Java的三种代理模式(Spring动态代理对象)
点击上方蓝色字体,选择“标星公众号”
优质文章,第一时间送达
1.代理模式
代理(Proxy)是一种设计模式,提供了对目标对象另外的访问方式;即通过代理对象访问目标对象.这样做的好处是:可以在目标对象实现的基础上,增强额外的功能操作,即扩展目标对象的功能.
这里使用到编程中的一个思想:不要随意去修改别人已经写好的代码或者方法,如果需改修改,可以通过代理的方式来扩展该方法
举个例子来说明代理的作用:假设我们想邀请一位明星,那么并不是直接连接明星,而是联系明星的经纪人,来达到同样的目的.明星就是一个目标对象,他只要负责活动中的节目,而其他琐碎的事情就交给他的代理人(经纪人)来解决.这就是代理思想在现实中的一个例子
用图表示如下:
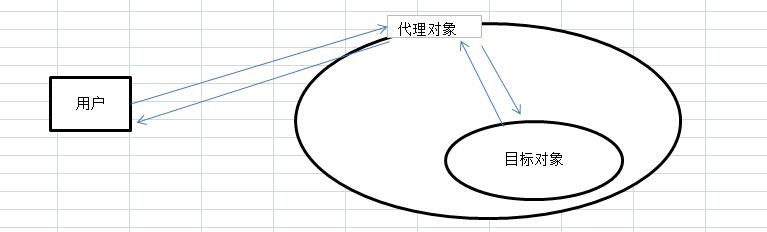
代理模式的关键点是:代理对象与目标对象.代理对象是对目标对象的扩展,并会调用目标对象
1.1.静态代理(类似于装饰者模式)
静态代理在使用时,需要定义接口或者父类,被代理对象与代理对象一起实现相同的接口或者是继承相同父类.
下面举个案例来解释:
模拟保存动作,定义一个保存动作的接口:IUserDao.java,然后目标对象实现这个接口的方法UserDao.java,此时如果使用静态代理方 式,就需要在代理对象(UserDaoProxy.java)中也实现IUserDao接口.调用的时候通过调用代理对象的方法来调用目标对象.
需要注意的是,代理对象与目标对象要实现相同的接口,然后通过调用相同的方法来调用目标对象的方法
代码示例:
接口:IUserDao.java
/**
* 接口
*/
public interface IUserDao {
void save();
}
目标对象:UserDao.java
/**
* 接口实现
* 目标对象
*/
public class UserDao implements IUserDao {
public void save() {
System.out.println("----已经保存数据!----");
}
}
代理对象:UserDaoProxy.java
/**
* 代理对象,静态代理
*/
public class UserDaoProxy implements IUserDao{
//接收保存目标对象
private IUserDao target;
public UserDaoProxy(IUserDao target){
this.target=target;
}
public void save() {
System.out.println("开始事务...");
target.save();//执行目标对象的方法
System.out.println("提交事务...");
}
}
测试类:App.java
/**
* 测试类
*/
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//目标对象
UserDao target = new UserDao();
//代理对象,把目标对象传给代理对象,建立代理关系
UserDaoProxy proxy = new UserDaoProxy(target);
proxy.save();//执行的是代理的方法
}
}
静态代理总结:
1.可以做到在不修改目标对象的功能前提下,对目标功能扩展.
2.缺点:
因为代理对象需要与目标对象实现一样的接口,所以会有很多代理类,类太多.同时,一旦接口增加方法,目标对象与代理对象都要维护.
如何解决静态代理中的缺点呢?答案是可以使用动态代理方式
1.2.动态代理
动态代理有以下特点:
1.代理对象,不需要实现接口
2.代理对象的生成,是利用JDK的API,动态的在内存中构建代理对象(需要我们指定创建代理对象/目标对象实现的接口的类型)
3.动态代理也叫做:JDK代理,接口代理
JDK中生成代理对象的API
代理类所在包:java.lang.reflect.Proxy
JDK实现代理只需要使用newProxyInstance方法,但是该方法需要接收三个参数,完整的写法是:
static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces,InvocationHandler h )
注意该方法是在Proxy类中是静态方法,且接收的三个参数依次为:
ClassLoader loader,:指定当前目标对象使用类加载器,获取加载器的方法是固定的Class<?>[] interfaces,:目标对象实现的接口的类型,使用泛型方式确认类型InvocationHandler h:事件处理,执行目标对象的方法时,会触发事件处理器的方法,会把当前执行目标对象的方法作为参数传入
代码示例:
接口类IUserDao.java以及接口实现类,目标对象UserDao是一样的,没有做修改.在这个基础上,增加一个代理工厂类 (ProxyFactory.java),将代理类写在这个地方,然后在测试类(需要使用到代理的代码)中先建立目标对象和代理对象的联系,然后代用代理 对象的中同名方法
接口和默认实现:
package aop;
public interface IUserDao {
void save();
void delete();
void saveAndDelete();
}
实现类:
package aop;
public class UserDao implements IUserDao {
public void save() {
System.out.println("save");
}
public void delete() {
System.out.println("delete");
}
public void saveAndDelete() {
save();
delete();
}
}
代理工厂类:ProxyFactory.java
package aop;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
/**
* 创建动态代理对象
* 动态代理不需要实现接口,但是需要指定接口类型
*/
public class ProxyFactory {
//维护一个目标对象
private Object target;
public ProxyFactory(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
//给目标对象生成代理对象
public Object getProxyInstance() {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
target.getClass().getClassLoader(),
target.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("开始事务2");
//运用反射执行目标对象方法
Object returnValue = method.invoke(target, args);
System.out.println("提交事务2");
return returnValue;
}
}
);
}
}
测试类:
package aop;
/**
* @author: 乔利强
* @date: 2020/12/11 19:55
* @description:
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标对象
UserDao target = new UserDao();
// class aop.UserDao
System.out.println(target.getClass());
// 给目标对象,创建代理对象
IUserDao proxy = (IUserDao) new ProxyFactory(target).getProxyInstance();
// class $Proxy0 内存中动态生成的代理对象
System.out.println(proxy.getClass());
proxy.save();
System.out.println("===1===");
proxy.delete();
System.out.println("===2===");
proxy.saveAndDelete();
}
}
结果:
class aop.UserDao
class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0
开始事务2
save
提交事务2
===1===
开始事务2
delete
提交事务2
===2===
开始事务2
save
delete
提交事务2
可以看出saveAndDelete 内部调用save和delete方法没有走拦截到的方法,这个很好理解,内部调用直接走的方法调用,没用代理对象。
如果我们想查看生产的代理类:
System.getProperties().put("sun.misc.ProxyGenerator.saveGeneratedFiles","true" );
总结:
代理对象不需要实现接口,但是目标对象一定要实现接口,否则不能用动态代理
1.3.Cglib代理(基于继承的方式实现)
pom如下:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/cglib/cglib -->
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>3.2.12</version>
</dependency>
上面的静态代理和动态代理模式都是要求目标对象是实现一个接口的目标对象,但是有时候目标对象只是一个单独的对象,并没有实现任何的接口,这个时候就可以使用以目标对象子类的方式类实现代理,这种方法就叫做:Cglib代理
Cglib代理,也叫作子类代理,它是在内存中构建一个子类对象从而实现对目标对象功能的扩展.
JDK的动态代理有一个限制,就是使用动态代理的对象必须实现一个或多个接口,如果想代理没有实现接口的类,就可以使用Cglib实现.
Cglib是一个强大的高性能的代码生成包,它可以在运行期扩展java类与实现java接口.它广泛的被许多AOP的框架使用,例如Spring AOP和synaop,为他们提供方法的interception(拦截)
Cglib包的底层是通过使用一个小而块的字节码处理框架ASM来转换字节码并生成新的类.不鼓励直接使用ASM,因为它要求你必须对JVM内部结构包括class文件的格式和指令集都很熟悉.
Cglib子类代理实现方法:
1.需要引入cglib的jar文件,但是Spring的核心包中已经包括了Cglib功能,所以直接引入pring-core-3.2.5.jar即可.
2.引入功能包后,就可以在内存中动态构建子类
3.代理的类不能为final,否则报错
4.目标对象的方法如果为final/static,那么就不会被拦截,即不会执行目标对象额外的业务方法.
5.如果方法为static,private则无法进行代理。
代码:
dao和接口同上面JDK代理。
Cglib代理工厂
package aop;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author: 乔利强
* @date: 2020/12/11 20:05
* @description:
*/
public class CglibProxyFactory implements MethodInterceptor {
public CglibProxyFactory() {
}
/**
* 1、代理对象;2、委托类方法;3、方法参数;4、代理方法的MethodProxy对象。
*
* @param o
* @param method
* @param objects
* @param methodProxy
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("事务开始......" + method.getName());
Object o1 = methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, objects);
System.out.println("事务结束......." + method.getName());
return o1;
}
}
测试类:
package aop;
import net.sf.cglib.core.DebuggingClassWriter;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
/**
* @author: 乔利强
* @date: 2020/12/11 20:07
* @description:
*/
public class CglibClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//在指定目录下生成动态代理类,我们可以反编译看一下里面到底是一些什么东西
System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "G:/proxy");
CglibProxyFactory cglibProxy = new CglibProxyFactory();
//jdk需要提供接口,cglib需要是非私有类,且不能处理final关键字修饰的方法
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
//设置父类
enhancer.setSuperclass(UserDao.class);
//设置回调对象
enhancer.setCallback(cglibProxy);
UserDao proxy = (UserDao) enhancer.create();
proxy.save();
System.out.println("===1===");
proxy.delete();
System.out.println("===2===");
proxy.saveAndDelete();
}
}
结果: 可以看出通过方法内部调用也走了代理。这个很好理解相当于是调用的是继承类的方法。
事务开始......save
save
事务结束.......save
===1===
事务开始......delete
delete
事务结束.......delete
===2===
事务开始......saveAndDelete
事务开始......save
save
事务结束.......save
事务开始......delete
delete
事务结束.......delete
事务结束.......saveAndDelete
关于cglib动态代理中invokeSuper和invoke的区别参考:https://blog.csdn.net/z69183787/article/details/106878203/
补充:在Spring的AOP中自调用AOP无效。简单研究了下,是调用invoke的效果,如下:
1.修改代理方法
package aop;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @Author: qlq
* @Description
* @Date: 20:23 2021/1/24
*/
public class CglibProxyFactory implements MethodInterceptor {
private Object target;
public CglibProxyFactory(Object target) {
super();
this.target = target;
}
/**
* 1、代理对象;2、委托类方法;3、方法参数;4、代理方法的MethodProxy对象。
*
* @param o
* @param method
* @param objects
* @param methodProxy
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("事务开始......" + method.getName());
Object o1 = methodProxy.invoke(target, objects);
System.out.println("事务结束......." + method.getName());
return o1;
}
}
2.测试类如下:
package aop;
import net.sf.cglib.core.DebuggingClassWriter;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
/**
* @Author: qlq
* @Description
* @Date: 20:26 2021/1/24
*/
public class CglibClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//在指定目录下生成动态代理类,我们可以反编译看一下里面到底是一些什么东西
System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "G:/proxy");
UserDao userDao = new UserDao();
CglibProxyFactory cglibProxy = new CglibProxyFactory(userDao);
//jdk需要提供接口,cglib需要是非私有类,且不能处理final关键字修饰的方法
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
//设置父类
enhancer.setSuperclass(UserDao.class);
//设置回调对象
enhancer.setCallback(cglibProxy);
UserDao proxy = (UserDao) enhancer.create();
proxy.save();
System.out.println("===1===");
proxy.delete();
System.out.println("===2===");
proxy.saveAndDelete();
}
}
结果:可以看到方法内部调用没有走代理
事务开始......save
save
事务结束.......save
===1===
事务开始......delete
delete
事务结束.......delete
===2===
事务开始......saveAndDelete
save
delete
事务结束.......saveAndDelete
简单理解,invoke方法调用的对象没有增强过(target 模板对象),invokeSuper方法调用的对象已经是增强了的(proxy 代理对象),所以会再走一遍 MethodInterceptor的 interceptor方法,如果是个拦截器链条,就会重新在走一次拦截器链。
而且在invoke和invokeSuper中,this指代的对象不同,
(1) methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, objects); 中this是代理对象:aop.UserDao$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$86ae564d@6a1aab78
(2) methodProxy.invoke(target, objects); 中this指向target对象:aop.UserDao@eafc191
补充:Spring的AOP调用也是用的invoke的套路,我们在AOP中打印this可以看出是目标target对象还是代理proxy对象。结果看出是目标target对象
com.xm.ggn.test.aop.TestServiceImpl@330fff8e也可以简单查看Spring代理:org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy.DynamicAdvisedInterceptor#intercept
@Override
@Nullable
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
Object target = null;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.getTargetSource();
try {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool...
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is,
// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target.
if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly.
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know
// it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot
// swapping or fancy proxying.
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
1.4 在Spring的AOP编程中代理的选择方式:
AOP调用时序图;

查看DefaultAopProxyFactory的源码:
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.aop.framework;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import org.springframework.aop.SpringProxy;
public class DefaultAopProxyFactory implements AopProxyFactory, Serializable {
public DefaultAopProxyFactory() {
}
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (!config.isOptimize() && !config.isProxyTargetClass() && !this.hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
} else {
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
} else {
return (AopProxy)(!targetClass.isInterface() && !Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass) ? new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config) : new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config));
}
}
}
private boolean hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(AdvisedSupport config) {
Class<?>[] ifcs = config.getProxiedInterfaces();
return ifcs.length == 0 || ifcs.length == 1 && SpringProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(ifcs[0]);
}
}
Spring中强制使用Cglib代理
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true" />
SpringBoot中强制使用Cglib代理

总结:
如果加入容器的目标对象有实现接口,用JDK代理
如果目标对象没有实现接口,用Cglib代理
如果目标对象实现了接口,且强制使用cglib代理,则会使用cglib代理
参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/qlqwjy/p/8533261.html
补充:查看JDK动态代理和cglib 代理的原理
Interface1 接口,采用JDK动态代理
package com.xm.ggn.test.proxy;
public interface Interface1 {
void method1();
void method2(String test);
}
CgClass1 类,采用cglib 代理
package com.xm.ggn.test.proxy;
public class CgClass1 {
void method1() {
System.out.println("com.xm.ggn.test.proxy.CgClass1.method1");
}
void method2(String test) {
System.out.println("com.xm.ggn.test.proxy.CgClass1.method2");
}
}
Client
package com.xm.ggn.test.proxy;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// jdk 动态代理
Interface1 o = (Interface1) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Interface1.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Interface1.class}, new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler.invoke " + method + " " + args);
return "123";
}
});
o.method1();
o.method2("Interface1 method2");
//****************cglib
//jdk需要提供接口,cglib需要是非私有类,且不能处理final关键字修饰的方法
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
//设置父类
enhancer.setSuperclass(CgClass1.class);
//设置回调对象
enhancer.setCallback(new MethodInterceptor() {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("方法前......" + method.getName());
Object o1 = methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, objects);
System.out.println("方法后......." + method.getName());
return o1;
}
});
CgClass1 cgClass1 = (CgClass1) enhancer.create();
cgClass1.method1();
cgClass1.method2("cg method2");
Thread.sleep(50 * 10000);
}
}
启动之后控制台如下:
java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler.invoke public abstract void com.xm.ggn.test.proxy.Interface1.method1() null
java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler.invoke public abstract void com.xm.ggn.test.proxy.Interface1.method2(java.lang.String) [Ljava.lang.Object;@5025a98f
方法前......method1
com.xm.ggn.test.proxy.CgClass1.method1
方法后.......method1
方法前......method2
com.xm.ggn.test.proxy.CgClass1.method2
方法后.......method2
然后采用arthas 进行查看
(1) 查看JDK动态代理
sc 查看类信息
[arthas@69520]$ sc *.Interface1
com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0
com.xm.ggn.test.proxy.Interface1
反编译查看代理类信息
[arthas@69520]$ jad com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0
ClassLoader:
+-sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
+-sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@35db61e9
Location:
/*
* Decompiled with CFR.
*
* Could not load the following classes:
* com.xm.ggn.test.proxy.Interface1
*/
package com.sun.proxy;
import com.xm.ggn.test.proxy.Interface1;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException;
public final class $Proxy0
extends Proxy
implements Interface1 {
private static Method m1;
private static Method m2;
private static Method m4;
private static Method m3;
private static Method m0;
public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler invocationHandler) {
super(invocationHandler);
}
public final boolean equals(Object object) {
try {
return (Boolean)this.h.invoke(this, m1, new Object[]{object});
}
catch (Error | RuntimeException throwable) {
throw throwable;
}
catch (Throwable throwable) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable);
}
}
public final String toString() {
try {
return (String)this.h.invoke(this, m2, null);
}
catch (Error | RuntimeException throwable) {
throw throwable;
}
catch (Throwable throwable) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable);
}
}
public final void method2(String string) {
try {
this.h.invoke(this, m4, new Object[]{string});
return;
}
catch (Error | RuntimeException throwable) {
throw throwable;
}
catch (Throwable throwable) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable);
}
}
public final void method1() {
try {
this.h.invoke(this, m3, null);
return;
}
catch (Error | RuntimeException throwable) {
throw throwable;
}
catch (Throwable throwable) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable);
}
}
public final int hashCode() {
try {
return (Integer)this.h.invoke(this, m0, null);
}
catch (Error | RuntimeException throwable) {
throw throwable;
}
catch (Throwable throwable) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable);
}
}
static {
try {
m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", Class.forName("java.lang.Object"));
m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString", new Class[0]);
m4 = Class.forName("com.xm.ggn.test.proxy.Interface1").getMethod("method2", Class.forName("java.lang.String"));
m3 = Class.forName("com.xm.ggn.test.proxy.Interface1").getMethod("method1", new Class[0]);
m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode", new Class[0]);
return;
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException noSuchMethodException) {
throw new NoSuchMethodError(noSuchMethodException.getMessage());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException classNotFoundException) {
throw new NoClassDefFoundError(classNotFoundException.getMessage());
}
}
}
可以看到是继承Proxy 对象,实现Interface1 接口。
1》构造方法会调用父类的构造,IDEA 查看父类构造
java.lang.reflect.Proxy#Proxy(java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler)
protected InvocationHandler h;
protected Proxy(InvocationHandler h) {
Objects.requireNonNull(h);
this.h = h;
}
2》 查看method1、method2 方法,实际是反射调用InvocationHandler, 也就是我们上面匿名类创建的对象(所以这个匿名类一般会根据方法名称判断是toString、hashcode方法进行特殊处理)
public final void method2(String string) {
try {
this.h.invoke(this, m4, new Object[]{string});
return;
}
catch (Error | RuntimeException throwable) {
throw throwable;
}
catch (Throwable throwable) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable);
}
}
public final void method1() {
try {
this.h.invoke(this, m3, null);
return;
}
catch (Error | RuntimeException throwable) {
throw throwable;
}
catch (Throwable throwable) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable);
}
}
(2) 查看Cglib 代理
1》搜索类
[arthas@104968]$ sc *.CgClass1
com.xm.ggn.test.proxy.CgClass1
com.xm.ggn.test.proxy.CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3
2》反编译查看类:可以看到主要是继承代理类,实现cglib 的类,核心是通过MethodInteceptor 进行处理的
[arthas@104968]$ jad com.xm.ggn.test.proxy.CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3
ClassLoader:
+-sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
+-sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@1f256477
Location:
/E:/xiangmu/bs-media-gitee/bs-media/media-server/target/classes/
/*
* Decompiled with CFR.
*
* Could not load the following classes:
* com.xm.ggn.test.proxy.CgClass1
*/
package com.xm.ggn.test.proxy;
import com.xm.ggn.test.proxy.CgClass1;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import net.sf.cglib.core.ReflectUtils;
import net.sf.cglib.core.Signature;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Callback;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Factory;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
public class CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3
extends CgClass1
implements Factory {
private boolean CGLIB$BOUND;
public static Object CGLIB$FACTORY_DATA;
private static final ThreadLocal CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS;
private static final Callback[] CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS;
private MethodInterceptor CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
private static Object CGLIB$CALLBACK_FILTER;
private static final Method CGLIB$method1$0$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$method1$0$Proxy;
private static final Object[] CGLIB$emptyArgs;
private static final Method CGLIB$method2$1$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$method2$1$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$equals$2$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$equals$2$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$toString$3$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$toString$3$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$hashCode$4$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$hashCode$4$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$clone$5$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$clone$5$Proxy;
static void CGLIB$STATICHOOK1() {
CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS = new ThreadLocal();
CGLIB$emptyArgs = new Object[0];
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.xm.ggn.test.proxy.CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3");
Class<?> clazz2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object");
Method[] methodArray = ReflectUtils.findMethods(new String[]{"equals", "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z", "toString", "()Ljava/lang/String;", "hashCode", "()I", "clone", "()Ljava/lang/Object;"}, clazz2.getDeclaredMethods());
CGLIB$equals$2$Method = methodArray[0];
CGLIB$equals$2$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(clazz2, clazz, "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z", "equals", "CGLIB$equals$2");
CGLIB$toString$3$Method = methodArray[1];
CGLIB$toString$3$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(clazz2, clazz, "()Ljava/lang/String;", "toString", "CGLIB$toString$3");
CGLIB$hashCode$4$Method = methodArray[2];
CGLIB$hashCode$4$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(clazz2, clazz, "()I", "hashCode", "CGLIB$hashCode$4");
CGLIB$clone$5$Method = methodArray[3];
CGLIB$clone$5$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(clazz2, clazz, "()Ljava/lang/Object;", "clone", "CGLIB$clone$5");
clazz2 = Class.forName("com.xm.ggn.test.proxy.CgClass1");
Method[] methodArray2 = ReflectUtils.findMethods(new String[]{"method1", "()V", "method2", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V"}, clazz2.getDeclaredMethods());
CGLIB$method1$0$Method = methodArray2[0];
CGLIB$method1$0$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(clazz2, clazz, "()V", "method1", "CGLIB$method1$0");
CGLIB$method2$1$Method = methodArray2[1];
CGLIB$method2$1$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(clazz2, clazz, "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", "method2", "CGLIB$method2$1");
}
final void CGLIB$method1$0() {
super.method1();
}
final void method1() {
MethodInterceptor methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (methodInterceptor == null) {
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
if (methodInterceptor != null) {
Object object = methodInterceptor.intercept(this, CGLIB$method1$0$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$method1$0$Proxy);
return;
}
super.method1();
}
final void CGLIB$method2$1(String string) {
super.method2(string);
}
final void method2(String string) {
MethodInterceptor methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (methodInterceptor == null) {
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
if (methodInterceptor != null) {
Object object = methodInterceptor.intercept(this, CGLIB$method2$1$Method, new Object[]{string}, CGLIB$method2$1$Proxy);
return;
}
super.method2(string);
}
final boolean CGLIB$equals$2(Object object) {
return super.equals(object);
}
public final boolean equals(Object object) {
MethodInterceptor methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (methodInterceptor == null) {
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
if (methodInterceptor != null) {
Object object2 = methodInterceptor.intercept(this, CGLIB$equals$2$Method, new Object[]{object}, CGLIB$equals$2$Proxy);
return object2 == null ? false : (Boolean)object2;
}
return super.equals(object);
}
final String CGLIB$toString$3() {
return super.toString();
}
public final String toString() {
MethodInterceptor methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (methodInterceptor == null) {
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
if (methodInterceptor != null) {
return (String)methodInterceptor.intercept(this, CGLIB$toString$3$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$toString$3$Proxy);
}
return super.toString();
}
final int CGLIB$hashCode$4() {
return super.hashCode();
}
public final int hashCode() {
MethodInterceptor methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (methodInterceptor == null) {
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
if (methodInterceptor != null) {
Object object = methodInterceptor.intercept(this, CGLIB$hashCode$4$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$hashCode$4$Proxy);
return object == null ? 0 : ((Number)object).intValue();
}
return super.hashCode();
}
final Object CGLIB$clone$5() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
protected final Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
MethodInterceptor methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (methodInterceptor == null) {
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
if (methodInterceptor != null) {
return methodInterceptor.intercept(this, CGLIB$clone$5$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$clone$5$Proxy);
}
return super.clone();
}
public static MethodProxy CGLIB$findMethodProxy(Signature signature) {
String string = ((Object)signature).toString();
switch (string.hashCode()) {
case -724084219: {
if (!string.equals("method1()V")) break;
return CGLIB$method1$0$Proxy;
}
case -518805714: {
if (!string.equals("method2(Ljava/lang/String;)V")) break;
return CGLIB$method2$1$Proxy;
}
case -508378822: {
if (!string.equals("clone()Ljava/lang/Object;")) break;
return CGLIB$clone$5$Proxy;
}
case 1826985398: {
if (!string.equals("equals(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z")) break;
return CGLIB$equals$2$Proxy;
}
case 1913648695: {
if (!string.equals("toString()Ljava/lang/String;")) break;
return CGLIB$toString$3$Proxy;
}
case 1984935277: {
if (!string.equals("hashCode()I")) break;
return CGLIB$hashCode$4$Proxy;
}
}
return null;
}
public CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3() {
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3 cgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3 = this;
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(cgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3);
}
public static void CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(Callback[] callbackArray) {
CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS.set(callbackArray);
}
public static void CGLIB$SET_STATIC_CALLBACKS(Callback[] callbackArray) {
CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS = callbackArray;
}
private static final void CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(Object object) {
block2: {
Object object2;
block3: {
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3 cgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3 = (CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3)object;
if (cgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3.CGLIB$BOUND) break block2;
cgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3.CGLIB$BOUND = true;
object2 = CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS.get();
if (object2 != null) break block3;
object2 = CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS;
if (CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS == null) break block2;
}
cgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 = (MethodInterceptor)((Callback[])object2)[0];
}
}
public Object newInstance(Callback[] callbackArray) {
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3.CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(callbackArray);
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3 cgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3 = new CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3();
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3.CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(null);
return cgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3;
}
public Object newInstance(Callback callback) {
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3.CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(new Callback[]{callback});
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3 cgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3 = new CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3();
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3.CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(null);
return cgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3;
}
public Object newInstance(Class[] classArray, Object[] objectArray, Callback[] callbackArray) {
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3 cgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3;
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3.CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(callbackArray);
Class[] classArray2 = classArray;
switch (classArray.length) {
case 0: {
cgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3 = new CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3();
break;
}
default: {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Constructor not found");
}
}
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3.CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(null);
return cgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3;
}
public Callback getCallback(int n) {
MethodInterceptor methodInterceptor;
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
switch (n) {
case 0: {
methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
break;
}
default: {
methodInterceptor = null;
}
}
return methodInterceptor;
}
public void setCallback(int n, Callback callback) {
switch (n) {
case 0: {
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 = (MethodInterceptor)callback;
break;
}
}
}
public Callback[] getCallbacks() {
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3 cgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3 = this;
return new Callback[]{this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0};
}
public void setCallbacks(Callback[] callbackArray) {
Callback[] callbackArray2 = callbackArray;
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3 cgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3 = this;
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 = (MethodInterceptor)callbackArray[0];
}
static {
CgClass1$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$f752d1b3.CGLIB$STATICHOOK1();
}
}
作者 | QiaoZhi
来源 | cnblogs.com/qlqwjy/p/7550609.html

