从零搭建Pytorch模型教程 | 搭建Transformer网络
点击下方“AI算法与图像处理”,一起进步!
重磅干货,第一时间送达
前言 本文介绍了Transformer的基本流程,分块的两种实现方式,Position Emebdding的几种实现方式,Encoder的实现方式,最后分类的两种方式,以及最重要的数据格式的介绍。
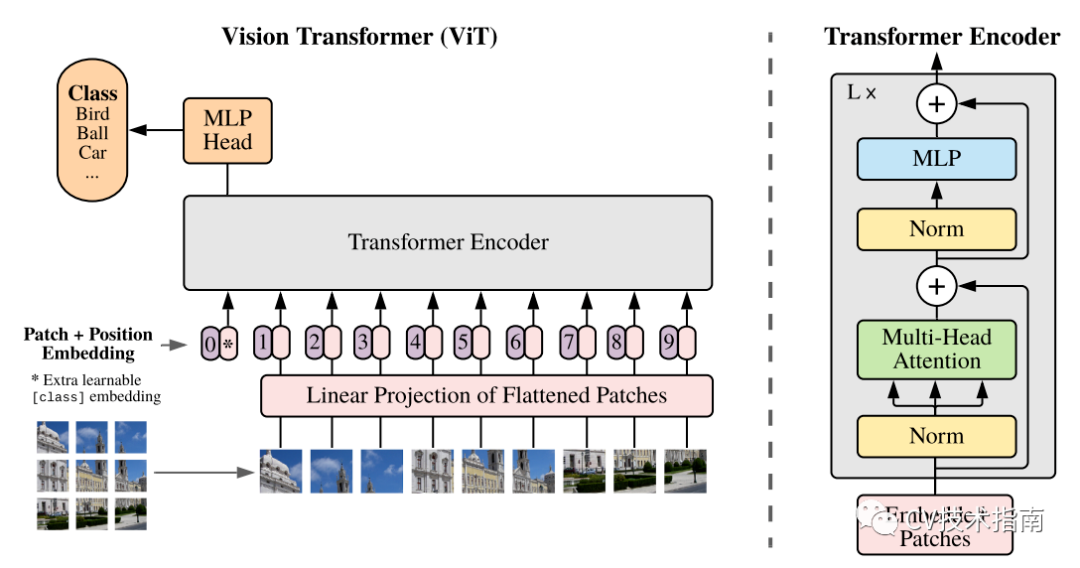
分块
目前有两种方式实现分块,一种是直接分割,一种是通过卷积核和步长都为patch大小的卷积来分割。
直接分割
from einops import rearrange, repeat
from einops.layers.torch import Rearrange
self.to_patch_embedding = nn.Sequential(
Rearrange('b c (h p1) (w p2) -> b (h w) (p1 p2 c)', p1 = patch_height, p2 = patch_width),
nn.Linear(patch_dim, dim),
)
#假设images的shape为[32,200,400,3]
#实现view和reshape的功能
Rearrange(images,'b h w c -> (b h) w c')#shape变为(32*200, 400, 3)
#实现permute的功能
Rearrange(images, 'b h w c -> b c h w')#shape变为(32, 3, 200, 400)
#实现这几个都很难实现的功能
Rearrange(images, 'b h w c -> (b c w) h')#shape变为(32*3*400, 200)
Rearrange('b c (h p1) (w p2) -> b (h w) (p1 p2 c)', p1 = patch_height, p2 = patch_width)
卷积分割
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_chans, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size)
x = self.proj(x).flatten(2).transpose(1, 2) # B Ph*Pw C
Position Embedding
self.pos_embedding = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, num_patches + 1, dim))
x += self.pos_embedding[:, :(n + 1)]
#之所以是n+1,是因为ViT中选择随机初始化一个class token,与分块得到的tokens拼接。所以patches的数量为num_patches+1。
from timm.models.layers import trunc_normal_
self.absolute_pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_patches, embed_dim))
trunc_normal_(self.absolute_pos_embed, std=.02)
self.pos_emb = torch.nn.Embedding(num_positions + 1, dim)
Encoder
Multi-head Self-attention
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, heads = 8, dim_head = 64, dropout = 0.):
super().__init__()
inner_dim = dim_head * heads
project_out = not (heads == 1 and dim_head == dim)
self.heads = heads
self.scale = dim_head ** -0.5
self.attend = nn.Softmax(dim = -1)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.to_qkv = nn.Linear(dim, inner_dim * 3, bias = False)
self.to_out = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(inner_dim, dim),
nn.Dropout(dropout)
) if project_out else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
qkv = self.to_qkv(x).chunk(3, dim = -1)
q, k, v = map(lambda t: rearrange(t, 'b n (h d) -> b h n d', h = self.heads), qkv)
dots = torch.matmul(q, k.transpose(-1, -2)) * self.scale
attn = self.attend(dots)
attn = self.dropout(attn)
out = torch.matmul(attn, v)
out = rearrange(out, 'b h n d -> b n (h d)')
return self.to_out(out)
FeedForward
class FeedForward(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, hidden_dim, dropout = 0.):
super().__init__()
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Dropout(dropout),
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, dim),
nn.Dropout(dropout)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.net(x)
class Transformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, depth, heads, dim_head, mlp_dim, dropout = 0.):
super().__init__()
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([])
for _ in range(depth):
self.layers.append(nn.ModuleList([
PreNorm(dim, Attention(dim, heads = heads, dim_head = dim_head, dropout = dropout)),
PreNorm(dim, FeedForward(dim, mlp_dim, dropout = dropout))
]))
def forward(self, x):
for attn, ff in self.layers:
x = attn(x) + x
x = ff(x) + x
return x
class PreNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, fn):
super().__init__()
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.fn = fn
def forward(self, x, **kwargs):
return self.fn(self.norm(x), **kwargs)
分类方法
#生成cls_token部分
from einops import repeat
self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, 1, dim))
cls_tokens = repeat(self.cls_token, '1 n d -> b n d', b = b)
x = torch.cat((cls_tokens, x), dim=1)
################################
#分类部分
self.mlp_head = nn.Sequential(
nn.LayerNorm(dim),
nn.Linear(dim, num_classes)
)
x = x.mean(dim = 1) if self.pool == 'mean' else x[:, 0]
x = self.to_latent(x)
return self.mlp_head(x)
在swin transformer中,没有选择cls_token。而是直接在经过Encoder后将所有数据取了个平均池化,再通过全连接层。
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool1d(1)
self.head = nn.Linear(self.num_features, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
x = self.avgpool(x.transpose(1, 2)) # B C 1
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.head(x)
组合以上这些就成了一个完整的模型
class ViT(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, *, image_size, patch_size, num_classes, dim, depth, heads, mlp_dim, pool = 'cls', channels = 3, dim_head = 64, dropout = 0., emb_dropout = 0.):
super().__init__()
image_height, image_width = pair(image_size)
patch_height, patch_width = pair(patch_size)
num_patches = (image_height // patch_height) * (image_width // patch_width)
patch_dim = channels * patch_height * patch_width
assert pool in {'cls', 'mean'}, 'pool type must be either cls (cls token) or mean (mean pooling)'
self.to_patch_embedding = nn.Sequential(
Rearrange('b c (h p1) (w p2) -> b (h w) (p1 p2 c)', p1 = patch_height, p2 = patch_width),
nn.Linear(patch_dim, dim),
)
self.pos_embedding = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, num_patches + 1, dim))
self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, 1, dim))
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(emb_dropout)
self.transformer = Transformer(dim, depth, heads, dim_head, mlp_dim, dropout)
self.pool = pool
self.to_latent = nn.Identity()
self.mlp_head = nn.Sequential(
nn.LayerNorm(dim),
nn.Linear(dim, num_classes)
)
def forward(self, img):
x = self.to_patch_embedding(img)
b, n, _ = x.shape
cls_tokens = repeat(self.cls_token, '1 n d -> b n d', b = b)
x = torch.cat((cls_tokens, x), dim=1)
x += self.pos_embedding[:, :(n + 1)]
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.transformer(x)
x = x.mean(dim = 1) if self.pool == 'mean' else x[:, 0]
x = self.to_latent(x)
return self.mlp_head(x)
数据的变换
Rearrange('b c (h p1) (w p2) -> b (h w) (p1 p2 c)', p1 = patch_height, p2 = patch_width)
ViT:https://github.com/lucidrains/vit-pytorch/blob/main/vit_pytorch/vit.py
swin: https://github.com/microsoft/Swin-Transformer/blob/main/models/swin_transformer.py
TimeSformer:https://github.com/lucidrains/TimeSformer-pytorch/blob/main/timesformer_pytorch/timesformer_pytorch.py
交流群
欢迎加入公众号读者群一起和同行交流,目前有美颜、三维视觉、计算摄影、检测、分割、识别、医学影像、GAN、算法竞赛等微信群
个人微信(如果没有备注不拉群!) 请注明:地区+学校/企业+研究方向+昵称
下载1:何恺明顶会分享
在「AI算法与图像处理」公众号后台回复:何恺明,即可下载。总共有6份PDF,涉及 ResNet、Mask RCNN等经典工作的总结分析
下载2:终身受益的编程指南:Google编程风格指南
在「AI算法与图像处理」公众号后台回复:c++,即可下载。历经十年考验,最权威的编程规范!
下载3 CVPR2021 在「AI算法与图像处理」公众号后台回复:CVPR,即可下载1467篇CVPR 2020论文 和 CVPR 2021 最新论文
评论

