整理了60个 Python 实战例子,拿来即用!
↓推荐关注↓
人生苦短,我用 Python!
大家好,最近有一些朋友问我有没有一些 Python 实战小案例。今天我整理排版了一遍,给大家分享一下。喜欢记得点赞、收藏、关注。
整理了60个Python小例子,拿来即用!
一、 数字
1 求绝对值
绝对值或复数的模
# 公众号:快学Python
In [1]: abs(-6)
Out[1]: 6
2 进制转化
十进制转换为二进制:
In [2]: bin(10)
Out[2]: '0b1010'
十进制转换为八进制:
In [3]: oct(9)
Out[3]: '0o11'
十进制转换为十六进制:
In [4]: hex(15)
Out[4]: '0xf'
3 整数和ASCII互转
十进制整数对应的ASCII字符
In [1]: chr(65)
Out[1]: 'A'
查看某个ASCII字符对应的十进制数
In [1]: ord('A')
Out[1]: 65
4 元素都为真检查
所有元素都为真,返回 True,否则为False
In [5]: all([1,0,3,6])
Out[5]: False
In [6]: all([1,2,3])
Out[6]: True
5 元素至少一个为真检查
至少有一个元素为真返回True,否则False
In [7]: any([0,0,0,[]])
Out[7]: False
In [8]: any([0,0,1])
Out[8]: True
6 判断是真是假
测试一个对象是True, 还是False.
In [9]: bool([0,0,0])
Out[9]: True
In [10]: bool([])
Out[10]: False
In [11]: bool([1,0,1])
Out[11]: True
7 创建复数
创建一个复数
In [1]: complex(1,2)
Out[1]: (1+2j)
8 取商和余数
分别取商和余数
In [1]: divmod(10,3)
Out[1]: (3, 1)
9 转为浮点类型
将一个整数或数值型字符串转换为浮点数
In [1]: float(3)
Out[1]: 3.0
如果不能转化为浮点数,则会报ValueError:
In [2]: float('a')
# ValueError: could not convert string to float: 'a'
10 转为整型
int(x, base =10) , x可能为字符串或数值,将x 转换为一个普通整数。如果参数是字符串,那么它可能包含符号和小数点。如果超出了普通整数的表示范围,一个长整数被返回。
In [1]: int('12',16)
Out[1]: 18
11 次幂
base为底的exp次幂,如果mod给出,取余
In [1]: pow(3, 2, 4)
Out[1]: 1
12 四舍五入
四舍五入,ndigits代表小数点后保留几位:
In [11]: round(10.0222222, 3)
Out[11]: 10.022
In [12]: round(10.05,1)
Out[12]: 10.1
13 链式比较
i = 3
print(1 < i < 3) # False
print(1 < i <= 3) # True
二、 字符串
14 字符串转字节
字符串转换为字节类型
In [12]: s = "apple"
In [13]: bytes(s,encoding='utf-8')
Out[13]: b'apple'
15 任意对象转为字符串
In [14]: i = 100
In [15]: str(i)
Out[15]: '100'
In [16]: str([])
Out[16]: '[]'
In [17]: str(tuple())
Out[17]: '()'
16 执行字符串表示的代码
将字符串编译成python能识别或可执行的代码,也可以将文字读成字符串再编译。
In [1]: s = "print('helloworld')"
In [2]: r = compile(s,"<string>", "exec")
In [3]: r
Out[3]: <code object <module> at 0x0000000005DE75D0, file "<string>", line 1>
In [4]: exec(r)
helloworld
17 计算表达式
将字符串str 当成有效的表达式来求值并返回计算结果取出字符串中内容
In [1]: s = "1 + 3 +5"
...: eval(s)
...:
Out[1]: 9
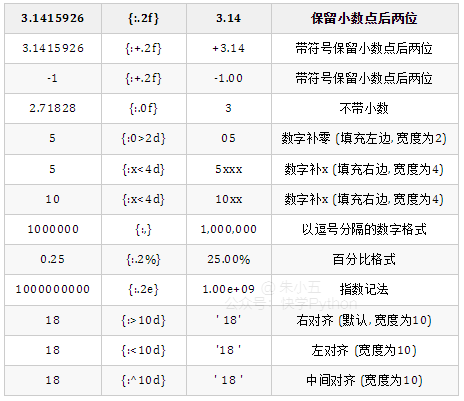
18 字符串格式化
格式化输出字符串,format(value, format_spec)实质上是调用了value的__format__(format_spec)方法。
In [1]: print("i am {0},age{1}".format("tom",18))
Out[1]:i am tom,age18
三、 函数
19 拿来就用的排序函数
排序:
In [1]: a = [1,4,2,3,1]
In [2]: sorted(a,reverse=True)
Out[2]: [4, 3, 2, 1, 1]
In [3]: a = [{'name':'xiaoming','age':18,'gender':'male'},{'name':'
...: xiaohong','age':20,'gender':'female'}]
In [4]: sorted(a,key=lambda x: x['age'],reverse=False)
Out[4]:
[{'name': 'xiaoming', 'age': 18, 'gender': 'male'},
{'name': 'xiaohong', 'age': 20, 'gender': 'female'}]
20 求和函数
求和:
In [181]: a = [1,4,2,3,1]
In [182]: sum(a)
Out[182]: 11
# 公众号:快学Python
In [185]: sum(a,10) #求和的初始值为10
Out[185]: 21
21 nonlocal用于内嵌函数中
关键词nonlocal常用于函数嵌套中,声明变量i为非局部变量;如果不声明,i+=1表明i为函数wrapper内的局部变量,因为在i+=1引用(reference)时,i未被声明,所以会报unreferenced variable的错误。
def excepter(f):
i = 0
t1 = time.time()
def wrapper():
try:
f()
except Exception as e:
nonlocal i
i += 1
print(f'{e.args[0]}: {i}')
t2 = time.time()
if i == n:
print(f'spending time:{round(t2-t1,2)}')
return wrapper
22 global 声明全局变量
先回答为什么要有global,一个变量被多个函数引用,想让全局变量被所有函数共享。有的伙伴可能会想这还不简单,这样写:
i = 5
def f():
print(i)
def g():
print(i)
pass
f()
g()
f和g两个函数都能共享变量i,程序没有报错,所以他们依然不明白为什么要用global.
但是,如果我想要有个函数对i递增,这样:
def h():
i += 1
h()
此时执行程序,bang, 出错了!抛出异常:UnboundLocalError,原来编译器在解释i+=1时会把i解析为函数h()内的局部变量,很显然在此函数内,编译器找不到对变量i的定义,所以会报错。
global就是为解决此问题而被提出,在函数h内,显式地告诉编译器i为全局变量,然后编译器会在函数外面寻找i的定义,执行完i+=1后,i还为全局变量,值加1:
i = 0
def h():
global i
i += 1
h()
print(i)
23 交换两元素
def swap(a, b):
return b, a
print(swap(1, 0))
输出:

24 操作函数对象
In [31]: def f():
...: print('i'm f')
...:
In [32]: def g():
...: print('i'm g')
...:
In [33]: [f,g][1]()
i'm g
创建函数对象的list,根据想要调用的index,方便统一调用。
25 生成逆序序列
list(range(10,-1,-1)) # [10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0]
第三个参数为负时,表示从第一个参数开始递减,终止到第二个参数(不包括此边界)
26 函数的五类参数使用例子
python五类参数:位置参数,关键字参数,默认参数,可变位置或关键字参数的使用。
def f(a,*b,c=10,**d):
print(f'a:{a},b:{b},c:{c},d:{d}')
默认参数c不能位于可变关键字参数d后.
调用f:
In [10]: f(1,2,5,width=10,height=20)
a:1,b:(2, 5),c:10,d:{'width': 10, 'height': 20}
可变位置参数b实参后被解析为元组(2,5);而c取得默认值10; d被解析为字典.
再次调用f:
In [11]: f(a=1,c=12)
a:1,b:(),c:12,d:{}
a=1传入时a就是关键字参数,b,d都未传值,c被传入12,而非默认值。
注意观察参数a, 既可以f(1),也可以f(a=1) 其可读性比第一种更好,建议使用f(a=1)。如果要强制使用f(a=1),需要在前面添加一个星号:
def f(*,a,**b):
print(f'a:{a},b:{b}')
此时f(1)调用,将会报错:TypeError: f() takes 0 positional arguments but 1 was given
只能f(a=1)才能OK.
说明前面的*发挥作用,它变为只能传入关键字参数,那么如何查看这个参数的类型呢?借助python的inspect模块:
In [22]: for name,val in signature(f).parameters.items():
...: print(name,val.kind)
...:
a KEYWORD_ONLY
b VAR_KEYWORD
可看到参数a的类型为KEYWORD_ONLY,也就是仅仅为关键字参数。
但是,如果f定义为:
def f(a,*b):
print(f'a:{a},b:{b}')
查看参数类型:
In [24]: for name,val in signature(f).parameters.items():
...: print(name,val.kind)
...:
a POSITIONAL_OR_KEYWORD
b VAR_POSITIONAL
可以看到参数a既可以是位置参数也可是关键字参数。
27 使用slice对象
生成关于蛋糕的序列cake1:
In [1]: cake1 = list(range(5,0,-1))
In [2]: b = cake1[1:10:2]
In [3]: b
Out[3]: [4, 2]
In [4]: cake1
Out[4]: [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
再生成一个序列:
In [5]: from random import randint
...: cake2 = [randint(1,100) for _ in range(100)]
...: # 同样以间隔为2切前10个元素,得到切片d
...: d = cake2[1:10:2]
In [6]: d
Out[6]: [75, 33, 63, 93, 15]
你看,我们使用同一种切法,分别切开两个蛋糕cake1,cake2. 后来发现这种切法极为经典,又拿它去切更多的容器对象。
那么,为什么不把这种切法封装为一个对象呢?于是就有了slice对象。
定义slice对象极为简单,如把上面的切法定义成slice对象:
perfect_cake_slice_way = slice(1,10,2)
#去切cake1
cake1_slice = cake1[perfect_cake_slice_way]
cake2_slice = cake2[perfect_cake_slice_way]
In [11]: cake1_slice
Out[11]: [4, 2]
In [12]: cake2_slice
Out[12]: [75, 33, 63, 93, 15]
与上面的结果一致。
对于逆向序列切片,slice对象一样可行:
a = [1,3,5,7,9,0,3,5,7]
a_ = a[5:1:-1]
named_slice = slice(5,1,-1)
a_slice = a[named_slice]
In [14]: a_
Out[14]: [0, 9, 7, 5]
In [15]: a_slice
Out[15]: [0, 9, 7, 5]
频繁使用同一切片的操作可使用slice对象抽出来,复用的同时还能提高代码可读性。
28 lambda 函数的动画演示
有些读者反映,lambda函数不太会用,问我能不能解释一下。
比如,下面求这个 lambda函数:
def max_len(*lists):
return max(*lists, key=lambda v: len(v))
有两点疑惑:
参数 v的取值?lambda函数有返回值吗?如果有,返回值是多少?
调用上面函数,求出以下三个最长的列表:
r = max_len([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6, 7], [8])
print(f'更长的列表是{r}')
程序完整运行过程,动画演示如下:
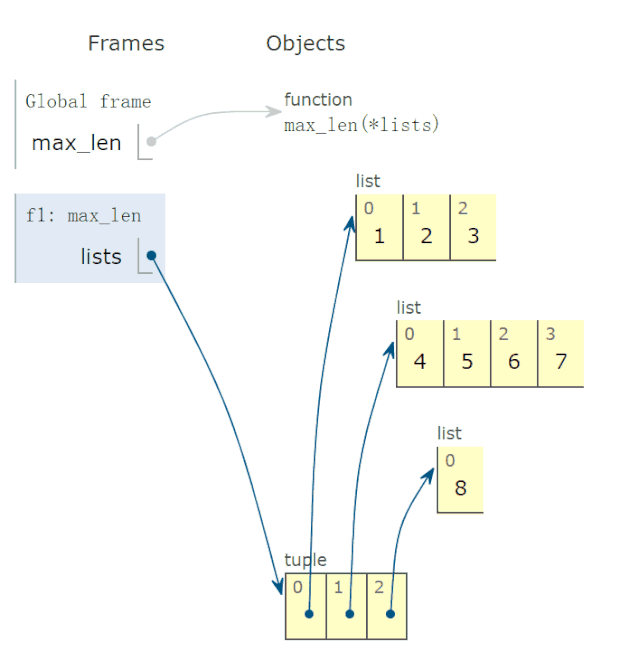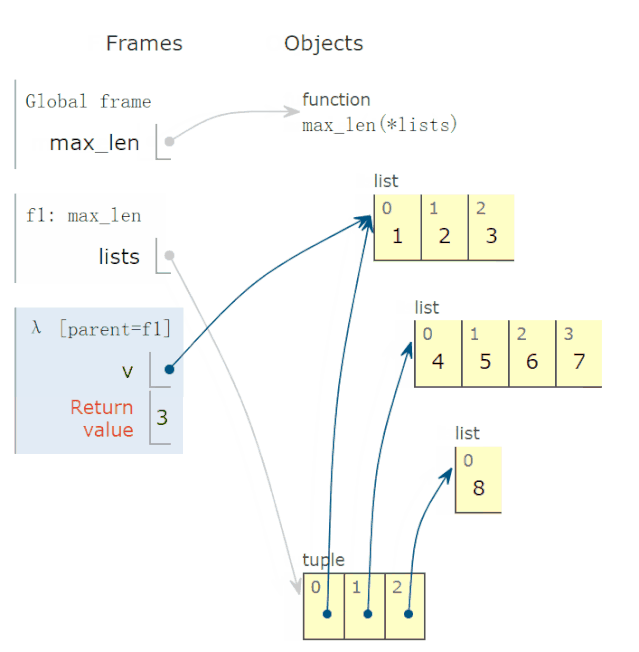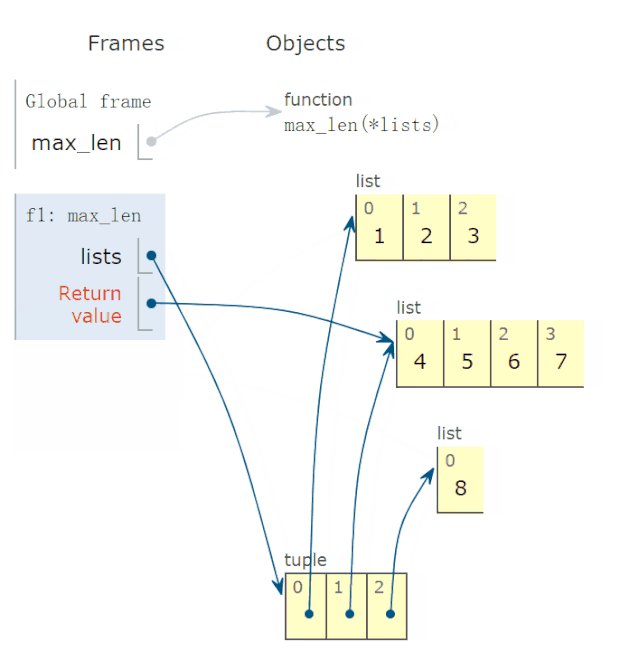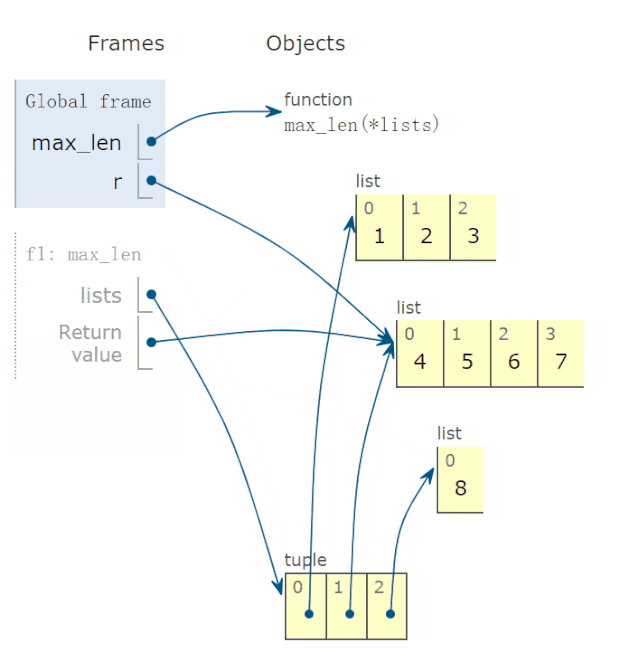
结论:
参数v的可能取值为 *lists,也就是tuple的一个元素。lambda函数返回值,等于lambda v冒号后表达式的返回值。
四、 数据结构
29 转为字典
创建数据字典
In [1]: dict()
Out[1]: {}
In [2]: dict(a='a',b='b')
Out[2]: {'a': 'a', 'b': 'b'}
In [3]: dict(zip(['a','b'],[1,2]))
Out[3]: {'a': 1, 'b': 2}
In [4]: dict([('a',1),('b',2)])
Out[4]: {'a': 1, 'b': 2}
30 冻结集合
创建一个不可修改的集合。
In [1]: frozenset([1,1,3,2,3])
Out[1]: frozenset({1, 2, 3})
因为不可修改,所以没有像set那样的add和pop方法
31 转为集合类型
返回一个set对象,集合内不允许有重复元素:
In [159]: a = [1,4,2,3,1]
In [160]: set(a)
Out[160]: {1, 2, 3, 4}
32 转为切片对象
class slice(start, stop[, step])
返回一个表示由 range(start, stop, step) 所指定索引集的 slice对象,它让代码可读性、可维护性变好。
In [1]: a = [1,4,2,3,1]
In [2]: my_slice_meaning = slice(0,5,2)
In [3]: a[my_slice_meaning]
Out[3]: [1, 2, 1]
33 转元组
tuple() 将对象转为一个不可变的序列类型
In [16]: i_am_list = [1,3,5]
In [17]: i_am_tuple = tuple(i_am_list)
In [18]: i_am_tuple
Out[18]: (1, 3, 5)
五、 类和对象
34 是否可调用
检查对象是否可被调用
In [1]: callable(str)
Out[1]: True
In [2]: callable(int)
Out[2]: True
In [18]: class Student():
...: def __init__(self,id,name):
...: self.id = id
...: self.name = name
...: def __repr__(self):
...: return 'id = '+self.id +', name = '+self.name
...
In [19]: xiaoming = Student('001','xiaoming')
In [20]: callable(xiaoming)
Out[20]: False
如果能调用xiaoming(), 需要重写Student类的__call__方法:
In [1]: class Student():
...: def __init__(self,id,name):
...: self.id = id
...: self.name = name
...: def __repr__(self):
...: return 'id = '+self.id +', name = '+self.name
...: def __call__(self):
...: print('I can be called')
...: print(f'my name is {self.name}')
...:
In [2]: t = Student('001','xiaoming')
In [3]: t()
I can be called
my name is xiaoming
35 ascii 展示对象
调用对象的 __repr__ 方法,获得该方法的返回值,如下例子返回值为字符串
>>> class Student():
def __init__(self,id,name):
self.id = id
self.name = name
def __repr__(self):
return 'id = '+self.id +', name = '+self.name
调用:
>>> xiaoming = Student(id='1',name='xiaoming')
>>> xiaoming
id = 1, name = xiaoming
>>> ascii(xiaoming)
'id = 1, name = xiaoming'
36 类方法
classmethod 装饰器对应的函数不需要实例化,不需要 self 参数,但第一个参数需要是表示自身类的 cls 参数,可以来调用类的属性,类的方法,实例化对象等。
In [1]: class Student():
...: def __init__(self,id,name):
...: self.id = id
...: self.name = name
...: def __repr__(self):
...: return 'id = '+self.id +', name = '+self.name
...: @classmethod
...: def f(cls):
...: print(cls)
37 动态删除属性
删除对象的属性
In [1]: delattr(xiaoming,'id')
In [2]: hasattr(xiaoming,'id')
Out[2]: False
38 一键查看对象所有方法
不带参数时返回当前范围内的变量、方法和定义的类型列表;带参数时返回参数的属性,方法列表。
In [96]: dir(xiaoming)
Out[96]:
['__class__',
'__delattr__',
'__dict__',
'__dir__',
'__doc__',
'__eq__',
'__format__',
'__ge__',
'__getattribute__',
'__gt__',
'__hash__',
'__init__',
'__init_subclass__',
'__le__',
'__lt__',
'__module__',
'__ne__',
'__new__',
'__reduce__',
'__reduce_ex__',
'__repr__',
'__setattr__',
'__sizeof__',
'__str__',
'__subclasshook__',
'__weakref__',
'name']
39 动态获取对象属性
获取对象的属性
In [1]: class Student():
...: def __init__(self,id,name):
...: self.id = id
...: self.name = name
...: def __repr__(self):
...: return 'id = '+self.id +', name = '+self.name
In [2]: xiaoming = Student(id='001',name='xiaoming')
In [3]: getattr(xiaoming,'name') # 获取xiaoming这个实例的name属性值
Out[3]: 'xiaoming'
40 对象是否有这个属性
In [1]: class Student():
...: def __init__(self,id,name):
...: self.id = id
...: self.name = name
...: def __repr__(self):
...: return 'id = '+self.id +', name = '+self.name
In [2]: xiaoming = Student(id='001',name='xiaoming')
In [3]: hasattr(xiaoming,'name')
Out[3]: True
In [4]: hasattr(xiaoming,'address')
Out[4]: False
41 对象门牌号
返回对象的内存地址
In [1]: id(xiaoming)
Out[1]: 98234208
42 isinstance
判断_object_是否为类_classinfo_的实例,是返回true
In [1]: class Student():
...: def __init__(self,id,name):
...: self.id = id
...: self.name = name
...: def __repr__(self):
...: return 'id = '+self.id +', name = '+self.name
In [2]: xiaoming = Student(id='001',name='xiaoming')
In [3]: isinstance(xiaoming,Student)
Out[3]: True
43 父子关系鉴定
In [1]: class undergraduate(Student):
...: def studyClass(self):
...: pass
...: def attendActivity(self):
...: pass
In [2]: issubclass(undergraduate,Student)
Out[2]: True
In [3]: issubclass(object,Student)
Out[3]: False
In [4]: issubclass(Student,object)
Out[4]: True
如果class是classinfo元组中某个元素的子类,也会返回True
In [1]: issubclass(int,(int,float))
Out[1]: True
44 所有对象之根
object 是所有类的基类
In [1]: o = object()
In [2]: type(o)
Out[2]: object
45 创建属性的两种方式
返回 property 属性,典型的用法:
class C:
def __init__(self):
self._x = None
def getx(self):
return self._x
def setx(self, value):
self._x = value
def delx(self):
del self._x
# 使用property类创建 property 属性
x = property(getx, setx, delx, "I'm the 'x' property.")
使用python装饰器,实现与上完全一样的效果代码:
class C:
def __init__(self):
self._x = None
@property
def x(self):
return self._x
@x.setter
def x(self, value):
self._x = value
@x.deleter
def x(self):
del self._x
46 查看对象类型
class type(name, bases, dict)
传入一个参数时,返回 object 的类型:
In [1]: class Student():
...: def __init__(self,id,name):
...: self.id = id
...: self.name = name
...: def __repr__(self):
...: return 'id = '+self.id +', name = '+self.name
...:
In [2]: xiaoming = Student(id='001',name='xiaoming')
In [3]: type(xiaoming)
Out[3]: __main__.Student
In [4]: type(tuple())
Out[4]: tuple
47 元类
xiaoming, xiaohong, xiaozhang 都是学生,这类群体叫做 Student.
Python 定义类的常见方法,使用关键字 class
In [36]: class Student(object):
...: pass
xiaoming, xiaohong, xiaozhang 是类的实例,则:
xiaoming = Student()
xiaohong = Student()
xiaozhang = Student()
创建后,xiaoming 的 __class__ 属性,返回的便是 Student类
In [38]: xiaoming.__class__
Out[38]: __main__.Student
问题在于,Student 类有 __class__属性,如果有,返回的又是什么?
In [39]: xiaoming.__class__.__class__
Out[39]: type
哇,程序没报错,返回 type
那么,我们不妨猜测:Student 类,类型就是 type
换句话说,Student类就是一个对象,它的类型就是 type
所以,Python 中一切皆对象,类也是对象
Python 中,将描述 Student 类的类被称为:元类。
按照此逻辑延伸,描述元类的类被称为:_元元类_,开玩笑了~ 描述元类的类也被称为元类。
聪明的朋友会问了,既然 Student 类可创建实例,那么 type 类可创建实例吗?如果能,它创建的实例就叫:类 了。你们真聪明!
说对了,type 类一定能创建实例,比如 Student 类了。
In [40]: Student = type('Student',(),{})
In [41]: Student
Out[41]: __main__.Student
它与使用 class 关键字创建的 Student 类一模一样。
Python 的类,因为又是对象,所以和 xiaoming,xiaohong 对象操作相似。支持:
赋值 拷贝 添加属性 作为函数参数
In [43]: StudentMirror = Student # 类直接赋值 # 类直接赋值
In [44]: Student.class_property = 'class_property' # 添加类属性
In [46]: hasattr(Student, 'class_property')
Out[46]: True
元类,确实使用不是那么多,也许先了解这些,就能应付一些场合。就连 Python 界的领袖 Tim Peters 都说:
“元类就是深度的魔法,99%的用户应该根本不必为此操心。
六、工具
48 枚举对象
返回一个可以枚举的对象,该对象的next()方法将返回一个元组。
In [1]: s = ["a","b","c"]
...: for i ,v in enumerate(s,1):
...: print(i,v)
...:
1 a
2 b
3 c
49 查看变量所占字节数
In [1]: import sys
In [2]: a = {'a':1,'b':2.0}
In [3]: sys.getsizeof(a) # 占用240个字节
Out[3]: 240
50 过滤器
在函数中设定过滤条件,迭代元素,保留返回值为True的元素:
In [1]: fil = filter(lambda x: x>10,[1,11,2,45,7,6,13])
In [2]: list(fil)
Out[2]: [11, 45, 13]
51 返回对象的哈希值
返回对象的哈希值,值得注意的是自定义的实例都是可哈希的,list, dict, set等可变对象都是不可哈希的(unhashable)
In [1]: hash(xiaoming)
Out[1]: 6139638
In [2]: hash([1,2,3])
# TypeError: unhashable type: 'list'
52 一键帮助
返回对象的帮助文档
In [1]: help(xiaoming)
Help on Student in module __main__ object:
class Student(builtins.object)
| Methods defined here:
|
| __init__(self, id, name)
|
| __repr__(self)
|
| Data descriptors defined here:
|
| __dict__
| dictionary for instance variables (if defined)
|
| __weakref__
| list of weak references to the object (if defined)
53 获取用户输入
获取用户输入内容
In [1]: input()
aa
Out[1]: 'aa'
54 创建迭代器类型
使用iter(obj, sentinel), 返回一个可迭代对象, sentinel可省略(一旦迭代到此元素,立即终止)
In [1]: lst = [1,3,5]
In [2]: for i in iter(lst):
...: print(i)
...:
1
3
5
In [1]: class TestIter(object):
...: def __init__(self):
...: self.l=[1,3,2,3,4,5]
...: self.i=iter(self.l)
...: def __call__(self): #定义了__call__方法的类的实例是可调用的
...: item = next(self.i)
...: print ("__call__ is called,fowhich would return",item)
...: return item
...: def __iter__(self): #支持迭代协议(即定义有__iter__()函数)
...: print ("__iter__ is called!!")
...: return iter(self.l)
In [2]: t = TestIter()
In [3]: t() # 因为实现了__call__,所以t实例能被调用
__call__ is called,which would return 1
Out[3]: 1
In [4]: for e in TestIter(): # 因为实现了__iter__方法,所以t能被迭代
...: print(e)
...:
__iter__ is called!!
1
3
2
3
4
5
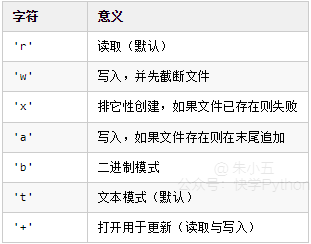
55 打开文件
返回文件对象
In [1]: fo = open('D:/a.txt',mode='r', encoding='utf-8')
In [2]: fo.read()
Out[2]: '\ufefflife is not so long,\nI use Python to play.'
mode取值表:
56 创建range序列
range(stop)
range(start, stop[,step])
生成一个不可变序列:
In [1]: range(11)
Out[1]: range(0, 11)
In [2]: range(0,11,1)
Out[2]: range(0, 11)
57 反向迭代器
In [1]: rev = reversed([1,4,2,3,1])
In [2]: for i in rev:
...: print(i)
...:
1
3
2
4
1
58 聚合迭代器
创建一个聚合了来自每个可迭代对象中的元素的迭代器:
In [1]: x = [3,2,1]
In [2]: y = [4,5,6]
In [3]: list(zip(y,x))
Out[3]: [(4, 3), (5, 2), (6, 1)]
In [4]: a = range(5)
In [5]: b = list('abcde')
In [6]: b
Out[6]: ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
In [7]: [str(y) + str(x) for x,y in zip(a,b)]
Out[7]: ['a0', 'b1', 'c2', 'd3', 'e4']
59 链式操作
from operator import (add, sub)
def add_or_sub(a, b, oper):
return (add if oper == '+' else sub)(a, b)
add_or_sub(1, 2, '-') # -1
60 对象序列化
对象序列化,是指将内存中的对象转化为可存储或传输的过程。很多场景,直接一个类对象,传输不方便。
但是,当对象序列化后,就会更加方便,因为约定俗成的,接口间的调用或者发起的 web 请求,一般使用 json 串传输。
实际使用中,一般对类对象序列化。先创建一个 Student 类型,并创建两个实例。
class Student():
def __init__(self,**args):
self.ids = args['ids']
self.name = args['name']
self.address = args['address']
xiaoming = Student(ids = 1,name = 'xiaoming',address = '北京')
xiaohong = Student(ids = 2,name = 'xiaohong',address = '南京')
导入 json 模块,调用 dump 方法,就会将列表对象 [xiaoming,xiaohong],序列化到文件 json.txt 中。
import json
with open('json.txt', 'w') as f:
json.dump([xiaoming,xiaohong], f, default=lambda obj: obj.__dict__, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2, sort_keys=True)
生成的文件内容,如下:
[
{
"address":"北京",
"ids":1,
"name":"xiaoming"
},
{
"address":"南京",
"ids":2,
"name":"xiaohong"
}
]
来源:https://github.com/jackzhenguo/python-small-examples
长按或扫描下方二维码,后台回复:加群,即可申请入群。一定要备注:来源+研究方向+学校/公司,否则不拉入群中,见谅!
(长按三秒,进入后台)
推荐阅读

