load the same* session. That thread will re-create a swapIn lock for that session,* quickly find that the session is already in sessions, use it and* carry on.*/// 额,总之就是有点复杂synchronized (this) {swapInLock = sessionSwapInLocks.get(id);if (swapInLock == null) {swapInLock = new Object();sessionSwapInLocks.put(id, swapInLock);}}Session session = null;synchronized (swapInLock) {// First check to see if another thread has loaded the session into// the managersession = sessions.get(id);if (session == null) {Session currentSwapInSession = sessionToSwapIn.get();try {if (currentSwapInSession == null || !id.equals(currentSwapInSession.getId())) {// 从存储中查找sessionsession = loadSessionFromStore(id);sessionToSwapIn.set(session);if (session != null && !session.isValid()) {log.error(sm.getString("persistentManager.swapInInvalid", id));session.expire();removeSession(id);session = null;}// 重新加入到内存 sessions 中if (session != null) {reactivateLoadedSession(id, session);}}} finally {sessionToSwapIn.remove();}}}// Make sure the lock is removedsynchronized (this) {sessionSwapInLocks.remove(id);}return session;}private Session loadSessionFromStore(String id) throws IOException {try {if (SecurityUtil.isPackageProtectionEnabled()){return securedStoreLoad(id);} else {// 依赖于store的实现了,比如 file, jdbc...return store.load(id);}} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {String msg = sm.getString("persistentManager.deserializeError", id);log.error(msg, e);throw new IllegalStateException(msg, e);}}// store 实现样例: fileStore// org.apache.catalina.session.FileStore#load/*** Load and return the Session associated with the specified session* identifier from this Store, without removing it. If there is no* such stored Session, return <code>null</code>.** @param id Session identifier of the session to load** @exception ClassNotFoundException if a deserialization error occurs* @exception IOException if an input/output error occurs*/@Overridepublic Session load(String id) throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException {// Open an input stream to the specified pathname, if anyFile file = file(id);if (file == null) {return null;}if (!file.exists()) {return null;}Context context = getManager().getContext();Log contextLog = context.getLogger();if (contextLog.isDebugEnabled()) {contextLog.debug(sm.getString(getStoreName()+".loading", id, file.getAbsolutePath()));}ClassLoader oldThreadContextCL = context.bind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, null);try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file.getAbsolutePath());ObjectInputStream ois = getObjectInputStream(fis)) {StandardSession session = (StandardSession) manager.createEmptySession();session.readObjectData(ois);session.setManager(manager);return session;} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {if (contextLog.isDebugEnabled()) {contextLog.debug("No persisted data file found");}return null;} finally {context.unbind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, oldThreadContextCL);}}private void reactivateLoadedSession(String id, Session session) {if(log.isDebugEnabled())log.debug(sm.getString("persistentManager.swapIn", id));session.setManager(this);// make sure the listeners know about it.((StandardSession)session).tellNew();// 添加回sessionsadd(session);((StandardSession)session).activate();// endAccess() to ensure timeouts happen correctly.// access() to keep access count correct or it will end up// negativesession.access();session.endAccess();}// 3. session 的移除@Overridepublic void remove(Session session, boolean update) {super.remove (session, update);// 和内存的实现差别就是,还要多一个对外部存储的管理维护if (store != null){removeSession(session.getIdInternal());}}
可以看到, PersistentManager 的实现还是有点复杂的,主要是在安全性和性能之间的平衡,它和 StandardManager 基本是一种包含关系,即除了要维护内存session外,还要维护外部存储的状态。
而现实情况是,既然已经需要自行维护外部状态了,为何还要去使用tomcat自带的session管理呢?而如果站在框架session管理的设计者的角度,这可能也是无可奈何的事。
而在我们自己的session管理实现中,一般的思路还是相通的,创建 -> 查找 -> 维持 -> 删除 。 可以基于数据库,缓存,或者其他,而且相信也不是件难事。

腾讯、阿里、滴滴后台面试题汇总总结 — (含答案)
面试:史上最全多线程面试题 !
最新阿里内推Java后端面试题
JVM难学?那是因为你没认真看完这篇文章

关注作者微信公众号 —《JAVA烂猪皮》
了解更多java后端架构知识以及最新面试宝典

看完本文记得给作者点赞+在看哦~~~大家的支持,是作者源源不断出文的动力
作者:等你归去来
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/yougewe/p/12902495.html
