【47期】六大类二叉树面试题汇总解答
阅读本文大概需要 2.8 分钟。
来自:juejin.im/post/5bab8d59e51d450e925239d9
0 概述
https://github.com/shishujuan/dsalg/tree/master/code/ds/tree/binary_tree
1 判断类问题
1.1 判断一棵二叉树是否是二叉搜索树(BST)
结点的左子树所有结点的值都小于等于该结点的值。
结点的右子树所有结点的值都大于该结点的值。
结点的左右子树同样都必须是二叉搜索树。
int isBSTError(BTNode *root)
{
if (!root) return 1;
if (root->left && root->left->value >= root->value)
return 0;
if (root->right && root->right->value < root->value)
return 0;
if (!isBSTError(root->left) || !isBSTError(root->right))
return 0;
return 1;
}
10
/ \
5 15 -------- binary tree(1) 符合上述条件的二叉树,但是并不是二叉搜索树。
/ \
6 20
判断结点左子树最大值是否大于等于结点的值,如果是,则该二叉树不是二叉搜索树,否则继续下一步判断…
判断右子树最小值是否小于或等于结点的值,如果是,则不是二叉搜索树,否则继续下一步判断。
递归判断左右子树是否是二叉搜索树。(代码中的 bstMax 和 bstMin 函数功能分别是返回二叉树中的最大值和最小值结点,这里假定二叉树为二叉搜索树,实际返回的不一定是最大值和最小值结点)
int isBSTUnefficient(BTNode *root)
{
if (!root) return 1;
if (root->left && bstMax(root->left)->value >= root->value)
return 0;
if (root->right && bstMin(root->right)->value < root->value)
return 0;
if (!isBSTUnefficient(root->left) || !isBSTUnefficient(root->right))
return 0;
return 1;
}
int isBSTEfficient(BTNode* root, BTNode *left, BTNode *right)
{
if (!root) return 1;
if (left && root->value <= left->value)
return 0;
if (right && root->value > right->value)
return 0;
return isBSTEfficient(root->left, left, root) && isBSTEfficient(root->right, root, right);
}
int isBSTInOrder(BTNode *root, BTNode *prev)
{
if (!root) return 1;
if (!isBSTInOrder(root->left, prev))
return 0;
if (prev && root->value < prev->value)
return 0;
return isBSTInOrder(root->right, root);
}
1.2 判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
int isCompleteBTLevelOrder(BTNode *root)
{
if (!root) return 1;
BTNodeQueue *queue = queueNew(btSize(root));
enqueue(queue, root);
int flag = 0;
while (QUEUE_SIZE(queue) > 0) {
BTNode *node = dequeue(queue);
if (node->left) {
if (flag) return 0;
enqueue(queue, node->left);
} else {
flag = 1;
}
if (node->right) {
if (flag) return 0;
enqueue(queue, node->right);
} else {
flag = 1;
}
}
return 1;
}
10(0)
/ \
5(1) 15(2) - 结点数目为5,如果是完全二叉树结点最大的序号应该是4,而它的是6,所以不是。
/ \
6(5) 20(6)
int isCompleteBTIndexMethod(BTNode *root, int index, int nodeCount)
{
if (!root) return 1;
if (index >= nodeCount)
return 0;
return (isCompleteBTIndexMethod(root->left, 2*index+1, nodeCount) &&
isCompleteBTIndexMethod(root->right, 2*index+2, nodeCount));
}
1.3 判断平衡二叉树
__2__
/ \
1 4 ---- 平衡二叉树示例
\ / \
3 5 6
int isBalanceBTTop2Down(BTNode *root)
{
if (!root) return 1;
int leftHeight = btHeight(root->left);
int rightHeight = btHeight(root->right);
int hDiff = abs(leftHeight - rightHeight);
if (hDiff > 1) return 0;
return isBalanceBTTop2Down(root->left) && isBalanceBTTop2Down(root->right);
}
int isBalanceBTDown2Top(BTNode *root, int *height)
{
if (!root) {
*height = 0;
return 1;
}
int leftHeight, rightHeight;
if (isBalanceBTDown2Top(root->left, &leftHeight) &&
isBalanceBTDown2Top(root->right, &rightHeight)) {
int diff = abs(leftHeight - rightHeight);
return diff > 1 ? 0 : 1;
}
return 0;
}
1.4 判断两棵二叉树是否同构
5 9 6
/ \ / \ / \
1 2 7 12 5 9
/ \ / \ \
4 3 5 8 10
二叉树(1) 二叉树(2) 二叉树(3)
int isOmorphism(BTNode *t1, BTNode *t2)
{
if (!t1 || !t2)
return (!t1) && (!t2);
return isOmorphism(t1->left, t2->left) && isOmorphism(t1->right, t2->right);
}
2 构建类问题
1 1
/ /
2 2
\ /
3 3
先序遍历:1 2 3
后序遍历:3 2 1
2.1 根据先序、中序遍历构建二叉树
先序遍历:7 10 4 3 1 2 8 11
中序遍历:4 10 3 1 7 11 8 2
二叉树如下:
7
/ \
10 2
/ \ /
4 3 8
\ /
1 11
先序遍历的第一个结点总是根结点。如上图中的二叉树,根结点为 7 。
可以观察到在中序遍历中,根结点7是第 4 个值(从0开始算起)。由于中序遍历顺序为:左子树,根结点,右子树。所以根结点7左边的 {4,10,3,1} 这四个结点属于左子树,而根结点7右边的 {11,8,2} 属于右子树。
据此可以写出递归式了。注意关于如何得到根结点在中序遍历中的位置代码中使用线性扫描查找位置,每次查找需要 O(N) 的时间,整个算法需要 O(N^2) 的时间。如果要提高效率,也可以哈希表来存储与查找根结点在中序遍历中的位置,每次查找只需要 O(1) 的时间,这样构建整棵树只需要 O(N)的时间。
调用方法为 buildBTFromPreInOrder(preorder, inorder, n, 0, n);,其中 preorder 和 inorder 分别为先序中序遍历数组,n 为数组大小。
/**
* 辅助函数,查找根结点在中序遍历中的位置。
*/
int findBTRootIndex(int inorder[], int count, int rootVal)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (inorder[i] == rootVal)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
/**
/**
* 根据先序和中序遍历构建二叉树
*/
BTNode *buildBTFromPreInOrder(int preorder[], int inorder[], int n, int offset, int count)
{
if (n == 0) return NULL;
int rootVal = preorder[0];
int rootIndex = findBTRootIndex(inorder, count, rootVal);
int leftCount = rootIndex - offset; // 左子树结点数目
int rightCount = n - leftCount - 1; // 右子树结点数目
BTNode *root = btNewNode(rootVal);
root->left = buildBTFromPreInOrder(preorder+1, inorder, leftCount, offset, count);
root->right = buildBTFromPreInOrder(preorder+leftCount+1, inorder, rightCount, offset+leftCount+1, count);
return root;
}
2.2 根据中序、后序遍历构建二叉树
中序遍历:4 10 3 1 7 11 8 2
后序遍历:4 1 3 10 11 8 2 7
二叉树如下:
7
/ \
10 2
/ \ /
4 3 8
\ /
1 11
/**
* 根据中序和后序遍历构建二叉树
*/
BTNode *buildBTFromInPostOrder(int postorder[], int inorder[], int n, int offset, int count)
{
if (n == 0) return NULL;
int rootVal = postorder[n-1];
int rootIndex = findBTRootIndex(inorder, count, rootVal);
int leftCount = rootIndex - offset; // 左子树结点数目
int rightCount = n - leftCount - 1; // 右子树结点数目
BTNode *root = btNewNode(rootVal);
root->left = buildBTFromInPostOrder(postorder, inorder, leftCount, offset, count);
root->right = buildBTFromInPostOrder(postorder+leftCount, inorder, rightCount, offset+leftCount+1, count);
return root;
}
3 存储类问题
3.1 二叉搜索树存储和恢复
30
/ \
20 40
/ / \
10 35 50
50
/
40
/
35
/
30
/
20
/
10
/**
* 存储二叉树到文件中-使用先序遍历
*/
void bstSave(BTNode *root, FILE *fp)
{
if (!root) return;
char temp[30];
sprintf(temp, "%d\n", root->value);
fputs(temp, fp);
bstSave(root->left, fp);
bstSave(root->right, fp);
}
/**
* 从文件中恢复二叉树
*/
BTNode *bstRestore(FILE *fp)
{
BTNode *root = NULL;
char *s;
char buf[30];
while ((s = fgets(buf, 30, fp))) {
int nodeValue = atoi(s);
root = bstInsert(root, nodeValue);
}
return root;
}
3.2 二叉树存储和恢复
注意:本题采用 # 保存 NULL 结点的方法存在缺陷,如本方法中二叉树结点值就不能是 #。如果要能保存各种字符,则需要采用其他方法来实现了。
30
/ \
10 20
/ / \
50 45 35
/**
* 存储二叉树到文件中
*/
void btSave(BTNode *root, FILE *fp)
{
if (!root) {
fputs("#\n", fp);
} else {
char temp[30];
sprintf(temp, "%d\n", root->value);
fputs(temp, fp);
btSave(root->left, fp);
btSave(root->right, fp);
}
}
/**
* 从文件恢复二叉树
*/
BTNode *btRestore(BTNode *root, FILE *fp)
{
char buf[30];
char *s = fgets(buf, 30, fp);
if (!s || strcmp(s, "#\n") == 0)
return NULL;
int nodeValue = atoi(s);
root = btNewNode(nodeValue);
root->left = btRestore(root->left, fp);
root->right = btRestore(root->right, fp);
return root;
}
4 查找类问题
4.1 二叉搜索树最低公共祖先结点
______6______
/ \
__2__ __8__
/ \ / \
0 4 7 9
/ \
3 5
两个结点都在树的左子树中:LCA一定在当前遍历结点的左子树中。
两个结点都在树的右子树中:LCA一定在当前遍历结点右子树中。
一个结点在树的左边,一个结点在树的右边:LCA就是当前遍历的结点。
当前结点等于这两个结点中的一个:LCA也是当前遍历的结点。
BTNode *bstLCA(BTNode *root, BTNode *p, BTNode *q)
{
if (!root || !p || !q) return NULL;
int maxValue = p->value >= q->value ? p->value : q->value;
int minValue = p->value < q->value ? p->value : q->value;
if (maxValue < root->value) {
return bstLCA(root->left, p, q);
} else if (minValue > root->value) {
return bstLCA(root->right, p, q);
} else {
return root;
}
}
4.2 二叉树(不一定是BST)最低公共祖先结点
_______3______
/ \
___5__ ___1__
/ \ / \
6 2 0 8
/ \
7 4
如果左子树包含两个结点,则它们的最低公共祖先结点也一定在左子树中。
如果右子树包含两个结点,则它们的最低公共祖先结点也一定在右子树中。
如果一个结点在左子树,而另一个结点在右子树中,则当前结点就是它们的最低公共祖先结点。
/**
* 二叉树最低公共祖先结点-自顶向下解法 O(N^2)
*/
BTNode *btLCATop2Down(BTNode *root, BTNode *p, BTNode *q)
{
if (!root || !p || !q) return NULL;
if (btExist(root->left, p) && btExist(root->left, q)) {
return btLCATop2Down(root->left, p, q);
} else if (btExist(root->right, p) && btExist(root->right, q)) {
return btLCATop2Down(root->right, p, q);
} else {
return root;
}
}
/**
* 二叉树结点存在性判断
*/
int btExist(BTNode *root, BTNode *node)
{
if (!root) return 0;
if (root == node) return 1;
return btExist(root->left, node) || btExist(root->right, node);
}
/**
* 二叉树最低公共祖先结点-自底向上解法 O(N)
*/
BTNode *btLCADown2Top(BTNode *root, BTNode *p, BTNode *q)
{
if (!root) return NULL;
if (root == p || root == q) return root;
BTNode *left = btLCADown2Top(root->left, p, q);
BTNode *right = btLCADown2Top(root->right, p, q);
if (left && right)
return root; // 如果p和q位于不同的子树
return left ? left: right; //p和q在相同的子树,或者p和q不在子树中
}
4.3 二叉树的最大二叉搜索子树
___10___
/ \
_5_ 15
/ \ \
1 8 7
___10____
/ \
_5_ 15 -------- subtree (1)
/ \
1 8
_5_
/ \ -------- subtree (2)
1 8
/**
* 查找二叉树最大的二叉搜索子树-自顶向下方法
*/
BTNode *largestSubBSTTop2Down(BTNode *root, int *bstSize)
{
if (!root) {
*bstSize = 0;
return NULL;
}
if (isBSTEfficient(root, NULL, NULL)) { //以root为根结点的树为BST,则设置结果为root并返回。
*bstSize = btSize(root);
return root;
}
int lmax, rmax;
BTNode *leftBST = largestSubBSTTop2Down(root->left, &lmax); //找出左子树中为BST的最大的子树
BTNode *rightBST = largestSubBSTTop2Down(root->right, &rmax); //找出右子树中为BST的最大的子树
*bstSize = lmax > rmax ? lmax : rmax; //设定结点最大数目
BTNode *result = lmax > rmax ? leftBST : rightBST;
return result;
}
/**
* 查找二叉树最大的二叉搜索子树-自底向上方法
*/
BTNode *largestSubBSTDown2Top(BTNode *root, int *bstSize)
{
BTNode *largestBST = NULL;
int min, max, maxNodes=0;
findLargestSubBST(root, &min, &max, &maxNodes, &largestBST);
*bstSize = maxNodes;
return largestBST;
}
/**
* 查找最大二叉搜索子树自底向上方法主体函数
* 如果是BST,则返回BST的结点数目,否则返回-1
*/
int findLargestSubBST(BTNode *root, int *min, int *max, int *maxNodes, BTNode **largestSubBST)
{
if (!root) return 0;
int isBST = 1;
int leftNodes = findLargestSubBST(root->left, min, max, maxNodes, largestSubBST);
int currMin = (leftNodes == 0) ? root->value : *min;
if (leftNodes == -1 || (leftNodes != 0 && root->value <= *max))
isBST = 0;
int rightNodes = findLargestSubBST(root->right, min, max, maxNodes, largestSubBST);
int currMax = (rightNodes == 0) ? root->value : *max;
if (rightNodes == -1 || (rightNodes != 0 && root->value > *min))
isBST = 0;
if (!isBST)
return -1;
*min = currMin;
*max = currMax;
int totalNodes = leftNodes + rightNodes + 1;
if (totalNodes > *maxNodes) {
*maxNodes = totalNodes;
*largestSubBST = root;
}
return totalNodes;
}
5 距离类问题
5.1 二叉树两个结点之间的最短距离
___1___
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
\
8
Distance(4, 5) = 2
Distance(4, 6) = 4
Distance(3, 4) = 3
Distance(2, 4) = 1
Distance(8, 5) = 5
/**
* 计算二叉树两个结点最短距离
*/
int distanceOf2BTNodes(BTNode *root, BTNode *p, BTNode *q)
{
if (!root) return 0;
BTNode *lca = btLCADown2Top(root, p, q);
int d1 = btDistanceFromRoot(lca, p, 0);
int d2 = btDistanceFromRoot(lca, q, 0);
return d1+d2;
}
/**
* 计算二叉树结点node和root的距离
*/
int btDistanceFromRoot(BTNode *root, BTNode *node, int level)
{
if (!root) return -1;
if (root == node) return level;
int left = btDistanceFromRoot(root->left, node, level+1);
if (left == -1)
return btDistanceFromRoot(root->right, node, level+1);
return left;
}
5.2 二叉搜索树两个结点的最短距离
/**
* 计算BST两个结点最短距离。
*/
int distanceOf2BSTNodes(BTNode *root, BTNode *p, BTNode *q)
{
if (!root) return 0;
if (root->value > p->value && root->value > q->value) {
return distanceOf2BSTNodes(root->left, p, q);
} else if(root->value <= p->value && root->value <= q->value){
return distanceOf2BSTNodes(root->right, p, q);
} else {
return bstDistanceFromRoot(root, p) + bstDistanceFromRoot(root, q);
}
}
/**
* 计算BST结点node和root的距离
*/
int bstDistanceFromRoot(BTNode *root, BTNode *node)
{
if (root->value == node->value)
return 0;
else if (root->value > node->value)
return 1 + bstDistanceFromRoot(root->left, node);
else
return 1 + bstDistanceFromRoot(root->right, node);
}
5.3 二叉树中结点的最大距离
路径为 左子树的最深节点 -> 根节点 -> 右子树的最深节点。
路径不穿过根节点,而是左子树或右子树的最大距离路径,取其大者。
___10___
/ \
_5_ 15 ------ 第1种情况
/ \ \
1 8 7
10
/
5
/ \ ------ 第2种情况
1 8
/ \
2 3
int btMaxDistance(BTNode *root, int *maxDepth)
{
if (!root) {
*maxDepth = 0;
return 0;
}
int leftMaxDepth, rightMaxDepth;
int leftMaxDistance = btMaxDistance(root->left, &leftMaxDepth);
int rightMaxDistance = btMaxDistance(root->right, &rightMaxDepth);
*maxDepth = max(leftMaxDepth+1, rightMaxDepth+1);
int maxDistance = max3(leftMaxDistance, rightMaxDistance, leftMaxDepth+rightMaxDepth); // max求两个数最大值,max3求三个数最大值,详见代码
return maxDistance;
}
5.4 二叉树最大宽度
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ \
4 5 8
/ \
6 7
/**
* 二叉树最大宽度
*/
int btMaxWidth(BTNode *root)
{
int h = btHeight(root);
int level, width;
int maxWidth = 0;
for (level = 1; level <= h; level++) {
width = btLevelWidth(root, level);
if (width > maxWidth)
maxWidth = width;
}
return maxWidth;
}
/**
* 二叉树第level层的宽度
*/
int btLevelWidth(BTNode *root, int level)
{
if (!root) return 0;
if (level == 1) return 1;
return btLevelWidth(root->left, level-1) + btLevelWidth(root->right, level-1);
}
/**
* 二叉树最大宽度-先序遍历法
*/
int btMaxWidthPreOrder(BTNode *root)
{
int h = btHeight(root);
int *count = (int *)calloc(sizeof(int), h);
btLevelWidthCount(root, 0, count);
int i, maxWidth = 0;
for (i = 0; i < h; i++) {
if (count[i] > maxWidth)
maxWidth = count[i];
}
return maxWidth;
}
/**
* 计算二叉树从 level 开始的每层宽度,并存储到数组 count 中。
*/
void btLevelWidthCount(BTNode *root, int level, int count[])
{
if (!root) return;
count[level]++;
btLevelWidthCount(root->left, level+1, count);
btLevelWidthCount(root->right, level+1, count);
}
6 混合类问题
6.1 根据有序数组构建平衡二叉搜索树
__3__
/ \
1 5 ---- 平衡二叉搜索树示例
\ / \
2 4 6
BTNode *sortedArray2BST(int a[], int start, int end)
{
if (start > end) return NULL;
int mid = start + (end-start)/2;
BTNode *root = btNewNode(a[mid]);
root->left = sortedArray2BST(a, start, mid-1);
root->right = sortedArray2BST(a, mid+1, end);
return root;
}
6.2 有序单向链表构建平衡二叉搜索树
BTNode *sortedList2BST(ListNode **pList, int start, int end)
{
if (start > end) return NULL;
int mid = start + (end-start)/2;
BTNode *left = sortedList2BST(pList, start, mid-1);
BTNode *parent = btNewNode((*pList)->value);
parent->left = left;
*pList = (*pList)->next;
parent->right = sortedList2BST(pList, mid+1, end);
return parent;
}
6.3 二叉搜索树转换为有序循环链表
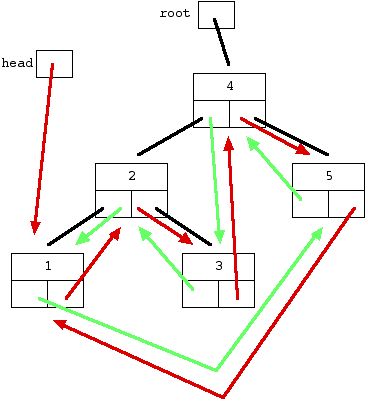
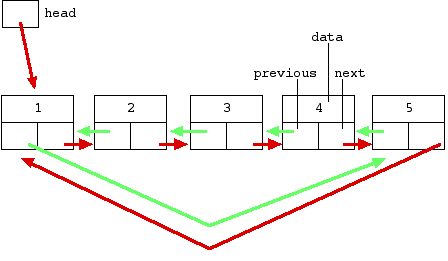
void bt2DoublyList(BTNode *node, BTNode **pPrev, BTNode **pHead)
{
if (!node) return;
bt2DoublyList(node->left, pPrev, pHead);
// 当前结点的left指向前一个结点pPrev
node->left = *pPrev;
if (*pPrev)
(*pPrev)->right = node; // 前一个结点的right指向当前结点
else
*pHead = node; // 如果前面没有结点,则设置head为当前结点(当前结点为最小的结点)。
// 递归结束后,head的left指针指向最后一个结点,最后一个结点的右指针指向head结点。
// 注意保存当前结点的right指针,因为在后面代码中会修改该指针。
BTNode *right = node->right;
(*pHead)->left = node;
node->right = (*pHead);
*pPrev = node;//更新前一个结点
bt2DoublyList(right, pPrev, pHead);
}
推荐阅读:
微信扫描二维码,关注我的公众号
朕已阅