自学HarmonyOS应用开发(58)- 接受来自Service的通知

PageAbility和ServiceAbility之间的交互可以有两种方式:一种是主动查询,也就是自学HarmonyOS应用开发(57)- 与Service进行交互中介绍的方式,还有一种是被动接受来自ServiceAbility的通知。本文介绍后一种方式。
涉及到的类比较多,关系比较复杂:
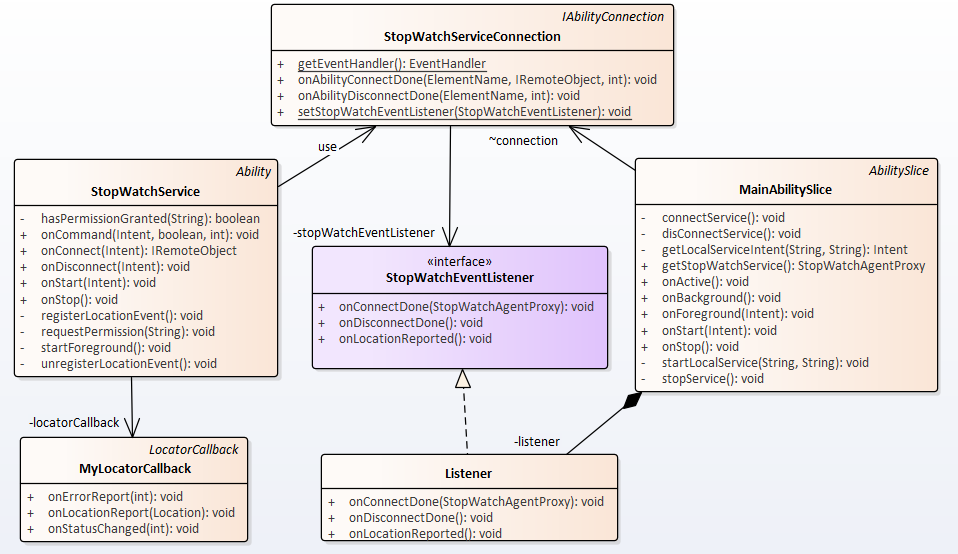
接受通知的接口类
首先在StopWatchServiceConnection类中定义接受ServiceAbilitty通知的接口类:
public interface StopWatchEventListener{void onConnectDone(StopWatchAgentProxy proxy);void onDisconnectDone();void onLocationReported();}
三个方法分别用于接受服务连接/切断和位置信息更新通知。
接下来在MainAbilitySlice中定义实现StopWatchEventListener接口的listener:
StopWatchServiceConnection.StopWatchEventListener listener = new StopWatchServiceConnection.StopWatchEventListener(){public void onConnectDone(StopWatchAgentProxy proxy) {stopWatchProxy = proxy;...}public void onDisconnectDone() {stopWatchProxy = null;}public void onLocationReported() {...}};
此处省略实际的处理过程,而将重点放在如何建立和利用通知渠道上。
建立通知渠道
在MainAbilitySlice建立与StopWatchService之间连接时,同时将listener登录到StopWatchConnection上:
private void connectService() {HiLog.info(LOG_LABEL, "MainAbilitySlice.connectService!");Intent intent = getLocalServiceIntent(LOCAL_BUNDLE, FOREGROUND_SERVICE);connection = new StopWatchServiceConnection();connection.setStopWatchEventListener(listener);connectAbility(intent, connection);}
定位信息通知过程
通过下图说明地图数据更新的过程:
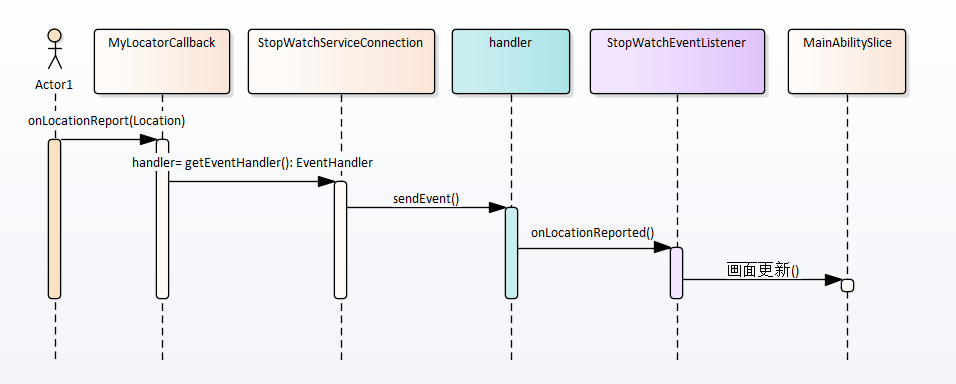
StopWatchService中的MyLocatorCallback接收到定位信息之后,获取StopWatchConnection的handler示例
MyLocatorCallback通过sendEvent向hander发送事件通知
hander进行上下文切换之后,调用StopWatchEventListener的onLocationReported方法。而这个实例就是MainAbilitySlice事先登录的那个。
StopWatchEventListener的onLocationReported中调用MainAbilitySlice的画面更新方法。
参考代码
完整代码可以从以下链接下载:
https://github.com/xueweiguo/Harmony/tree/master/StopWatch
华为官方示例代码:
https://gitee.com/openharmony/app_samples/tree/master/ability/AbilityConnection
作者著作介绍
《实战Python设计模式》是作者去年3月份出版的技术书籍,该书利用Python 的标准GUI 工具包tkinter,通过可执行的示例对23 个设计模式逐个进行说明。这样一方面可以使读者了解真实的软件开发工作中每个设计模式的运用场景和想要解决的问题;另一方面通过对这些问题的解决过程进行说明,让读者明白在编写代码时如何判断使用设计模式的利弊,并合理运用设计模式。

对设计模式感兴趣而且希望随学随用的读者通过本书可以快速跨越从理解到运用的门槛;希望学习Python GUI 编程的读者可以将本书中的示例作为设计和开发的参考;使用Python 语言进行图像分析、数据处理工作的读者可以直接以本书中的示例为基础,迅速构建自己的系统架构。
觉得本文有帮助?请分享给更多人。
关注微信公众号【面向对象思考】轻松学习每一天!
面向对象开发,面向对象思考!
