Introducing GraphQL
GraphQL 是一种用于 API 的查询语言, 并且提供已有数据查询的运行时, 它诞生于 2015 年, 由 Facebook 开发, 2018 年 11 月 7 日,Facebook 将 GraphQL 项目转移到新成立的 GraphQL 基金会. 目前 Facebook, Twitter, Netflix, PayPal 各厂已经在生产环境使用 GraphQL 了, GitHub API v4 也已全面使用 GraphQL.

精准、可预测地返回数据
传统的 RESTful 接口, 后端传递多少字段, 前端就得接收多少字段. 因此, 有时候前端只需要几个字段, 但后端返回一大串(尤其是历史悠久的接口), 这不但对前端筛选接口字段增加了难度, 还可能会造成潜在的性能问题. 而 GraphQL 使得客户端能够准确地获得它需要的数据, 而且没有任何冗余, 并且 GraphQL 筛选这些字段的过程不依赖于服务器, 而是它自己运行时.
export const POSTS = gql`query Posts($input: PaginationInput!) {posts(input: $input) {totalpagepageSizeitems {_idtitlesummary}}}
@ObjectType()export class SMSModel {@Field()@IsMobilePhone("zh-CN")@IsNotEmpty()public readonly phoneNumber: string;@Field()@Length(6)@IsNumberString()@IsNotEmpty()public readonly smsCode: string;}
只请求一个接口
下面这个例子是一个经典的 RESTful 风格接口, 可以看到一套增删改查需要请求不同的 url, 这就导致了需要进行多个 TCP 连接. 虽然 HTTP2 提供了多路复用(同域名下所有通信都在单个连接上完成, 同个域名只需要占用一个 TCP 连接, 使用一个连接并行发送多个请求和响应)的特性. 但在网络仍然较慢的移动环境下, 我们仍希望尽可能的减少 HTTP 请求, GraphQL 的应用也能表现得足够迅速.
GET /postsGET /post/:idPOST /postPUT /post/:idDELETE /post/:id
{operationName: "Posts",query: "...",variables: {input: {page: 1,pageSize: 10,},},}
SDL(schema definition languages)
Type Language
GraphQL 不依赖于任何编程语言, 因为我们并不依赖于任何特定语言的句法句式, 它有自己的一套模式.
type Language {code: String!name: String!native: String!}type Location {geoname_id: Float!capital: String!languages: [Language!]!country_flag: String!country_flag_emoji: String!country_flag_emoji_unicode: String!calling_code: String!is_eu: Boolean!created_at: DateTime!}
Language代表 GraphQL对象类型, 一般用来约定后端的 response.code,name,native是Language类型上的字段, 这意味着你在查询Language时只能查找这三个字段中的一个或多个, 查找任何其他字段将会报错.code: String!意味着code的标量是String, 感叹号意味着该字段是非空的, 如果后端返回改字段是空的, 也会报错.languages: [Language!]!意味着languages的类型是Language 数组, 且该数组不能为空.
type Query {getPosts(input: PaginationInput!): PostModel!}type Mutation {createPost(input: CreatePostInput!): PostItemModel!}input CreatePostInput {posterUrl: String!title: String!summary: String!content: String!tags: [String!]!lastModifiedDate: String!isPublic: Boolean}
Query 和 Mutation 是两个内置的特殊类型, 你可以将其理解为 RESTful 中的 GET 和 POST, 前者用于查询, 后者用于增删改. 虽然使用 Query 可以进行增删改, 但为了语义化, 建议分开使用.
第一个语句定义一个查询, getPost 可以类比为 RESTful 接口中的路径; 而 input 则可以类比放在 body 中的参数, 它是 CreatePostInput 类型, 且是必传的, input 类型定义一次查询或变更中传递的对象参数; 该查询返回 PostModel 类型的数据, 且该数据必须为非空. 第二个语句定义一次变更, 语义同理.
Scalar
"标量", 可以理解为 GraphQL 中字段的基础类型, 默认有 Int, Float, String, Boolean, ID 五种. 有时候你需要扩展适合自己业务的标量, 每个标量需要实现 parseValue, serialize, parseLiteral 三个方法, 如下是 DateScalar.
import { Scalar, CustomScalar } from "@nestjs/graphql";import { Kind, ValueNode } from "graphql";@Scalar("Date")export class DateScalar implements CustomScalar<number, Date> {description = "Date custom scalar type";parseValue(value: number): Date {return new Date(value); // value from the client}serialize(value: Date): number {return value.getTime(); // value sent to the client}parseLiteral(ast: ValueNode): Date {if (ast.kind === Kind.INT) {return new Date(ast.value);}return null;}}
标量的目的是能够更加精确的确定一个字段的类型, 不过写个新的确实比较麻烦, 好在 graphql-scalars 预设了大约 50 个标量, 比如 PositiveInt, NegativeInt, DateTime, Date, EmailAddress, HexColorCode 等等.
Enum
枚举类型是一种特殊的标量, 它限制在一个特殊的可选值集合内. 这让你能够:
验证这个类型的任何参数是可选值的某一个 与类型系统沟通, 一个字段总是一个有限值集合的其中一个值
enum PostStatus {DRAFTPUBLISH}
Interfaces
跟许多类型系统一样, GraphQL 支持接口. 一个接口是一个抽象类型, 它包含某些字段, 而对象类型必须包含这些字段, 才能算实现了这个接口.
interface Common {status_msg: String!status_code: Int!}type User implements Common {id: ID!name: String!email: String!status_msg: String!status_code: Int!}
代码优先
在真实的开发中, 我们可以像上面一样, 通过编写 GraphQL 原生语言来创建 GraphQL SDL, 当然我们也可以通过代码优先的方式, 即通过 TypeScript 装饰器来生成. 下面的代码, 除了定义字段的类型, 比如 posterUrl 的类型是 String 标量, 且为非空; 还能"夹带私货", 比如限制 posterUrl 是 url 格式的字符串, 这样就更加细粒度的对数据类型进行限制.
@InputType()export class CreatePostInput {@Field({ nullable: false })@IsString()@IsUrl({ protocols: ["https"], require_protocol: true })@IsNotEmpty()public readonly posterUrl: string;@Field({ nullable: false })@IsString()@MinLength(1)@MaxLength(20)@IsNotEmpty()public readonly title: string;@Field({ nullable: false })@IsString()@IsNotEmpty()public readonly summary: string;@Field({ nullable: false })@IsString()@IsNotEmpty()public readonly content: string;@Field(() => [String], { nullable: false })@IsArray()@IsString({ each: true })@ArrayNotEmpty()@ArrayUnique()@IsNotEmpty()public readonly tags: string[];@Field({ nullable: false })@IsString()@IsNotEmpty()public readonly lastModifiedDate: string;@Field({ nullable: true })public readonly isPublic?: boolean;}
下面的代码则是 GraphQL 的解析器, 同样通过注解的方式来创建 Query 和 Mutation:
@Query(() => PostItemModel)代表着返回值为PostItemModel类型;getPostById定义这个查询的名称;@Args({ name: "id", type: () => ID })用来定义传参, 我需要传递一个字段 id, 它的标量为 ID
@Resolver()export class PostsResolver {constructor(private readonly postsService: PostsService) {this.postsService = postsService;}@Query(() => PostItemModel)public async getPostById(@Args({ name: "id", type: () => ID }) id: string) {return this.postsService.findOneById(id); // 处理 SQL}@Mutation(() => PostItemModel)@UseGuards(GqlAuthGuard)public async createPost(@Args("input") input: CreatePostInput) {return this.postsService.create(input); // 处理 SQL}}
前端
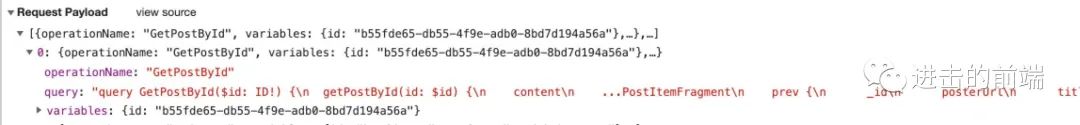
GraphQL 在前端的本质表现就是向你的接口, 如 https://api.example.com/graphql 上发送一个 POST 请求, 而请求的 body 就如上图所示. 但为了更加的和 GrapqhQL 语法配合, 前端涌现了一些不错的库, 如 Facebook 自家的 relay, relay 经历了两次重大迭代, 目前 Facebook 官网用的是最新一代, 名字叫 relay morden.
虽然 relay 是一个开源项目, 但它更多是为 Facebook 内部业务服务, 因此外部人用起来比较难受. 目前最广泛的框架则是 Apollo, 它支持基于 Hooks 的 React 前端框架, 也支持 Vue, Angular, Android 和 iOS, 也提供了基于 Node.js 的后端框架 Appolo Server.
fragment 是用来定义片段, 如下面的例子, 我们定义查询一篇文章, 返回的是一篇文章实体; 修改一篇文章, 返回的也是文章修改后的实体. 这样它们的返回值基本都是一样的, 为了不写多次, 可以通过 fragment 来进行提取, 简化代码书写.
第二段代码, 请求的变更是 createPost, 它的参数 input 是 CreatePostInput 类型, 且为必传. 因为我们使用了 fragment, 因此需要将相应片段注入进来.
第三段代码就是真正在 jsx 中发起请求了, 通过 hooks 可以方便的处理请求体, loading, 返回值, 错误处理等等...
const POST_FRAGMENT = gql`fragment PostFragment on PostItemModel {_idposterUrltitlesummarycontenttagslastModifiedDatelikepvisPubliccreatedAtupdatedAt}`;export const CREATE_ONE_POST = gql`mutation CreatePost($input: CreatePostInput!) {createPost(input: $input) {...PostFragment}}${POST_FRAGMENT}`;const [createPost, { loading }] = useMutation<CreatePostMutation,CreatePostVars>(CREATE_ONE_POST, {onCompleted(data) {const newPost = data.createPost;enqueueSnackbar("Create success!", { variant: "success" });},onError() {},});
Introspection
在真实的开发中, 我们会在后端定义一系列的 query, mutation, input, type, enum, scalar, interface. 而 GraphQL 支持一套强大的内省系统, 通过内省系统, 我们可以反查后端设计的 schema 的集合. 内省系统的另一个功能则是辅助开发 GraphQL 工具, 通过查询出来的内部 schema, 可以搭建出强大的 IDE. 如下代码可以查询出 PostItemModel 这个类型的所有信息.
{__type(name: "PostItemModel") {namefields {nametype {namekind}}}}
{"data": {"__type": {"name": "PostItemModel","fields": [{"name": "_id","type": {"name": null,"kind": "NON_NULL"}},{"name": "posterUrl","type": {"name": null,"kind": "NON_NULL"}},{"name": "title","type": {"name": null,"kind": "NON_NULL"}},{"name": "summary","type": {"name": null,"kind": "NON_NULL"}},{"name": "content","type": {"name": null,"kind": "NON_NULL"}},{"name": "tags","type": {"name": null,"kind": "NON_NULL"}},{"name": "lastModifiedDate","type": {"name": null,"kind": "NON_NULL"}},{"name": "like","type": {"name": null,"kind": "NON_NULL"}},{"name": "pv","type": {"name": null,"kind": "NON_NULL"}},{"name": "isPublic","type": {"name": null,"kind": "NON_NULL"}},{"name": "createdAt","type": {"name": null,"kind": "NON_NULL"}},{"name": "updatedAt","type": {"name": null,"kind": "NON_NULL"}},{"name": "prev","type": {"name": "PostItemModel","kind": "OBJECT"}},{"name": "next","type": {"name": "PostItemModel","kind": "OBJECT"}}]}}}
安全
生产环境关闭 debug
如果开启 debug 模式, 在出错时会展示错误的堆栈信息.

生产环境关闭 playground
playground 应当作为一种辅助自测工具, 其不应该暴露到线上.
生产环境关闭 introspection
得益于自省, 可以轻松获取到 GraphQL server 内部的信息, 如各种类型, 标量等. 这些信息不应该在线上被三方直接通过代码采集到.
控制多层深度的查询
如下可能会造成昂贵的查询, 重则导致后端崩溃. 可以使用 graphql-depth-limit 来指定最多查询的层级.
query {author(id: 42) {posts {author {posts {author {posts {author {# and so on...}}}}}}}}
控制分页数据量
如下最多一次将能获取十万条数据, 显而易见会带来性能问题. 你可以通过 graphql-input-number 在 resolver 中限制数字的最大值.
query {authors(first: 1000) {nameposts(last: 100) {titlecontent}}}
当然, 如果你使用了 class-validator, 也可以通过如下方式来限制.
@InputType()export class SomeNumberInput {@IsInt()@Min(1)@Max(10)public readonly pageSize: number;}
参考
9 Ways To Secure your GraphQL API — GraphQL Security Checklist GraphQL | A query language for your API
