【关于 新词发现】那些你不知道的事
作者:杨夕
个人github:https://github.com/km1994/nlp_paper_study
NLP百面百搭:https://github.com/km1994/NLP-Interview-Notes
【注:手机阅读可能图片打不开!!!】
一、动机
网络文档和领域文档文本的特点在于包含大量新词,一般词典的涵盖程度比较低。对于领域文档,各领域的专家可以人工构建知识本体,拓展已有词库的不健全,但是需要消耗大量的人力成本资源。
那么有没有一种有效方法能够发现上述两种文本中的新词呢?
二、 新词发现模块 有哪些阶段?
新词发现模块 主要包含两个阶段:
离线阶段:从海量文本语料中挖掘出高质量的 短语及其属性;
在线阶段:识别给定文本中出现的 短语 供下游模块使用。
三、 新词发现模块 的需求有哪些?
热更新。相比于其他任务,由于网络文档和领域文档的文本更新较快,所以新词发现模块需要持续积累和更新;
及时性。网络文档和领域文档的文本更新后,新词发现需要及时更新 资源库,以满足 任务需求。
四、 新词发现模块 的任务形式是怎么样的?
phrase挖掘
输入:一堆文本语料,输出:语料中出现的phrase;
phrase识别
输入:一段文本(query/title),输出:文本中出现的phrase(需要消歧);
五、什么样的新词才属于高质量的新词?
首先,看一下这个表格:
会发现,新词存在两个特点:
构成形式无规律性。新词构成形式比较开放,并无明显规律可循;
类别多。新词类别较多。
因此,什么样的新词才属于高质量的新词呢?
从上述表格看出,高质量的 新词 需要满足以下条件:
Popularity:候选phrase要有一定的热度;(eg:“信息检索”> “多语种信息检索”)
Concordance:候选phrase的内凝度应该比较高;(eg:“深度学习”> “学习分类器”)
Informative:候选phrase要包含一定的信息量,表示某个特定话题;(eg:“今天早晨”“该文中”虽然频次很高,但不表示特定话题,信息量低)
Completeness:候选phrase相比于父(存在冗余)/子(不可切分)phrase更适合作为phrase;(eg:“幽门螺旋杆菌”>“幽门螺旋”)
六、新词发现算法介绍
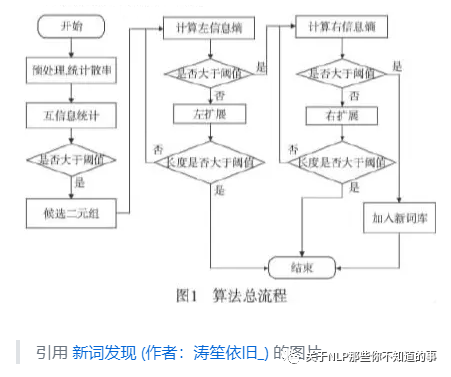
6.1 出现频次
介绍:新词在 段落中出现频率往往比其他词要高,所以当出现频率越高,越有可能是新词。
代码实现:
将 text 进行 n_gram
# 功能:将 text 进行 n_gram
def n_gram_words(self,text):
"""
功能:将 text 进行 n_gram
input:
text : String 输入句子
return:
words_freq:Dict 词频 字典
"""
words = []
for i in range(1,self.n_gram+1):
words += [text[j:j+i] for j in range(len(text)-i+1)]
words_freq = dict(Counter(words))
new_words_freq = {}
for word,freq in words_freq.items():
new_words_freq[word]=freq
return new_words_freq
6.2 点间互信息(Pointwise Mutual Information)
动机:新词一般在文本中出现频率较高,但是出现频率越高的词并代表一定是新词;
eg:“的电影”出现了 389 次,“电影院”只出现了 175 次,然而我们却更倾向于把“电影院”当作一个词,因为直觉上看,“电影”和“院”凝固得更紧一些。
思考:在出现频率较高的候选新词中,我们需要 计算 这些候选新词的凝固程度,因为词的内部凝聚度越高,越容易成词
做法:采用互信息计算方式,衡量知道一个词之后另一个词不确定性的减少程度。
公式:

结论:点间互信息越大,说明这两个词经常出现在一起,意味着两个词的凝固程度越大,其组成一个新词的可能性也就越大。
代码实现:
# 功能:PMI 过滤掉 噪声词
def PMI_filter(self, word_freq_dic):
"""
功能:PMI 过滤掉 噪声词
input:
words_freq:Dict 词频 字典
return:
new_words_dic:Dict PMI 过滤噪声后 剩余新词
"""
new_words_dic = {}
for word in word_freq_dic:
if len(word) == 1:
pass
else:
p_x_y = min([word_freq_dic.get(word[:i])* word_freq_dic.get(word[i:]) for i in range(1,len(word))])
mpi = p_x_y/word_freq_dic.get(word)
if mpi > self.min_p:
new_words_dic[word] = [mpi]
return new_words_dic
6.3 左右熵(Information Entropy)
动机:如果一个n-gram能够算作一个phrase的话,它应该能够灵活地出现在各种不同的环境中,具有非常丰富的左邻字集合和右邻字集合。左右搭配越丰富,越可能独立成词。
eg:“被子”和“辈子”右邻字信息熵分别为3.87和4.11。而“被子”的左邻字搭配却丰富得多,有叠被子、盖被子、抢被子、新被子、掀被子等等。“辈子”的左邻字搭配则非常少,只有这辈子、八辈子、上辈子等。
做法:信息熵是一种衡量信息量大小的方式,熵越大,所含信息量越大,不确定性越高。因此可以分别计算n-gram的左邻字信息熵和右邻字信息熵,并取两者的最小值。
公式:
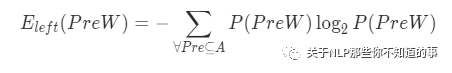
结论:左右熵值越大,说明该词的周边词越丰富,意味着词的自由程度越大,其成为一个独立的词的可能性也就越大。
代码实现:
计算字符列表的熵
# 功能:计算字符列表的熵
def calculate_entropy(self, char_list):
"""
功能:计算字符列表的熵
input:
char_list: List 字符列表
return:
entropy: float 熵
"""
char_freq_dic = dict(Counter(char_list))
entropy = (-1)*sum([ char_freq_dic.get(i)/len(char_list)*np.log2(char_freq_dic.get(i)/len(char_list)) for i in char_freq_dic])
return entropy
通过熵阈值从限定词字典中过滤出最终的新词
# 功能:通过熵阈值从限定词字典中过滤出最终的新词
def Entropy_left_right_filter(self,condinate_words_dic,text):
"""
功能:通过熵阈值从限定词字典中过滤出最终的新词
input:
condinate_words_dic:Dict 限定词字典
text:String 句子
output:
final_words_list:List 最终的新词列表
"""
final_words_list = []
for word in condinate_words_dic.keys():
left_right_char =re.findall('(.)%s(.)'%word,text)
left_char = [i[0] for i in left_right_char]
left_entropy = self.calculate_entropy(left_char)
right_char = [i[1] for i in left_right_char]
right_entropy = self.calculate_entropy(right_char)
score = condinate_words_dic[word][0]-min(left_entropy,right_entropy)
if min(right_entropy,left_entropy)> self.min_entropy and score<self.max_score and score>self.min_score:
final_words_list.append({
"word":word,
"pmi":condinate_words_dic[word][0],
"left_entropy":left_entropy,
"right_entropy":right_entropy,
"score":score
})
final_words_list = sorted(final_words_list, key=lambda x: x['score'], reverse=True)
return final_words_list
七、新词发现代码实现
7.1 导库
from collections import Counter
import numpy as np
import re,os
import glob
import six
import codecs
import math
7.2 函数定义
7.2.1 停用词加载
# 功能:停用词加载
def get_stop_word(stop_word_path):
#停用词列表,默认使用哈工大停用词表
f = open(stop_word_path,encoding='utf-8')
stop_words = list()
for stop_word in f.readlines():
stop_words.append(stop_word[:-1])
return stop_words
7.2.2 语料生成器,并且初步预处理语料
# 语料生成器,并且初步预处理语料
def text_generator(file_path):
txts = glob.glob(f'{file_path}/*.txt')
for txt in txts:
d = codecs.open(txt, encoding='utf-8').read()
title = d.split("\n")[0]
d = d.replace(u'\u3000', '').strip()
yield title,re.sub(u'[^\u4e00-\u9fa50-9a-zA-Z ]+', '', d)
7.3 新词发现类定义
class NewWordFind():
def __init__(self, n_gram=5, min_p=2 , min_entropy=1, max_score=100, min_score=2):
'''
input:
n_gram: int n_gram 的 粒度
min_p: int 最小 信息熵 阈值
min_entropy: int 左右熵 阈值
max_score: int 综合得分最大阈值
min_score: int 综合得分最小阈值
'''
self.n_gram = n_gram
self.min_p = min_p
self.min_entropy = min_entropy
self.max_score = max_score
self.min_score = min_score
# 功能:将 text 进行 n_gram
def n_gram_words(self,text):
"""
功能:将 text 进行 n_gram
input:
text : String 输入句子
return:
words_freq:Dict 词频 字典
"""
words = []
for i in range(1,self.n_gram+1):
words += [text[j:j+i] for j in range(len(text)-i+1)]
words_freq = dict(Counter(words))
new_words_freq = {}
for word,freq in words_freq.items():
new_words_freq[word]=freq
return new_words_freq
# 功能:PMI 过滤掉 噪声词
def PMI_filter(self, word_freq_dic):
"""
功能:PMI 过滤掉 噪声词
input:
words_freq:Dict 词频 字典
return:
new_words_dic:Dict PMI 过滤噪声后 剩余新词
"""
new_words_dic = {}
for word in word_freq_dic:
if len(word) == 1:
pass
else:
p_x_y = min([word_freq_dic.get(word[:i])* word_freq_dic.get(word[i:]) for i in range(1,len(word))])
mpi = p_x_y/word_freq_dic.get(word)
if mpi > self.min_p:
new_words_dic[word] = [mpi]
return new_words_dic
# 功能:计算字符列表的熵
def calculate_entropy(self, char_list):
"""
功能:计算字符列表的熵
input:
char_list: List 字符列表
return:
entropy: float 熵
"""
char_freq_dic = dict(Counter(char_list))
entropy = (-1)*sum([ char_freq_dic.get(i)/len(char_list)*np.log2(char_freq_dic.get(i)/len(char_list)) for i in char_freq_dic])
return entropy
# 功能:通过熵阈值从限定词字典中过滤出最终的新词
def Entropy_left_right_filter(self,condinate_words_dic,text):
"""
功能:通过熵阈值从限定词字典中过滤出最终的新词
input:
condinate_words_dic:Dict 限定词字典
text:String 句子
output:
final_words_list:List 最终的新词列表
"""
final_words_list = []
for word in condinate_words_dic.keys():
left_right_char =re.findall('(.)%s(.)'%word,text)
left_char = [i[0] for i in left_right_char]
left_entropy = self.calculate_entropy(left_char)
right_char = [i[1] for i in left_right_char]
right_entropy = self.calculate_entropy(right_char)
score = condinate_words_dic[word][0]-min(left_entropy,right_entropy)
if min(right_entropy,left_entropy)> self.min_entropy and score<self.max_score and score>self.min_score:
final_words_list.append({
"word":word,
"pmi":condinate_words_dic[word][0],
"left_entropy":left_entropy,
"right_entropy":right_entropy,
"score":score
})
final_words_list = sorted(final_words_list, key=lambda x: x['score'], reverse=True)
return final_words_list
7.4 新词发现类 测试
# read the data and preprocessing the data to a whole str
stop_word= get_stop_word("resource/stopword.txt")
file_path = "data/"
n_gram = 5
min_p = 2
min_entropy = 1
max_score = 100
min_score = 2
new_word_find = NewWordFind( n_gram=n_gram, min_p=min_p , min_entropy=min_entropy, max_score=max_score, min_score=min_score)
for index,(title,text) in enumerate(text_generator(file_path)):
print(f"\n index :{index} => title:{title}")
for i in stop_word:
text=text.replace(i,"")
n_gram = new_word_find.n_gram_words(text)
new_words_dic = new_word_find.PMI_filter(n_gram)
new_words_list = new_word_find.Entropy_left_right_filter(new_words_dic,text)
for new_words in new_words_list:
print(f"{new_words}")
7.5 新词发现结果展示
index :0 => title:##习近平在第六届东方经济论坛全会开幕式上的致辞(全文)
{'word': '方面', 'pmi': 18.666666666666668, 'left_entropy': 1.584962500721156, 'right_entropy': 1.584962500721156, 'score': 17.08170416594551}
{'word': '合作', 'pmi': 13.75, 'left_entropy': 3.0, 'right_entropy': 3.0, 'score': 10.75}
{'word': '中国', 'pmi': 12.0, 'left_entropy': 1.584962500721156, 'right_entropy': 1.584962500721156, 'score': 10.415037499278844}
{'word': '中俄', 'pmi': 6.0, 'left_entropy': 1.584962500721156, 'right_entropy': 1.584962500721156, 'score': 4.415037499278844}
{'word': '发展', 'pmi': 5.0, 'left_entropy': 1.584962500721156, 'right_entropy': 1.584962500721156, 'score': 3.415037499278844}
{'word': '世界', 'pmi': 5.0, 'left_entropy': 2.321928094887362, 'right_entropy': 2.321928094887362, 'score': 2.678071905112638}
参考
基于互信息和左右熵的新词发现算法——python实现
学习NLP的第20天——基于信息熵和互信息的新词提取实现_数据艺术家-程序员宅基地
反作弊基于左右信息熵和互信息的新词挖掘
重新写了之前的新词发现算法:更快更好的新词发现
新词发现
