spring:我是如何解决循环依赖的?
1.由同事抛的一个问题开始
最近项目组的一个同事遇到了一个问题,问我的意见,一下子引起的我的兴趣,因为这个问题我也是第一次遇到。平时自认为对spring循环依赖问题还是比较了解的,直到遇到这个和后面的几个问题后,重新刷新了我的认识。
我们先看看当时出问题的代码片段:
@Service
public class TestService1 {
@Autowired
private TestService2 testService2;
@Async
public void test1() {
}
}
@Service
public class TestService2 {
@Autowired
private TestService1 testService1;
public void test2() {
}
}
这两段代码中定义了两个Service类:TestService1和TestService2,在TestService1中注入了TestService2的实例,同时在TestService2中注入了TestService1的实例,这里构成了循环依赖。
只不过,这不是普通的循环依赖,因为TestService1的test1方法上加了一个@Async注解。
大家猜猜程序启动后运行结果会怎样?
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCurrentlyInCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'testService1': Bean with name 'testService1' has been injected into other beans [testService2] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using 'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.
报错了。。。原因是出现了循环依赖。
「不科学呀,spring不是号称能解决循环依赖问题吗,怎么还会出现?」
如果把上面的代码稍微调整一下:
@Service
public class TestService1 {
@Autowired
private TestService2 testService2;
public void test1() {
}
}
把TestService1的test1方法上的@Async注解去掉,TestService1和TestService2都需要注入对方的实例,同样构成了循环依赖。
但是重新启动项目,发现它能够正常运行。这又是为什么?
带着这两个问题,让我们一起开始spring循环依赖的探秘之旅。
2.什么是循环依赖?
循环依赖:说白是一个或多个对象实例之间存在直接或间接的依赖关系,这种依赖关系构成了构成一个环形调用。
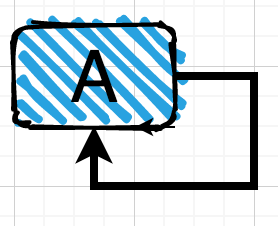
第一种情况:自己依赖自己的直接依赖
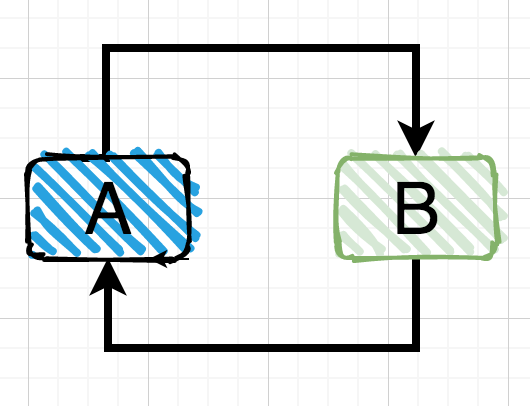
第二种情况:两个对象之间的直接依赖
第三种情况:多个对象之间的间接依赖
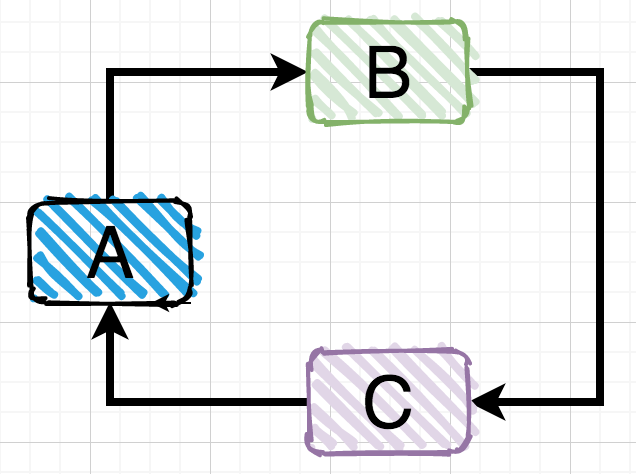
前面两种情况的直接循环依赖比较直观,非常好识别,但是第三种间接循环依赖的情况有时候因为业务代码调用层级很深,不容易识别出来。
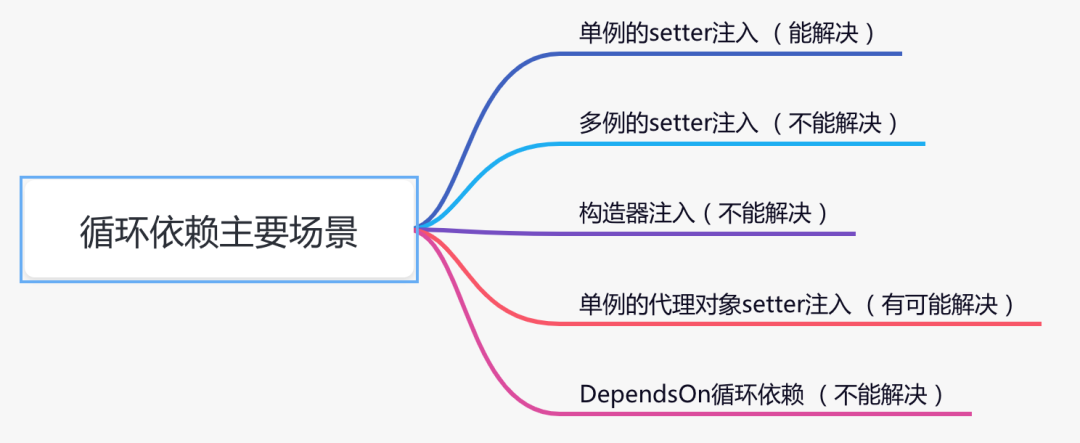
3.循环依赖的N种场景
spring中出现循环依赖主要有以下场景:
单例的setter注入
这种注入方式应该是spring用的最多的,代码如下:
@Service
public class TestService1 {
@Autowired
private TestService2 testService2;
public void test1() {
}
}
@Service
public class TestService2 {
@Autowired
private TestService1 testService1;
public void test2() {
}
}
这是一个经典的循环依赖,但是它能正常运行,得益于spring的内部机制,让我们根本无法感知它有问题,因为spring默默帮我们解决了。
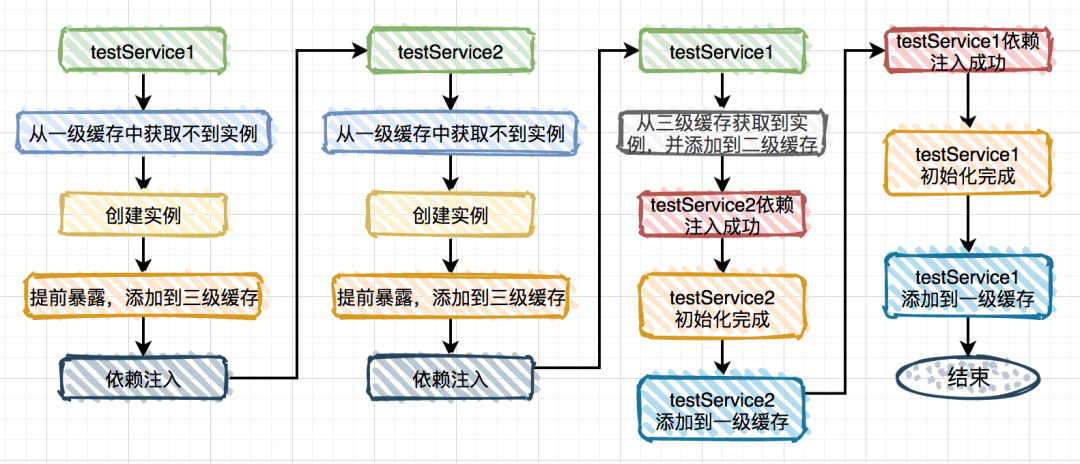
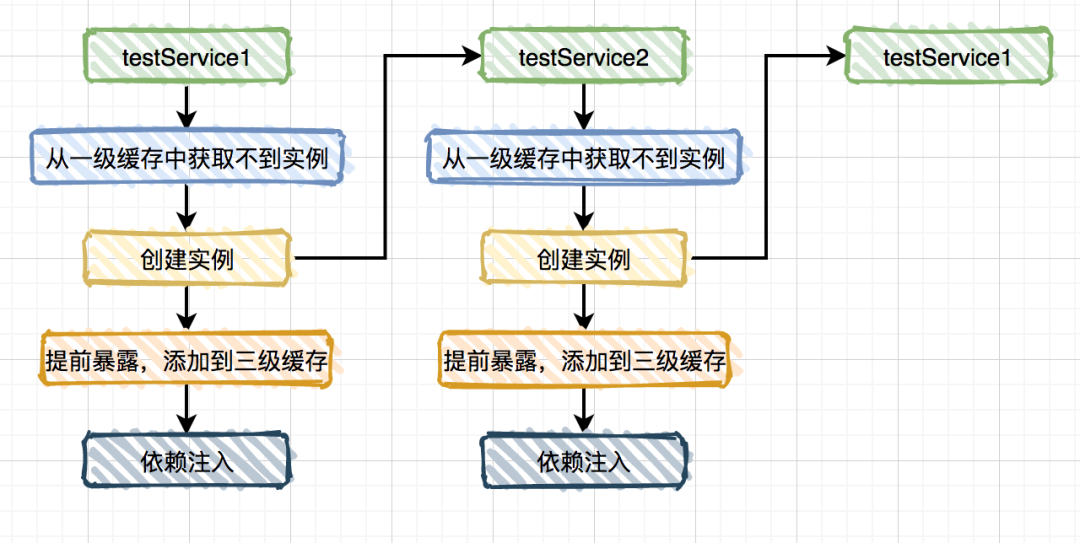
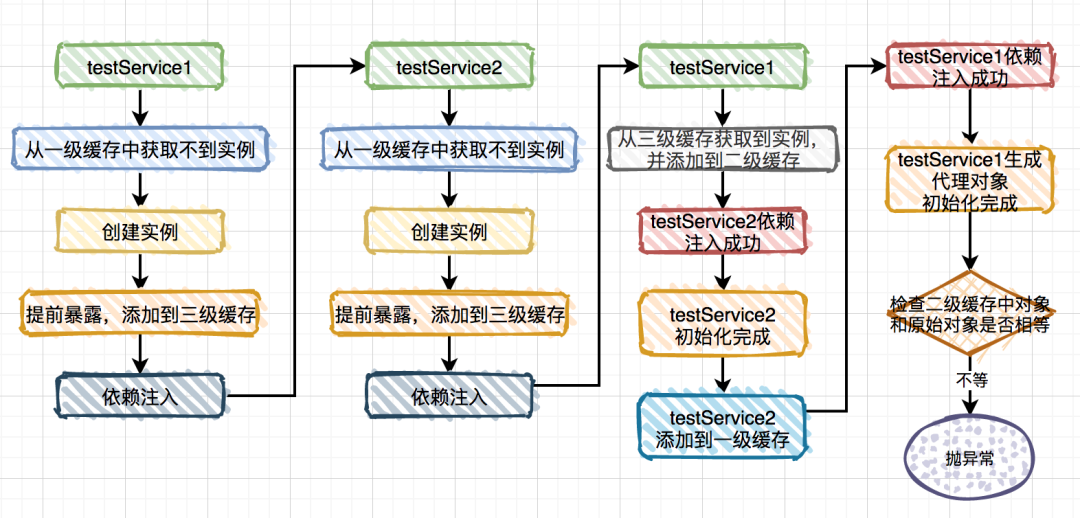
spring内部有三级缓存:
singletonObjects 一级缓存,用于保存实例化、注入、初始化完成的bean实例 earlySingletonObjects 二级缓存,用于保存实例化完成的bean实例 singletonFactories 三级缓存,用于保存bean创建工厂,以便于后面扩展有机会创建代理对象。
@Service
public class TestService1 {
@Autowired
private TestService2 testService2;
@Autowired
private TestService3 testService3;
public void test1() {
}
}
@Service
public class TestService2 {
@Autowired
private TestService1 testService1;
public void test2() {
}
}
@Service
public class TestService3 {
@Autowired
private TestService1 testService1;
public void test3() {
}
}
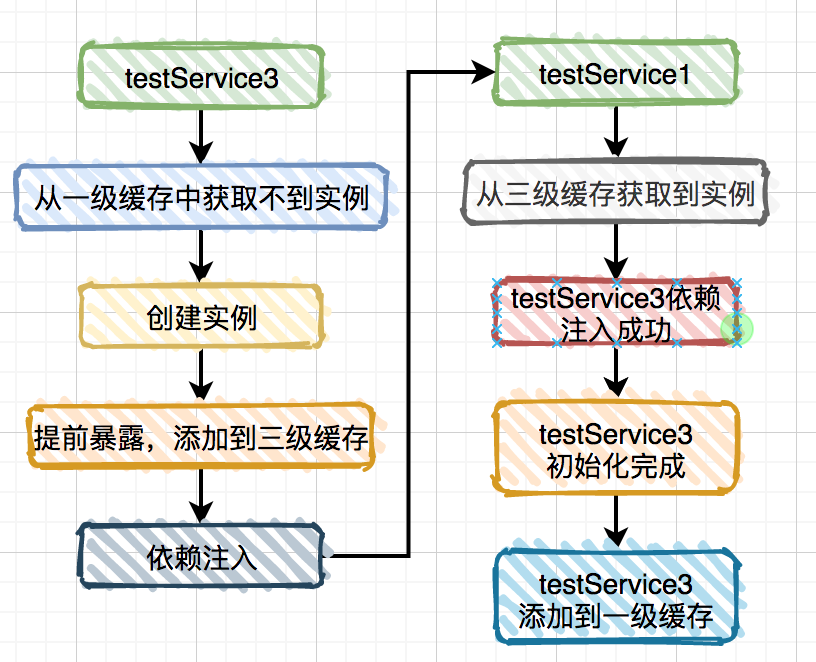
ObjectFactory对象。说白了,两次从三级缓存中获取都是ObjectFactory对象,而通过它创建的实例对象每次可能都不一样的。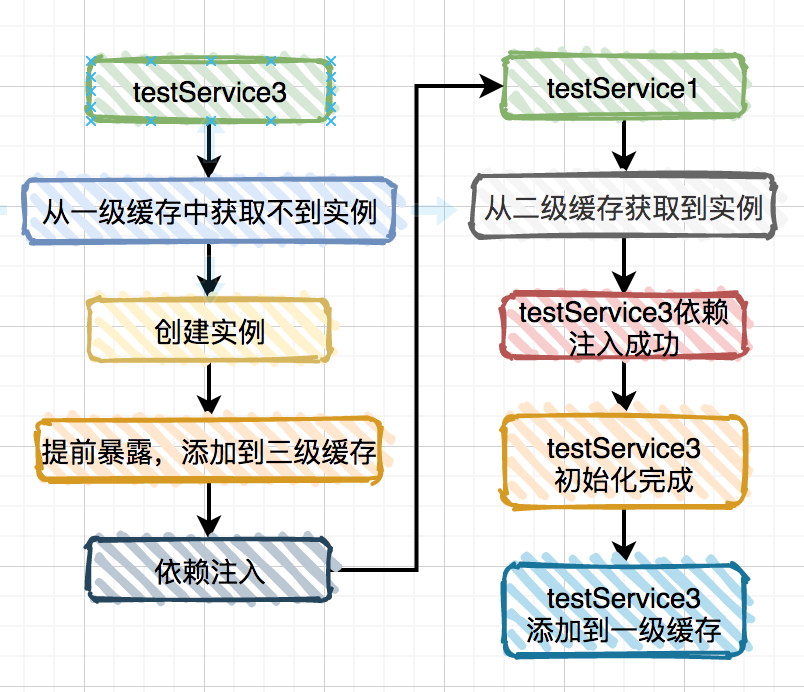
ObjectFactory对象,直接保存实例对象不行吗?AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类doCreateBean方法的这段代码中: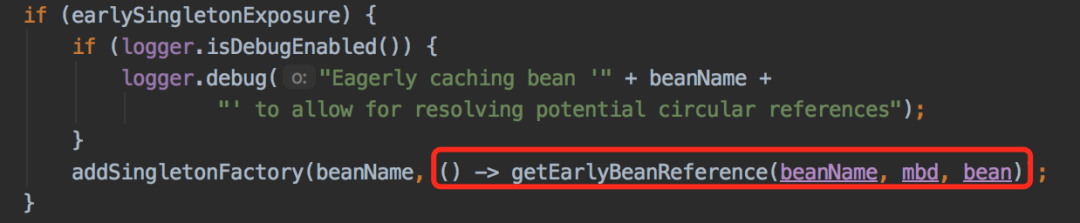
getEarlyBeanReference方法获取代理对象,其实底层是通过AbstractAutoProxyCreator类的getEarlyBeanReference生成代理对象。多例的setter注入
@Scope(ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
@Service
public class TestService1 {
@Autowired
private TestService2 testService2;
public void test1() {
}
}
@Scope(ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
@Service
public class TestService2 {
@Autowired
private TestService1 testService1;
public void test2() {
}
}
AbstractApplicationContext类的refresh方法中告诉了我们答案,它会调用finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法,该方法的作用是为了spring容器启动的时候提前初始化一些bean。该方法的内部又调用了preInstantiateSingletons方法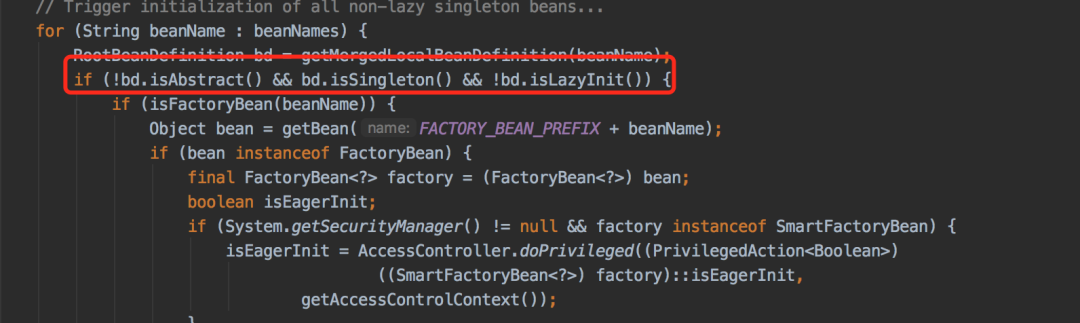
SCOPE_PROTOTYPE类型的类,非单例,不会被提前初始化bean,所以程序能够正常启动。@Service
public class TestService3 {
@Autowired
private TestService1 testService1;
}
Requested bean is currently in creation: Is there an unresolvable circular reference?
构造器注入
@Service
public class TestService1 {
public TestService1(TestService2 testService2) {
}
}
@Service
public class TestService2 {
public TestService2(TestService1 testService1) {
}
}
Requested bean is currently in creation: Is there an unresolvable circular reference?
单例的代理对象setter注入
@Async注解的场景,会通过AOP自动生成代理对象。@Service
public class TestService1 {
@Autowired
private TestService2 testService2;
@Async
public void test1() {
}
}
@Service
public class TestService2 {
@Autowired
private TestService1 testService1;
public void test2() {
}
}
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCurrentlyInCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'testService1': Bean with name 'testService1' has been injected into other beans [testService2] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using 'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.
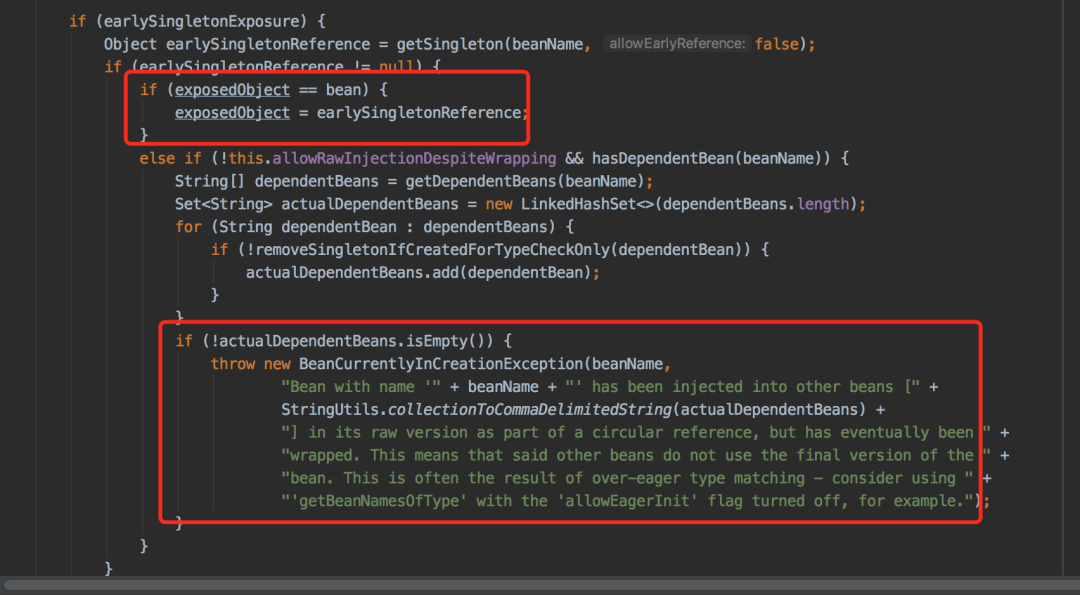
@Service
publicclass TestService6 {
@Autowired
private TestService2 testService2;
@Async
public void test1() {
}
}
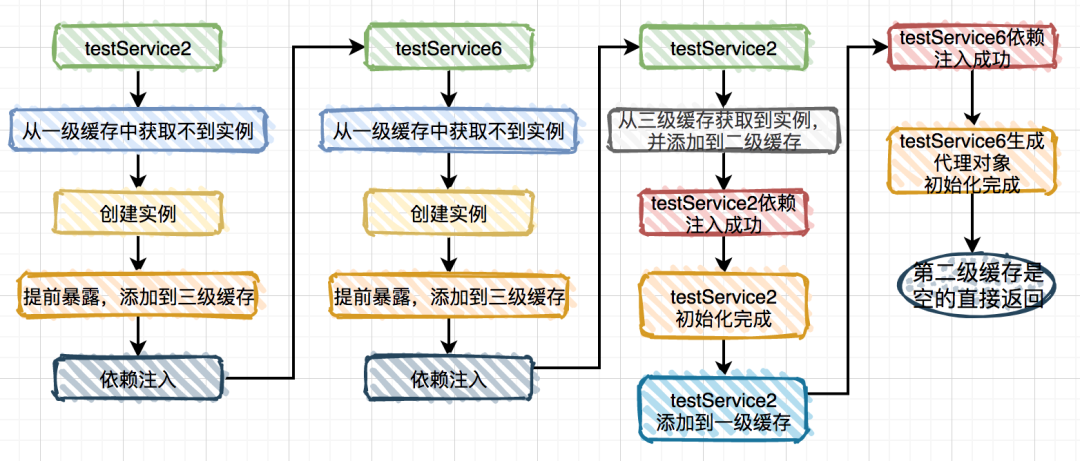
DependsOn循环依赖
@DependsOn注解。@DependsOn(value = "testService2")
@Service
public class TestService1 {
@Autowired
private TestService2 testService2;
public void test1() {
}
}
@DependsOn(value = "testService1")
@Service
public class TestService2 {
@Autowired
private TestService1 testService1;
public void test2() {
}
}
Circular depends-on relationship between 'testService2' and 'testService1'
@DependsOn注解是没问题的,反而加了这个注解会出现循环依赖问题。AbstractBeanFactory类的doGetBean方法的这段代码中: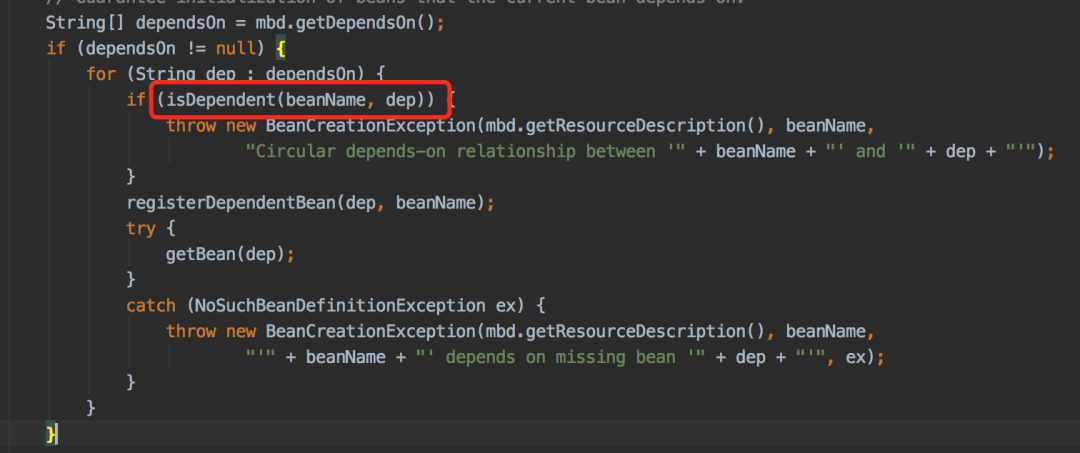
4.出现循环依赖如何解决?
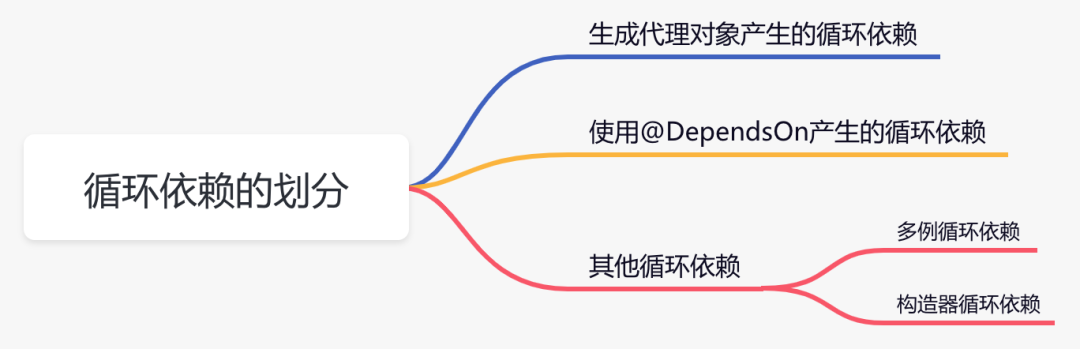
生成代理对象产生的循环依赖
使用 @Lazy注解,延迟加载使用 @DependsOn注解,指定加载先后关系修改文件名称,改变循环依赖类的加载顺序
使用@DependsOn产生的循环依赖
@DependsOn注解循环依赖的地方,迫使它不循环依赖就可以解决问题。多例循环依赖
构造器循环依赖
@Lazy注解解决。有道无术,术可成;有术无道,止于术
欢迎大家关注Java之道公众号
好文章,我在看❤️
