Spring之事件机制详解
源 / CSDN 文/ 敲代码的小小酥
这里我们来分析Spring事件机制的原理。
先上UML图,不熟悉UML规则的可以看UML类图的制作规则。
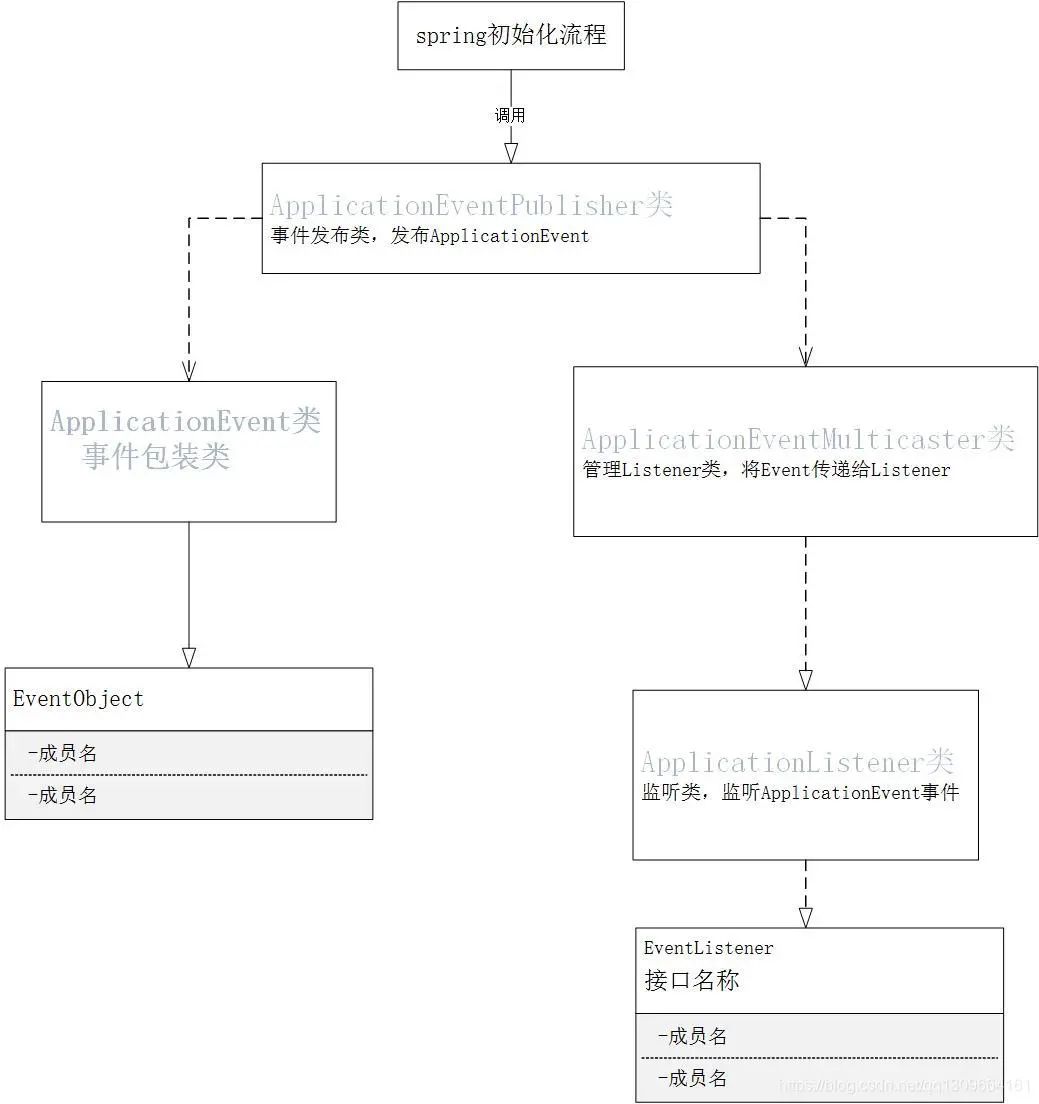
下面我们对上图中涉及到的几个类进行讲解。
ApplicationEvent:
抽象类,继承了JDK的EventObject接口,起到包装事件源的作用。
ApplicationListener:
实现了JDK的EventListener接口,起到监听器的作用。
在观察者模式中,一定要有一个管理维护监听者列表的功能。在Spring的事件机制中,将维护监听者列表的功能单独定义了一个接口,即ApplicationEventMulticaster接口。这也体现了单一责任原则的设计思想。我们看其源码:
public interface ApplicationEventMulticaster {
/**
* Add a listener to be notified of all events.
* @param listener the listener to add
*/
void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener listener);
/**
* Add a listener bean to be notified of all events.
* @param listenerBeanName the name of the listener bean to add
*/
void addApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName);
/**
* Remove a listener from the notification list.
* @param listener the listener to remove
*/
void removeApplicationListener(ApplicationListener listener);
/**
* Remove a listener bean from the notification list.
* @param listenerBeanName the name of the listener bean to remove
*/
void removeApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName);
/**
* Remove all listeners registered with this multicaster.
*After a remove call, the multicaster will perform no action
* on event notification until new listeners are registered.
*/
void removeAllListeners();
/**
* Multicast the given application event to appropriate listeners.
*Consider using {@link #multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent, ResolvableType)}
* if possible as it provides better support for generics-based events.
* @param event the event to multicast
*/
void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event);
/**
* Multicast the given application event to appropriate listeners.
*If the {@code eventType} is {@code null}, a default type is built
* based on the {@code event} instance.
* @param event the event to multicast
* @param eventType the type of event (can be {@code null})
* @since 4.2
*/
void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType);
}
ApplicationEventPublisher:
Spring设计的事件发布类,我们看其源码:
public interface ApplicationEventPublisher {
/**
* Notify all matching listeners registered with this
* application of an application event. Events may be framework events
* (such as ContextRefreshedEvent) or application-specific events.
*Such an event publication step is effectively a hand-off to the
* multicaster and does not imply synchronous/asynchronous execution
* or even immediate execution at all. Event listeners are encouraged
* to be as efficient as possible, individually using asynchronous
* execution for longer-running and potentially blocking operations.
* @param event the event to publish
* @see #publishEvent(Object)
* @see org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent
* @see org.springframework.context.event.ContextClosedEvent
*/
default void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
publishEvent((Object) event);
}
/**
* Notify all matching listeners registered with this
* application of an event.
*If the specified {@code event} is not an {@link ApplicationEvent},
* it is wrapped in a {@link PayloadApplicationEvent}.
*Such an event publication step is effectively a hand-off to the
* multicaster and does not imply synchronous/asynchronous execution
* or even immediate execution at all. Event listeners are encouraged
* to be as efficient as possible, individually using asynchronous
* execution for longer-running and potentially blocking operations.
* @param event the event to publish
* @since 4.2
* @see #publishEvent(ApplicationEvent)
* @see PayloadApplicationEvent
*/
void publishEvent(Object event);
}
通过上面几个类的描述,我们总结一下spring事件机制的流程:
流程的核心,就是PublishEvent。Event对象以参数的形式传入PublishEvent对象。然后将Event事件传入ApplicationEventMulticaster类中,由ApplicationEventMulticaster类将事件传给其维护的监听者,执行监听者方法。
领悟
应用
这就需要我们结合源码进行解读了。
笔者找到一篇写的很好的博文,大家可以参考:浅谈Spring事件监听。
@Component
public class MyEventSource {
public void ccc(){
System.out.println("事件源方法");
}
}
@Component
public class MyEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
public MyEvent(MyEventSource source) {
super(source);
}
public void eventMethod(){
System.out.println("事件自定义方法");
}
}
@Component
public class MyListener implements ApplicationListener {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent applicationEvent) {
if(applicationEvent instanceof MyEvent) {
((MyEvent)applicationEvent).eventMethod();
MyEventSource eventSource = (MyEventSource) applicationEvent.getSource();
eventSource.ccc();
System.out.println("监听者发生一些改变");
}
}
}
如果我们想特定的事件发布给特定的监听者,那我们只能自己实现Spring的发布类和ApplicationEventMulticaster类,自己定义事件的发布机制。
ApplicationListener类是支持泛型的,在类后定义泛型,可以过滤掉其他的事件对象,只接收泛型类事件。
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
Object o=applicationContext.getBean("myEvent");
applicationContext.publishEvent(applicationContext.getBean("myEvent"));
}
}
总结
在单机环境中,我们要实现代码的解耦,可以采用事件机制。例如:在前面讲观察者模式时,我们把监听者的放在事件类中维护的方式,就是高耦合的。而Spring将其进行了解耦。
补充:
ContextRefreshedEvent(上下文更新完成事件):在spring容器初始化流程完成后,触发事件。事件的触发(即调用publishEvent方法)是Spring自己调用的,我们只需定义Listener监听者处理业务即可。
如之前一个项目,在项目启动的时候有一个while(true){…}死循环,造成了项目无法正常启动。当时的解决方案是将死循环另起了一个线程解决的。现在可以采用ContextRefreshedEvent事件解决。当容器加载完成后,再执行死循环业务。代码如下:
@Component
public class MyListener implements ApplicationListener{
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
while (true){
System.out.println("执行业务");
}
}
}
END


顶级程序员:topcoding
做最好的程序员社区:Java后端开发、Python、大数据、AI
一键三连「分享」、「点赞」和「在看」
