《精通react/vue组件设计》之实现一个健壮的警告提示(Alert)组件

前言
本文是笔者写组件设计的第七篇文章, 今天带大家实现一个自带主题且可关闭的Alert组件, 该组件在诸如Antd或者elementUI等第三方组件库中都会出现,主要用来提供系统的用户反馈.
之所以会写组件设计相关的文章,是因为作为一名前端优秀的前端工程师,面对各种繁琐而重复的工作,我们不应该按部就班的去"辛勤劳动",而是要根据已有前端的开发经验,总结出一套自己的高效开发的方法.
前端组件一般会划分为如下几种类型:
通用型组件: 比如Button, Icon等.
布局型组件: 比如Grid, Layout布局等.
导航型组件: 比如面包屑Breadcrumb, 下拉菜单Dropdown, 菜单Menu等.
数据录入型组件: 比如form表单, Switch开关, Upload文件上传等.
数据展示型组件: 比如Avator头像, Table表格, List列表等.
反馈型组件: 比如Progress进度条, Drawer抽屉, Modal对话框等.
其他业务类型
正文
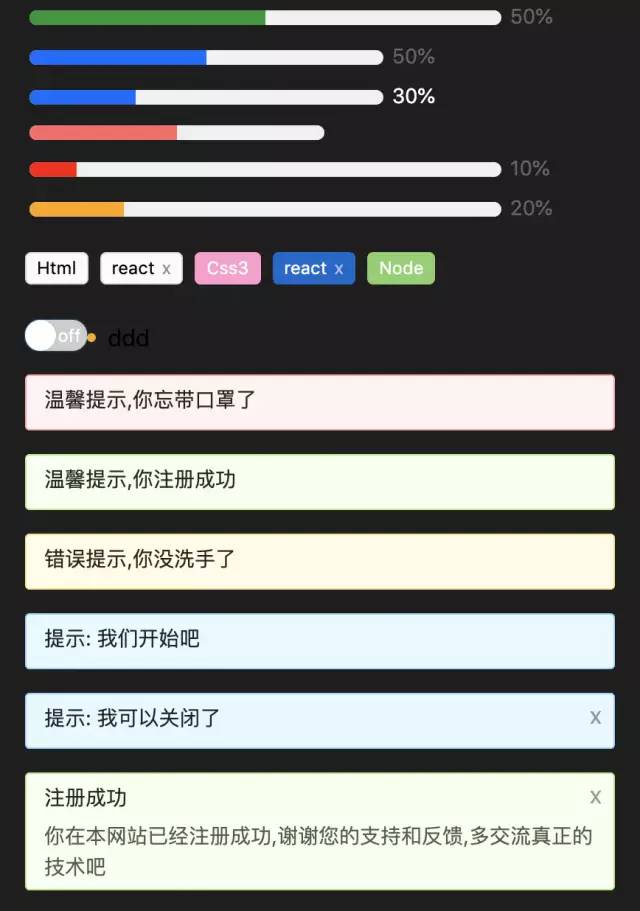
在开始组件设计之前希望大家对css3和js有一定的基础,并了解基本的react/vue语法.我们先看看实现后的组件效果:
1. 组件设计思路
按照之前笔者总结的组件设计原则,我们第一步是要确认需求. 一个警告提示(Alert)组件会有如下需求点:
能控制Alert组件的样式
能控制Alert组件的关闭按钮是否显示
用户可以自己输入提示内容
能控制关闭按钮的文本,或者自定义关闭按钮
支持显示提示内容的辅助文本
内置提供不同类型的警告提示样式,比如成功, 错误, 警告等
关闭提示时能提供自定义事件
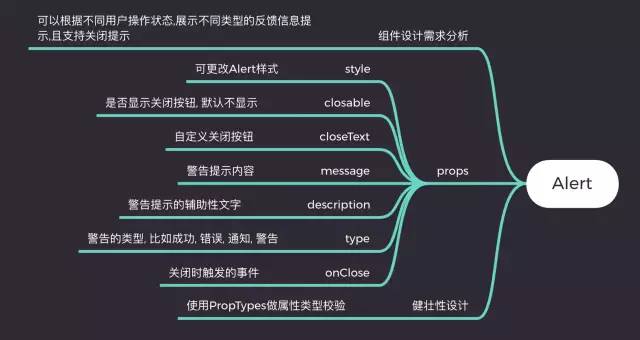
对于react选手来说,如果没用typescript,建议大家都用PropTypes, 它是react内置的类型检测工具,我们可以直接在项目中导入. vue有自带的属性检测方式,这里就不一一介绍了.
通过以上需求分析, 我们发现实现一个Alert非常简单, 它属于反馈型组件,所以不会涉及到太多功能.接下来我们就来看看具体实现.
2. 基于react实现一个Alert组件
2.1. Alert组件框架设计
首先我们先根据需求将组件框架写好,这样后面写业务逻辑会更清晰:
import classnames from 'classnames'
import styles from './index.less'
/**
* 警告提示组件
* @param {style} object 更改Alert样式
* @param {closable} bool 是否显示关闭按钮, 默认不显示
* @param {closeText} string|reactNode 自定义关闭按钮
* @param {message} string 警告提示内容
* @param {description} string 警告提示的辅助性文字
* @param {type} string 警告的类型
* @param {onClose} func 关闭时触发的事件
*/
function Alert(props) {
const {
style,
closable,
closeText,
message,
description,
type,
onClose
} = props
return <div className={styles.xAlertWrap}>
<div className={styles.alertMes}>{ message }</div>
<div className={styles.alertDesc}>{ description }</div>
<span className={styles.closeBtn}>{ closeText ? closeText : 'x' }</span>
</div>
}
export default Alert
有了这个框架,我们就来往里面实现内容吧.
2.2 实现style,closeText,message, description,type
这几个功能在框架搭建好之后已经部分实现了,是因为他们都比较简单,不会牵扯到其他复杂逻辑.只需要对外暴露属性并使用属性即可. 具体实现如下:
function Alert(props) {
const {
style,
closable,
closeText,
message,
description,
type,
onClose
} = props
return <div
className={classnames(styles.xAlertWrap, styles[type] || styles.warning)}
style={{
...style
}}
>
<div className={styles.alertMes}>{ message }</div>
<div className={styles.alertDesc}>{ description }</div>
<span className={styles.closeBtn}>{ closeText ? closeText : 'x' }</span>
</div>
}
以上代码可以发现笔者采用了classnames这个第三方工具, 他可以组合我们的class以实现更灵活的配置. 对于type的实现,我的思路是提前预制好几种类型样式, 通过用户手动配置来匹配到对应的样式:
.xAlertWrap {
box-sizing: border-box;
position: relative;
padding: 5px 12px;
margin-bottom: 16px;
border-radius: 3px;
&.success {
background-color: #f6ffed;
border: 1px solid #b7eb8f;
}
&.info {
background-color: #e6f7ff;
border: 1px solid #91d5ff;
}
&.error {
background-color: #fffbe6;
border: 1px solid #ffe58f;
}
&.warning {
background-color: #fff1f0;
border: 1px solid #ffa39e;
}
}
2.3 实现closable和onClose
closable主要是用来让用户能手动关闭Alert,onClose是对外暴露的关闭时的方法, 因为没必要也不需要向外暴露属性来让Alert关闭, 所以最好的方式是在组件内部实现, 我们会通过useState这个钩子来处理,代码如下:
function Alert(props) {
const {
style,
closable,
closeText,
message,
description,
type,
onClose
} = props
let [visible, setVisible] = useState(true)
const handleColse = () => {
setVisible(false)
onClose && onClose()
}
return visible ?
<div
className={classnames(styles.xAlertWrap, styles[type] || styles.warning)}
style={{
opacity: visible ? '1' : '0',
...style
}}
>
<div className={styles.alertMes}>{ message }</div>
<div className={styles.alertDesc}>{ description }</div>
{
!!closable && <span className={styles.closeBtn} onClick={handleColse}>{ closeText ? closeText : 'x' }</span>
}
</div> : null
}
通过控制visible来控制Alert的出现和消失, 并且当点击关闭按钮时能调用外部暴露的onClose方法.
2.4 健壮性支持, 我们采用react提供的propTypes工具:
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
// ...
Alert.propTypes = {
style: PropTypes.object,
closable: PropTypes.bool,
closeText: PropTypes.oneOfType([
PropTypes.string,
PropTypes.element
]),
message: PropTypes.string,
description: PropTypes.string,
type: PropTypes.string,
onClose: PropTypes.func
}
关于prop-types的使用官网上有很详细的案例,这里说一点就是oneOfType的用法, 它用来支持一个组件可能是多种类型中的一个. 组件完整css代码如下:
{
: border-box;
position: relative;
padding: 5px 12px;
: 16px;
: 3px;
{
: #f6ffed;
border: 1px solid #b7eb8f;
}
{
: #e6f7ff;
border: 1px solid #91d5ff;
}
{
: #fffbe6;
border: 1px solid #ffe58f;
}
{
: #fff1f0;
border: 1px solid #ffa39e;
}
{
:5px;
color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.85);
: 14px;
: 1.5em;
}
{
color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.65);
: 14px;
: 1.5em;
: break-all;
}
{
position: absolute;
right: 8px;
top: 5px;
color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.4);
cursor: pointer;
}
}
通过以上步骤, 一个健壮的的Alert组件就完成了,关于代码中的css module和classnames的使用大家可以自己去官网学习,非常简单.如果不懂的可以在趣谈前端技术群里提问,笔者看到后会第一时间解答.
2.5 使用Alert组件
我们可以通过如下方式使用它:
<Alert message="温馨提示,你忘带口罩了" />
<Alert message="温馨提示,你注册成功" type="success" />
<Alert message="错误提示,你没洗手了" type="error" />
<Alert message="提示: 我们开始吧" type="info" />
<Alert message="提示: 我可以关闭了" type="info" closable onClose={() => { alert(111) }} /><Alert message="注册成功" description="你在本网站已经注册成功,谢谢您的支持和反馈,多交流真正的技术吧" closable type="success" />
笔者已经将实现过的组件发布到npm上了,大家如果感兴趣可以直接用npm安装后使用,方式如下:
npm i /xui
// 导入xui
import {
Button,
Skeleton,
Empty,
Progress,
Tag,
Switch,
Drawer,
Badge,
Alert
} from '@alex_xu/xui'
该组件库支持按需导入,我们只需要在项目里配置babel-plugin-import即可,具体配置如下:
// .babelrc
"plugins": [
["import", { "libraryName": "@alex_xu/xui", "style": true }]
]
npm库截图如下:
最后
我在之前的文章中已实现:
modal(模态窗),
badge(徽标),
table(表格),
tooltip(工具提示条),
Skeleton(骨架屏),
Message(全局提示),
form(form表单),
switch(开关),
日期/日历,
二维码识别器组件
等组件, 欢迎学习参考.
如果想获取组件设计系列完整源码, 或者想学习更多H5游戏, webpack,node,gulp,css3,javascript,nodeJS,canvas数据可视化等前端知识和实战,欢迎在公号《趣谈前端》加入我们的技术群一起学习讨论,共同探索前端的边界。
如果对于react/vue组件设计原理不熟悉的,可以参考我的之前写的组件设计系列文章:
《精通react/vue组件设计》之配合React Portals实现一个功能强大的抽屉(Drawer)组件
《精通react/vue组件设计》之5分钟实现一个Tag(标签)组件和Empty(空状态)组件
《精通react/vue组件设计》之用纯css打造类materialUI的按钮点击动画并封装成react组件
《精通react/vue组件设计》之快速实现一个可定制的进度条组件
《精通react/vue组件设计》之基于jsoneditor二次封装一个可实时预览的json编辑器组件(react版)
