Android实现三角形兼梯形布局
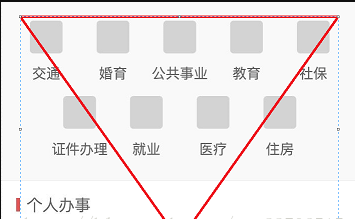
在最近的项目开发中遇到了这种UI:

传统的办法就是通过两个线性布局进行计算,但是第二行每个item的宽度是根据第一行计算出来的,而第一行每个Item的宽度又得根据屏幕宽度来计算。且第二行还有一个偏移量需要计算。如果有多行这种梯形布局。比如键盘。又该怎么处理呢。

于是我想能不能有一种梯形布局来实现这种递减的效果。实现自动布局,我们只需要将View放置在其中就可以了。但是应该叫什么名字,最后发现其实这种布局最终的效果就是一个三角形。只是这个三角形不完整。于是我给我的Layout起名为——TriangleLayout
效果
先看效果,如果觉得效果好,你可以继续看怎么实现,否则就没必要浪费时间了,不是吗。
1.自动计算三角形高度
只需要添加view即可,TriangleLayout会自动计算高度并拼出一个三角形
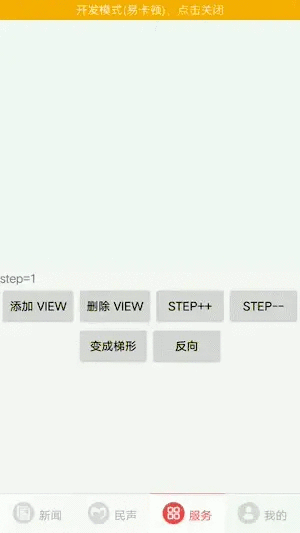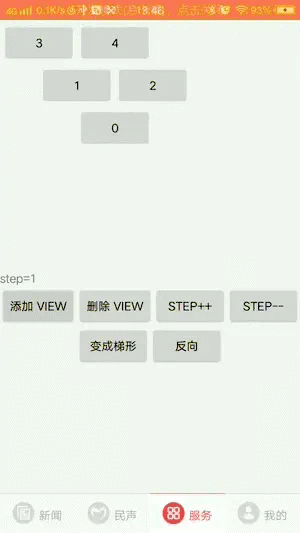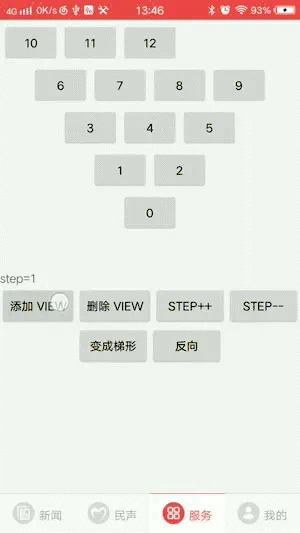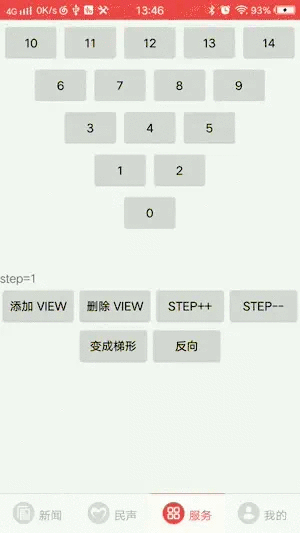
2.支持正三角和倒三角转换

3.支持梯形布局
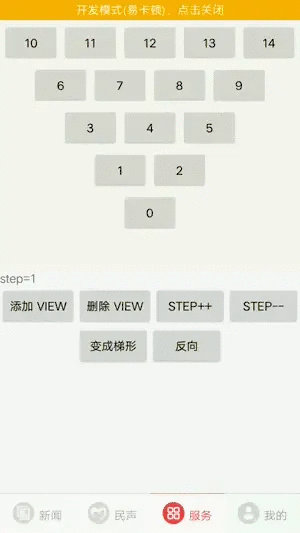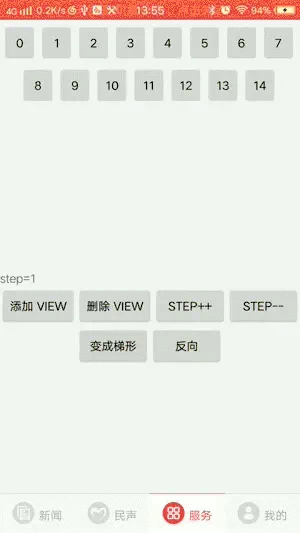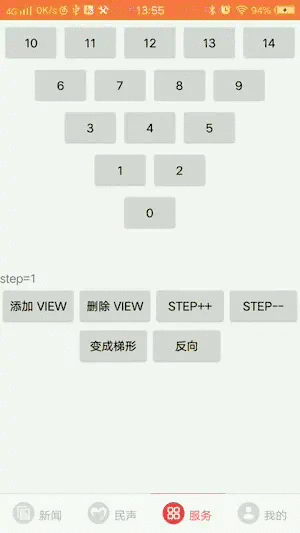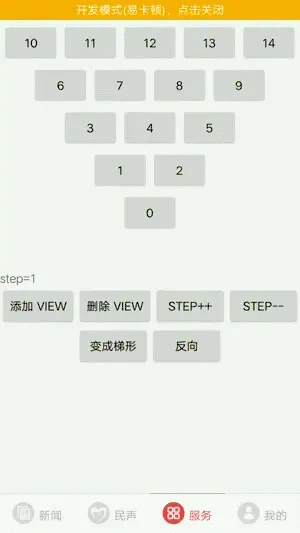
4.支持三角形的形状改变
step表示相邻两行item个数的差值,如果step越小则三角形会越陡。

5.支持大小不同的子View
其中心点在一个三角形上。
6.支持自动计算Padding
如果设置了TriangleLayout的高度和宽度,则TriangleLayout会根据最宽那个Item的宽度作为Item的平均值,然后自动计算padding。同样也可以指定padding,然后设置TriangleLayout为wrap_content则自适应宽度。比如你想让你的TriangleLayout显示一行最多5个,Padding自动则可以如下设置:
<com.trs.cqjb.gov.view.TriangleLayoutandroid:id="@+id/triangleLayout"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="300dp"app:rl_item_height_padding="auto_padding"app:rl_item_width_padding="auto_padding"app:rl_max_line_item_size="5"app:rl_step="1"app:rl_style="rl_style_un_regular_triangle" />
实现
TriangleLayout继承自ViewGroup所以我会按照:测量,布局。来说明。
测量宽高
我们可以发现TriangleLayout的宽度和最大行item的个数与item水平方向之间的Padding有关。
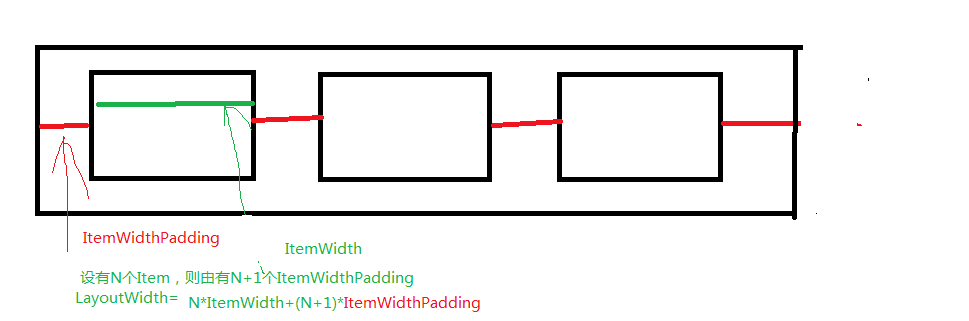
而TriangleLayout的高度和行数与item竖直方向的Padding有关。如图:
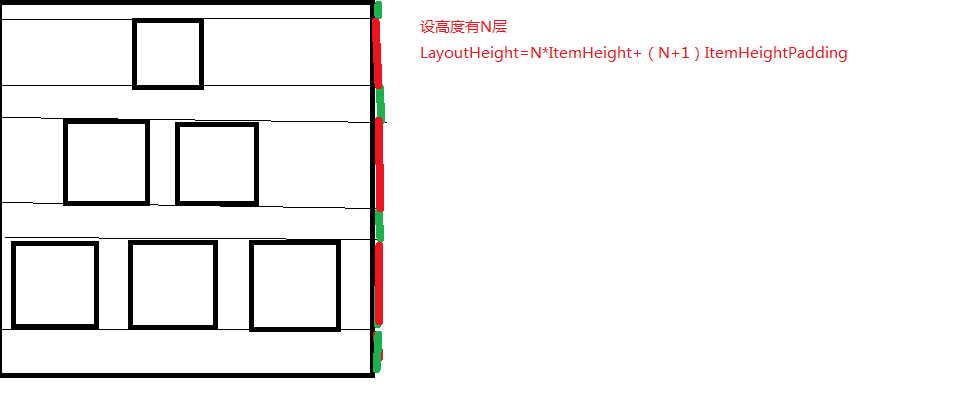
因此要测量TriangleLayout的宽高,则必须先知道三角形的高度和最后一层Item的数量。
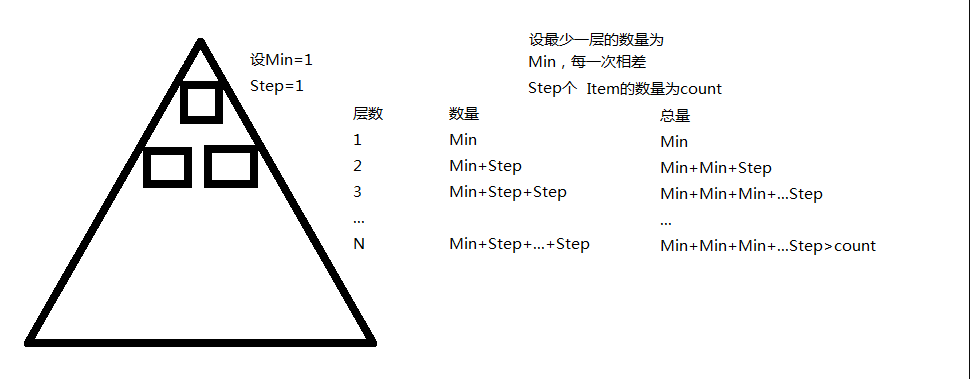
求三角形的高度和最后一层Item的数量。
一共有两种计算方法,从少到多与从多到少,其核心思想是从最初行开始计算,加上或减去Step形成新的一行。累加新行的个数,如果总数还是小于实际的总数则继续形成新行。
如图,从小到大的示意图
实际代码,就是一个While循环:
需要注意的是如果指定了最大行的数量,则会从大大小开始计算三角形的高度,这也是梯形布局的原理,即一个不完整的三角形而已。
/*** 计算一共有多少行*/private void calculateLineSize() {int count = getChildCount();mLines.clear();if (count == 0) {mLineSize = 0;return;} else {//标识是否从多到少进行计算boolean MaxToMin = false;if (mWantMaxLineItemSize != AUTO_MAX) {MaxToMin = true;mRealMaxLineItemSize = mWantMaxLineItemSize;}int lineNumber = MaxToMin ? mWantMaxLineItemSize : mMinLineNumber;//当前行的个数int sum = lineNumber;//所以行的个数int lineSize = 1;LineInfo firstLine = new LineInfo();firstLine.lineNumber = 1;firstLine.begin = 0;firstLine.end = lineNumber - 1;mLines.add(firstLine);while (sum < count) {LineInfo lineInfo = new LineInfo();if (MaxToMin) {lineNumber -= mStep;} else {lineNumber += mStep;}lineInfo.begin = sum;sum += lineNumber;lineInfo.end = sum - 1;lineSize++;lineInfo.lineNumber = lineSize;mLines.add(lineInfo);}mLineSize = lineSize;if (!MaxToMin) {//保存实际的最大大小mRealMaxLineItemSize = lineNumber;//因为draw相关的函数是在MaxToMin模式下完成的//所以在MinToMax的时候需要将行号倒置for (int i = 1; i <= mLineSize; i++) {mLines.get(mLines.size() - i).lineNumber = i;}}//对最后一行的结束位置进行调整,因为可能超出边界mLines.get(mLines.size() - 1).end = count - 1;}}
测量宽高
其核心思想是根据父控件传递的测量模式和尺寸,确定子布局的测量尺寸,然后遍历子View获取最大的宽度和高度,作为平均值,根据我们的宽高公式得出TriangleLayout的宽高,需要注意的是如果padding为AutoPadding,则需要先计算出子View的宽度,再用总的宽度减去需要的宽度得到padding。
@Overrideprotected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {//计算一共的行数calculateLineSize();if (getChildCount() == 0) {super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);return;}int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);int childWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec;int childHeightMeasureSpec = heightMeasureSpec;if (widthMode != MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED) {//计算一个item最大可能的宽度int itemMaxIdealWidth = 0;if (autoWidthPadding) {//先不考虑padding,后面计算itemMaxIdealWidth = widthSize / mRealMaxLineItemSize;} else {itemMaxIdealWidth = (widthSize - (mRealMaxLineItemSize + 1) * mItemWidthPadding) / mRealMaxLineItemSize;}childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(itemMaxIdealWidth, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);}if (heightMode != MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED) {//计算一个item最大可能的高度度int itemMaxIdealHeight = 0;if (autoHeightPadding) {//先不考虑padding,后面计算itemMaxIdealHeight = heightSize / mLineSize;} else {itemMaxIdealHeight = (heightSize - (mLineSize + 1) * mItemHeightPadding) / mLineSize;}childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(itemMaxIdealHeight, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);}int realChildMaxWidth = 0;int realChildMaxHeight = 0;//遍历子View获取实际的最大宽高for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {getChildAt(i).measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);int childWidth = getChildAt(i).getMeasuredWidth();int childHeight = getChildAt(i).getMeasuredHeight();if (childWidth > realChildMaxWidth) {realChildMaxWidth = childWidth;}if (childHeight > realChildMaxHeight) {realChildMaxHeight = childHeight;}}mItemWidth = realChildMaxWidth;mItemHeight = realChildMaxHeight;if (autoWidthPadding) {//确定最终的padding;mItemWidthPadding = (widthSize - mRealMaxLineItemSize * mItemWidth) / (mRealMaxLineItemSize + 1);}if (autoHeightPadding) {mItemHeightPadding = (heightSize - mLineSize * mItemHeight) / (mLineSize + 1);}//根据最大值设置Layout的宽高int mWidth = mRealMaxLineItemSize * mItemWidth + (mRealMaxLineItemSize + 1) * mItemWidthPadding;int mHeight = mLineSize * (mItemHeight + mItemHeightPadding) + mItemHeightPadding;setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, mHeight);}
布局
在计算宽高的时候使用了一个内部类保存每一行的信息,在布局的时候只需要遍历这个类的集合就可以了。其相关的计算公式如下:
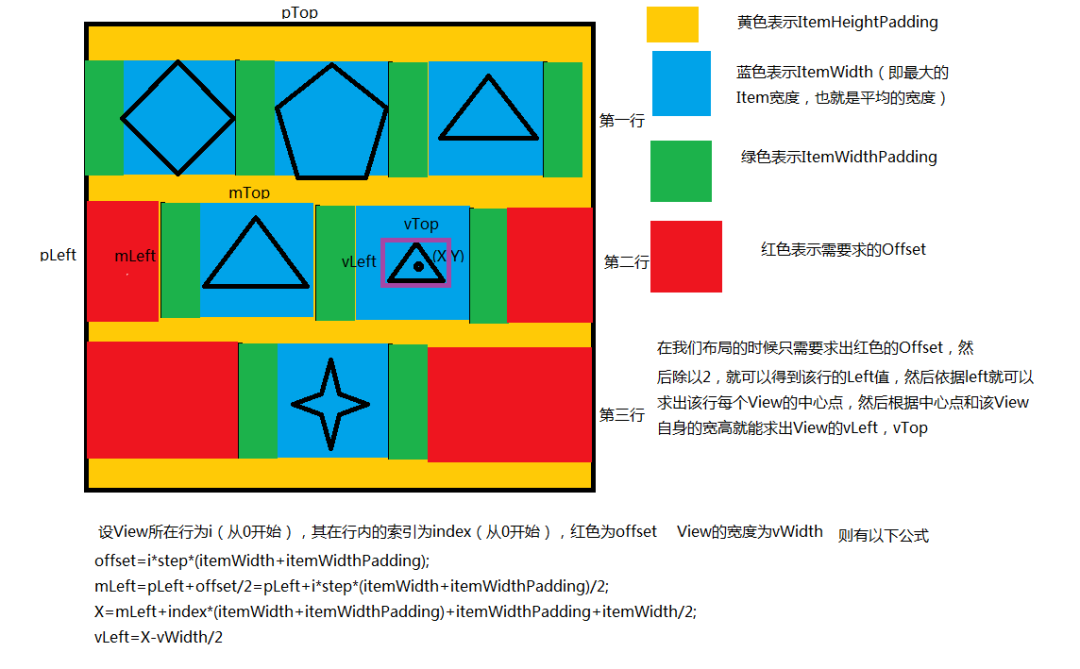
代码如下:
@Overrideprotected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {if (isRegularTriangle) {layoutDownToTop(l, t, r, b);} else {layoutTopToDown(l, t, r, b);}}/*** 自上而下的布局** @param l* @param t* @param r* @param b*/private void layoutTopToDown(int l, int t, int r, int b) {for (LineInfo info : mLines) {info.layoutChildTopToDown(l, t, r, b);}}private void layoutDownToTop(int l, int t, int r, int b) {for (LineInfo info : mLines) {info.layoutChildDownToTop(l, t, r, b);}}/*** 保存每一行的信息*/private class LineInfo {//所在行数 从1开始int lineNumber;//负责布局的孩子在child中的索引,前后闭区间[begin,end]int begin = -1, end = -1;public void layoutChildTopToDown(int l, int t, int r, int b) {//当前行的left偏移量int mLeft = l + mItemWidthPadding + (lineNumber - 1) * (mItemWidth + mItemWidthPadding) * mStep / 2;//当前行top的偏移量int mTop = t + (lineNumber - 1) * (mItemHeightPadding + mItemHeight) + mItemHeightPadding;if (begin < 0 || end < 0) {return;}int index = 0;for (int i = begin; i <= end; i++) {View view = getChildAt(i);int height = view.getMeasuredHeight();int width = view.getMeasuredWidth();//计算中心点根据中心点确定left;int middleWidth = mLeft + index * (mItemWidthPadding + mItemWidth) + mItemWidth / 2;int middleHeight = mTop + mItemHeight / 2;int cLeft = middleWidth - width / 2;int cTop = middleHeight - height / 2;int cRight = cLeft + width;int cDown = cTop + height;view.layout(cLeft, cTop, cRight, cDown);index++;}}public void layoutChildDownToTop(int l, int t, int r, int b) {int mLeft = l + mItemWidthPadding + (lineNumber - 1) * ((mItemWidth + mItemWidthPadding) * mStep / 2);int mTop = t + (mLineSize - lineNumber) * (mItemHeightPadding + mItemHeight) + mItemHeightPadding;if (begin < 0 || end < 0) {return;}int index = 0;for (int i = begin; i <= end; i++) {View view = getChildAt(i);int height = view.getMeasuredHeight();int width = view.getMeasuredWidth();//计算中间点根据中间点确定left;int middleWidth = mLeft + index * (mItemWidthPadding + mItemWidth) + mItemWidth / 2;int middleHeight = mTop + mItemHeight / 2;int cLeft = middleWidth - width / 2;int cTop = middleHeight - height / 2;int cRight = cLeft + width;int cDown = cTop + height;view.layout(cLeft, cTop, cRight, cDown);index++;}}}
自定义属性
最重要的是rl_max_line_item_size,如果设置了的话三角形的最大边将会固定,因此可以形成一个不完整的三角形也就是一个矩形比如这种布局只需要将rl_max_line_item_size设置为10,rl_style设置为rl_style_un_regular_triangle也就是倒三角,然后填充指定的数量即可。
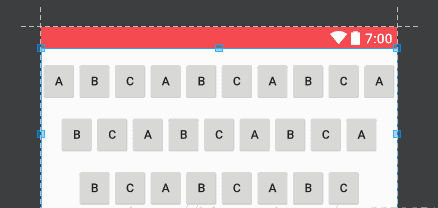
属性如下:
<declare-styleable name="TriangleLayout"><!--一行最多item的个数,如果设置了的话则优先满足最大边,否则设置为auto自动计算成一个三角形--><attr name="rl_max_line_item_size" format="integer|enum"><enum name="auto" value="-1" /></attr><!--每一行相差的数量--><attr name="rl_step" format="integer" /><!--item水平方向的padding--><attr name="rl_item_width_padding" format="dimension|enum|reference"><enum name="auto_padding" value="-1" /></attr><!--item竖直方向的padding--><attr name="rl_item_height_padding" format="dimension|enum|reference"><enum name="auto_padding" value="-1" /></attr><!--显示样式 正三角或--><attr name="rl_style" format="enum"><enum name="rl_style_regular_triangle" value="0" /><enum name="rl_style_un_regular_triangle" value="1" /></attr></declare-styleable>
读取多种类型的属性值,例如声明rl_item_width_padding时,其可能的值有三种,但是如果在不知道类型的情况下就去读取的话,会引起崩溃,于是我开始阅读TypedArray的源码,在其中看到了这个。
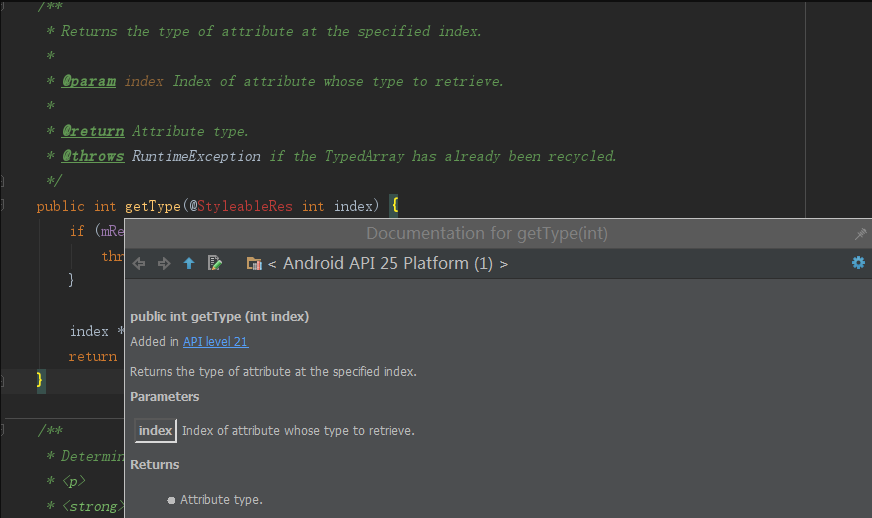
不过这是API21才添加的,为了系统的兼容性,我又找到了这个。
利用这个函数,实现了读取多种类型属性的功能
TypedArray array = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.TriangleLayout);TypedValue widthPaddingValue = array.peekValue(R.styleable.TriangleLayout_rl_item_width_padding);if (widthPaddingValue != null) {if (widthPaddingValue.type == TypedValue.TYPE_DIMENSION) {mItemWidthPadding = array.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.TriangleLayout_rl_item_width_padding, 0);if (mItemWidthPadding < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("ItemWidthPadding must be a positive number");}autoWidthPadding = false;} else {autoWidthPadding = true;mItemWidthPadding = 0;}}
源码地址:
https://github.com/zhuguohui/TrigangleLayoutDemo
到这里就结束啦.
