Pytorch图像检索实践
点击上方“小白学视觉”,选择加"星标"或“置顶”
重磅干货,第一时间送达
随着电子商务和在线网站的出现,图像检索在我们的日常生活中的应用一直在增加。
亚马逊、阿里巴巴、Myntra等公司一直在大量利用图像检索技术。当然,只有当通常的信息检索技术失败时,图像检索才会开始工作。
背景
图像检索的基本本质是根据查询图像的特征从集合或数据库中查找图像。
大多数情况下,这种特征是图像之间简单的视觉相似性。在一个复杂的问题中,这种特征可能是两幅图像在风格上的相似性,甚至是互补性。
由于原始形式的图像不会在基于像素的数据中反映这些特征,因此我们需要将这些像素数据转换为一个潜空间,在该空间中,图像的表示将反映这些特征。
一般来说,在潜空间中,任何两个相似的图像都会相互靠近,而不同的图像则会相隔很远。这是我们用来训练我们的模型的基本管理规则。一旦我们这样做,检索部分只需搜索潜在空间,在给定查询图像表示的潜在空间中拾取最近的图像。大多数情况下,它是在最近邻搜索的帮助下完成的。
因此,我们可以将我们的方法分为两部分:
-
图像表现
-
搜索
我们将在Oxford 102 Flowers数据集上解决这两个部分。
你可以在这里下载并阅读有关数据集的信息:
https://www.tensorflow.org/datasets/catalog/oxford_flowers102
图像表现
我们将使用一种叫做暹罗模型的东西,它本身并不是一种全新的模型,而是一种训练模型的技术。大多数情况下,这是与triplet loss一起使用的。这个技术的基本组成部分是三元组。
三元组是3个独立的数据样本,比如A(锚点),B(阳性)和C(阴性);其中A和B相似或具有相似的特征(可能是同一类),而C与A和B都不相似。这三个样本共同构成了训练数据的一个单元——三元组。
注:任何图像检索任务的90%都体现在暹罗网络、triplet loss和三元组的创建中。如果你成功地完成了这些,那么整个努力的成功或多或少是有保证的。
首先,我们将创建管道的这个组件——数据。下面我们将在PyTorch中创建一个自定义数据集和数据加载器,它将从数据集中生成三元组。
class TripletData(Dataset):
def __init__(self, path, transforms, split="train"):
self.path = path
self.split = split # train or valid
self.cats = 102 # number of categories
self.transforms = transforms
def __getitem__(self, idx):
# our positive class for the triplet
idx = str(idx%self.cats + 1)
# choosing our pair of positive images (im1, im2)
positives = os.listdir(os.path.join(self.path, idx))
im1, im2 = random.sample(positives, 2)
# choosing a negative class and negative image (im3)
negative_cats = [str(x+1) for x in range(self.cats)]
negative_cats.remove(idx)
negative_cat = str(random.choice(negative_cats))
negatives = os.listdir(os.path.join(self.path, negative_cat))
im3 = random.choice(negatives)
im1,im2,im3 = os.path.join(self.path, idx, im1), os.path.join(self.path, idx, im2), os.path.join(self.path, negative_cat, im3)
im1 = self.transforms(Image.open(im1))
im2 = self.transforms(Image.open(im2))
im3 = self.transforms(Image.open(im3))
return [im1, im2, im3]
# we'll put some value that we want since there can be far too many triplets possible
# multiples of the number of images/ number of categories is a good choice
def __len__(self):
return self.cats*8
# Transforms
train_transforms = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224,224)),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465), (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010)),
])
val_transforms = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465), (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010)),
])
# Datasets and Dataloaders
train_data = TripletData(PATH_TRAIN, train_transforms)
val_data = TripletData(PATH_VALID, val_transforms)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset = train_data, batch_size=32, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)
val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset = val_data, batch_size=32, shuffle=False, num_workers=4)
现在我们有了数据,让我们转到暹罗网络。
暹罗网络给人的印象是2个或3个模型,但是它本身是一个单一的模型。所有这些模型共享权重,即只有一个模型。
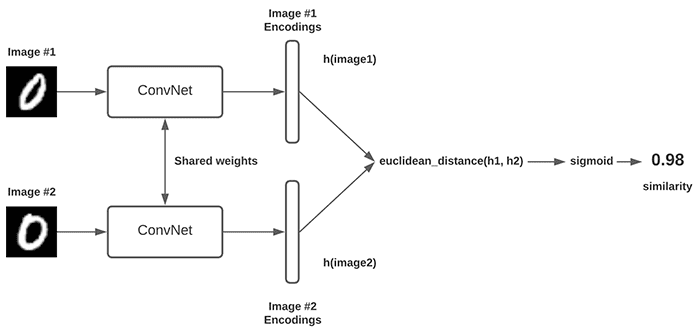
如前所述,将整个体系结构结合在一起的关键因素是triplet loss。triplet loss产生了一个目标函数,该函数迫使相似输入对(锚点和正)之间的距离小于不同输入对(锚点和负)之间的距离,并限定一定的阈值。
下面我们来看看triplet loss以及训练管道实现。
class TripletLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, margin=1.0):
super(TripletLoss, self).__init__()
self.margin = margin
def calc_euclidean(self, x1, x2):
return (x1 - x2).pow(2).sum(1)
# Distances in embedding space is calculated in euclidean
def forward(self, anchor, positive, negative):
distance_positive = self.calc_euclidean(anchor, positive)
distance_negative = self.calc_euclidean(anchor, negative)
losses = torch.relu(distance_positive - distance_negative + self.margin)
return losses.mean()
device = 'cuda'
# Our base model
model = models.resnet18().cuda()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
triplet_loss = TripletLoss()
# Training
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
epoch_loss = 0.0
for data in tqdm(train_loader):
optimizer.zero_grad()
x1,x2,x3 = data
e1 = model(x1.to(device))
e2 = model(x2.to(device))
e3 = model(x3.to(device))
loss = triplet_loss(e1,e2,e3)
epoch_loss += loss
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print("Train Loss: {}".format(epoch_loss.item()))
class TripletLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, margin=1.0):
super(TripletLoss, self).__init__()
self.margin = margin
def calc_euclidean(self, x1, x2):
return (x1 - x2).pow(2).sum(1)
# Distances in embedding space is calculated in euclidean
def forward(self, anchor, positive, negative):
distance_positive = self.calc_euclidean(anchor, positive)
distance_negative = self.calc_euclidean(anchor, negative)
losses = torch.relu(distance_positive - distance_negative + self.margin)
return losses.mean()
device = 'cuda'
# Our base model
model = models.resnet18().cuda()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
triplet_loss = TripletLoss()
# Training
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
epoch_loss = 0.0
for data in tqdm(train_loader):
optimizer.zero_grad()
x1,x2,x3 = data
e1 = model(x1.to(device))
e2 = model(x2.to(device))
e3 = model(x3.to(device))
loss = triplet_loss(e1,e2,e3)
epoch_loss += loss
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print("Train Loss: {}".format(epoch_loss.item()))
到目前为止,我们的模型已经经过训练,可以将图像转换为一个嵌入空间。接下来,我们进入搜索部分。
搜索
我们可以很容易地使用Scikit Learn提供的最近邻搜索。我们将探索新的更好的东西,而不是走简单的路线。
我们将使用Faiss。这比最近的邻居要快得多,如果我们有大量的图像,这种速度上的差异会变得更加明显。
下面我们将演示如何在给定查询图像时,在存储的图像表示中搜索最近的图像。
#!pip install faiss-gpu
import faiss
faiss_index = faiss.IndexFlatL2(1000) # build the index
# storing the image representations
im_indices = []
with torch.no_grad():
for f in glob.glob(os.path.join(PATH_TRAIN, '*/*')):
im = Image.open(f)
im = im.resize((224,224))
im = torch.tensor([val_transforms(im).numpy()]).cuda()
preds = model(im)
preds = np.array([preds[0].cpu().numpy()])
faiss_index.add(preds) #add the representation to index
im_indices.append(f) #store the image name to find it later on
# Retrieval with a query image
with torch.no_grad():
for f in os.listdir(PATH_TEST):
# query/test image
im = Image.open(os.path.join(PATH_TEST,f))
im = im.resize((224,224))
im = torch.tensor([val_transforms(im).numpy()]).cuda()
test_embed = model(im).cpu().numpy()
_, I = faiss_index.search(test_embed, 5)
print("Retrieved Image: {}".format(im_indices[I[0][0]]))
这涵盖了基于现代深度学习的图像检索,但不会使其变得太复杂。大多数检索问题都可以通过这个基本管道解决。
相关资源:
笔记本链接:https://www.kaggle.com/mayukh18/oxford-flowers-image-retrieval-pytorch
图像检索社区中流行的基准数据集:https://paperswithcode.com/task/image-retrieva
下载1:OpenCV-Contrib扩展模块中文版教程
在「小白学视觉」公众号后台回复:扩展模块中文教程,即可下载全网第一份OpenCV扩展模块教程中文版,涵盖扩展模块安装、SFM算法、立体视觉、目标跟踪、生物视觉、超分辨率处理等二十多章内容。
下载2:Python视觉实战项目52讲
在「小白学视觉」公众号后台回复:Python视觉实战项目,即可下载包括图像分割、口罩检测、车道线检测、车辆计数、添加眼线、车牌识别、字符识别、情绪检测、文本内容提取、面部识别等31个视觉实战项目,助力快速学校计算机视觉。
下载3:OpenCV实战项目20讲
在「小白学视觉」公众号后台回复:OpenCV实战项目20讲,即可下载含有20个基于OpenCV实现20个实战项目,实现OpenCV学习进阶。
交流群
欢迎加入公众号读者群一起和同行交流,目前有SLAM、三维视觉、传感器、自动驾驶、计算摄影、检测、分割、识别、医学影像、GAN、算法竞赛等微信群(以后会逐渐细分),请扫描下面微信号加群,备注:”昵称+学校/公司+研究方向“,例如:”张三 + 上海交大 + 视觉SLAM“。请按照格式备注,否则不予通过。添加成功后会根据研究方向邀请进入相关微信群。请勿在群内发送广告,否则会请出群,谢谢理解~


