python管理文件神器os.walk
原文:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35866846/article/details/107823636
作者:诡途
遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议
大家好,欢迎来到 Crossin的编程教室 !
有没有想过用python写一个文件管理程序?听起来似乎没思路?
其实并不难,因为python已经为你准备好了神器 os.walk,它是一个简单易用的文件、目录遍历器,可以帮助我们高效的处理文件、目录方面的事情。
本文将介绍 os.walk 模块,最后使用 os.walk 模块实现一个在指定日志整理文件的程序。
基本介绍
os.walk():扫描某个指定目录下所包含的子目录和文件,返回的是一个迭代器。
基本使用
假设文件夹data有如下的目录结构(cmd 命令:tree /f)
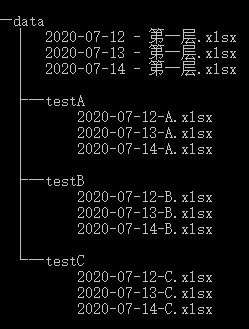
2.1 扫描所有文件
扫描内容:
子文件夹和文件
子文件夹下的文件
输出内容:
文件夹名称/文件名称
扫描路径:
自顶向下 topdown=True(默认)
自底向上 topdown=False
from os import walkpath="data"for curDir, dirs, files in walk(path):#for curDir, dirs, files in walk(path,topdown=False):print("现在的目录:" ,curDir)print("该目录下包含的子目录:" , str(dirs))print("该目录下包含的文件:",str(files))print("*"*20)
自顶向下扫描结果:
现在的目录:data该目录下包含的子目录:['testA', 'testB', 'testC']该目录下包含的文件:['2020-07-12 - 第一层.xlsx', '2020-07-13 - 第一层.xlsx', '2020-07-14 - 第一层.xlsx']********************现在的目录:data\testA该目录下包含的子目录:[]该目录下包含的文件:['2020-07-12-A.xlsx', '2020-07-13-A.xlsx', '2020-07-14-A.xlsx']********************现在的目录:data\testB该目录下包含的子目录:[]该目录下包含的文件:['2020-07-12-B.xlsx', '2020-07-13-B.xlsx', '2020-07-14-B.xlsx']********************现在的目录:data\testC该目录下包含的子目录:[]该目录下包含的文件:['2020-07-12-C.xlsx', '2020-07-13-C.xlsx', '2020-07-14-C.xlsx']********************
自底向上扫描结果:
现在的目录:data\testA该目录下包含的子目录:[]该目录下包含的文件:['2020-07-12-A.xlsx', '2020-07-13-A.xlsx', '2020-07-14-A.xlsx']********************现在的目录:data\testB该目录下包含的子目录:[]该目录下包含的文件:['2020-07-12-B.xlsx', '2020-07-13-B.xlsx', '2020-07-14-B.xlsx']********************现在的目录:data\testC该目录下包含的子目录:[]该目录下包含的文件:['2020-07-12-C.xlsx', '2020-07-13-C.xlsx', '2020-07-14-C.xlsx']********************现在的目录:data该目录下包含的子目录:['testA', 'testB', 'testC']该目录下包含的文件:['2020-07-12 - 第一层.xlsx', '2020-07-13 - 第一层.xlsx', '2020-07-14 - 第一层.xlsx']********************
2.2 扫描输出所有文件的路径
输出所有文件:
import ospath="data"for curDir, dirs, files in os.walk(path):for file in files:print(os.path.join(curDir, file))
data\2020-07-12 - 第一层.xlsxdata\2020-07-13 - 第一层.xlsxdata\2020-07-14 - 第一层.xlsxdata\testA\2020-07-12-A.xlsxdata\testA\2020-07-13-A.xlsxdata\testA\2020-07-14-A.xlsxdata\testB\2020-07-12-B.xlsxdata\testB\2020-07-13-B.xlsxdata\testB\2020-07-14-B.xlsxdata\testC\2020-07-12-C.xlsxdata\testC\2020-07-13-C.xlsxdata\testC\2020-07-14-C.xlsx
输出指定类型文件
#endswith 截取文件后缀import ospath="data"for curDir, dirs, files in os.walk(path):[print(os.path.join(curDir, file)) for file in files if file.endswith(".xlsx")]
2.3 扫描输出所有的子目录(子文件夹)
# 使用os.walk输出某个目录下的所有文件import ospath="data"for curDir, dirs, files in os.walk(path):for _dir in dirs:print(os.path.join(curDir, _dir))
data\testAdata\testBdata\testC
案例代码
综合运用 os.walk() ——文件指定日期整理程序
import pandas as pdimport numpy as npimport os,openpyxl#移动符合条件文件,并删除二级文件夹和多余文件def move_file(file_path,_new_path,date_xl_str):#本月文件移动至对应新建文件夹,非本月文件直接删除for curDir, dirs, files in os.walk(file_path):for file in files:old_path = os.path.join(curDir, file)new_path = os.path.join(_new_path, file)file_date=file.split("_")[-1][:10]try:os.rename(old_path,new_path) if file_date in date_xl_str else os.remove(old_path)except:os.remove(old_path)#移除子文件夹for curDir, dirs, files in os.walk(file_path):for _dir in dirs:os.removedirs(os.path.join(curDir, _dir))os.mkdir("data")#文件去重-相同日期文件def qch_date(file_path):wj_names=os.listdir(file_path)wj_list=[]num=0for wj in wj_names:new_wj=wj[:-11]if new_wj not in wj_list:wj_list.append(new_wj)else:os.remove(file_path+"\\"+wj)num+=1return num#更新数据源def refresh_data(file_path,sheet_name,data):book=openpyxl.load_workbook(file_path)writer=pd.ExcelWriter(file_path,engine="openpyxl")#在ExcelWriter的源代码中,它初始化空工作簿并删除所有工作表,#writer.book = book将原来表里面的内容保存到writer中writer.book=book#activate激活指定sheet工作表ws=book[sheet_name]#清空当前活动表数据for row in ws.iter_rows():for cell in row:cell.value=None#dataframe行列数idx_num,col_num=data.shape#新数据写入当前活动表-注意索引偏移for i in range(1,idx_num+1):for j in range(1,col_num+1):ws.cell(row=i,column=j).value=data.iloc[i-1,j-1]#保存关闭writerwriter.save()writer.close()return None#文件检查def check_file(file_path,check_file="文件检查.xlsx"):wj_names=os.listdir(file_path)data=pd.DataFrame([wj.split("_")[2:] for wj in wj_names],columns=["店铺名称","日期"])data['日期']=data['日期'].str[:10]#标题columns放到dataframe中nind=data.index.insert(0,'0')data1=data.reindex(index=nind)data1.loc['0']=data.columnsdata1.reset_index(drop=True,inplace=True)#刷新数据源refresh_data(check_file,"数据源",data1)return Nonefile_path="data"#日期格式:xxxx-xx eg:2020-07-01start_date=input("请输入开始日期:")end_date=input("请输入开始日期:")#生成日期区间-字符串类型date_xl_str=[str(i)[:10] for i in pd.date_range(start_date,end_date,freq='D')]#创建指定文件夹new_path=start_date+"~"+end_datetry:os.mkdir(new_path)except:print("文件夹 【%s】 已存在"%new_path)#移动符合条件文件,并删除二级文件夹和多余文件move_file(file_path,new_path,date_xl_str)#文件去重num=qch_date(new_path)print("去除重复文件 %s 个"%num)#文件检查check_file(new_path)
以上就是对 os.walk 的基本介绍和演示。
如果文章对你有帮助,欢迎转发/点赞/收藏~
_往期文章推荐_
评论
