项目实战:使用 Go 构建 GraphQL API

2020/5/16 更新:大家好,我刚刚更新了该项目以使用 Go module。不幸的是,realize[1]很长时间没有更新并且无法正常工作。如果您想使用实时重新加载器,则还有其他选择,例如 air[2]。否则,请随意忽略帖子中有关 realize 的任何内容,并按通常的方式运行项目。
本博文中将使用 Go、GraphQL、PostgreSQL 创建一个 API。我已在项目结构上迭代几个版本,这是我最喜欢的一个。在大部分的时间,我创建 web APIs 都是通过 Node.js 和 Ruby/Rails。而第一次使用 Go 设计 Web apis 时,需要费很大的劲儿。Ben Johnson 的 Structuring Applications in Go[3] 文章对我有很大的帮助,本博文中的部分代码就得益于 Ben Johnson 文章的指导,推荐阅读。
配置
首先,从项目的配置开始。在本篇博文中,我将在 macOS 中完成,但这并不重要。如果在你的 macOS 上还没有 Go 和 PostGreSQL,bradford-hamilton/go-graphql-api[4] 详细讲解了如何在 macOS 上配置 Go 和 PostgreSQL.
创建一个新项目--go-graphal-api,整体项目结构如下:
├── gql
│ ├── gql.go
│ ├── queries.go
│ ├── resolvers.go
│ └── types.go
├── main.go
├── postgres
│ └── postgres.go
└── server
└── server.go
有一些额外依赖需要安装。开发中热加载的 realize[5],go-chi 的轻量级路由 chi[6] 和管理 request/response 负载的 render[7],以及 graphql-go/graphql[8]。
go get github.com/oxequa/realize
go get github.com/go-chi/chi
go get github.com/go-chi/render
go get github.com/graphql-go/graphql
go get github.com/lib/pq
最后,创建一个数据库和一些测试使用的数据,在 Postgres 的命令行中输入 psql,创建一个数据库:
CREATE DATABASE go_graphql_db;
然后连接上该库:
\c go_graphql_db
连接上后,将以下 sql 语句粘贴到命令行:
CREATE TABLE users (
id serial PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR (50) NOT NULL,
age INT NOT NULL,
profession VARCHAR (50) NOT NULL,
friendly BOOLEAN NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO users VALUES
(1, 'kevin', 35, 'waiter', true),
(2, 'angela', 21, 'concierge', true),
(3, 'alex', 26, 'zoo keeper', false),
(4, 'becky', 67, 'retired', false),
(5, 'kevin', 15, 'in school', true),
(6, 'frankie', 45, 'teller', true);
我们创建了一个基础的用户表并新增了 6 条新用户数据,对本博文来说已经足够。接下来开始构建我们的 API。
API
在这篇博文中,所有的代码片段都会包含一些注释,以帮助理解每一步。
从 main.go 开始:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"github.com/bradford-hamilton/go-graphql-api/gql"
"github.com/bradford-hamilton/go-graphql-api/postgres"
"github.com/bradford-hamilton/go-graphql-api/server"
"github.com/go-chi/chi"
"github.com/go-chi/chi/middleware"
"github.com/go-chi/render"
"github.com/graphql-go/graphql"
)
func main() {
// Initialize our API and return a pointer to our router for http.ListenAndServe
// and a pointer to our db to defer its closing when main() is finished
router, db := initializeAPI()
defer db.Close()
// Listen on port 4000 and if there's an error log it and exit
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":4000", router))
}
func initializeAPI() (*chi.Mux, *postgres.Db) {
// Create a new router
router := chi.NewRouter()
// Create a new connection to our pg database
db, err := postgres.New(
postgres.ConnString("localhost", 5432, "bradford", "go_graphql_db"),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Create our root query for graphql
rootQuery := gql.NewRoot(db)
// Create a new graphql schema, passing in the the root query
sc, err := graphql.NewSchema(
graphql.SchemaConfig{Query: rootQuery.Query},
)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error creating schema: ", err)
}
// Create a server struct that holds a pointer to our database as well
// as the address of our graphql schema
s := server.Server{
GqlSchema: &sc,
}
// Add some middleware to our router
router.Use(
render.SetContentType(render.ContentTypeJSON), // set content-type headers as application/json
middleware.Logger, // log API request calls
middleware.DefaultCompress, // compress results, mostly gzipping assets and json
middleware.StripSlashes, // match paths with a trailing slash, strip it, and continue routing through the mux
middleware.Recoverer, // recover from panics without crashing server
)
// Create the graphql route with a Server method to handle it
router.Post("/graphql", s.GraphQL())
return router, db
}
在上面导入的 gql、postgres 和 server 的路径应该是你本地的路径,以及 postgres.ConnString() 中连接 PostgreSQL 的用户名也应该是你自己的,和我的不一样。
initializeAPI() 分为几大块主要的部分,接下来我们逐步构建每一块。
使用 chi.NewRouter() 创建 router 并返回一个 mux,接下来是创建一个 PostgreSQL 数据库连接。
使用 postgres.ConnString() 创建一个 string 类型的连接配置,并封装到 postgres.New() 函数中。这些逻辑在我们自己包中的 postgres.go 文件中构建:
package postgres
import (
"database/sql"
"fmt"
// postgres driver
_ "github.com/lib/pq"
)
// Db is our database struct used for interacting with the database
type Db struct {
*sql.DB
}
// New makes a new database using the connection string and
// returns it, otherwise returns the error
func New(connString string) (*Db, error) {
db, err := sql.Open("postgres", connString)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Check that our connection is good
err = db.Ping()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &Db{db}, nil
}
// ConnString returns a connection string based on the parameters it's given
// This would normally also contain the password, however we're not using one
func ConnString(host string, port int, user string, dbName string) string {
return fmt.Sprintf(
"host=%s port=%d user=%s dbname=%s sslmode=disable",
host, port, user, dbName,
)
}
// User shape
type User struct {
ID int
Name string
Age int
Profession string
Friendly bool
}
// GetUsersByName is called within our user query for graphql
func (d *Db) GetUsersByName(name string) []User {
// Prepare query, takes a name argument, protects from sql injection
stmt, err := d.Prepare("SELECT * FROM users WHERE name=$1")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("GetUserByName Preperation Err: ", err)
}
// Make query with our stmt, passing in name argument
rows, err := stmt.Query(name)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("GetUserByName Query Err: ", err)
}
// Create User struct for holding each row's data
var r User
// Create slice of Users for our response
users := []User{}
// Copy the columns from row into the values pointed at by r (User)
for rows.Next() {
err = rows.Scan(
&r.ID,
&r.Name,
&r.Age,
&r.Profession,
&r.Friendly,
)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error scanning rows: ", err)
}
users = append(users, r)
}
return users
}
上面的思想是:创建数据库的连接并返回持有该连接的Db对象。然后创建了一个 db 的 GetUserByUsername() 方法。
将关注点重新回到 main.go 文件,在 40 行处创建了一个 root query 用于构建 GraphQL 的 schema。我们在 gql 包下的 queries.go 中创建:
package gql
import (
"github.com/bradford-hamilton/go-graphql-api/postgres"
"github.com/graphql-go/graphql"
)
// Root holds a pointer to a graphql object
type Root struct {
Query *graphql.Object
}
// NewRoot returns base query type. This is where we add all the base queries
func NewRoot(db *postgres.Db) *Root {
// Create a resolver holding our databse. Resolver can be found in resolvers.go
resolver := Resolver{db: db}
// Create a new Root that describes our base query set up. In this
// example we have a user query that takes one argument called name
root := Root{
Query: graphql.NewObject(
graphql.ObjectConfig{
Name: "Query",
Fields: graphql.Fields{
"users": &graphql.Field{
// Slice of User type which can be found in types.go
Type: graphql.NewList(User),
Args: graphql.FieldConfigArgument{
"name": &graphql.ArgumentConfig{
Type: graphql.String,
},
},
Resolve: resolver.UserResolver,
},
},
},
),
}
return &root
}
在 NewRoot() 方法中传入 db,并使用该 db 创建一个 Resolver。在Resolver方法中对数据库进行操作。
然后创建了一个 new root 用于用户的查询,需要name作为查询参数。类型是 graphql.NewList 的 User(切片或者数组类型),在 gql 包下的 type.go 文件中定义。如果有其他类型的查询,就在这个 root 中增加。要把引入的 postgres 包改成自己本地的包。
接下来看一下 resolvers.go:
package gql
import (
"github.com/bradford-hamilton/go-graphql-api/postgres"
"github.com/graphql-go/graphql"
)
// Resolver struct holds a connection to our database
type Resolver struct {
db *postgres.Db
}
// UserResolver resolves our user query through a db call to GetUserByName
func (r *Resolver) UserResolver(p graphql.ResolveParams) (interface{}, error) {
// Strip the name from arguments and assert that it's a string
name, ok := p.Args["name"].(string)
if ok {
users := r.db.GetUsersByName(name)
return users, nil
}
return nil, nil
}
这里导入的 postgres 包同样是你本地的。在这个地方还可以增加其他需要的解析器。
接下来看 types.go:
package gql
import "github.com/graphql-go/graphql"
// User describes a graphql object containing a User
var User = graphql.NewObject(
graphql.ObjectConfig{
Name: "User",
Fields: graphql.Fields{
"id": &graphql.Field{
Type: graphql.Int,
},
"name": &graphql.Field{
Type: graphql.String,
},
"age": &graphql.Field{
Type: graphql.Int,
},
"profession": &graphql.Field{
Type: graphql.String,
},
"friendly": &graphql.Field{
Type: graphql.Boolean,
},
},
},
)
类似的,在这里添加我们不同的类型,每一个字段都指定了类型。在 main.go 文件的 42 行使用 root query 创建了一个新的查询。
差不多好了
在 main.go 往下的 51 行处,创建一个新的 server,server 持有 GraphQL schema 的指针。下面是 server.go 的内容:
package server
import (
"encoding/json"
"net/http"
"github.com/bradford-hamilton/go-graphql-api/gql"
"github.com/go-chi/render"
"github.com/graphql-go/graphql"
)
// Server will hold connection to the db as well as handlers
type Server struct {
GqlSchema *graphql.Schema
}
type reqBody struct {
Query string `json:"query"`
}
// GraphQL returns an http.HandlerFunc for our /graphql endpoint
func (s *Server) GraphQL() http.HandlerFunc {
return func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// Check to ensure query was provided in the request body
if r.Body == nil {
http.Error(w, "Must provide graphql query in request body", 400)
return
}
var rBody reqBody
// Decode the request body into rBody
err := json.NewDecoder(r.Body).Decode(&rBody)
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, "Error parsing JSON request body", 400)
}
// Execute graphql query
result := gql.ExecuteQuery(rBody.Query, *s.GqlSchema)
// render.JSON comes from the chi/render package and handles
// marshalling to json, automatically escaping HTML and setting
// the Content-Type as application/json.
render.JSON(w, r, result)
}
}
在 server 中有一个 GraphQL 的方法,这个方法的主要作用就是处理 GraphQL 的查询。记得将 gql 的路径更新为你本地的路径。
接下来看最后一个文件 gql.go:
package gql
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/graphql-go/graphql"
)
// ExecuteQuery runs our graphql queries
func ExecuteQuery(query string, schema graphql.Schema) *graphql.Result {
result := graphql.Do(graphql.Params{
Schema: schema,
RequestString: query,
})
// Error check
if len(result.Errors) > 0 {
fmt.Printf("Unexpected errors inside ExecuteQuery: %v", result.Errors)
}
return result
}
这里只有一个简单的 ExecuteQuery() 函数用来执行 GraphQL 查询。在这里可能会有一个类似于 ExecuteMutation() 函数用来处理 GraphQL 的 mutations。
在 initializeAPI() 的最后,在 router 中增加一些中间工具,以及增加处理 /graphql POSTs 请求的 GraphQL server 方法。并且在这个地方增加其他 RESTful 请求的路由,并在 server 中增加处理路由的方法。
然后在项目的根目录运行 realize init,会有两次提示信息并且两次都输入 n
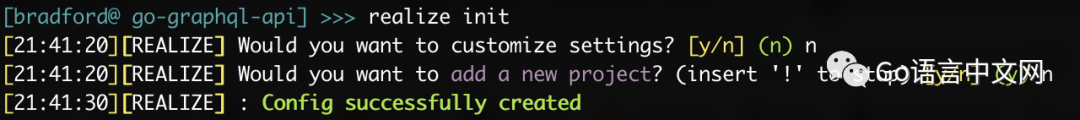
下面是在你项目的根目录下创建的 .realize.yaml 文件:
settings:
legacy:
force: false
interval: 0s
schema:
- name: go-graphql-api
path: .
commands:
run:
status: true
watcher:
extensions:
- go
paths:
- /
ignored_paths:
- .git
- .realize
- vendor
这段配置对于监控你项目里面的改变非常重要,如果检测到有改变,将自动重启 server 并重新运行 main.go 文件。
有一些开发 GraphQL API 非常好的工具,比如:graphiql[9]、insomnia[10]、graphql-playground[11],还可以发送一个 application/json 请求体的 POST 请求,比如:
{
"query": "{users(name:\"kevin\"){id, name, age}}"
}
在 Postman[12] 里像下面这样:

在查询中可以只请求一个属性或者多个属性的组合。在 GraphQL 的正式版中,可以只请求我们希望通过网络发送的信息。
很成功
大功告成!希望这篇博文对你在 Go 中编写 GraphQL API 有帮助。我尝试将功能分解到不同的包或文件中,使其更容易扩展,而且每一块也很容易测试。
via: https://medium.com/@bradford_hamilton/building-an-api-with-graphql-and-go-9350df5c9356
作者:Bradford Lamson-Scribner[13]译者:HelloJavaWorld123[14]校对:polaris1119[15]
本文由 GCTT[16] 原创编译,Go 中文网[17] 荣誉推出
参考资料
realize: https://github.com/oxequa/realize
[2]air: https://github.com/cosmtrek/air
[3]Structuring Applications in Go: https://medium.com/@benbjohnson/structuring-applications-in-go-3b04be4ff091
[4]bradford-hamilton/go-graphql-api: https://github.com/github.com/bradford-hamilton/go-graphql-api
[5]realize: https://github.com/oxequa/realize
[6]chi: https://github.com/go-chi/chi
[7]render: https://github.com/go-chi/render
[8]graphql-go/graphql: https://github.com/graphql-go/graphql
[9]graphiql: https://github.com/graphql/graphiql
[10]insomnia: https://insomnia.rest/
[11]graphql-playground: https://github.com/prisma/graphql-playground
[12]Postman: https://www.getpostman.com/
[13]Bradford Lamson-Scribner: https://medium.com/@bradford_hamilton
[14]HelloJavaWorld123: https://github.com/HelloJavaWorld123
[15]polaris1119: https://github.com/polaris1119
[16]GCTT: https://github.com/studygolang/GCTT
[17]Go 中文网: https://studygolang.com/
推荐阅读
