std 源码剖析及 C++ 内存管理(二)

大家好,我是唐唐!
本文关于 C++ 内存管理学习笔记自侯捷,上次笔记见 C++ 内存管理(一)。
1.各个标准分配器实现
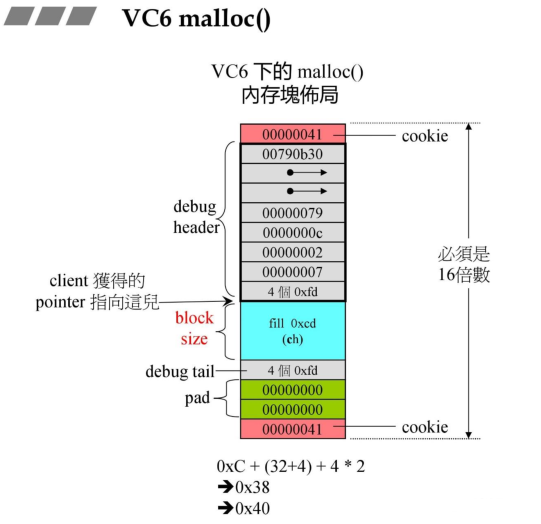
1.1 VC6.0 malloc
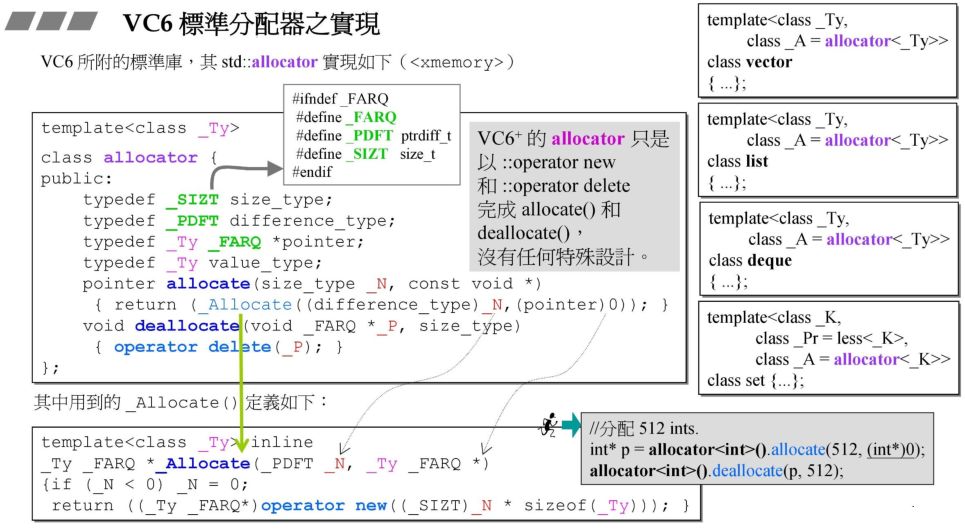
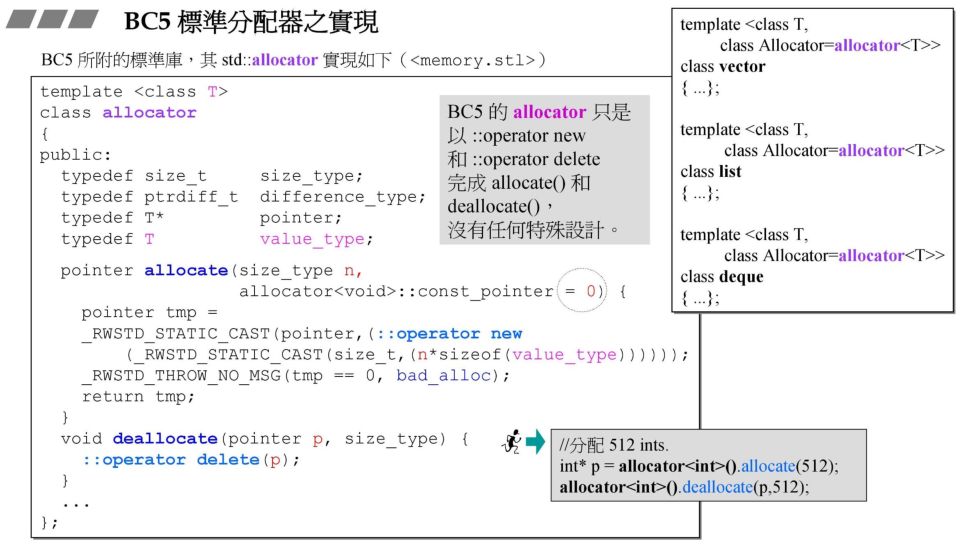
1.2 VC6.0标准分配器
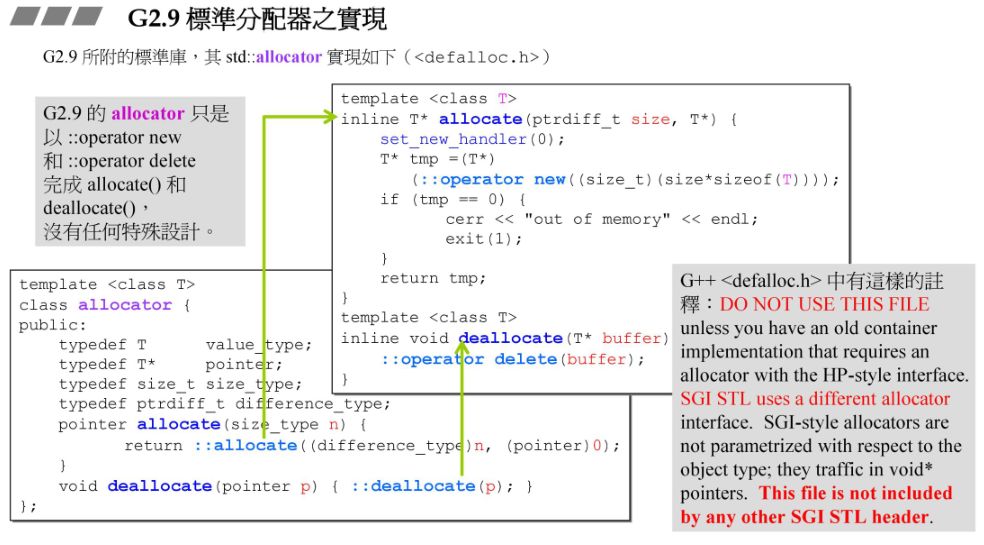
1.3 G2.9 malloc
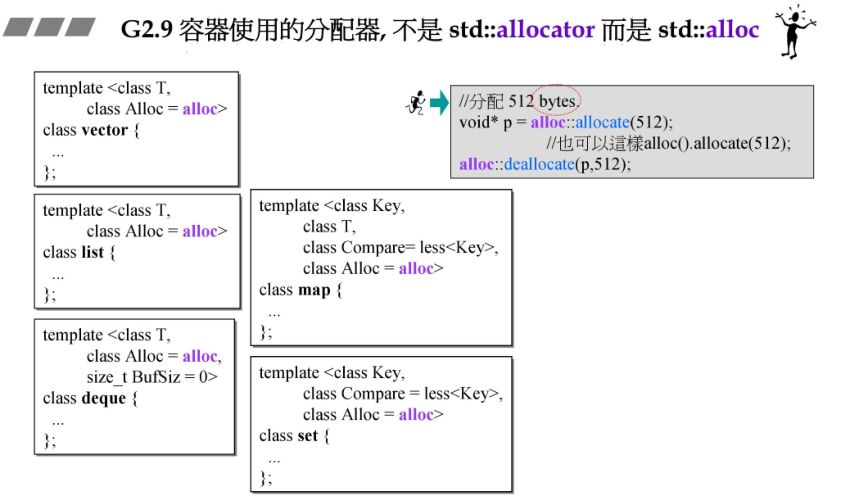
1.4 G4.9 malloc
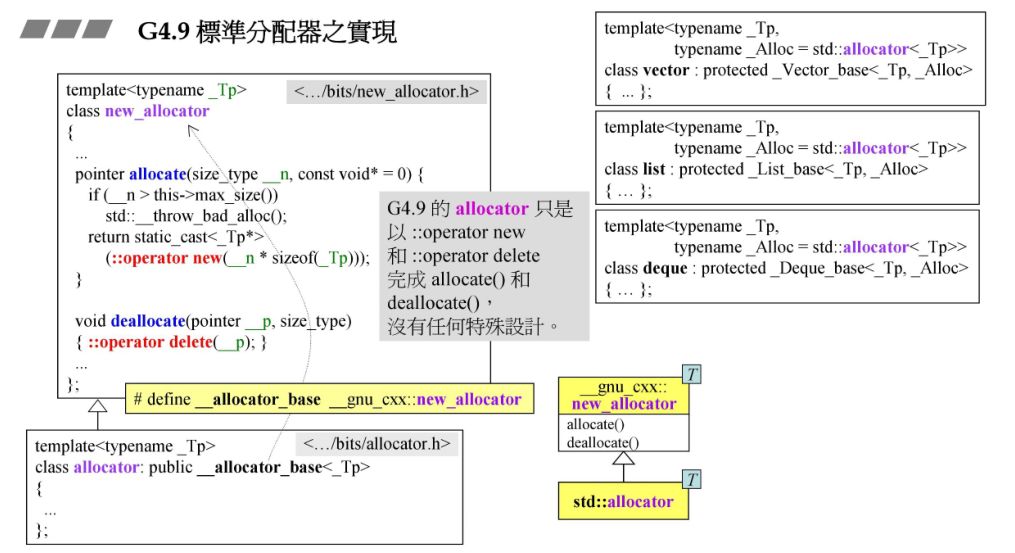
1.5 G4.9结构
#include <iostream>#include <vector>#include <ext/pool_allocator.h>using namespace std;template<typename Alloc>void cookie_test(Alloc alloc, size_t n){typename Alloc::value_type *p1, *p2, *p3;//需有 typenamep1 = alloc.allocate(n); //allocate() and deallocate() 是 non-static, 需以 object 呼叫之.p2 = alloc.allocate(n);p3 = alloc.allocate(n);cout << "p1= " << p1 << '\t' << "p2= " << p2 << '\t' << "p3= " << p3 << '\n';alloc.deallocate(p1,sizeof(typename Alloc::value_type)); //需有 typenamealloc.deallocate(p2,sizeof(typename Alloc::value_type)); //有些 allocator 對於 2nd argument 的值無所謂alloc.deallocate(p3,sizeof(typename Alloc::value_type));}int main(void){cout << sizeof(__gnu_cxx::__pool_alloc<double>) << endl;vector<int, __gnu_cxx::__pool_alloc<double> > vecPool;cookie_test(__gnu_cxx::__pool_alloc<double>(), 1);cout << "----------------------" << endl;cout << sizeof(std::allocator<double>) << endl;vector<int, std::allocator<double> > vecPool2;cookie_test(std::allocator<double>(), 1);return 0;}
1p1= 0x5557fc0f1280p2= 0x5557fc0f1288p3= 0x5557fc0f1290----------------------1p1= 0x5557fc0f13d0p2= 0x5557fc0f13f0p3= 0x5557fc0f14102.std::alloc
2.1 G2.9 运作模式
32*20*2 大小,用一条链表管理,然后让数组的#3链表指针管理这条链表。接着讲该以 32 为一个单元的链表的中的一个单元( 32 字节)分给用户。(对应图中绿色部分).32*20*2?32*20 空间是分配给用户的,但是后面的 32*20 空间是预留的,如图所示,如果这时用户需要一个 64 字节的空间,那么剩下的 32*20 空间将变成 64*10,然后将其中 64 字节分配给用户,而不用再一次地构建链表和申请空间。其中 20 是开发团队设计的一个值。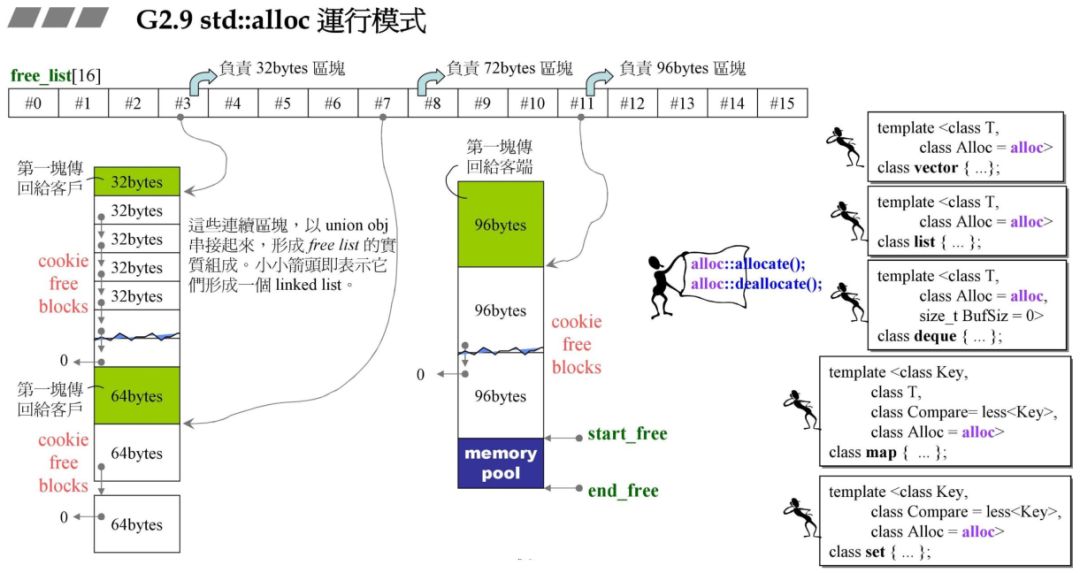
2.2 std::alloc运行过程
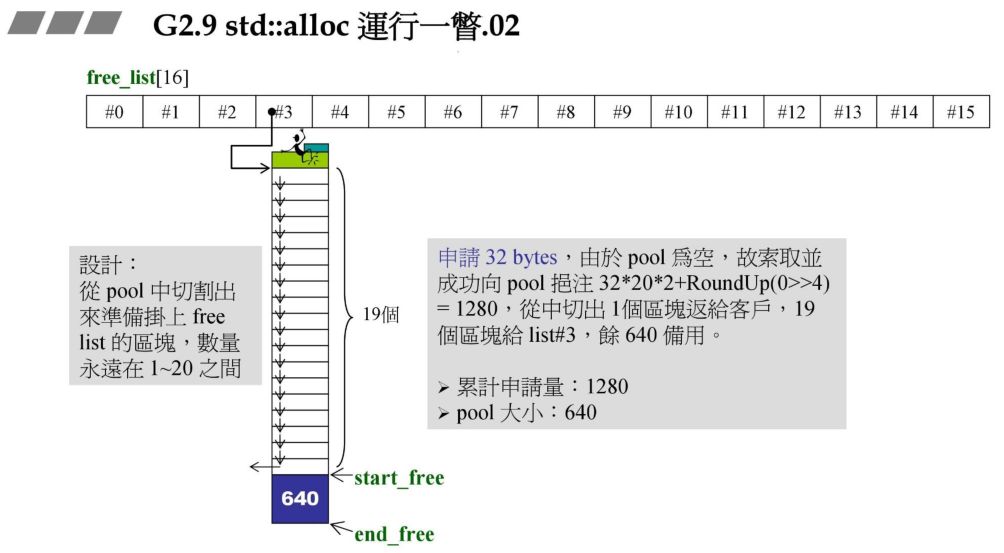
32*20*2+RoundUp(0>>4=1280) ,从中切出一块返回给客户,剩余 19 块,累计申请量有 1280 字节,战备池有 640 字节.RoundUp 实现 8 字节对齐.例如传入 13,传出的就是 16. 0>>4 表示右移 4 位,每次除以 16.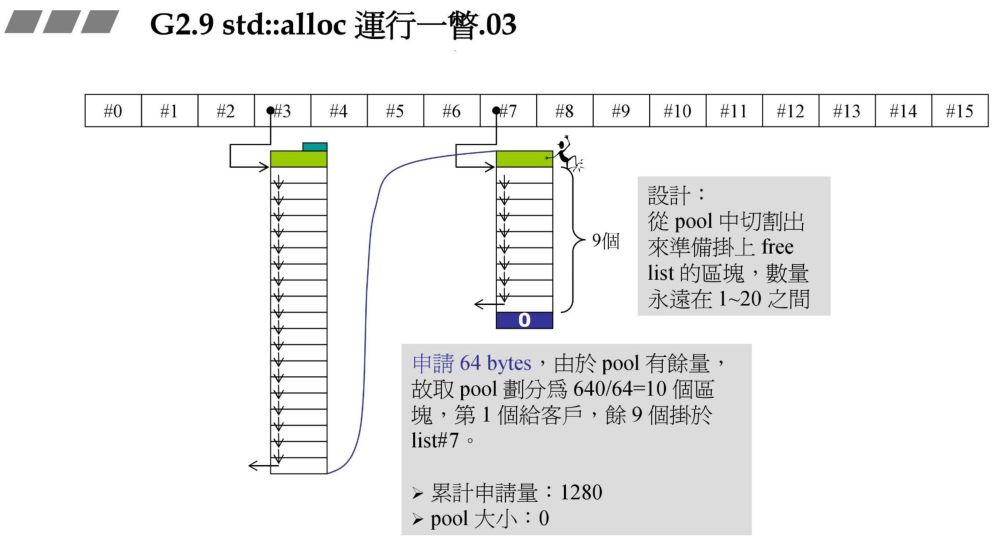
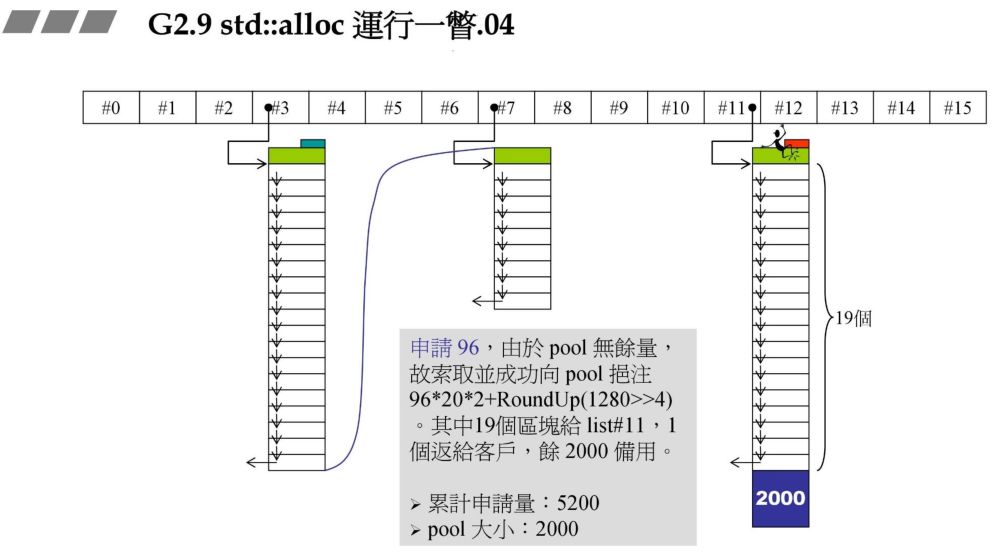
96*20*2+RoundUp(1280>>4) 其余原理同上。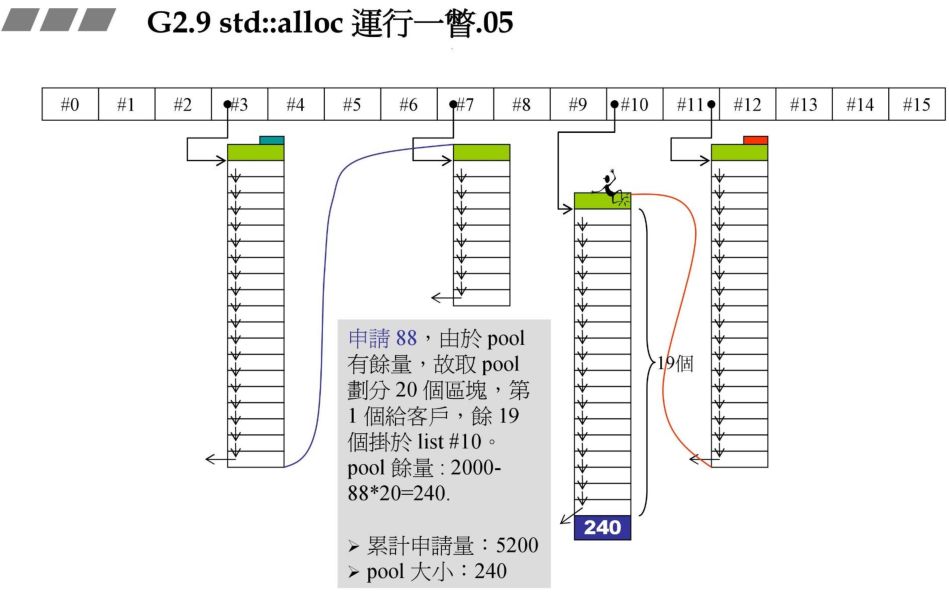
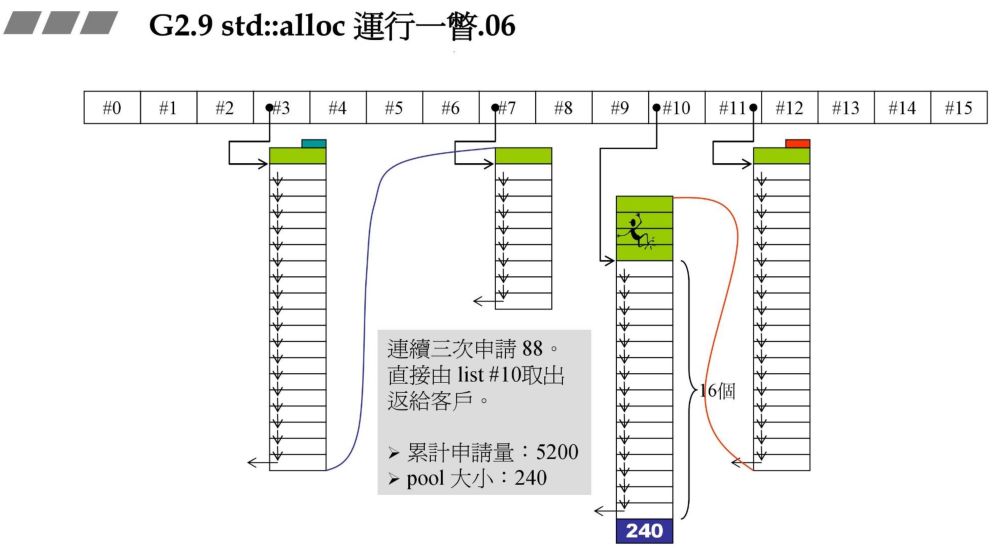
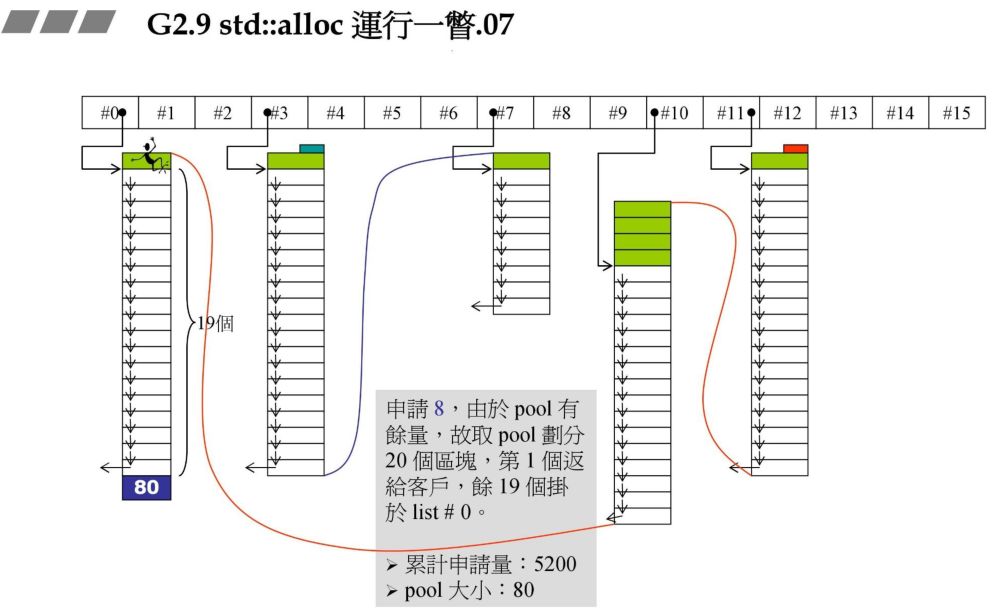
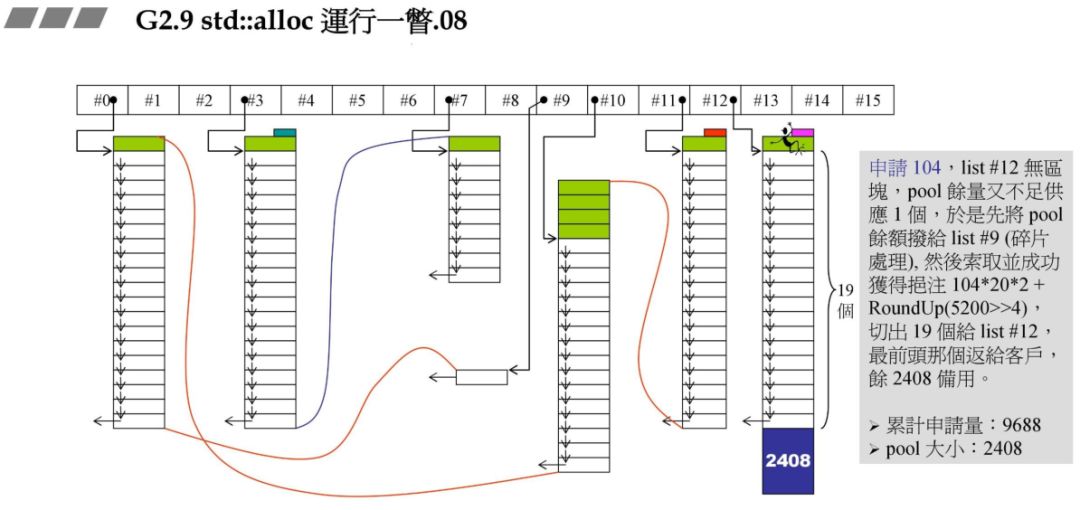
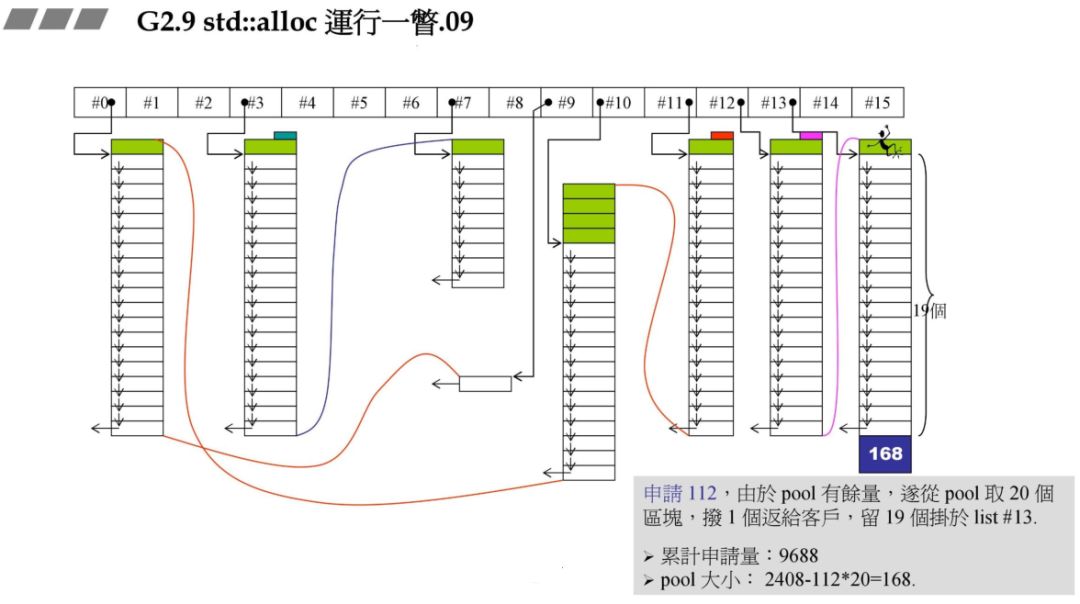
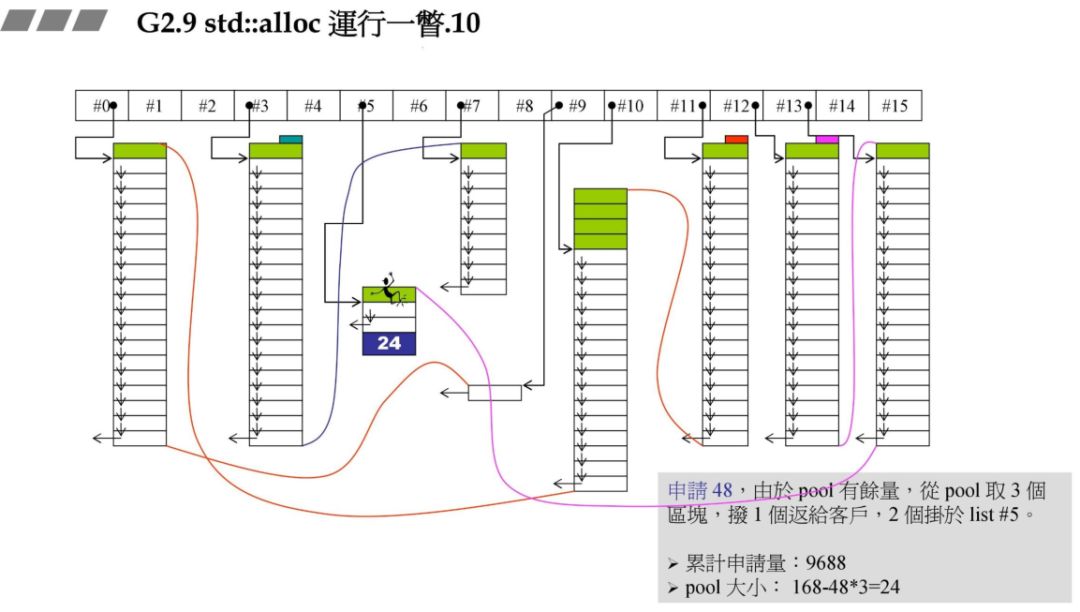
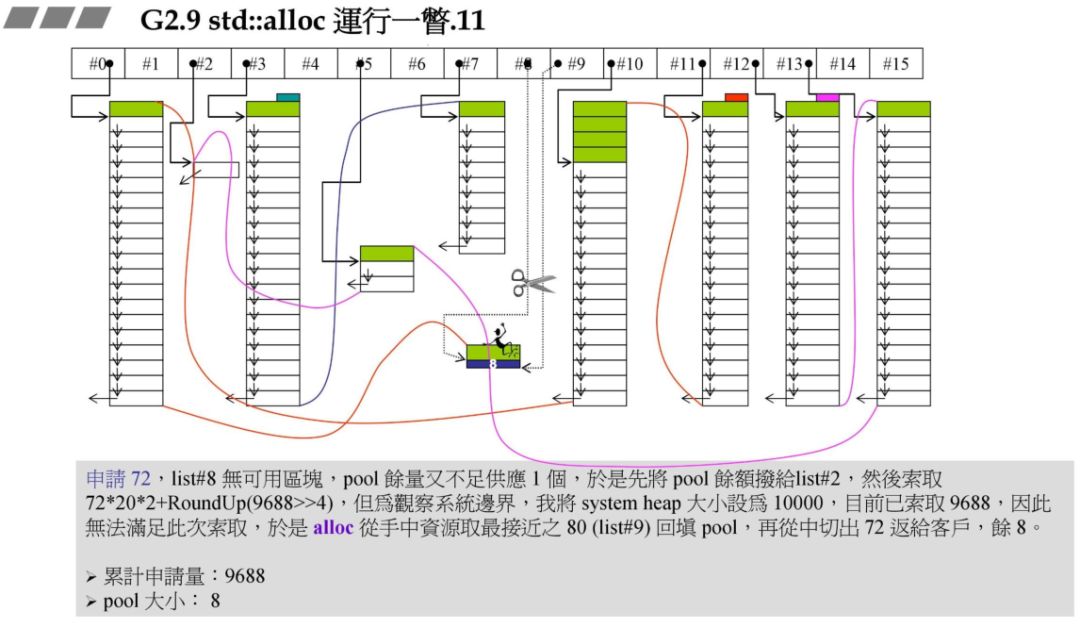
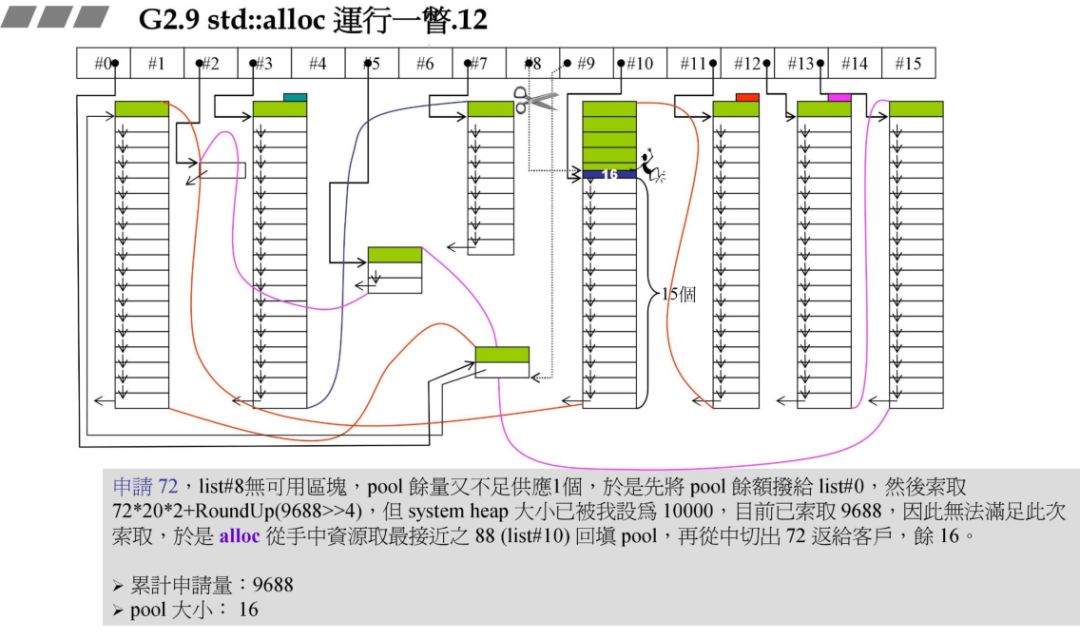
72*20*2+RoundUp(9688>>4 再加上之前的累计申请量,更新后就超过了 10000,资源不够了,那此时就需要从后面最近的链表元素借。在上一个图中我们发现 #9 满足,此时 80 - 72=8,也就是战备池为 8。切除了 72 返回给用户。
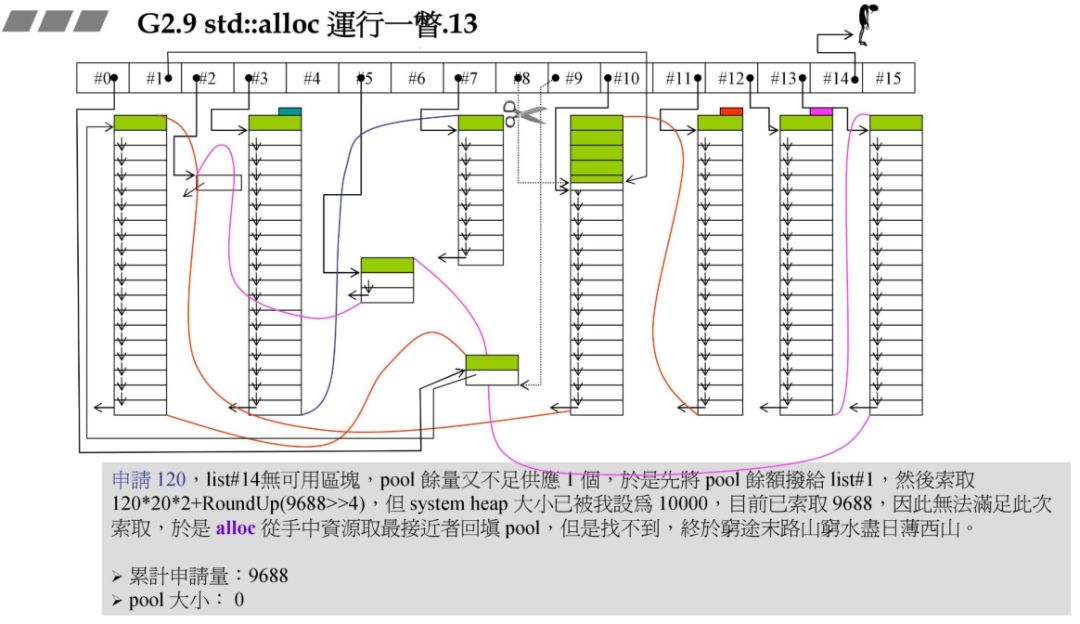
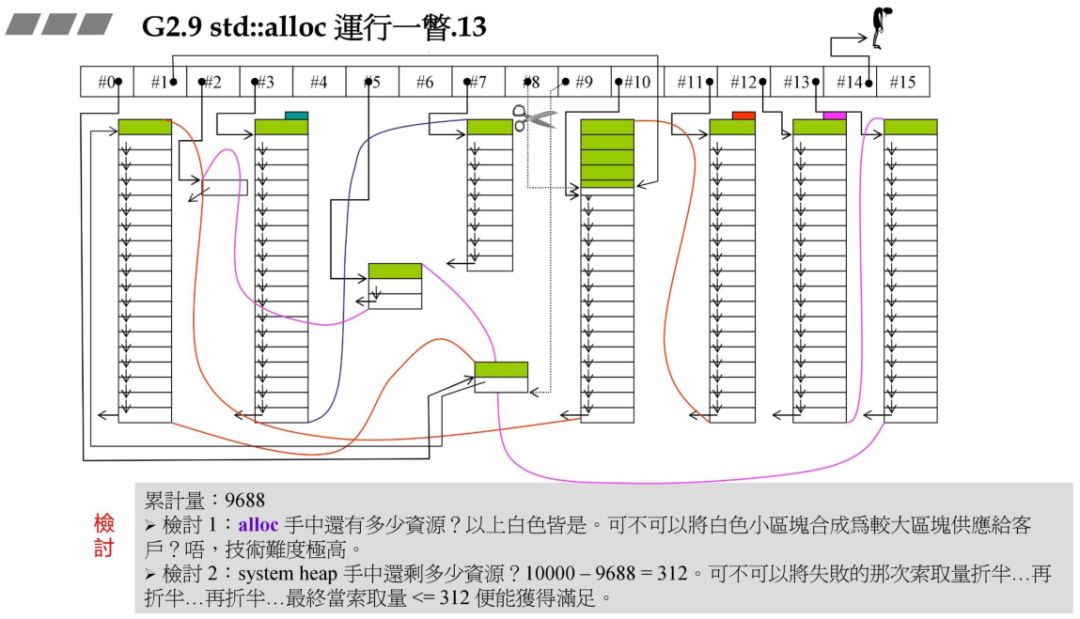
3.std::allloc 源码剖析
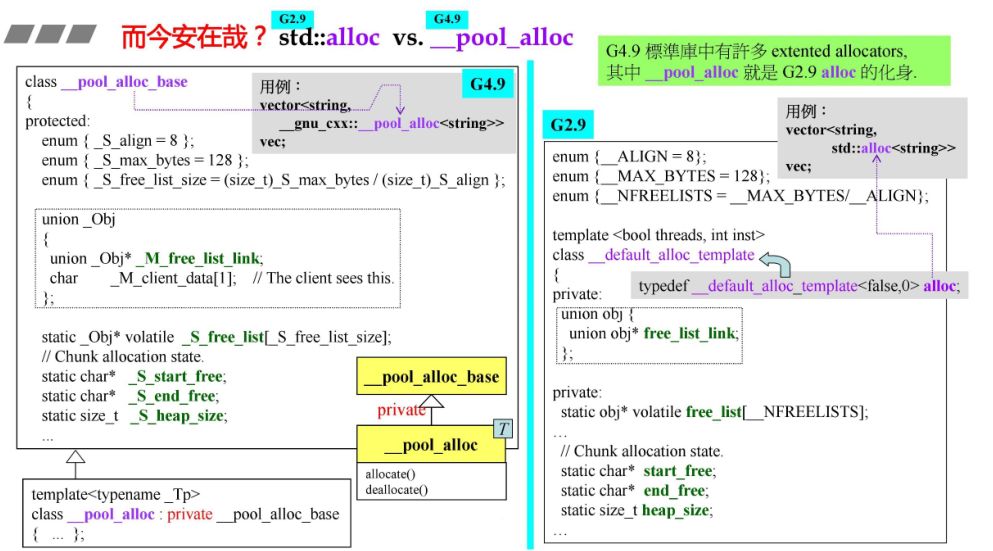
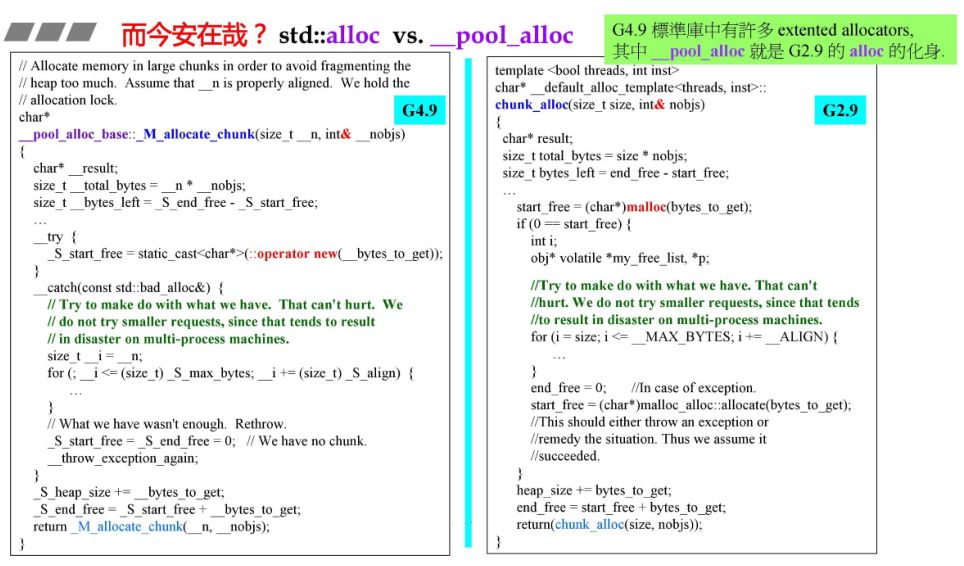
3.1 G2.9 与 G4.9 简要对比
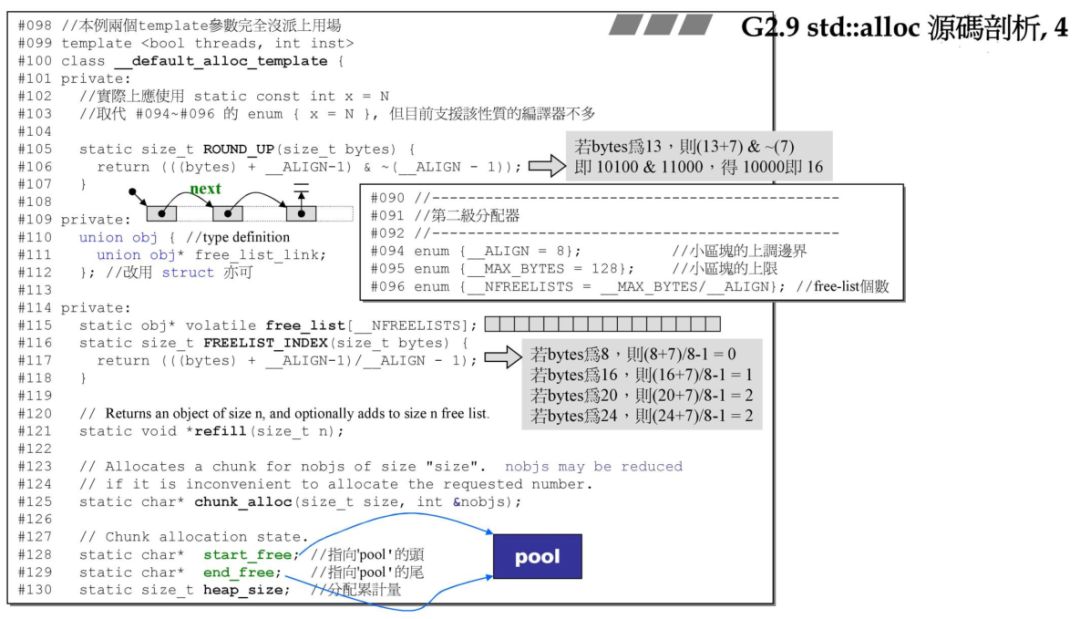
class __pool_alloc_base{protected:enum { _S_align = 8 };enum { _S_max_bytes = 128 };enum { _S_free_list_size = (size_t)_S_max_bytes / (size_t)_S_align };union _Obj{union _Obj* _M_free_list_link;char _M_client_data[1]; // The client sees this.};static _Obj* volatile _S_free_list[_S_free_list_size];// Chunk allocation state.static char* _S_start_free;static char* _S_end_free;static size_t _S_heap_size;size_t_M_round_up(size_t __bytes){ return ((__bytes + (size_t)_S_align - 1) & ~((size_t)_S_align - 1)); }_GLIBCXX_CONST _Obj* volatile*_M_get_free_list(size_t __bytes) throw ();// Returns an object of size __n, and optionally adds to size __n// free list.void*_M_refill(size_t __n);// Allocates a chunk for nobjs of size size. nobjs may be reduced// if it is inconvenient to allocate the requested number.char*_M_allocate_chunk(size_t __n, int& __nobjs);};
https://github.com/gcc-mirror/gcc/blob/master/libstdc%2B%2B-v3/include/ext/pool_allocator.h
__pool_alloc_base::_M_get_free_list(size_t __bytes) throw (){size_t __i = ((__bytes + (size_t)_S_align - 1) / (size_t)_S_align - 1);return _S_free_list + __i;}
https://github.com/gcc-mirror/gcc/blob/master/libstdc%2B%2B-v3/src/c%2B%2B98/pool_allocator.cc
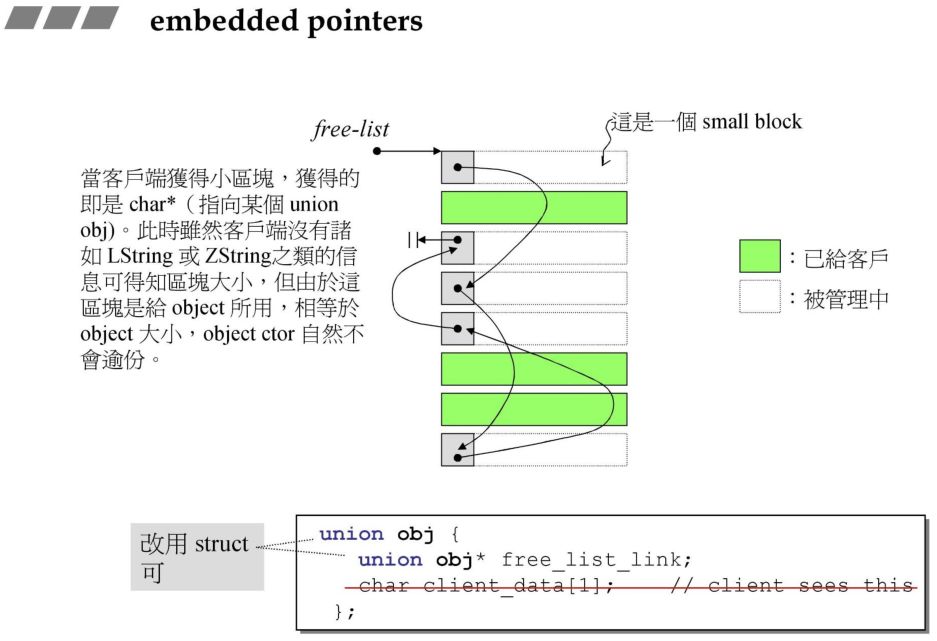
__i 与上述的 FREELIST_INDEX 相同,但是返回前面加了个 _S_free_list。实际上在 G2.9 中的 alloc 函数中可以找到对应代码,在 G4.9 中把 G2.9中 的这一块进行了封装而已。result -> _M_free_list_link,也可以当作该元素的值,例如 *__my_free_list。整个 free lists 的结构便是一串使用后者的元素构成的节点,每个节点的值是使用前者构成的单向链表的首地址。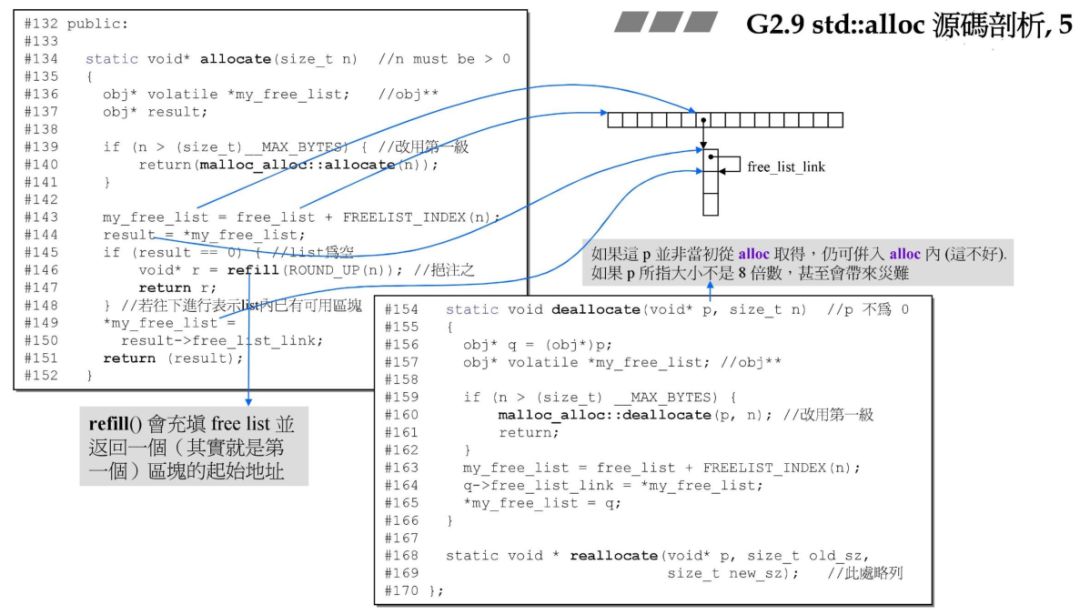
template<typename _Tp>class __pool_alloc : private __pool_alloc_base{.........pointerallocate(size_type __n, const void* = 0);voiddeallocate(pointer __p, size_type __n);};template<typename _Tp>_Tp*__pool_alloc<_Tp>::allocate(size_type __n, const void*){pointer __ret = 0;if (__builtin_expect(__n != 0, true)){if (__n > this->max_size())std::__throw_bad_alloc();const size_t __bytes = __n * sizeof(_Tp);if (__bytes > size_t(_S_max_bytes) || _S_force_new > 0)__ret = static_cast<_Tp*>(::operator new(__bytes));else{_Obj* volatile* __free_list = _M_get_free_list(__bytes);_Obj* __restrict__ __result = *__free_list;if (__builtin_expect(__result == 0, 0))__ret = static_cast<_Tp*>(_M_refill(_M_round_up(__bytes)));else{*__free_list = __result->_M_free_list_link;__ret = reinterpret_cast<_Tp*>(__result);}if (__ret == 0)std::__throw_bad_alloc();}}return __ret;}template<typename _Tp>void__pool_alloc<_Tp>::deallocate(pointer __p, size_type __n){if (__builtin_expect(__n != 0 && __p != 0, true)){const size_t __bytes = __n * sizeof(_Tp);if (__bytes > static_cast<size_t>(_S_max_bytes) || _S_force_new > 0)::operator delete(__p);else{_Obj* volatile* __free_list = _M_get_free_list(__bytes);_Obj* __q = reinterpret_cast<_Obj*>(__p);__q ->_M_free_list_link = *__free_list;*__free_list = __q;}}}
3.2 allocate函数
obj* volatile *my_free_list;
_free_list) 指向的是 free_list 中 16 个元素中的任何一个,*my_free_list 则取出 free_list 某元素中的值,该值指向一条分配内存的链表。所以 my_free_list 要定义为二级指针。result 则保存分配给用户的一块内存的地址。对应到 G4.9 就是 _ret。if (n > (size_t)__MAX_BYTES) {return(malloc_alloc::allocate(n));}
if (__bytes > size_t(_S_max_bytes) || _S_force_new > 0)__ret = static_cast<_Tp*>(::operator new(__bytes));
S_force_new 是一个int类型,与互斥锁相关,可暂时以不用管。my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n);
_Obj* volatile* __free_list = _M_get_free_list(__bytes);
result = *my_free_list;
_Obj* __restrict__ __result = *__free_list;
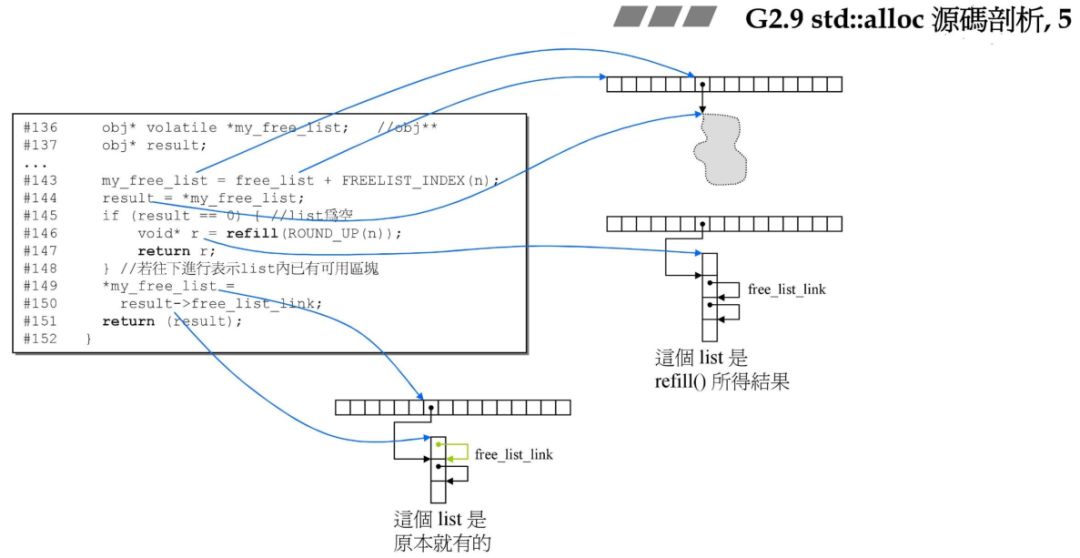
if (result == 0) {void* r = refill(ROUND_UP(n));return r;}
if (__builtin_expect(__result == 0, 0))__ret = static_cast<_Tp*>(_M_refill(_M_round_up(__bytes)));
__ret,最后做返回。返回用户区块
移动链表区块指向
*my_free_list = result->free_list_link;return (result);
*__free_list = __result->_M_free_list_link;__ret = reinterpret_cast<_Tp*>(__result);
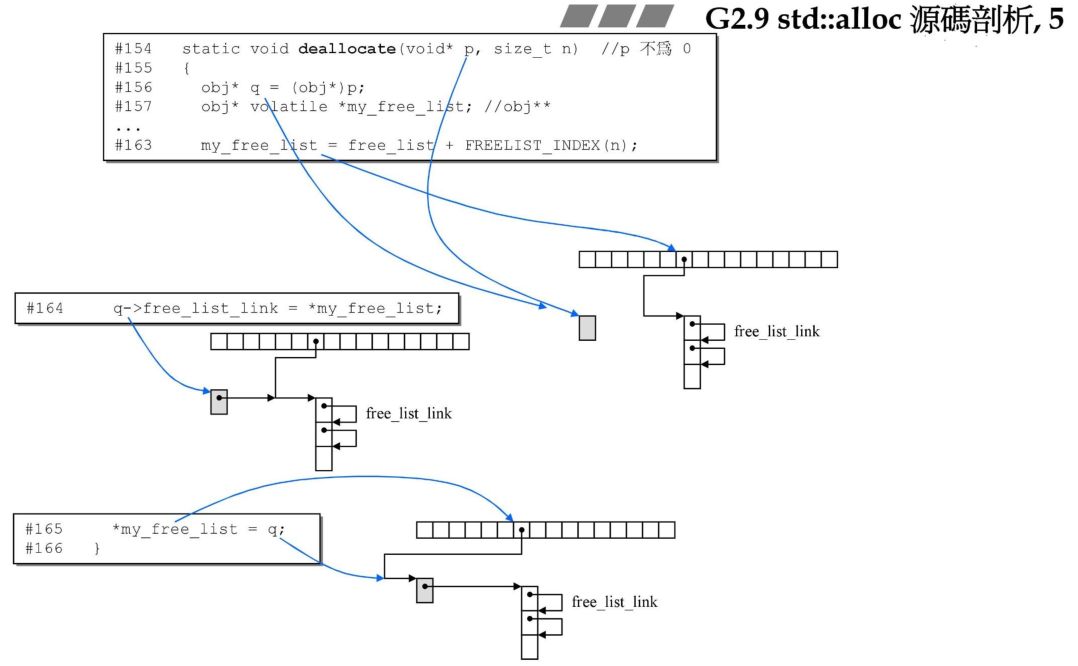
3.3 deallocate函数
static void deallocate(void *p, size_t n) //p may not be 0{obj* q = (obj*)p;obj* volatile *my_free_list; //obj** my_free_list;if (n > (size_t) __MAX_BYTES) {malloc_alloc::deallocate(p, n);return;}my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n);q->free_list_link = *my_free_list;*my_free_list = q;}
template<typename _Tp>void __pool_alloc<_Tp>::deallocate(pointer __p, size_type __n){if (__builtin_expect(__n != 0 && __p != 0, true)){const size_t __bytes = __n * sizeof(_Tp);if (__bytes > static_cast<size_t>(_S_max_bytes) || _S_force_new > 0)::operator delete(__p);else{_Obj* volatile* __free_list = _M_get_free_list(__bytes);_Obj* __q = reinterpret_cast<_Obj*>(__p);__q ->_M_free_list_link = *__free_list;*__free_list = __q;}}}
typedef __malloc_alloc_template<0> malloc_alloc;
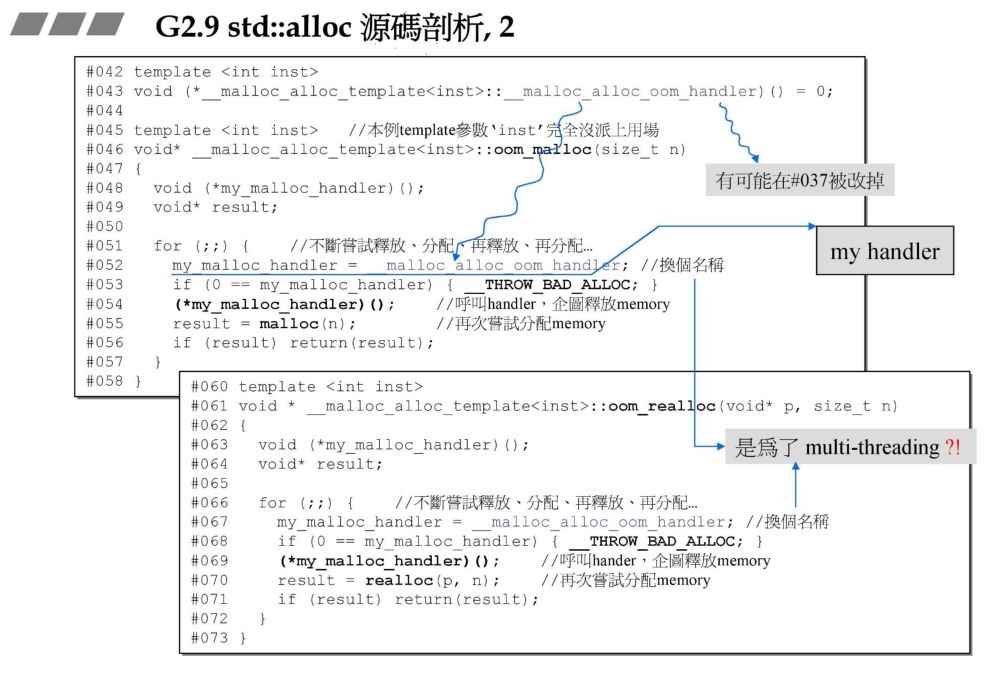
3.4 chunk_alloc函数
https://github.com/gcc-mirror/gcc/blob/master/libstdc%2B%2B-v3/src/c%2B%2B98/pool_allocator.cc
char* result;size_t total_bytes = size * nobjs;size_t bytes_left = end_free - start_free;
char* __result;size_t __total_bytes = __n * __nobjs;size_t __bytes_left = _S_end_free - _S_start_free;
if (bytes_left >= total_bytes) {result = start_free;start_free += total_bytes;return(result);}
if (__bytes_left >= __total_bytes){__result = _S_start_free;_S_start_free += __total_bytes;return __result ;}
else if (bytes_left >= size) {nobjs = bytes_left / size;total_bytes = size * nobjs;result = start_free;start_free += total_bytes;return(result);}
else if (__bytes_left >= __n){__nobjs = (int)(__bytes_left / __n);__total_bytes = __n * __nobjs;__result = _S_start_free;_S_start_free += __total_bytes;return __result;}
if (bytes_left > 0) {obj* volatile *my_free_list =free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(bytes_left);((obj*)start_free)->free_list_link = *my_free_list;*my_free_list = (obj*)start_free;}
// Try to make use of the left-over piece.if (__bytes_left > 0){_Obj* volatile* __free_list = _M_get_free_list(__bytes_left);((_Obj*)(void*)_S_start_free)->_M_free_list_link = *__free_list;*__free_list = (_Obj*)(void*)_S_start_free;}
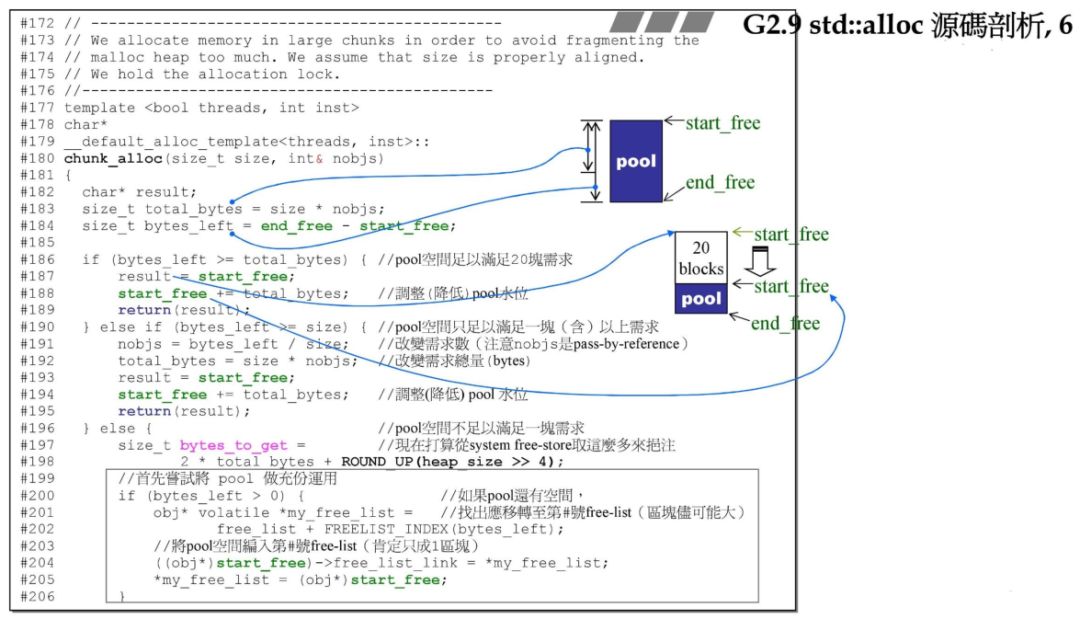
size_t bytes_to_get =2 * total_bytes + ROUND_UP(heap_size >> 4);start_free = (char*)malloc(bytes_to_get);if (0 == start_free) {int i;obj* volatile *my_free_list, *p;//Try to make do with what we have. That can't//hurt. We do not try smaller requests, since that tends//to result in disaster on multi-process machines.for (i = size; i <= __MAX_BYTES; i += __ALIGN) {my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(i);p = *my_free_list;if (0 != p) {*my_free_list = p -> free_list_link;start_free = (char*)p;end_free = start_free + i;return(chunk_alloc(size, nobjs));//Any leftover piece will eventually make it to the//right free list.}}end_free = 0; //In case of exception.start_free = (char*)malloc_alloc::allocate(bytes_to_get);//This should either throw an exception or//remedy the situation. Thus we assume it//succeeded.}heap_size += bytes_to_get;end_free = start_free + bytes_to_get;return(chunk_alloc(size, nobjs));
size_t __bytes_to_get = (2 * __total_bytes+ _M_round_up(_S_heap_size >> 4));__try{_S_start_free = static_cast<char*>(::operator new(__bytes_to_get));}__catch(const std::bad_alloc&){// Try to make do with what we have. That can't hurt. We// do not try smaller requests, since that tends to result// in disaster on multi-process machines.size_t __i = __n;for (; __i <= (size_t) _S_max_bytes; __i += (size_t) _S_align){_Obj* volatile* __free_list = _M_get_free_list(__i);_Obj* __p = *__free_list;if (__p != 0){*__free_list = __p->_M_free_list_link;_S_start_free = (char*)__p;_S_end_free = _S_start_free + __i;return _M_allocate_chunk(__n, __nobjs);// Any leftover piece will eventually make it to the// right free list.}}// What we have wasn't enough. Rethrow._S_start_free = _S_end_free = 0; // We have no chunk.__throw_exception_again;}_S_heap_size += __bytes_to_get;_S_end_free = _S_start_free + __bytes_to_get;return _M_allocate_chunk(__n, __nobjs);
3.5 refill函数
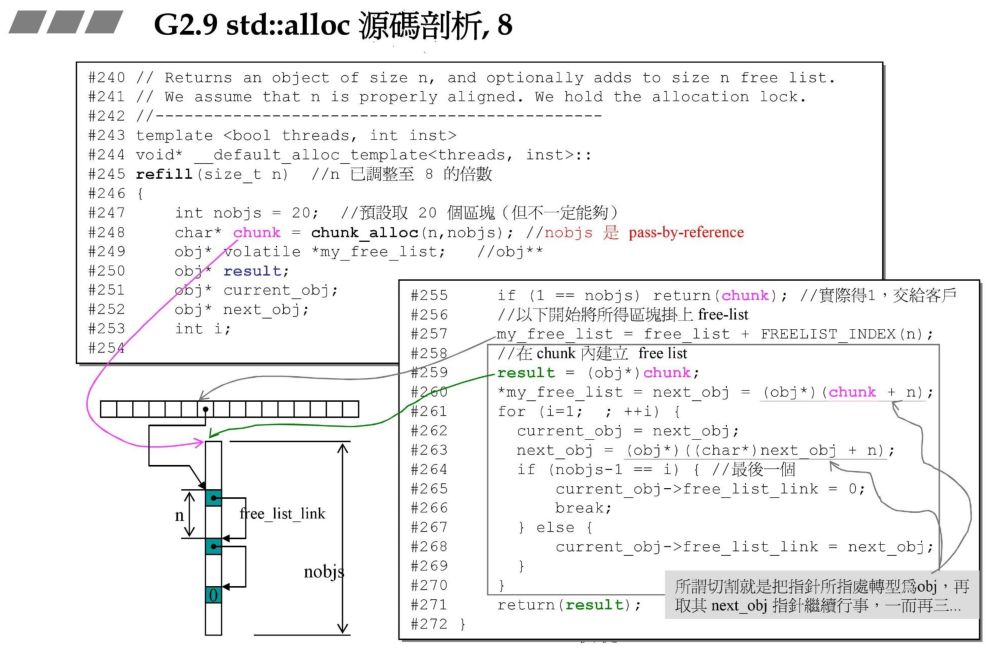
32*20*2与累积量,战备池中剩余量计算函数,不断为战备池充值。void*__pool_alloc_base::_M_refill(size_t __n){int __nobjs = 20;char* __chunk = _M_allocate_chunk(__n, __nobjs);_Obj* volatile* __free_list;_Obj* __result;_Obj* __current_obj;_Obj* __next_obj;if (__nobjs == 1)return __chunk;__free_list = _M_get_free_list(__n);// Build free list in chunk.__result = (_Obj*)(void*)__chunk;*__free_list = __next_obj = (_Obj*)(void*)(__chunk + __n);for (int __i = 1; ; __i++){__current_obj = __next_obj;__next_obj = (_Obj*)(void*)((char*)__next_obj + __n);if (__nobjs - 1 == __i){__current_obj->_M_free_list_link = 0;break;}else__current_obj->_M_free_list_link = __next_obj;}return __result;}
https://github.com/gcc-mirror/gcc/blob/master/libstdc%2B%2B-v3/src/c%2B%2B98/pool_allocator.cc
4. std::alloc概念大整理
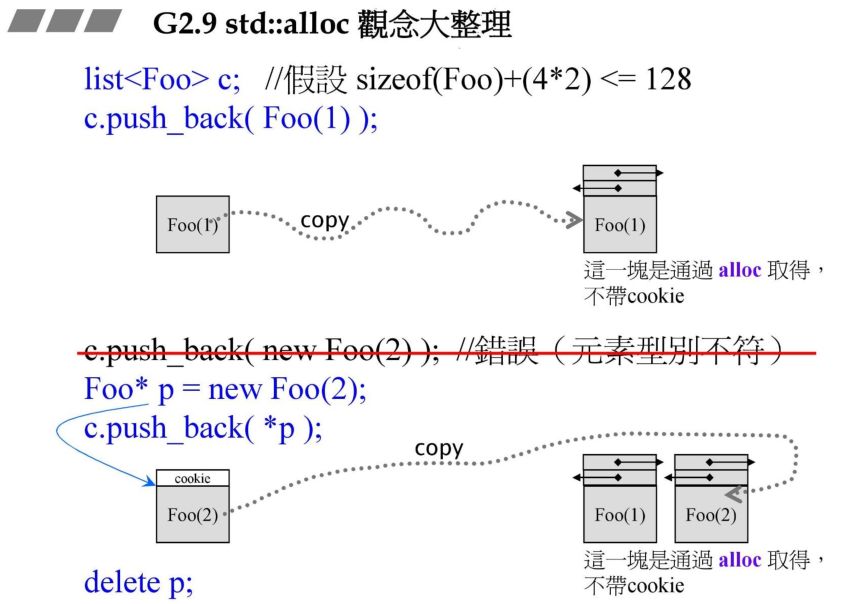
5.std::alloc批斗大会
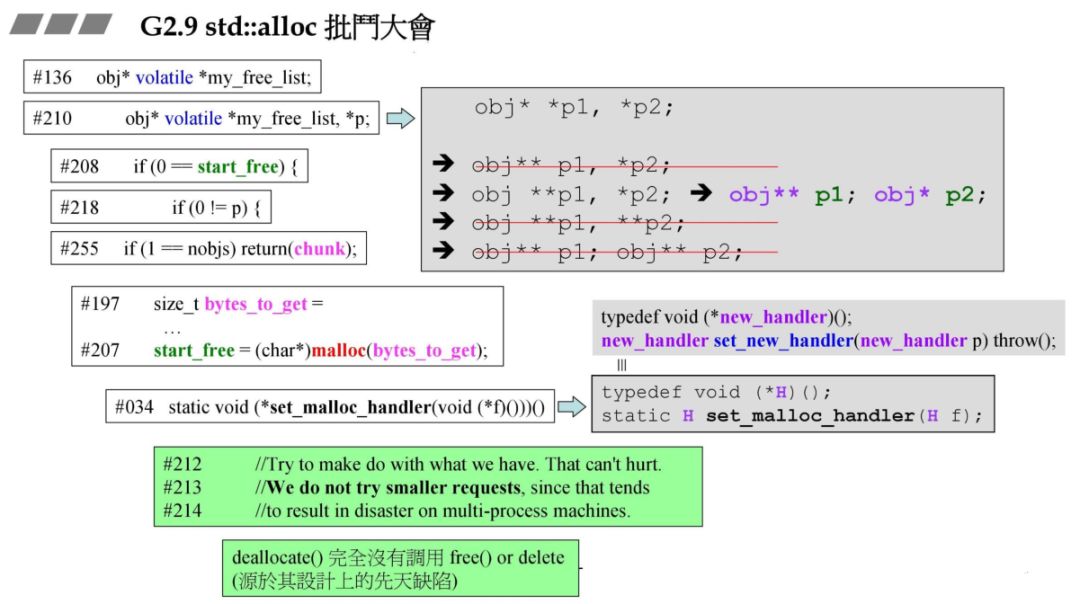
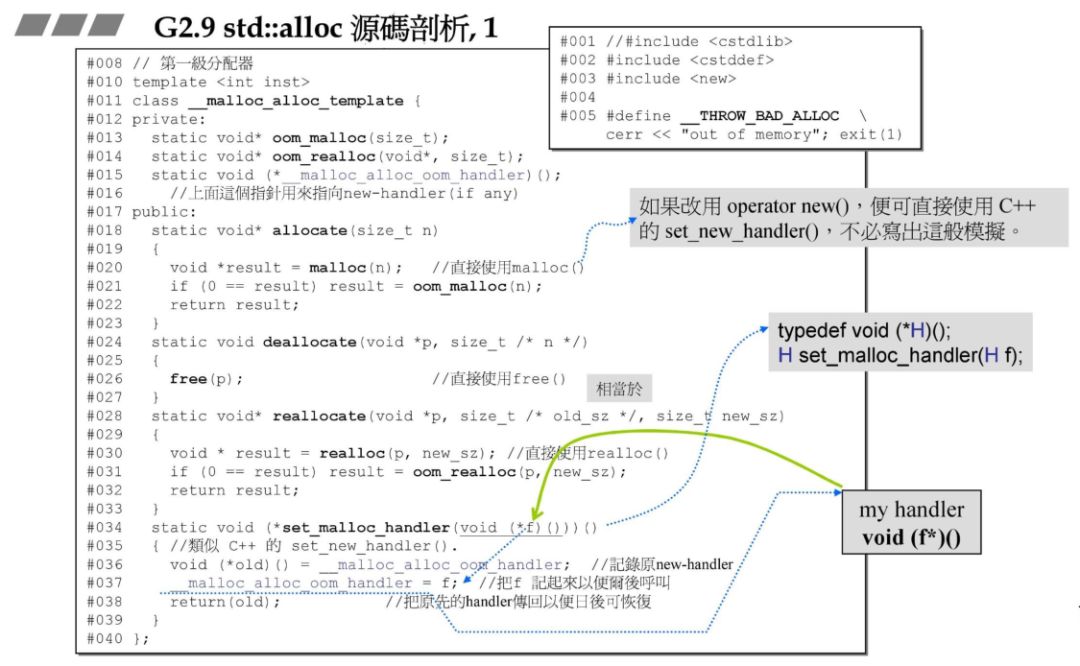
obj* *_free_list,*p容易使人误解为指针的指针,实际上只等价于右边的定义,_free_list是指针的指针,而p则是指针。malloc 分配,不可重载,可以采用 operator new 来替代。
static void 一大堆函数指针嵌套太难理解。
if 判断将值放在变量前面,这样可以避免少写等号,编译器不报错问题。
6.C 实现

评论
