Redis(十二):请求转发的实现
请求转发一般的原因为:1. 该请求自身无法处理,需要转发给对应的服务器处理;2. 为实现负载均衡,使用路由服务,选择目标实例进行转发;
在集群模式下,请求可以打到任何一台redis服务器上。然而并不是所有的服务器都会处理真正的请求,而是只有符合redis slot规则的实例才会处理真正的请求;
这就存在一个情况,当请求打到了一台不应该打到的redis实例上,它应该是要进行转发的。
那么,这个转发该如何做呢?
1:集群模式下的命令转发如何实现?
// server.c, 在统一处理请求时,会判断出集群模式,进行处理int processCommand(client *c) {.../* If cluster is enabled perform the cluster redirection here.* However we don't perform the redirection if:* 1) The sender of this command is our master.* 2) The command has no key arguments. */// 集群模下,根据 hashslot 找到对应的redis节点处理if (server.cluster_enabled &&!(c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) &&!(c->flags & CLIENT_LUA &&server.lua_caller->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) &&!(c->cmd->getkeys_proc == NULL && c->cmd->firstkey == 0)){int hashslot;if (server.cluster->state != CLUSTER_OK) {flagTransaction(c);clusterRedirectClient(c,NULL,0,CLUSTER_REDIR_DOWN_STATE);return C_OK;} else {int error_code;// 查找相应的redis节点clusterNode *n = getNodeByQuery(c,c->cmd,c->argv,c->argc,&hashslot,&error_code);// 除非是应该自己处理的数据,否则响应数据节点不在此处,让客户端另外查找数据节点// 因此 redis 节点不做数据转发,只是提示客户再寻找// 客户端拿送返回的信息,再向对应的节点发起请求处理if (n == NULL || n != server.cluster->myself) {flagTransaction(c);clusterRedirectClient(c,n,hashslot,error_code);return C_OK;}}}...}// cluster.c, 查找key对应的redis节点/* Return the pointer to the cluster node that is able to serve the command.* For the function to succeed the command should only target either:** 1) A single key (even multiple times like LPOPRPUSH mylist mylist).* 2) Multiple keys in the same hash slot, while the slot is stable (no* resharding in progress).** On success the function returns the node that is able to serve the request.* If the node is not 'myself' a redirection must be perfomed. The kind of* redirection is specified setting the integer passed by reference* 'error_code', which will be set to CLUSTER_REDIR_ASK or* CLUSTER_REDIR_MOVED.** When the node is 'myself' 'error_code' is set to CLUSTER_REDIR_NONE.** If the command fails NULL is returned, and the reason of the failure is* provided via 'error_code', which will be set to:** CLUSTER_REDIR_CROSS_SLOT if the request contains multiple keys that* don't belong to the same hash slot.** CLUSTER_REDIR_UNSTABLE if the request contains multiple keys* belonging to the same slot, but the slot is not stable (in migration or* importing state, likely because a resharding is in progress).** CLUSTER_REDIR_DOWN_UNBOUND if the request addresses a slot which is* not bound to any node. In this case the cluster global state should be* already "down" but it is fragile to rely on the update of the global state,* so we also handle it here. */clusterNode *getNodeByQuery(client *c, struct redisCommand *cmd, robj **argv, int argc, int *hashslot, int *error_code) {clusterNode *n = NULL;robj *firstkey = NULL;int multiple_keys = 0;multiState *ms, _ms;multiCmd mc;int i, slot = 0, migrating_slot = 0, importing_slot = 0, missing_keys = 0;/* Set error code optimistically for the base case. */if (error_code) *error_code = CLUSTER_REDIR_NONE;/* We handle all the cases as if they were EXEC commands, so we have* a common code path for everything */if (cmd->proc == execCommand) {/* If CLIENT_MULTI flag is not set EXEC is just going to return an* error. */if (!(c->flags & CLIENT_MULTI)) return myself;ms = &c->mstate;} else {/* In order to have a single codepath create a fake Multi State* structure if the client is not in MULTI/EXEC state, this way* we have a single codepath below. */ms = &_ms;_ms.commands = &mc;_ms.count = 1;mc.argv = argv;mc.argc = argc;mc.cmd = cmd;}/* Check that all the keys are in the same hash slot, and obtain this* slot and the node associated. */for (i = 0; i < ms->count; i++) {struct redisCommand *mcmd;robj **margv;int margc, *keyindex, numkeys, j;mcmd = ms->commands[i].cmd;margc = ms->commands[i].argc;margv = ms->commands[i].argv;// 获取所有的 keyIndex, 用于后续依次取 keykeyindex = getKeysFromCommand(mcmd,margv,margc,&numkeys);for (j = 0; j < numkeys; j++) {robj *thiskey = margv[keyindex[j]];// 计算hashSlot, crc16 算法int thisslot = keyHashSlot((char*)thiskey->ptr,sdslen(thiskey->ptr));if (firstkey == NULL) {/* This is the first key we see. Check what is the slot* and node. */firstkey = thiskey;slot = thisslot;n = server.cluster->slots[slot];/* Error: If a slot is not served, we are in "cluster down"* state. However the state is yet to be updated, so this was* not trapped earlier in processCommand(). Report the same* error to the client. */if (n == NULL) {getKeysFreeResult(keyindex);if (error_code)*error_code = CLUSTER_REDIR_DOWN_UNBOUND;return NULL;}/* If we are migrating or importing this slot, we need to check* if we have all the keys in the request (the only way we* can safely serve the request, otherwise we return a TRYAGAIN* error). To do so we set the importing/migrating state and* increment a counter for every missing key. */if (n == myself &&server.cluster->migrating_slots_to[slot] != NULL){migrating_slot = 1;} else if (server.cluster->importing_slots_from[slot] != NULL) {importing_slot = 1;}} else {/* If it is not the first key, make sure it is exactly* the same key as the first we saw. */if (!equalStringObjects(firstkey,thiskey)) {if (slot != thisslot) {/* Error: multiple keys from different slots. */getKeysFreeResult(keyindex);if (error_code)*error_code = CLUSTER_REDIR_CROSS_SLOT;return NULL;} else {/* Flag this request as one with multiple different* keys. */multiple_keys = 1;}}}/* Migarting / Improrting slot? Count keys we don't have. */// 查找0号库是否存在该值,没找到则增加未命中率if ((migrating_slot || importing_slot) &&lookupKeyRead(&server.db[0],thiskey) == NULL){missing_keys++;}}getKeysFreeResult(keyindex);}/* No key at all in command? then we can serve the request* without redirections or errors. */if (n == NULL) return myself;/* Return the hashslot by reference. */if (hashslot) *hashslot = slot;/* MIGRATE always works in the context of the local node if the slot* is open (migrating or importing state). We need to be able to freely* move keys among instances in this case. */if ((migrating_slot || importing_slot) && cmd->proc == migrateCommand)return myself;/* If we don't have all the keys and we are migrating the slot, send* an ASK redirection. */if (migrating_slot && missing_keys) {if (error_code) *error_code = CLUSTER_REDIR_ASK;return server.cluster->migrating_slots_to[slot];}/* If we are receiving the slot, and the client correctly flagged the* request as "ASKING", we can serve the request. However if the request* involves multiple keys and we don't have them all, the only option is* to send a TRYAGAIN error. */if (importing_slot &&(c->flags & CLIENT_ASKING || cmd->flags & CMD_ASKING)){if (multiple_keys && missing_keys) {if (error_code) *error_code = CLUSTER_REDIR_UNSTABLE;return NULL;} else {return myself;}}/* Handle the read-only client case reading from a slave: if this* node is a slave and the request is about an hash slot our master* is serving, we can reply without redirection. */if (c->flags & CLIENT_READONLY &&cmd->flags & CMD_READONLY &&nodeIsSlave(myself) &&myself->slaveof == n){return myself;}/* Base case: just return the right node. However if this node is not* myself, set error_code to MOVED since we need to issue a rediretion. */if (n != myself && error_code) *error_code = CLUSTER_REDIR_MOVED;return n;}// cluster.c, 计算hashSlot, 使用 crc16算法// 特殊语法: {key_with_hash}key_without_hash/* We have 16384 hash slots. The hash slot of a given key is obtained* as the least significant 14 bits of the crc16 of the key.** However if the key contains the {...} pattern, only the part between* { and } is hashed. This may be useful in the future to force certain* keys to be in the same node (assuming no resharding is in progress). */unsigned int keyHashSlot(char *key, int keylen) {int s, e; /* start-end indexes of { and } */for (s = 0; s < keylen; s++)if (key[s] == '{') break;/* No '{' ? Hash the whole key. This is the base case. */if (s == keylen) return crc16(key,keylen) & 0x3FFF;/* '{' found? Check if we have the corresponding '}'. */for (e = s+1; e < keylen; e++)if (key[e] == '}') break;/* No '}' or nothing betweeen {} ? Hash the whole key. */if (e == keylen || e == s+1) return crc16(key,keylen) & 0x3FFF;/* If we are here there is both a { and a } on its right. Hash* what is in the middle between { and }. */return crc16(key+s+1,e-s-1) & 0x3FFF;}// 根据状态值,响应客户端,数据节点不在本节点/* Send the client the right redirection code, according to error_code* that should be set to one of CLUSTER_REDIR_* macros.** If CLUSTER_REDIR_ASK or CLUSTER_REDIR_MOVED error codes* are used, then the node 'n' should not be NULL, but should be the* node we want to mention in the redirection. Moreover hashslot should* be set to the hash slot that caused the redirection. */void clusterRedirectClient(client *c, clusterNode *n, int hashslot, int error_code) {if (error_code == CLUSTER_REDIR_CROSS_SLOT) {addReplySds(c,sdsnew("-CROSSSLOT Keys in request don't hash to the same slot\r\n"));} else if (error_code == CLUSTER_REDIR_UNSTABLE) {/* The request spawns mutliple keys in the same slot,* but the slot is not "stable" currently as there is* a migration or import in progress. */addReplySds(c,sdsnew("-TRYAGAIN Multiple keys request during rehashing of slot\r\n"));} else if (error_code == CLUSTER_REDIR_DOWN_STATE) {addReplySds(c,sdsnew("-CLUSTERDOWN The cluster is down\r\n"));} else if (error_code == CLUSTER_REDIR_DOWN_UNBOUND) {addReplySds(c,sdsnew("-CLUSTERDOWN Hash slot not served\r\n"));} else if (error_code == CLUSTER_REDIR_MOVED ||error_code == CLUSTER_REDIR_ASK){// 当对应的数据节点不是自身,而且已经找到了应当处理的节点时,响应客户端对应信息// ASK错误说明数据正在迁移,不知道何时迁移完成,因此重定向是临时的,不应刷新slot缓存// MOVED错误重定向则是(相对)永久的,应刷新slot缓存addReplySds(c,sdscatprintf(sdsempty(),"-%s %d %s:%d\r\n",(error_code == CLUSTER_REDIR_ASK) ? "ASK" : "MOVED",hashslot,n->ip,n->port));} else {serverPanic("getNodeByQuery() unknown error.");}}
所以,redis集群模式下的请求转发,并非redis服务端直接转发请求,而是通过向客户端响应 转移指令,由客户端重新发起目标请求,从而实现命令转发的。
其实,redis做响应转移的处理,应只会发生在redis节点发生变更的时候,比如增加节点或减少节点时,redis为实现数据再均衡,才会出现。正常情况下,具体哪个数据应该请求向哪个redis节点,则完全由客户端负责。这也是集群的优势所在,各个数据节点只处理对应的范围数据。因此,需要客户端将服务端的slot存放规则或者位置缓存起来(通过 cluster slots 可以获取槽存放信息),从而实现向正确的节点请求操作。
2. 主从模式的命令转发如何实现?
主从模式下,只有主节点可以写请求,而从节点则负责同步主节点的数据即可。然而,在我们做读写分离的时候,从节点是可以承受读流量的。但是,如果写流程打到了从节点上,这是否又涉及到一个请求转发呢?我们来看一下:
// 主从的命令处理判断,也是在 processCommand 中统一处理的int processCommand(client *c) {.../* Don't accept write commands if this is a read only slave. But* accept write commands if this is our master. */// 针对从节点,只能接受读请求,如果是写请求,直接响应if (server.masterhost && server.repl_slave_ro &&// master 请求除外,因为master过来的请求,是用于同步数据的!(c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) &&c->cmd->flags & CMD_WRITE){// -READONLY You can't write against a read only slave.addReply(c, shared.roslaveerr);return C_OK;}...return C_OK;}
所以,redis主从模式下,服务端并不做转发处理。而要实现读写分离的功能,必然要客户端自行处理了。比如要自行定位master节点,然后将写请求发送过去,读请求则可以做负载均衡处理。这也是很多数据库中间件的职责所在。
3. 如何使用redis集群?
redis集群,本质上提供了数据的分片存储能力(当然要实现这个功能有相当多的工作要做),但是访问数据需要客户端自行处理。所以,我们以jedis作为客户端,看看客户端都是如何利用集群的吧!测试用例如下:
@Testpublic void testCluster() throws Exception {// 添加集群的服务节点Set集合Set<HostAndPort> hostAndPortsSet = new HashSet<HostAndPort>();// 添加节点hostAndPortsSet.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.1.103", 7000));hostAndPortsSet.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.1.103", 7001));hostAndPortsSet.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.1.103", 8000));hostAndPortsSet.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.1.103", 8001));hostAndPortsSet.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.1.103", 9000));hostAndPortsSet.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.1.103", 9001));// Jedis连接池配置JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig();// 最大空闲连接数, 默认8个jedisPoolConfig.setMaxIdle(5);// 最大连接数, 默认8个jedisPoolConfig.setMaxTotal(10);//最小空闲连接数, 默认0jedisPoolConfig.setMinIdle(0);// 获取连接时的最大等待毫秒数(如果设置为阻塞时BlockWhenExhausted),如果超时就抛异常, 小于零:阻塞不确定的时间, 默认-1jedisPoolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(2000);//对拿到的connection进行validateObject校验jedisPoolConfig.setTestOnBorrow(true);// JedisCluster 会继承 JedisSlotBasedConnectionHandler, 即会处理 slot 定位问题JedisCluster jedis = new JedisCluster(hostAndPortsSet, jedisPoolConfig);String key = "key1";String value = "Value1";jedis.set(key, value);System.out.println("set a value to Redis over. " + key + "->" + value);value = jedis.get("key1");System.out.println("get a value from Redis over. " + key + "->" + value);jedis.close();}
如上,就是jedis访问redis集群的方式了,sdk封装之后的应用,总是简单易用。主要就是通过 JedisCluster 进行访问即可。而与单机的redis访问的很大不同点,是在于数据key的定位上,我们可以详细看看。
如下是 JedisCluster 的类继承图:
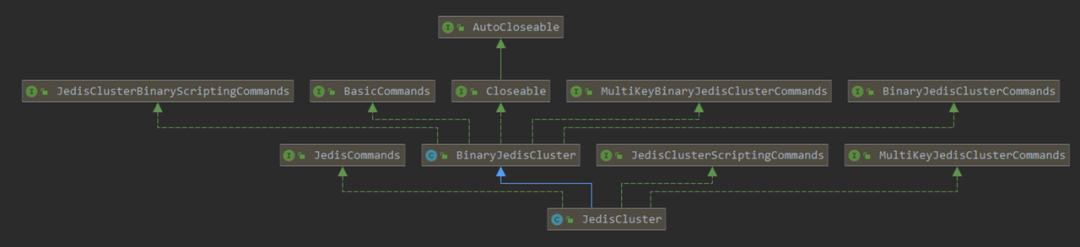
与之对比的是 Jedis 的类继承图:
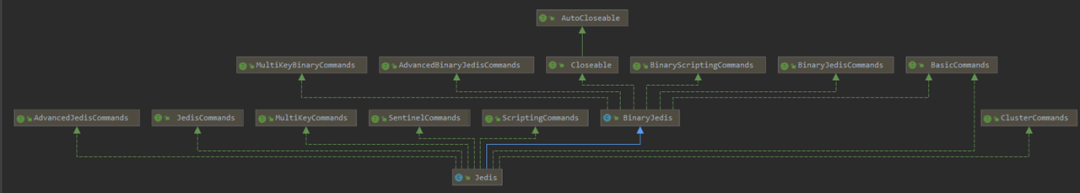
它们两个都实现的接口有: BasicCommands, Closeable, JedisCommands.
可见,cluster下的redis操作上,与普通的redis还是有许多不同的。不过,我们只想探讨的是,key如何定位的问题,所以一个set/get就够了。
// JedisCluster 初始化时会初始化 slot 信息到本地缓存中// redis.clients.jedis.JedisClusterConnectionHandler#JedisClusterConnectionHandlerpublic JedisClusterConnectionHandler(Set<HostAndPort> nodes,final GenericObjectPoolConfig poolConfig, int connectionTimeout, int soTimeout, String password) {this.cache = new JedisClusterInfoCache(poolConfig, connectionTimeout, soTimeout, password);// 在初始化 JedisCluster 时,会先触发一次 slot 信息的拉取,以备后续使用initializeSlotsCache(nodes, poolConfig, password);}private void initializeSlotsCache(Set<HostAndPort> startNodes, GenericObjectPoolConfig poolConfig, String password) {for (HostAndPort hostAndPort : startNodes) {Jedis jedis = new Jedis(hostAndPort.getHost(), hostAndPort.getPort());if (password != null) {jedis.auth(password);}try {// 只要某个节点成功响应,就够了// 遍历的目的,是为了高可用保证,为了避免某些节点故障而拿不到信息cache.discoverClusterNodesAndSlots(jedis);break;} catch (JedisConnectionException e) {// try next nodes} finally {if (jedis != null) {jedis.close();}}}}// set 的操作,则是使用 JedisClusterCommand 包装了一层 Jedis// redis.clients.jedis.JedisCluster#set(java.lang.String, java.lang.String)@Overridepublic String set(final String key, final String value) {// connectionHandler 是 JedisSlotBasedConnectionHandler 的实例// 默认重试次数: 5return new JedisClusterCommand<String>(connectionHandler, maxAttempts) {@Overridepublic String execute(Jedis connection) {return connection.set(key, value);}}.run(key);}// redis.clients.jedis.JedisClusterCommand#run(java.lang.String)public T run(String key) {if (key == null) {throw new JedisClusterException("No way to dispatch this command to Redis Cluster.");}return runWithRetries(SafeEncoder.encode(key), this.maxAttempts, false, false);}// 带重试的访问 redis 节点, 重试的场景有:数据节点不在访问节点; 访问的节点正在进行数据迁移; 访问节点不可用;// redis.clients.jedis.JedisClusterCommand#runWithRetriesprivate T runWithRetries(byte[] key, int attempts, boolean tryRandomNode, boolean asking) {if (attempts <= 0) {throw new JedisClusterMaxRedirectionsException("Too many Cluster redirections?");}Jedis connection = null;try {if (asking) {// TODO: Pipeline asking with the original command to make it// faster....connection = askConnection.get();connection.asking();// if asking success, reset asking flagasking = false;} else {if (tryRandomNode) {connection = connectionHandler.getConnection();} else {// 直接调用 connectionHandler.getConnectionFromSlot 获取对应的redis连接// 此处计算的 slot 就是redis服务端实现的那套 crc16 % 0x3FFF, 即各端保持一致,就可以做出相同的判定了connection = connectionHandler.getConnectionFromSlot(JedisClusterCRC16.getSlot(key));}}return execute(connection);} catch (JedisNoReachableClusterNodeException jnrcne) {throw jnrcne;} catch (JedisConnectionException jce) {// release current connection before recursionreleaseConnection(connection);connection = null;if (attempts <= 1) {//We need this because if node is not reachable anymore - we need to finally initiate slots renewing,//or we can stuck with cluster state without one node in opposite case.//But now if maxAttempts = 1 or 2 we will do it too often. For each time-outed request.//TODO make tracking of successful/unsuccessful operations for node - do renewing only//if there were no successful responses from this node last few secondsthis.connectionHandler.renewSlotCache();//no more redirections left, throw original exception, not JedisClusterMaxRedirectionsException, because it's not MOVED situationthrow jce;}// 连接异常,再次请求随机节点return runWithRetries(key, attempts - 1, tryRandomNode, asking);} catch (JedisRedirectionException jre) {// if MOVED redirection occurred,if (jre instanceof JedisMovedDataException) {// it rebuilds cluster's slot cache// recommended by Redis cluster specificationthis.connectionHandler.renewSlotCache(connection);}// release current connection before recursion or renewingreleaseConnection(connection);connection = null;if (jre instanceof JedisAskDataException) {asking = true;askConnection.set(this.connectionHandler.getConnectionFromNode(jre.getTargetNode()));} else if (jre instanceof JedisMovedDataException) {} else {throw new JedisClusterException(jre);}// 收到 MOVED/ASK 响应,刷新slot信息后,重新再访问return runWithRetries(key, attempts - 1, false, asking);} finally {releaseConnection(connection);}}// 计算hashSlot值// redis.clients.util.JedisClusterCRC16#getSlot(byte[])public static int getSlot(byte[] key) {int s = -1;int e = -1;boolean sFound = false;for (int i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {if (key[i] == '{' && !sFound) {s = i;sFound = true;}if (key[i] == '}' && sFound) {e = i;break;}}if (s > -1 && e > -1 && e != s + 1) {return getCRC16(key, s + 1, e) & (16384 - 1);}return getCRC16(key) & (16384 - 1);}// 根据hashSlot, 得到对应的 redis 连接实例@Overridepublic Jedis getConnectionFromSlot(int slot) {// 先从缓存中获取slot对应的连接信息,初始时自然是空的JedisPool connectionPool = cache.getSlotPool(slot);if (connectionPool != null) {// It can't guaranteed to get valid connection because of node// assignmentreturn connectionPool.getResource();} else {// 刷新slot缓存信息,大概就是请求 cluster slot, 获取slot的分布信息,然后存入JedisClusterInfoCache中renewSlotCache(); //It's abnormal situation for cluster mode, that we have just nothing for slot, try to rediscover stateconnectionPool = cache.getSlotPool(slot);// 如果还是获取不到,则随机选择一个连接// 此时请求该随机节点,服务端有可能会响应正确的节点位置信息if (connectionPool != null) {return connectionPool.getResource();} else {//no choice, fallback to new connection to random nodereturn getConnection();}}}// redis.clients.jedis.JedisClusterConnectionHandler#renewSlotCache()public void renewSlotCache() {cache.renewClusterSlots(null);}// redis.clients.jedis.JedisClusterInfoCache#renewClusterSlotspublic void renewClusterSlots(Jedis jedis) {//If rediscovering is already in process - no need to start one more same rediscovering, just returnif (!rediscovering) {try {w.lock();rediscovering = true;if (jedis != null) {try {discoverClusterSlots(jedis);return;} catch (JedisException e) {//try nodes from all pools}}// 依次遍历集群节点,直到有一个正确的响应为止for (JedisPool jp : getShuffledNodesPool()) {try {jedis = jp.getResource();discoverClusterSlots(jedis);return;} catch (JedisConnectionException e) {// try next nodes} finally {if (jedis != null) {jedis.close();}}}} finally {rediscovering = false;w.unlock();}}}private void discoverClusterSlots(Jedis jedis) {// 发送 cluster slots, 命令,获取 slot 分布信息List<Object> slots = jedis.clusterSlots();this.slots.clear();for (Object slotInfoObj : slots) {List<Object> slotInfo = (List<Object>) slotInfoObj;/* Format: 1) 1) start slot* 2) end slot* 3) 1) master IP* 2) master port* 3) node ID* 4) 1) replica IP* 2) replica port* 3) node ID* ... continued until done*/if (slotInfo.size() <= MASTER_NODE_INDEX) {continue;}List<Integer> slotNums = getAssignedSlotArray(slotInfo);// hostInfos// 第三个元素是 master 信息List<Object> hostInfos = (List<Object>) slotInfo.get(MASTER_NODE_INDEX);if (hostInfos.isEmpty()) {continue;}// at this time, we just use master, discard slave informationHostAndPort targetNode = generateHostAndPort(hostInfos);// 只存储master信息assignSlotsToNode(slotNums, targetNode);}}private List<Integer> getAssignedSlotArray(List<Object> slotInfo) {List<Integer> slotNums = new ArrayList<Integer>();// 依次将所管辖slot范围,添加到列表中// 如 0 ~ 5999for (int slot = ((Long) slotInfo.get(0)).intValue(); slot <= ((Long) slotInfo.get(1)).intValue(); slot++) {slotNums.add(slot);}return slotNums;}// 将所有给定的 slot, 放到 targetNode 的管辖范围,方便后续获取// redis.clients.jedis.JedisClusterInfoCache#assignSlotsToNodepublic void assignSlotsToNode(List<Integer> targetSlots, HostAndPort targetNode) {// 此处的锁为读写锁 ReentrantReadWriteLock 中的 writeLockw.lock();try {// 创建redis连接JedisPool targetPool = setupNodeIfNotExist(targetNode);// 依次将范围内的slot指向 targetNode// 正常情况下,slots的大小应该都是16384for (Integer slot : targetSlots) {// slots = new HashMap<Integer, JedisPool>();slots.put(slot, targetPool);}} finally {w.unlock();}}// redis.clients.jedis.JedisClusterInfoCache#setupNodeIfNotExist(redis.clients.jedis.HostAndPort)public JedisPool setupNodeIfNotExist(HostAndPort node) {w.lock();try {String nodeKey = getNodeKey(node);JedisPool existingPool = nodes.get(nodeKey);if (existingPool != null) return existingPool;JedisPool nodePool = new JedisPool(poolConfig, node.getHost(), node.getPort(),connectionTimeout, soTimeout, password, 0, null, false, null, null, null);nodes.put(nodeKey, nodePool);return nodePool;} finally {w.unlock();}}// 刷新slot缓存信息后,再重新请求获取redis连接就简单了// redis.clients.jedis.JedisClusterInfoCache#getSlotPoolpublic JedisPool getSlotPool(int slot) {r.lock();try {return slots.get(slot);} finally {r.unlock();}}
从上面的描述,我们清楚了整个客户如何处理集群请求的。整体就两个步骤:1. 通过 cluster slot 获取redis集群的slot分布信息,然后缓存到本地;2. 根据slot分布信息,向对应的redis节点发起请求即可。
另外,还有些意外情况,即客户端拿到的 slot 信息如果是错误的怎么办?如何保持客户端缓存与服务端的一致性?
事实上,客户端既不保证slot信息的准确性,也不保证与服务端数据的一致性,而是在发生错误的时候,再进行刷新即可。通过 JedisClusterCommand#runWithRetries, 进行错误重试,slot数据刷新。
4. 通常的请求转发如何实现?
可以看到,redis实际上一直避开了转发这个问题。
那么,实际中,我们的转发工作都是如何实现的呢?
最简单的,接收到客户端的请求之后,将数据重新封装好,然后构建一个目标地址的新请求,发送过去,然后等待结果响应。当目标服务器响应后,再将结果响应给客户端即可。如:应用网关、代理服务器;
其次,是响应客户端一个状态码(如302),让客户端自主进行跳转。这和redis实现倒是如出一辙;
相对复杂的,直接使用流进行对接,接收到客户端的请求后,直接将数据传到目标服务器,同样,目标服务器响应后,直接将数据写入客户端通道即可。这种情况避免大量数据的重新封装,极大减少了转发带来的性能损失,从而提高响应速度。这种场景,一般用于传输大文件。

腾讯、阿里、滴滴后台面试题汇总总结 — (含答案)
面试:史上最全多线程面试题 !
最新阿里内推Java后端面试题
JVM难学?那是因为你没认真看完这篇文章

关注作者微信公众号 —《JAVA烂猪皮》
了解更多java后端架构知识以及最新面试宝典

看完本文记得给作者点赞+在看哦~~~大家的支持,是作者源源不断出文的动力
作者:等你归去来
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/yougewe/p/12546817.html
