文件上传下载原理:http协议分析及实现
我们现在用得非常多互联网下载文件,非常直观。有一个下载按钮,然后我点击了下载,然后文件慢慢就下载到本地了。就好像是一个复制的过程。
而既然是互联网,那么必然会是使用网络进行传输的。那么到底是怎样传输的呢?
当然,下载文件有两种方式:一是直接针对某个文件资源进行下载,无需应用开发代码;二是应用代码临时生成需要的内容文件,然后输出给到下载端。
其中,直接下载资源文件的场景给我们感觉是下载就是针对这个文件本身的一个操作,和复制一样没有什么疑义。而由应用代码进行下载文件时,又当如何处理呢?
1:上传下载文件demo
在网上你可以非常容易地找到相应的模板代码,然后处理掉。基本的样子就是设置几个头信息,然后将数据写入到response中。
demo1. 服务端接收文件上传,并同时输出文件到客户端
@PostMapping("fileUpDownTest")@ResponseBodypublic Object fileUpDownTest(@ModelAttribute EncSingleDocFileReqModel reqModel,MultipartFile file,HttpServletResponse response) {// 做两件事:1. 接收上传的文件;2. 将文件下载给到上传端;// 即向双向文件的传输,下载的文件可以是你处理之后的任意文件。String tmpPath = saveMultipartToLocalFile(file);outputEncFileStream(tmpPath, response);System.out.println("path:" + tmpPath);return null;}/*** 保存文件到本地路径** @param file 文件流* @return 本地存储路径*/private String saveMultipartToLocalFile(MultipartFile file) {try (InputStream inputStream = file.getInputStream()){// 往临时目录写文件String fileSuffix = file.getOriginalFilename().substring(file.getOriginalFilename().lastIndexOf('.'));File tmpFile = File.createTempFile(file.getName(), ".tmp" + fileSuffix);FileUtils.copyInputStreamToFile(inputStream, tmpFile);return tmpFile.getCanonicalPath();}catch (Exception e){log.error("【加密文件】文件流处理失败:" + file.getName(), e);throw new EncryptSysException("0011110", "文件接收失败");}}/*** 输出文件流数据** @param encFileLocalPath 文件所在路径* @param response servlet io 流*/private void outputEncFileStream(String encFileLocalPath, HttpServletResponse response) {File outFile = new File(encFileLocalPath);OutputStream os = null;InputStream inputStream = null;try {response.reset();response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate");// response.setHeader("Content-Length", file.getContentLength()+"");String outputFileName = encFileLocalPath.substring(encFileLocalPath.lastIndexOf('/') + 1);response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", String.format("attachment; filename=%s", URLEncoder.encode(outputFileName, "UTF-8")));response.setContentType("application/octet-stream; charset=utf-8");response.setHeader("Pragma", "no-cache");response.setHeader("Expires", "0");inputStream = new FileInputStream(outFile);//写入信息os = CommonUtil.readInputStream(inputStream, response.getOutputStream());}catch (Exception re) {log.error("输出文件流失败,", re);throw new RuntimeException("0011113: 输出加密后的文件失败");}finally {if (os != null) {try {os.flush();os.close();}catch (IOException e) {log.error("输出流文件失败", e);}}if(inputStream != null) {try {inputStream.close();}catch (IOException e) {log.error("加密文件输入流关闭失败", e);}}}}
我们在做开发时,面对的仅仅是 Request, Response 这种什么都有对象,直接问其要相关信息即可。给我们提供方便的同时,也失去了了解真相的机会。
demo2. 服务端转发文件到另一个服务端,并同接收处理响应回来的文件流数据
/*** 使用本地文件,向加密服务器请求加密文件,并输出到用户端** @param localFilePath 想要下载的文件* @return 文件流*/@GetMapping("transLocalFileToEnc")public Object transLocalFileToEnc(@ModelAttribute EncSingleDocFileReqModel reqModel,@RequestParam String localFilePath,HttpServletResponse response) {File localFileIns = new File(localFilePath);if(!localFileIns.exists()) {return ResponseInfoBuilderUtil.fail("指定文件未找到");}try(InputStream sourceFileInputStream = new FileInputStream(localFileIns);) {//这个url是要上传到另一个服务器上接口, 此处模拟向本机发起加密请求String url = "http://localhost:8082/encrypt/testEnc";int lastFileSeparatorIndex = localFilePath.lastIndexOf('/');String filename = lastFileSeparatorIndex == -1? localFilePath.substring(localFilePath.lastIndexOf('\\')): localFilePath.substring(lastFileSeparatorIndex);Object object = null;// 创建HttpClients实体类CloseableHttpClient aDefault = HttpClients.createDefault();try {HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(url);MultipartEntityBuilder builder = MultipartEntityBuilder.create();//使用这个,另一个服务就可以接收到这个file文件了builder.addBinaryBody("file", sourceFileInputStream, ContentType.create("multipart/form-data"), URLEncoder.encode(filename, "utf-8"));builder.addTextBody("systemCode", "self");String encOutputFilename = filename;builder.addTextBody("encOutputFileName", encOutputFilename);HttpEntity entity = builder.build();httpPost.setEntity(entity);ResponseHandler<Object> rh = new ResponseHandler<Object>() {@Overridepublic Object handleResponse(HttpResponse re) throws IOException {HttpEntity entity = re.getEntity();if(entity.getContentType().toString().contains("application/json")) {// 通过判断响应类型来判断是否输出文件流,非严谨的做法String retMsg = EntityUtils.toString(entity, "UTF-8");return JSONObject.parseObject(retMsg, ResponseInfo.class);}InputStream input = entity.getContent();// String result = EntityUtils.toString(entity, "UTF-8");// 写入响应流信息OutputStream os = null;try {response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate");// response.setHeader("Content-Length", file.getContentLength()+"");response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", String.format("attachment; filename=%s", URLEncoder.encode(filename, "UTF-8")));response.setContentType("application/octet-stream; charset=utf-8");response.setHeader("Pragma", "no-cache");response.setHeader("Expires", "0");// 往临时目录写文件File tmpFile = File.createTempFile(filename, "");FileUtils.copyInputStreamToFile(input, tmpFile);String encFilePathTmp = tmpFile.getCanonicalPath();File encFileIns = new File(encFilePathTmp);if(encFileIns.exists()) {FileInputStream zipStream = new FileInputStream(encFileIns);os = CommonUtil.readInputStream(zipStream, response.getOutputStream());}}finally {if(os != null) {os.flush();os.close();}}// 已向客户端输出文件流return Boolean.TRUE;}};object = aDefault.execute(httpPost, rh);return object == Boolean.TRUE? "加密成功,下载文件去!": object;}catch (Exception e) {log.error("", e);}finally {try {aDefault.close();} catch (IOException e) {log.error("关闭错误", e);}}}catch (FileNotFoundException e) {log.error("要加密的文件不存在", e);}catch (IOException e) {log.error("要加密的文件不存在", e);}return "处理失败";}// 抽出写socket流的逻辑,方便统一控制/*** 从输入流中获取字节数组** @param inputStream 输入流* @return 输出流,超过5000行数据,刷写一次网络* @throws IOException*/public static OutputStream readInputStream(InputStream inputStream, OutputStream os) throws IOException {byte[] bytes = new byte[2048];int i = 0;int read = 0;//按字节逐个写入,避免内存占用过高while ((read = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {os.write(bytes, 0, read);i++;// 每5000行if (i % 5000 == 0) {os.flush();}}inputStream.close();return os;}
此处仅是使用后端代码展现了前端的一人 form 提交过程,并无技巧可言。不过,这里说明了一个问题:文件流同样可以任意在各服务器间流转。只要按照协议规范实现即可。(注意以上代码可能需要引入pom依赖:org.apache.httpcomponents:httpclient:4.5.6,org.apache.httpcomponents:httpmime:4.5.6)
2. http 协议之文件处理
一般地,我们应对的互联网上的整个上传下载文件,基本都是基于http协议的。所以,要从根本上理解上传下载文件的原理,来看看http协议就好了。
我们可以通过上面的demo看下上传时候的数据样子,我们通过 fiddler进行抓包查看数据即可得如下:
POST http://localhost:8082/test/fileUpDownTest?systemCode=1111&outputFileName=111 HTTP/1.1Host: localhost:8082Connection: keep-aliveContent-Length: 197Accept: */*X-Requested-With: XMLHttpRequestUser-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/81.0.4044.129 Safari/537.36 OPR/68.0.3618.63Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=----WebKitFormBoundaryen2ZJyNfx7WhA3yOOrigin: http://localhost:8082Sec-Fetch-Site: same-originSec-Fetch-Mode: corsSec-Fetch-Dest: emptyReferer: http://localhost:8082/swagger-ui.htmlAccept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, brAccept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9,en-US;q=0.8,en;q=0.7Cookie: JSESSIONID=40832A6766FB11E105717690AEF826AA------WebKitFormBoundaryen2ZJyNfx7WhA3yOContent-Disposition: form-data; name="file"; filename="123.txt"Content-Type: text/plain123contentover------WebKitFormBoundaryen2ZJyNfx7WhA3yOContent-Disposition: form-data; name="file2"; filename="123-2.txt"Content-Type: text/plain2222content2over------WebKitFormBoundaryen2ZJyNfx7WhA3yO--
因为fiddler会做解码操作,且http是一种基于字符串的传输协议,所以,我们看到的都是可读的文件信息。我这里模拟是使用一个 123.txt 的文件,里面输入了少量字符:“123content\nover”;
我们知道,http协议是每行作为一个header的,其中前三是固定的,不必多说。
与我们相关的有:
Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=----WebKitFormBoundaryen2ZJyNfx7WhA3yO
Content-Type是个重要的标识字段,当我们用文件上传时,multipart/form-data代表了这是一个多部分上传的文件类型请求,即此处的文件上传请求。后面的 boundary 代表在上传的实际多个部分内容时的分界线,该值应是在每次请求时随机生成且避免与业务数据的冲突。
Content-Length: 197.
这个值是由浏览器主动计算出来的负载内容长度,服务端收到该信息后,只会读取这么多的长度即认为传输完成。
http协议的包体是从遇到第一个两个连续的换行符开始的。(所以,如果在header中包含了此特征时,需要自行编码后再请求,否则将发生协议冲突。)
每个part部分的内容,以boundary作为分界线。part部分的内容可以是文件、流、或者纯粹的key-value。
根据以上数据格式,服务端作出相应的反向解析就可以得到相应的内容了。
如果服务响应的结果是一个文件下载,那么对于响应的结果示例如下:
HTTP/1.1 200Cache-Control: no-cache, no-store, must-revalidateContent-Disposition: attachment; filename=file5983940017135638617.tmp.txtPragma: no-cacheExpires: 0Content-Type: application/octet-stream;charset=utf-8Transfer-Encoding: chunkedDate: Sun, 17 May 2020 05:30:57 GMT10123contentover0
重要字段说明:
Content-Disposition: attachment; filename=file5983940017135638617.tmp.txt
该字段说明本次响应的值应该作为一个附件形式下载保存到本地,这会被几乎所有浏览器支持。但如果你自己写代码接收,那就随你意好了,它只是一个标识而已;其中 filename 是用作用户下载时的默认保存名称,如果本地已存在一般会被添加(xxx)的后缀以避免下载覆盖。
Content-Type: application/octet-stream;charset=utf-8
代表这是一个二进制的文件,也就是说,浏览器一般无法作出相应的处理。当然,这也只是一个建议,至于你输出的是啥也无所谓了,反正只要追加到文件之后,就可以还原文件内容了。同样,遇到第一个连续的换行之后,代表正式的文件内容开始了。
如上的输出中,并没有 Content-Length 字段,所以无法直接推断出下载的数据大小,所以会在前后加一些字符器,用于判定结束。这样做可能导致浏览器上无法判定已下载的数据量占比,即无法展示进度条。虽然不影响最终下载数据,但是一般别这么干。
如下,我们加下content-length之后的响应如下:
HTTP/1.1 200Cache-Control: no-cache, no-store, must-revalidateContent-Disposition: attachment; filename=file4383190990004865558.tmp.txtPragma: no-cacheExpires: 0Content-Type: application/octet-stream;charset=utf-8Content-Length: 16Date: Sun, 17 May 2020 07:26:47 GMT123contentover
如上,就是http协议对于文件的处理方式了,只要你按照协议规定进行请求时,对端就能接受你的文件上传。只要服务按照协议规定输出响应数据,浏览器端就可以进行相应文件下载。
http协议头更多信息可以参考:https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers
3. http协议上传下载的背后,还有什么?
我们知道,http协议是基于tcp协议上实现的一个应用层协议。上一节我们说到的,如何进行上传下载文件,也是基于应用层去说的。说直接点就是,如果把网络比作黑盒,那么我们认为这个黑盒会给我们正确的数据。我们只要基于这些数据,就可以解析相应的文件信息了。
实际上,tcp协议是一种可靠的传输协议。至于如何可靠,额,这么说吧:网络上的信息是非常复杂和无序的,你从一个端点发送数据到另一个网络站点,会使用IP协议通过网络传送出去,而这些传输是单向的,多包的。它会受到外部复杂环境的影响,可能有的包丢失,可能有的包后发先到等等。如果不能处理好它们的这些丢包、乱序,重复等问题,那么网络发过来的数据将是无法使用的。(基本就是数据损坏这个结论)
tcp则是专门为处理这些问题而设计的,具体嘛,就很复杂了。总之一句话,使用了tcp协议后,你就无需关注复杂的网络环境了,你可以无条件相信你从操作系统tcp层给你的数据就是有序的完整的数据。你可以去看书,或者查看更多网上资料。(书更可靠些,只是更费时间精力)可以参考这篇文章: http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2017/06/tcp-protocol.html
4. java中对于文件上传的处理实现?
虽然前面我们解读完成http协议对于文件的上传处理方式,但是,到具体如何实现,又当如何呢?如果给你一个socket的入口lib,你又如何去处理这些http请求呢?
可以大概这么思考:1. 接收到头信息,判断出是文件类型的上传;2. 取出 boundary, 取出content-length, 备用;3. 继续读取后续的网络流数据,当发现传输的是key-value数据时,将其放入内存缓冲中存起来,当发现是文件类型的数据时,创建一个临时文件,将读取到的数据写入其中,直到该部分文件传输完成,并存储临时文件信息;4. 读取完整个http协议指定的数据后,封装相应的请求给到应用代码,待应用处理完成后响应给客户端;
以tomcat为例,它会依次解析各个参数值。
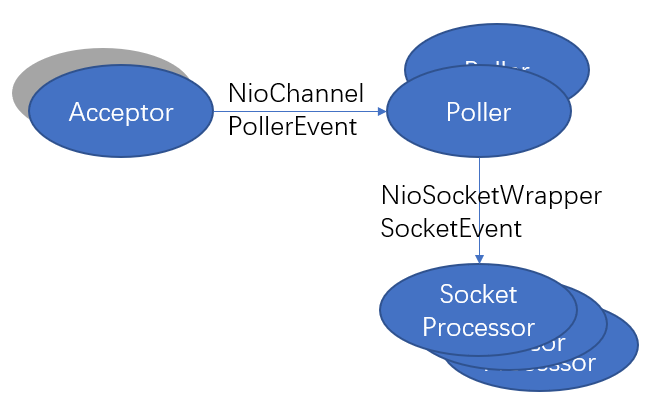
有兴趣的的同学可以先看看它是如何接入http请求的吧:(基于nio socket)大概流程为(下图为其线程模型):Accepter -> Pollor -> SocketProcessor 。
// org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.Acceptor@Overridepublic void run() {int errorDelay = 0;// Loop until we receive a shutdown commandwhile (running) {// Loop if endpoint is pausedwhile (paused && running) {state = AcceptorState.PAUSED;try {Thread.sleep(50);} catch (InterruptedException e) {// Ignore}}if (!running) {break;}state = AcceptorState.RUNNING;try {//if we have reached max connections, waitcountUpOrAwaitConnection();SocketChannel socket = null;try {// Accept the next incoming connection from the server// socket// Nio 的 ServerSocketChannelImpl, 阻塞等待socket accept 事件socket = serverSock.accept();} catch (IOException ioe) {// We didn't get a socketcountDownConnection();if (running) {// Introduce delay if necessaryerrorDelay = handleExceptionWithDelay(errorDelay);// re-throwthrow ioe;} else {break;}}// Successful accept, reset the error delayerrorDelay = 0;// Configure the socketif (running && !paused) {// setSocketOptions() will hand the socket off to// an appropriate processor if successful// 处理socket事件if (!setSocketOptions(socket)) {closeSocket(socket);}} else {closeSocket(socket);}} catch (Throwable t) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"), t);}}state = AcceptorState.ENDED;}/*** Process the specified connection.* @param socket The socket channel* @return <code>true</code> if the socket was correctly configured* and processing may continue, <code>false</code> if the socket needs to be* close immediately*/protected boolean setSocketOptions(SocketChannel socket) {// Process the connectiontry {//disable blocking, APR style, we are gonna be polling it// 组装channel,交给 Pollorsocket.configureBlocking(false);Socket sock = socket.socket();socketProperties.setProperties(sock);NioChannel channel = nioChannels.pop();if (channel == null) {SocketBufferHandler bufhandler = new SocketBufferHandler(socketProperties.getAppReadBufSize(),socketProperties.getAppWriteBufSize(),socketProperties.getDirectBuffer());if (isSSLEnabled()) {channel = new SecureNioChannel(socket, bufhandler, selectorPool, this);} else {channel = new NioChannel(socket, bufhandler);}} else {channel.setIOChannel(socket);channel.reset();}// 添加到 Pollor 队列中,Poller 的获取使用轮询方式获取getPoller0().register(channel);} catch (Throwable t) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);try {log.error("",t);} catch (Throwable tt) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(tt);}// Tell to close the socketreturn false;}return true;}/*** Return an available poller in true round robin fashion.** @return The next poller in sequence*/public Poller getPoller0() {// 第1次取1,第2次取2,第3次取1... 轮询int idx = Math.abs(pollerRotater.incrementAndGet()) % pollers.length;return pollers[idx];}// org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.Poller#register/*** Registers a newly created socket with the poller.** @param socket The newly created socket*/public void register(final NioChannel socket) {socket.setPoller(this);NioSocketWrapper ka = new NioSocketWrapper(socket, NioEndpoint.this);socket.setSocketWrapper(ka);ka.setPoller(this);ka.setReadTimeout(getSocketProperties().getSoTimeout());ka.setWriteTimeout(getSocketProperties().getSoTimeout());ka.setKeepAliveLeft(NioEndpoint.this.getMaxKeepAliveRequests());ka.setSecure(isSSLEnabled());ka.setReadTimeout(getConnectionTimeout());ka.setWriteTimeout(getConnectionTimeout());PollerEvent r = eventCache.pop();// 注册OP_READ事件,给selector使用ka.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);//this is what OP_REGISTER turns into.// 将socket信息添加到 PollerEvent 中if ( r==null) r = new PollerEvent(socket,ka,OP_REGISTER);else r.reset(socket,ka,OP_REGISTER);addEvent(r);}// 添加事件并唤醒selector// org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.Poller#addEventprivate void addEvent(PollerEvent event) {events.offer(event);// 正在select()阻塞中的 selector, wakeupCounter=-1, 即可被唤醒状态if ( wakeupCounter.incrementAndGet() == 0 ) selector.wakeup();}// step2. Poller 使用selector池处理读就绪事件/*** The background thread that adds sockets to the Poller, checks the* poller for triggered events and hands the associated socket off to an* appropriate processor as events occur.*/@Overridepublic void run() {// Loop until destroy() is calledwhile (true) {boolean hasEvents = false;try {if (!close) {// events() 会检查是否有acceptor提交过来的 PollerEvent, 如果有,会先初始化event// 向selector注册读事件等等,以便后续 select() 生效hasEvents = events();if (wakeupCounter.getAndSet(-1) > 0) {//if we are here, means we have other stuff to do//do a non blocking selectkeyCount = selector.selectNow();} else {keyCount = selector.select(selectorTimeout);}wakeupCounter.set(0);}if (close) {events();timeout(0, false);try {selector.close();} catch (IOException ioe) {log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.selectorCloseFail"), ioe);}break;}} catch (Throwable x) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(x);log.error("",x);continue;}//either we timed out or we woke up, process events firstif ( keyCount == 0 ) hasEvents = (hasEvents | events());Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator =keyCount > 0 ? selector.selectedKeys().iterator() : null;// Walk through the collection of ready keys and dispatch// any active event.while (iterator != null && iterator.hasNext()) {SelectionKey sk = iterator.next();NioSocketWrapper attachment = (NioSocketWrapper)sk.attachment();// Attachment may be null if another thread has called// cancelledKey()if (attachment == null) {iterator.remove();} else {// 把key监听移除,然后去处理具体key, 网络接入成功iterator.remove();processKey(sk, attachment);}}//while//process timeoutstimeout(keyCount,hasEvents);}//whilegetStopLatch().countDown();}// org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.Poller#processKeyprotected void processKey(SelectionKey sk, NioSocketWrapper attachment) {try {if ( close ) {cancelledKey(sk);} else if ( sk.isValid() && attachment != null ) {if (sk.isReadable() || sk.isWritable() ) {// sendfileif ( attachment.getSendfileData() != null ) {processSendfile(sk,attachment, false);} else {// 取消事件监听,那么后续如何读数据呢?// 这意味着当前socket将会从epoll的表中移除掉,不再被其管理,但并不影响后续的read// 后续的read() 操作将以bio等式展开unreg(sk, attachment, sk.readyOps());boolean closeSocket = false;// Read goes before write// 优先处理读事件,再处理写事件if (sk.isReadable()) {if (!processSocket(attachment, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ, true)) {closeSocket = true;}}if (!closeSocket && sk.isWritable()) {if (!processSocket(attachment, SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE, true)) {closeSocket = true;}}if (closeSocket) {cancelledKey(sk);}}}} else {//invalid keycancelledKey(sk);}} catch ( CancelledKeyException ckx ) {cancelledKey(sk);} catch (Throwable t) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);log.error("",t);}}// org.apache.tomcat.util.net.AbstractEndpoint#processSocket/*** Process the given SocketWrapper with the given status. Used to trigger* processing as if the Poller (for those endpoints that have one)* selected the socket.** @param socketWrapper The socket wrapper to process* @param event The socket event to be processed* @param dispatch Should the processing be performed on a new* container thread** @return if processing was triggered successfully*/public boolean processSocket(SocketWrapperBase<S> socketWrapper,SocketEvent event, boolean dispatch) {try {if (socketWrapper == null) {return false;}// 使用线程池处理单个读事件SocketProcessorBase<S> sc = processorCache.pop();if (sc == null) {sc = createSocketProcessor(socketWrapper, event);} else {sc.reset(socketWrapper, event);}// 线程池默认10个核心线程// 此处的线程池并非原生jdk的线程池ThreadPoolExecutor,而是经过tomcat继承过来的 org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.ThreadPoolExecutor, 主要用于做一次统计类工作// 最终的socket处理将会由 SocketProcessor 进行统一调度具体的Handler处理Executor executor = getExecutor();if (dispatch && executor != null) {executor.execute(sc);} else {sc.run();}} catch (RejectedExecutionException ree) {getLog().warn(sm.getString("endpoint.executor.fail", socketWrapper) , ree);return false;} catch (Throwable t) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);// This means we got an OOM or similar creating a thread, or that// the pool and its queue are fullgetLog().error(sm.getString("endpoint.process.fail"), t);return false;}return true;}// 以上过程,请求就从 Poller 中提交到了 SocketProcessor 了,将由 SocketProcessor 进行统一处理// org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.SocketProcessor#doRun@Overrideprotected void doRun() {NioChannel socket = socketWrapper.getSocket();SelectionKey key = socket.getIOChannel().keyFor(socket.getPoller().getSelector());try {int handshake = -1;try {if (key != null) {if (socket.isHandshakeComplete()) {// No TLS handshaking required. Let the handler// process this socket / event combination.handshake = 0;} else if (event == SocketEvent.STOP || event == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT ||event == SocketEvent.ERROR) {// Unable to complete the TLS handshake. Treat it as// if the handshake failed.handshake = -1;} else {handshake = socket.handshake(key.isReadable(), key.isWritable());// The handshake process reads/writes from/to the// socket. status may therefore be OPEN_WRITE once// the handshake completes. However, the handshake// happens when the socket is opened so the status// must always be OPEN_READ after it completes. It// is OK to always set this as it is only used if// the handshake completes.event = SocketEvent.OPEN_READ;}}} catch (IOException x) {handshake = -1;if (log.isDebugEnabled()) log.debug("Error during SSL handshake",x);} catch (CancelledKeyException ckx) {handshake = -1;}if (handshake == 0) {SocketState state = SocketState.OPEN;// Process the request from this socketif (event == null) {state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ);} else {// org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol$ConnectionHandler// 根据具体协议,创建不同的processor处理 如: Http11Processor// 此处hander统一调用外部类的父类处理为: org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol$ConnectionHandlerstate = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, event);}// 如果具体协议处理结果是 CLOSED, 那么就把该close关闭掉// 从这个意义上来说,普通的请求实际上都是进行长连接的(当然了,客户端一般会主动再调用一个close(),这就没法了)if (state == SocketState.CLOSED) {close(socket, key);}} else if (handshake == -1 ) {close(socket, key);} else if (handshake == SelectionKey.OP_READ){socketWrapper.registerReadInterest();} else if (handshake == SelectionKey.OP_WRITE){socketWrapper.registerWriteInterest();}} catch (CancelledKeyException cx) {socket.getPoller().cancelledKey(key);} catch (VirtualMachineError vme) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(vme);} catch (Throwable t) {log.error("", t);socket.getPoller().cancelledKey(key);} finally {socketWrapper = null;event = null;//return to cache// 复用 proccosor 处理器if (running && !paused) {processorCache.push(this);}}}}// 以上,就是整个http请求如何转交给应用处理的大体流程了。// 不过还有一个问题:就是http请求处理完成之后,是关闭连接不是保持连接又当如何判定呢?// 实际上它是通过协议处理完成后返回一个 SocketState 来决定的,你如果有兴趣,请继续往下:// org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol.ConnectionHandler#process// 该 ConnectionHandler 将会统一管理实际的可复用的 Processor, 并针对无效的请求直接返回 SocketState.CLOSED, 以便直接关闭会话@Overridepublic SocketState process(SocketWrapperBase<S> wrapper, SocketEvent status) {if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.process",wrapper.getSocket(), status));}if (wrapper == null) {// Nothing to do. Socket has been closed.return SocketState.CLOSED;}S socket = wrapper.getSocket();// 针对socket的处理,ConnectionHandler又使用了一个可复用的容器进行管理processors, 避免大量创建processor的开销Processor processor = connections.get(socket);if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.connectionsGet",processor, socket));}// Async timeouts are calculated on a dedicated thread and then// dispatched. Because of delays in the dispatch process, the// timeout may no longer be required. Check here and avoid// unnecessary processing.if (SocketEvent.TIMEOUT == status && (processor == null ||!processor.isAsync() || !processor.checkAsyncTimeoutGeneration())) {// This is effectively a NO-OPreturn SocketState.OPEN;}if (processor != null) {// Make sure an async timeout doesn't firegetProtocol().removeWaitingProcessor(processor);} else if (status == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT || status == SocketEvent.ERROR) {// Nothing to do. Endpoint requested a close and there is no// longer a processor associated with this socket.return SocketState.CLOSED;}ContainerThreadMarker.set();try {if (processor == null) {String negotiatedProtocol = wrapper.getNegotiatedProtocol();if (negotiatedProtocol != null) {UpgradeProtocol upgradeProtocol =getProtocol().getNegotiatedProtocol(negotiatedProtocol);if (upgradeProtocol != null) {processor = upgradeProtocol.getProcessor(wrapper, getProtocol().getAdapter());} else if (negotiatedProtocol.equals("http/1.1")) {// Explicitly negotiated the default protocol.// Obtain a processor below.} else {// TODO:// OpenSSL 1.0.2's ALPN callback doesn't support// failing the handshake with an error if no// protocol can be negotiated. Therefore, we need to// fail the connection here. Once this is fixed,// replace the code below with the commented out// block.if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.negotiatedProcessor.fail",negotiatedProtocol));}return SocketState.CLOSED;/** To replace the code above once OpenSSL 1.1.0 is* used.// Failed to create processor. This is a bug.throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.negotiatedProcessor.fail",negotiatedProtocol));*/}}}if (processor == null) {processor = recycledProcessors.pop();if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.processorPop",processor));}}if (processor == null) {processor = getProtocol().createProcessor();register(processor);}processor.setSslSupport(wrapper.getSslSupport(getProtocol().getClientCertProvider()));// Associate the processor with the connectionconnections.put(socket, processor);SocketState state = SocketState.CLOSED;do {// 该state最终会由 具体的processor决定, 如: Http11Processorstate = processor.process(wrapper, status);if (state == SocketState.UPGRADING) {// Get the HTTP upgrade handlerUpgradeToken upgradeToken = processor.getUpgradeToken();// Retrieve leftover inputByteBuffer leftOverInput = processor.getLeftoverInput();if (upgradeToken == null) {// Assume direct HTTP/2 connectionUpgradeProtocol upgradeProtocol = getProtocol().getUpgradeProtocol("h2c");if (upgradeProtocol != null) {processor = upgradeProtocol.getProcessor(wrapper, getProtocol().getAdapter());wrapper.unRead(leftOverInput);// Associate with the processor with the connectionconnections.put(socket, processor);} else {if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.negotiatedProcessor.fail","h2c"));}return SocketState.CLOSED;}} else {HttpUpgradeHandler httpUpgradeHandler = upgradeToken.getHttpUpgradeHandler();// Release the Http11 processor to be re-usedrelease(processor);// Create the upgrade processorprocessor = getProtocol().createUpgradeProcessor(wrapper, upgradeToken);if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.upgradeCreate",processor, wrapper));}wrapper.unRead(leftOverInput);// Mark the connection as upgradedwrapper.setUpgraded(true);// Associate with the processor with the connectionconnections.put(socket, processor);// Initialise the upgrade handler (which may trigger// some IO using the new protocol which is why the lines// above are necessary)// This cast should be safe. If it fails the error// handling for the surrounding try/catch will deal with// it.if (upgradeToken.getInstanceManager() == null) {httpUpgradeHandler.init((WebConnection) processor);} else {ClassLoader oldCL = upgradeToken.getContextBind().bind(false, null);try {httpUpgradeHandler.init((WebConnection) processor);} finally {upgradeToken.getContextBind().unbind(false, oldCL);}}}}} while ( state == SocketState.UPGRADING);if (state == SocketState.LONG) {// In the middle of processing a request/response. Keep the// socket associated with the processor. Exact requirements// depend on type of long polllongPoll(wrapper, processor);if (processor.isAsync()) {getProtocol().addWaitingProcessor(processor);}} else if (state == SocketState.OPEN) {// In keep-alive but between requests. OK to recycle// processor. Continue to poll for the next request.connections.remove(socket);release(processor);wrapper.registerReadInterest();} else if (state == SocketState.SENDFILE) {// Sendfile in progress. If it fails, the socket will be// closed. If it works, the socket either be added to the// poller (or equivalent) to await more data or processed// if there are any pipe-lined requests remaining.} else if (state == SocketState.UPGRADED) {// Don't add sockets back to the poller if this was a// non-blocking write otherwise the poller may trigger// multiple read events which may lead to thread starvation// in the connector. The write() method will add this socket// to the poller if necessary.if (status != SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE) {longPoll(wrapper, processor);}} else if (state == SocketState.SUSPENDED) {// Don't add sockets back to the poller.// The resumeProcessing() method will add this socket// to the poller.} else {// Connection closed. OK to recycle the processor. Upgrade// processors are not recycled.connections.remove(socket);if (processor.isUpgrade()) {UpgradeToken upgradeToken = processor.getUpgradeToken();HttpUpgradeHandler httpUpgradeHandler = upgradeToken.getHttpUpgradeHandler();InstanceManager instanceManager = upgradeToken.getInstanceManager();if (instanceManager == null) {httpUpgradeHandler.destroy();} else {ClassLoader oldCL = upgradeToken.getContextBind().bind(false, null);try {httpUpgradeHandler.destroy();} finally {try {instanceManager.destroyInstance(httpUpgradeHandler);} catch (Throwable e) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);getLog().error(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.error"), e);}upgradeToken.getContextBind().unbind(false, oldCL);}}} else {release(processor);}}// 将处理的状态,返回给总控 Processor, 以便决定是否close socketreturn state;} catch(java.net.SocketException e) {// SocketExceptions are normalgetLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.socketexception.debug"), e);} catch (java.io.IOException e) {// IOExceptions are normalgetLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.ioexception.debug"), e);} catch (ProtocolException e) {// Protocol exceptions normally mean the client sent invalid or// incomplete data.getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.protocolexception.debug"), e);}// Future developers: if you discover any other// rare-but-nonfatal exceptions, catch them here, and log as// above.catch (Throwable e) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);// any other exception or error is odd. Here we log it// with "ERROR" level, so it will show up even on// less-than-verbose logs.getLog().error(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.error"), e);} finally {ContainerThreadMarker.clear();}// Make sure socket/processor is removed from the list of current// connectionsconnections.remove(socket);release(processor);return SocketState.CLOSED;}// org.apache.coyote.AbstractProcessorLight#process// Http11Processor 继承该 AbstractProcessorLight, 使用模板方法模式处理细节不同点@Overridepublic SocketState process(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper, SocketEvent status)throws IOException {SocketState state = SocketState.CLOSED;Iterator<DispatchType> dispatches = null;do {if (dispatches != null) {DispatchType nextDispatch = dispatches.next();state = dispatch(nextDispatch.getSocketStatus());} else if (status == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT) {// Do nothing here, just wait for it to get recycled} else if (isAsync() || isUpgrade() || state == SocketState.ASYNC_END) {state = dispatch(status);if (state == SocketState.OPEN) {// There may be pipe-lined data to read. If the data isn't// processed now, execution will exit this loop and call// release() which will recycle the processor (and input// buffer) deleting any pipe-lined data. To avoid this,// process it now.state = service(socketWrapper);}} else if (status == SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE) {// Extra write event likely after async, ignorestate = SocketState.LONG;} else if (status == SocketEvent.OPEN_READ){// 普通的http请求,将会被处理为 OPEN_READstate = service(socketWrapper);} else {// Default to closing the socket if the SocketEvent passed in// is not consistent with the current state of the Processorstate = SocketState.CLOSED;}if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug("Socket: [" + socketWrapper +"], Status in: [" + status +"], State out: [" + state + "]");}if (state != SocketState.CLOSED && isAsync()) {state = asyncPostProcess();if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug("Socket: [" + socketWrapper +"], State after async post processing: [" + state + "]");}}if (dispatches == null || !dispatches.hasNext()) {// Only returns non-null iterator if there are// dispatches to process.dispatches = getIteratorAndClearDispatches();}// 循环处理请求,直接状态是 CLOSE, 或者异步结束} while (state == SocketState.ASYNC_END ||dispatches != null && state != SocketState.CLOSED);return state;}// org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11Processor#service// 具体的协议处理方法,将返回处理结果状态,决定是否关闭 socket@Overridepublic SocketState service(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper)throws IOException {// 由 RequestInfo 来管理整个处理的生命周期// STAGE_PARSE -> STAGE_PREPARE -> STAGE_SERVICE -> STAGE_ENDINPUT -> STAGE_ENDOUTPUT -> STAGE_KEEPALIVE -> STAGE_ENDEDRequestInfo rp = request.getRequestProcessor();rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_PARSE);// Setting up the I/OsetSocketWrapper(socketWrapper);inputBuffer.init(socketWrapper);outputBuffer.init(socketWrapper);// FlagskeepAlive = true;openSocket = false;readComplete = true;boolean keptAlive = false;SendfileState sendfileState = SendfileState.DONE;// 此处会循环读取 inputStream 进行处理,如果只是一次 http 请求,则第一次处理完成之后,第二次将会产生 IOException// 从而触发socket的关闭过程while (!getErrorState().isError() && keepAlive && !isAsync() && upgradeToken == null &&sendfileState == SendfileState.DONE && !endpoint.isPaused()) {// Parsing the request headertry {if (!inputBuffer.parseRequestLine(keptAlive)) {if (inputBuffer.getParsingRequestLinePhase() == -1) {return SocketState.UPGRADING;} else if (handleIncompleteRequestLineRead()) {break;}}if (endpoint.isPaused()) {// 503 - Service unavailableresponse.setStatus(503);setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, null);} else {keptAlive = true;// Set this every time in case limit has been changed via JMXrequest.getMimeHeaders().setLimit(endpoint.getMaxHeaderCount());if (!inputBuffer.parseHeaders()) {// We've read part of the request, don't recycle it// instead associate it with the socketopenSocket = true;readComplete = false;break;}if (!disableUploadTimeout) {socketWrapper.setReadTimeout(connectionUploadTimeout);}}} catch (IOException e) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug(sm.getString("http11processor.header.parse"), e);}setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CONNECTION_NOW, e);break;} catch (Throwable t) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);UserDataHelper.Mode logMode = userDataHelper.getNextMode();if (logMode != null) {String message = sm.getString("http11processor.header.parse");switch (logMode) {case INFO_THEN_DEBUG:message += sm.getString("http11processor.fallToDebug");//$FALL-THROUGH$case INFO:log.info(message, t);break;case DEBUG:log.debug(message, t);}}// 400 - Bad Requestresponse.setStatus(400);setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, t);getAdapter().log(request, response, 0);}// Has an upgrade been requested?Enumeration<String> connectionValues = request.getMimeHeaders().values("Connection");boolean foundUpgrade = false;while (connectionValues.hasMoreElements() && !foundUpgrade) {foundUpgrade = connectionValues.nextElement().toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH).contains("upgrade");}if (foundUpgrade) {// Check the protocolString requestedProtocol = request.getHeader("Upgrade");UpgradeProtocol upgradeProtocol = httpUpgradeProtocols.get(requestedProtocol);if (upgradeProtocol != null) {if (upgradeProtocol.accept(request)) {// TODO Figure out how to handle request bodies at this// point.response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS);response.setHeader("Connection", "Upgrade");response.setHeader("Upgrade", requestedProtocol);action(ActionCode.CLOSE, null);getAdapter().log(request, response, 0);InternalHttpUpgradeHandler upgradeHandler =upgradeProtocol.getInternalUpgradeHandler(getAdapter(), cloneRequest(request));UpgradeToken upgradeToken = new UpgradeToken(upgradeHandler, null, null);action(ActionCode.UPGRADE, upgradeToken);return SocketState.UPGRADING;}}}if (!getErrorState().isError()) {// Setting up filters, and parse some request headersrp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_PREPARE);try {prepareRequest();} catch (Throwable t) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug(sm.getString("http11processor.request.prepare"), t);}// 500 - Internal Server Errorresponse.setStatus(500);setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, t);getAdapter().log(request, response, 0);}}if (maxKeepAliveRequests == 1) {keepAlive = false;} else if (maxKeepAliveRequests > 0 &&socketWrapper.decrementKeepAlive() <= 0) {keepAlive = false;}// Process the request in the adapterif (!getErrorState().isError()) {try {rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_SERVICE);// 使用适配器处理 request, 并忽略其返回状态值, 此处真正的协议处理服务,后续就是许多的 filterChain 处理了getAdapter().service(request, response);// Handle when the response was committed before a serious// error occurred. Throwing a ServletException should both// set the status to 500 and set the errorException.// If we fail here, then the response is likely already// committed, so we can't try and set headers.if(keepAlive && !getErrorState().isError() && !isAsync() &&statusDropsConnection(response.getStatus())) {setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, null);}} catch (InterruptedIOException e) {setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CONNECTION_NOW, e);} catch (HeadersTooLargeException e) {log.error(sm.getString("http11processor.request.process"), e);// The response should not have been committed but check it// anyway to be safeif (response.isCommitted()) {setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_NOW, e);} else {response.reset();response.setStatus(500);setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, e);response.setHeader("Connection", "close"); // TODO: Remove}} catch (Throwable t) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);log.error(sm.getString("http11processor.request.process"), t);// 500 - Internal Server Errorresponse.setStatus(500);setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, t);getAdapter().log(request, response, 0);}}// Finish the handling of the requestrp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDINPUT);if (!isAsync()) {// If this is an async request then the request ends when it has// been completed. The AsyncContext is responsible for calling// endRequest() in that case.// 非异步请求,则处理 input 上下文// 同时处理outputendRequest();}rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDOUTPUT);// If there was an error, make sure the request is counted as// and error, and update the statistics counterif (getErrorState().isError()) {response.setStatus(500);}if (!isAsync() || getErrorState().isError()) {request.updateCounters();// 更换request,response 为空,以便proccor池安全复用if (getErrorState().isIoAllowed()) {inputBuffer.nextRequest();outputBuffer.nextRequest();}}if (!disableUploadTimeout) {int soTimeout = endpoint.getConnectionTimeout();if(soTimeout > 0) {socketWrapper.setReadTimeout(soTimeout);} else {socketWrapper.setReadTimeout(0);}}rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_KEEPALIVE);// 正常处理完成一次请求,接着会进入下一次处理流程,一般会以 IOException 结束sendfileState = processSendfile(socketWrapper);}rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDED);// 所以,普通http请求,一般都会得到一次 CLOSE_CONNECTION_NOW 的状态,触发立即关闭 socketif (getErrorState().isError() || endpoint.isPaused()) {return SocketState.CLOSED;} else if (isAsync()) {return SocketState.LONG;} else if (isUpgrade()) {return SocketState.UPGRADING;} else {if (sendfileState == SendfileState.PENDING) {return SocketState.SENDFILE;} else {if (openSocket) {if (readComplete) {return SocketState.OPEN;} else {return SocketState.LONG;}} else {return SocketState.CLOSED;}}}}
当把网络请求接入进来后,先会经历一系列的filterChain处理,然后其中某个Filter就会解析具体参数。
对于文件处理,我们从对 multipart/form-data 的分支处理开始观察:
// org.apache.catalina.connector.Request#parseParameters/*** Parse request parameters.*/protected void parseParameters() {parametersParsed = true;Parameters parameters = coyoteRequest.getParameters();boolean success = false;try {...String contentType = getContentType();if (contentType == null) {contentType = "";}int semicolon = contentType.indexOf(';');if (semicolon >= 0) {contentType = contentType.substring(0, semicolon).trim();} else {contentType = contentType.trim();}// 如果是 multipart 类型数据,解析每个 part 数据if ("multipart/form-data".equals(contentType)) {parseParts(false);success = true;return;}...success = true;} finally {if (!success) {parameters.setParseFailedReason(FailReason.UNKNOWN);}}}// 对 mulipart 的处理实现// org.apache.catalina.connector.Request#parsePartsprivate void parseParts(boolean explicit) {// Return immediately if the parts have already been parsedif (parts != null || partsParseException != null) {return;}...boolean success = false;// Create a new file upload handlerDiskFileItemFactory factory = new DiskFileItemFactory();try {factory.setRepository(location.getCanonicalFile());} catch (IOException ioe) {parameters.setParseFailedReason(FailReason.IO_ERROR);partsParseException = ioe;return;}factory.setSizeThreshold(mce.getFileSizeThreshold());// 使用 ServletFileUplad 组件去解析文件信息ServletFileUpload upload = new ServletFileUpload();upload.setFileItemFactory(factory);upload.setFileSizeMax(mce.getMaxFileSize());upload.setSizeMax(mce.getMaxRequestSize());parts = new ArrayList<>();try {// step1. 使用 ServletFileUpload 解析参数为 FileItemList<FileItem> items =upload.parseRequest(new ServletRequestContext(this));int maxPostSize = getConnector().getMaxPostSize();int postSize = 0;Charset charset = getCharset();// step2. 将解析出的 FileItem 包装为 ApplicationPart, 添加到当前Request的 parts 容器中for (FileItem item : items) {ApplicationPart part = new ApplicationPart(item, location);parts.add(part);// 文件名处理if (part.getSubmittedFileName() == null) {String name = part.getName();String value = null;try {value = part.getString(charset.name());} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException uee) {// Not possible}if (maxPostSize >= 0) {// Have to calculate equivalent size. Not completely// accurate but close enough.postSize += name.getBytes(charset).length;if (value != null) {// Equals signpostSize++;// Value lengthpostSize += part.getSize();}// Value separatorpostSize++;if (postSize > maxPostSize) {parameters.setParseFailedReason(FailReason.POST_TOO_LARGE);throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString("coyoteRequest.maxPostSizeExceeded"));}}parameters.addParameter(name, value);}}success = true;}...} finally {// This might look odd but is correct. setParseFailedReason() only// sets the failure reason if none is currently set. This code could// be more efficient but it is written this way to be robust with// respect to changes in the remainder of the method.if (partsParseException != null || !success) {parameters.setParseFailedReason(FailReason.UNKNOWN);}}}
以上就是对文件上传的大概处理逻辑:1. 使用 ServletFileUpload 解析参数为 List<FileItem>; 2. 使用 ApplicationPart 包装FileItem, 放到 Request的parts字段中,以备后续使用。可见,对文件的解析是在 ServletFileUpload 中完成的。
// ServletFileUplad, 处理文件解析// org.apache.tomcat.util.http.fileupload.FileUploadBase#parseRequest/*** Processes an <a href="http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc1867.txt">RFC 1867</a>* compliant <code>multipart/form-data</code> stream.** @param ctx The context for the request to be parsed.** @return A list of <code>FileItem</code> instances parsed from the* request, in the order that they were transmitted.** @throws FileUploadException if there are problems reading/parsing* the request or storing files.*/public List<FileItem> parseRequest(RequestContext ctx)throws FileUploadException {List<FileItem> items = new ArrayList<>();boolean successful = false;try {// 依次迭代各part数据FileItemIterator iter = getItemIterator(ctx);FileItemFactory fac = getFileItemFactory();if (fac == null) {throw new NullPointerException("No FileItemFactory has been set.");}while (iter.hasNext()) {// 每进行一次迭代,就会创建一个 FileItemStreamImpl, 创建一个新的 InputStreamfinal FileItemStream item = iter.next();// Don't use getName() here to prevent an InvalidFileNameException.final String fileName = ((FileItemIteratorImpl.FileItemStreamImpl) item).name;// 为每个key 创建一个FileItem,用于输出数据流FileItem fileItem = fac.createItem(item.getFieldName(), item.getContentType(),item.isFormField(), fileName);items.add(fileItem);try {// 将socket中的数据流,写入到 fileItem 创建的临时文件中,达到框架上传的目的// fileItem.getOutputStream() 会创建临时文件// item.openStream() 会使用网络io流作为数据来源,当读取到 -1, 认为输入结束了// 最终会将所有单个part的数据全部写入当前的临时文件中Streams.copy(item.openStream(), fileItem.getOutputStream(), true);} catch (FileUploadIOException e) {throw (FileUploadException) e.getCause();} catch (IOException e) {throw new IOFileUploadException(String.format("Processing of %s request failed. %s",MULTIPART_FORM_DATA, e.getMessage()), e);}final FileItemHeaders fih = item.getHeaders();fileItem.setHeaders(fih);}successful = true;return items;} catch (FileUploadIOException e) {throw (FileUploadException) e.getCause();} catch (IOException e) {throw new FileUploadException(e.getMessage(), e);} finally {if (!successful) {// 如果部分失败,则全部将已上传部分删除for (FileItem fileItem : items) {try {fileItem.delete();} catch (Exception ignored) {// ignored TODO perhaps add to tracker delete failure list somehow?}}}}}
以上就是整个文件的上传框架解析过程了。大概步骤就是:
1. 基于 boundary, 使用迭代器模式依次创建InputStream();
2. 每次失败创建一个 DiskFileItem 实例,用于存放读取出的数据流;
3. 将网络InputStream 写入到Disk的临时文件中;
4. 将各DiskFileItem作为输入参数信息一起返回给应用;
下面,我们来看看它是如何基于 boundary 进行迭代 FileItemIteratorImpl 的吧:
// 1. 单个文件流的迭代准备工作// FileItemIteratorImpl 会解析出content-Type, boundary 等信息,为后续迭代准备// org.apache.tomcat.util.http.fileupload.FileUploadBase.FileItemIteratorImpl#FileItemIteratorImpl/*** Creates a new instance.** @param ctx The request context.* @throws FileUploadException An error occurred while* parsing the request.* @throws IOException An I/O error occurred.*/FileItemIteratorImpl(RequestContext ctx)throws FileUploadException, IOException {if (ctx == null) {throw new NullPointerException("ctx parameter");}String contentType = ctx.getContentType();if ((null == contentType)|| (!contentType.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH).startsWith(MULTIPART))) {throw new InvalidContentTypeException(String.format("the request doesn't contain a %s or %s stream, content type header is %s",MULTIPART_FORM_DATA, MULTIPART_MIXED, contentType));}final long requestSize = ((UploadContext) ctx).contentLength();InputStream input; // N.B. this is eventually closed in MultipartStream processingif (sizeMax >= 0) {if (requestSize != -1 && requestSize > sizeMax) {throw new SizeLimitExceededException(String.format("the request was rejected because its size (%s) exceeds the configured maximum (%s)",Long.valueOf(requestSize), Long.valueOf(sizeMax)),requestSize, sizeMax);}// N.B. this is eventually closed in MultipartStream processinginput = new LimitedInputStream(ctx.getInputStream(), sizeMax) {@Overrideprotected void raiseError(long pSizeMax, long pCount)throws IOException {FileUploadException ex = new SizeLimitExceededException(String.format("the request was rejected because its size (%s) exceeds the configured maximum (%s)",Long.valueOf(pCount), Long.valueOf(pSizeMax)),pCount, pSizeMax);throw new FileUploadIOException(ex);}};} else {// 从 ServletRequestContext 中获取inputStreaminput = ctx.getInputStream();}String charEncoding = headerEncoding;if (charEncoding == null) {charEncoding = ctx.getCharacterEncoding();}// 解析 boundary 参数,如: ----WebKitFormBoundarydyG19jnnVWC9U1zYboundary = getBoundary(contentType);if (boundary == null) {IOUtils.closeQuietly(input); // avoid possible resource leakthrow new FileUploadException("the request was rejected because no multipart boundary was found");}notifier = new MultipartStream.ProgressNotifier(listener, requestSize);try {multi = new MultipartStream(input, boundary, notifier);} catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) {IOUtils.closeQuietly(input); // avoid possible resource leakthrow new InvalidContentTypeException(String.format("The boundary specified in the %s header is too long", CONTENT_TYPE), iae);}multi.setHeaderEncoding(charEncoding);skipPreamble = true;// 同样会初始化第一个可被迭代的对象,后续的初始化动作则是由 hasNext() 触发。findNextItem();}// 在迭代输入数据时,会调用迭代方法 FileItemIteratorImpl next(); 读取数据// org.apache.tomcat.util.http.fileupload.FileUploadBase.FileItemIteratorImpl#hasNext/*** Returns, whether another instance of {@link FileItemStream}* is available.** @throws FileUploadException Parsing or processing the* file item failed.* @throws IOException Reading the file item failed.* @return True, if one or more additional file items* are available, otherwise false.*/@Overridepublic boolean hasNext() throws FileUploadException, IOException {if (eof) {return false;}if (itemValid) {return true;}try {// 迭代出下一个part文件return findNextItem();} catch (FileUploadIOException e) {// unwrap encapsulated SizeExceptionthrow (FileUploadException) e.getCause();}}// org.apache.tomcat.util.http.fileupload.FileUploadBase.FileItemIteratorImpl#findNextItem/*** Called for finding the next item, if any.** @return True, if an next item was found, otherwise false.* @throws IOException An I/O error occurred.*/private boolean findNextItem() throws IOException {if (eof) {return false;}if (currentItem != null) {currentItem.close();currentItem = null;}for (;;) {boolean nextPart;// 首次读取时,使用新的 boundary 跳过// 后续则基于首个连续换行符进行数据获取, \r\n\r\nif (skipPreamble) {nextPart = multi.skipPreamble();} else {nextPart = multi.readBoundary();}// 如果没有读取到更多的part, 则返回if (!nextPart) {// 读取第一个没有 boundary 的数据,再搜索一次,如果还是没有 boundary, 则认为数据已结束if (currentFieldName == null) {// Outer multipart terminated -> No more dataeof = true;return false;}// Inner multipart terminated -> Return to parsing the outermulti.setBoundary(boundary);// 将当前字段信息置空,下次如果再读取不到 boundary, 则读取结束currentFieldName = null;continue;}// 以下有更多的 part 输入FileItemHeaders headers = getParsedHeaders(multi.readHeaders());if (currentFieldName == null) {// We're parsing the outer multipart// 如: file, file2 ...String fieldName = getFieldName(headers);if (fieldName != null) {String subContentType = headers.getHeader(CONTENT_TYPE);if (subContentType != null&& subContentType.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH).startsWith(MULTIPART_MIXED)) {currentFieldName = fieldName;// Multiple files associated with this field namebyte[] subBoundary = getBoundary(subContentType);multi.setBoundary(subBoundary);skipPreamble = true;continue;}// 获取文件名称从 header 中// Content-Disposition: form-data; name="file2"; filename="123-2.txt"String fileName = getFileName(headers);// 创建 FileItemStreamImpl, 以备后续迭代输出,其构造方法将会创建 stream 实例// FileItemStreamImpl 是迭代器的一个内部类,共享 multi 对象// FileItemStreamImpl 会将网络io流封装为单个可读取的inputStream, 备用currentItem = new FileItemStreamImpl(fileName,fieldName, headers.getHeader(CONTENT_TYPE),fileName == null, getContentLength(headers));currentItem.setHeaders(headers);notifier.noteItem();itemValid = true;return true;}} else {String fileName = getFileName(headers);if (fileName != null) {currentItem = new FileItemStreamImpl(fileName,currentFieldName,headers.getHeader(CONTENT_TYPE),false, getContentLength(headers));currentItem.setHeaders(headers);notifier.noteItem();itemValid = true;return true;}}// 其他情况,直接丢弃当前 body 数据multi.discardBodyData();}}// org.apache.tomcat.util.http.fileupload.FileUploadBase.FileItemIteratorImpl.FileItemStreamImpl#FileItemStreamImpl/*** Creates a new instance.** @param pName The items file name, or null.* @param pFieldName The items field name.* @param pContentType The items content type, or null.* @param pFormField Whether the item is a form field.* @param pContentLength The items content length, if known, or -1* @throws IOException Creating the file item failed.*/FileItemStreamImpl(String pName, String pFieldName,String pContentType, boolean pFormField,long pContentLength) throws IOException {name = pName;fieldName = pFieldName;contentType = pContentType;formField = pFormField;// 创建一个inputStream 的流,备读// 读到哪里算是结束呢?当 read() 返回-1时,认为输入结束了final ItemInputStream itemStream = multi.newInputStream();InputStream istream = itemStream;if (fileSizeMax != -1) {if (pContentLength != -1&& pContentLength > fileSizeMax) {FileSizeLimitExceededException e =new FileSizeLimitExceededException(String.format("The field %s exceeds its maximum permitted size of %s bytes.",fieldName, Long.valueOf(fileSizeMax)),pContentLength, fileSizeMax);e.setFileName(pName);e.setFieldName(pFieldName);throw new FileUploadIOException(e);}// 限制最大大小,该值用 spring.http.multipart.max-file-size 配置, 但往往还会同时有一个参数需要配置: spring.http.multipart.max-request-size,// 因为当文件很大时,请求也会非常大,所以一般会要求同时设置这两个参数,否则都会抛出超出最大允许大小限制异常// 使用 LimitedInputStream 包装提供的读写大小判定功能,原始istream接收网络io输入istream = new LimitedInputStream(istream, fileSizeMax) {@Overrideprotected void raiseError(long pSizeMax, long pCount)throws IOException {itemStream.close(true);FileSizeLimitExceededException e =new FileSizeLimitExceededException(String.format("The field %s exceeds its maximum permitted size of %s bytes.",fieldName, Long.valueOf(pSizeMax)),pCount, pSizeMax);e.setFieldName(fieldName);e.setFileName(name);throw new FileUploadIOException(e);}};}stream = istream;}// 为每个part创建一个 DiskFileItem, 用于存储网络io的文件流,备用// org.apache.tomcat.util.http.fileupload.disk.DiskFileItemFactory#createItem/*** Create a new {@link DiskFileItem}* instance from the supplied parameters and the local factory* configuration.** @param fieldName The name of the form field.* @param contentType The content type of the form field.* @param isFormField <code>true</code> if this is a plain form field;* <code>false</code> otherwise.* @param fileName The name of the uploaded file, if any, as supplied* by the browser or other client.** @return The newly created file item.*/@Overridepublic FileItem createItem(String fieldName, String contentType,boolean isFormField, String fileName) {DiskFileItem result = new DiskFileItem(fieldName, contentType,isFormField, fileName, sizeThreshold, repository);result.setDefaultCharset(defaultCharset);return result;}// next() 进行迭代, 使用 itemValid 来控制单次迭代使用/*** Returns the next available {@link FileItemStream}.** @throws java.util.NoSuchElementException No more items are* available. Use {@link #hasNext()} to prevent this exception.* @throws FileUploadException Parsing or processing the* file item failed.* @throws IOException Reading the file item failed.* @return FileItemStream instance, which provides* access to the next file item.*/@Overridepublic FileItemStream next() throws FileUploadException, IOException {if (eof || (!itemValid && !hasNext())) {throw new NoSuchElementException();}itemValid = false;return currentItem;}
// 2. 从网络io流到临时文件流的写入// 主要分为三步:网络io流的获取;本地文件输出流的获取;流的对接;// 网络io流即是在创建 FileItemStreamImpl 时生成的 stream;// org.apache.tomcat.util.http.fileupload.FileUploadBase.FileItemIteratorImpl.FileItemStreamImpl#openStream/*** Returns an input stream, which may be used to* read the items contents.** @return Opened input stream.* @throws IOException An I/O error occurred.*/@Overridepublic InputStream openStream() throws IOException {if (((Closeable) stream).isClosed()) {throw new FileItemStream.ItemSkippedException();}return stream;}// 而本地文件输出流则是一个本地临时文件,用于对接任意大小的输入流// org.apache.tomcat.util.http.fileupload.disk.DiskFileItem#getOutputStream/*** Returns an {@link java.io.OutputStream OutputStream} that can* be used for storing the contents of the file.** @return An {@link java.io.OutputStream OutputStream} that can be used* for storing the contents of the file.** @throws IOException if an error occurs.*/@Overridepublic OutputStream getOutputStream()throws IOException {if (dfos == null) {// 创建临时文件输出File outputFile = getTempFile();// 使用 DeferredFileOutputStream 包装临时文件,dfos = new DeferredFileOutputStream(sizeThreshold, outputFile);}return dfos;}// org.apache.tomcat.util.http.fileupload.disk.DiskFileItem#getTempFile/*** Creates and returns a {@link java.io.File File} representing a uniquely* named temporary file in the configured repository path. The lifetime of* the file is tied to the lifetime of the <code>FileItem</code> instance;* the file will be deleted when the instance is garbage collected.* <p>* <b>Note: Subclasses that override this method must ensure that they return the* same File each time.</b>** @return The {@link java.io.File File} to be used for temporary storage.*/protected File getTempFile() {if (tempFile == null) {File tempDir = repository;if (tempDir == null) {tempDir = new File(System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir"));}// uid 同进程相同, getUniqueId() 会返回一个自增的id, 保证进程唯一,加上 uid 后,就可以确定临时文件唯一了String tempFileName =String.format("upload_%s_%s.tmp", UID, getUniqueId());tempFile = new File(tempDir, tempFileName);}return tempFile;}/*** Returns an identifier that is unique within the class loader used to* load this class, but does not have random-like appearance.** @return A String with the non-random looking instance identifier.*/private static String getUniqueId() {final int limit = 100000000;int current = COUNTER.getAndIncrement();String id = Integer.toString(current);// If you manage to get more than 100 million of ids, you'll// start getting ids longer than 8 characters.if (current < limit) {id = ("00000000" + id).substring(id.length());}return id;}// 最后,将网络io流对接到临时文件流中,完成数据的接收// org.apache.tomcat.util.http.fileupload.util.Streams#copy/*** Copies the contents of the given {@link InputStream}* to the given {@link OutputStream}. Shortcut for* <pre>* copy(pInputStream, pOutputStream, new byte[8192]);* </pre>** @param inputStream The input stream, which is being read.* It is guaranteed, that {@link InputStream#close()} is called* on the stream.* @param outputStream The output stream, to which data should* be written. May be null, in which case the input streams* contents are simply discarded.* @param closeOutputStream True guarantees, that {@link OutputStream#close()}* is called on the stream. False indicates, that only* {@link OutputStream#flush()} should be called finally.** @return Number of bytes, which have been copied.* @throws IOException An I/O error occurred.*/public static long copy(InputStream inputStream, OutputStream outputStream, boolean closeOutputStream)throws IOException {// 8096return copy(inputStream, outputStream, closeOutputStream, new byte[DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE]);}/*** Copies the contents of the given {@link InputStream}* to the given {@link OutputStream}.** @param inputStream The input stream, which is being read.* It is guaranteed, that {@link InputStream#close()} is called* on the stream.* @param outputStream The output stream, to which data should* be written. May be null, in which case the input streams* contents are simply discarded.* @param closeOutputStream True guarantees, that {@link OutputStream#close()}* is called on the stream. False indicates, that only* {@link OutputStream#flush()} should be called finally.* @param buffer Temporary buffer, which is to be used for* copying data.* @return Number of bytes, which have been copied.* @throws IOException An I/O error occurred.*/public static long copy(InputStream inputStream,OutputStream outputStream, boolean closeOutputStream,byte[] buffer)throws IOException {OutputStream out = outputStream;InputStream in = inputStream;try {long total = 0;for (;;) {// 阻塞式获取文件数据流,写入到临时文件中// 所以,如果我们上传超大文件时,实际上有相当大部分的时间,只是框架和客户端在交互,应用代码则不会感知到// 直到所有上传已完成int res = in.read(buffer);if (res == -1) {break;}if (res > 0) {total += res;if (out != null) {out.write(buffer, 0, res);}}}if (out != null) {// 关闭输出流,即关闭临时文件实例if (closeOutputStream) {out.close();} else {out.flush();}out = null;}in.close();in = null;return total;} finally {IOUtils.closeQuietly(in);if (closeOutputStream) {IOUtils.closeQuietly(out);}}}
总结:主要点在于 boundary 的解析处理,难点在于io流的对接。包括接收请求io流,以及在响应客户端的os.flush(), 都是在做复杂的io操作。
5. 使用过后的清理工作?
外部请求的文件上传,一般都会使用临时文件进行接收,比如上面的实现。虽说是临时文件,但如果不做清理,每次上传都生成一个临时文件,则必然占用大量磁盘空间,迟早得耗尽资源。这不是一个好的框架该做的事。
比如:spring框架中,DispatcherServlet会在使用完成 MultipartFile 后,会主动做一些清理操作。
// org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#doDispatch/*** Process the actual dispatching to the handler.* <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order.* The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters* to find the first that supports the handler class.* <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers* themselves to decide which methods are acceptable.* @param request current HTTP request* @param response current HTTP response* @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure*/protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);try {ModelAndView mv = null;Exception dispatchException = null;try {// 如果是文件类型,则会用 StandardMultipartHttpServletRequest 再包装一层的处理processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);// Determine handler for the current request.mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);return;}// Determine handler adapter for the current request.HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.String method = request.getMethod();boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);}if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {return;}}if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {return;}// Actually invoke the handler.mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {return;}applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);}catch (Exception ex) {dispatchException = ex;}catch (Throwable err) {// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);}processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);}catch (Exception ex) {triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);}catch (Throwable err) {triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));}finally {if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletionif (mappedHandler != null) {mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);}}else {// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.// 如果本次有解析文件,则会做清理操作if (multipartRequestParsed) {cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);}}}}// org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#cleanupMultipart/*** Clean up any resources used by the given multipart request (if any).* @param request current HTTP request* @see MultipartResolver#cleanupMultipart*/protected void cleanupMultipart(HttpServletRequest request) {// 获取 MultipartHttpServletRequest 实例MultipartHttpServletRequest multipartRequest =WebUtils.getNativeRequest(request, MultipartHttpServletRequest.class);if (multipartRequest != null) {// 清理文件this.multipartResolver.cleanupMultipart(multipartRequest);}}// org.springframework.web.multipart.support.StandardServletMultipartResolver#cleanupMultipart@Overridepublic void cleanupMultipart(MultipartHttpServletRequest request) {if (!(request instanceof AbstractMultipartHttpServletRequest) ||((AbstractMultipartHttpServletRequest) request).isResolved()) {// To be on the safe side: explicitly delete the parts,// but only actual file parts (for Resin compatibility)try {for (Part part : request.getParts()) {if (request.getFile(part.getName()) != null) {// 调用各part部分的接口,delete()part.delete();}}}catch (Throwable ex) {LogFactory.getLog(getClass()).warn("Failed to perform cleanup of multipart items", ex);}}}// org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationPart#delete@Overridepublic void delete() throws IOException {fileItem.delete();}// org.apache.tomcat.util.http.fileupload.disk.DiskFileItem#delete/*** Deletes the underlying storage for a file item, including deleting any* associated temporary disk file. Although this storage will be deleted* automatically when the <code>FileItem</code> instance is garbage* collected, this method can be used to ensure that this is done at an* earlier time, thus preserving system resources.*/@Overridepublic void delete() {cachedContent = null;// 获取临时文件实例,如果存在则删除File outputFile = getStoreLocation();if (outputFile != null && !isInMemory() && outputFile.exists()) {outputFile.delete();}}// org.apache.tomcat.util.http.fileupload.disk.DiskFileItem#getStoreLocation/*** Returns the {@link java.io.File} object for the <code>FileItem</code>'s* data's temporary location on the disk. Note that for* <code>FileItem</code>s that have their data stored in memory,* this method will return <code>null</code>. When handling large* files, you can use {@link java.io.File#renameTo(java.io.File)} to* move the file to new location without copying the data, if the* source and destination locations reside within the same logical* volume.** @return The data file, or <code>null</code> if the data is stored in* memory.*/public File getStoreLocation() {if (dfos == null) {return null;}if (isInMemory()) {return null;}return dfos.getFile();}
大概思路就是:1. 判断是否存在文件类型的上传;2. 从request中取出ApplicationPart;3. 遍历每个FileItem, 依次获取文件信息删除;
6. 断点续传
http1.1 中增加了标准准头如:Range: bytes=0-2000 , Content-range: bytes 100-2000 用于请求服务器文件的部分内容,服务端只需按照要求取出相应的数据流返回即可。
这样做的好处是,增大了客户端的控制力。客户端只要在必要的时候记录这个偏移量,在发生网络等故障,恢复后就可以从上次断开的地方进行请求,从而紧接上次未完下载任务,实现断点续传。
我们以http协议作为出发点,讲解了文件上传下载的基本原理,以tomcat的处理过程为样板看了对该协议的实现方式。实际上协议可以有很多,比如各im工具,各下载工具,一般都会有自己的一套传输协议。不能说一样吧,但大方向应该是相通的。

腾讯、阿里、滴滴后台面试题汇总总结 — (含答案)
面试:史上最全多线程面试题 !
最新阿里内推Java后端面试题
JVM难学?那是因为你没认真看完这篇文章

关注作者微信公众号 —《JAVA烂猪皮》
了解更多java后端架构知识以及最新面试宝典

看完本文记得给作者点赞+在看哦~~~大家的支持,是作者源源不断出文的动力
作者:等你归去来
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/yougewe/p/12916211.html
