vue-axios-vuex-全家桶
Github来源: | 求星星 ✨ | 给个❤️关注,❤️点赞,❤️鼓励一下作者
https://1024bibi.com/2021/09/01/vue-axios-vuex-%E5%85%A8%E5%AE%B6%E6%A1%B6/

axios
Axios 是一个基于 promise 的 HTTP 库,可以用在浏览器和 node.js 中。简单来说就是前端最火最简单的一个http请求解决方案。
功能
从浏览器中创建 XMLHttpRequests 从 node.js 创建 http 请求 支持 Promise API 拦截请求和响应 转换请求数据和响应数据 取消请求 自动转换 JSON 数据 客户端支持防御 XSRF
代码封装
工具类封装
// 引入axios
import axios from 'axios';
// 创建axios实例
const httpService = axios.create({
// url前缀-'https://some-domain.com/api/'
baseURL: process.env.BASE_API, // 需自定义
// 请求超时时间
timeout: 3000 // 需自定义
});
// request拦截器
httpService.interceptors.request.use(
config => {
// 根据条件加入token-安全携带
if (true) { // 需自定义
// 让每个请求携带token
config.headers['User-Token'] = '';
}
return config;
},
error => {
// 请求错误处理
Promise.reject(error);
}
)
// respone拦截器
httpService.interceptors.response.use(
response => {
// 统一处理状态
const res = response.data;
if (res.statuscode != 1) { // 需自定义
// 返回异常
return Promise.reject({
status: res.statuscode,
message: res.message
});
} else {
return response.data;
}
},
// 处理处理
error => {
if (error && error.response) {
switch (error.response.status) {
case 400:
error.message = '错误请求';
break;
case 401:
error.message = '未授权,请重新登录';
break;
case 403:
error.message = '拒绝访问';
break;
case 404:
error.message = '请求错误,未找到该资源';
break;
case 405:
error.message = '请求方法未允许';
break;
case 408:
error.message = '请求超时';
break;
case 500:
error.message = '服务器端出错';
break;
case 501:
error.message = '网络未实现';
break;
case 502:
error.message = '网络错误';
break;
case 503:
error.message = '服务不可用';
break;
case 504:
error.message = '网络超时';
break;
case 505:
error.message = 'http版本不支持该请求';
break;
default:
error.message = `未知错误${error.response.status}`;
}
} else {
error.message = "连接到服务器失败";
}
return Promise.reject(error);
}
)
/*网络请求部分*/
/*
* get请求
* url:请求地址
* params:参数
* */
export function get(url, params = {}) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
httpService({
url: url,
method: 'get',
params: params
}).then(response => {
resolve(response);
}).catch(error => {
reject(error);
});
});
}
/*
* post请求
* url:请求地址
* params:参数
* */
export function post(url, params = {}) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
httpService({
url: url,
method: 'post',
data: params
}).then(response => {
resolve(response);
}).catch(error => {
reject(error);
});
});
}
/*
* 文件上传
* url:请求地址
* params:参数
* */
export function fileUpload(url, params = {}) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
httpService({
url: url,
method: 'post',
data: params,
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'multipart/form-data' }
}).then(response => {
resolve(response);
}).catch(error => {
reject(error);
});
});
}
export default {
get,
post,
fileUpload
}
使用
// 引入工具类-目录自定义
import fetch from '@/util/fetch'
// 使用
const TMPURL = ''; // url地址
const params = {}; // 参数
fetch.post(TMPURL + '/login/login', params);
vuex是什么?
vuex是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。chrome安装调试工具 devtools extension
单向数据流
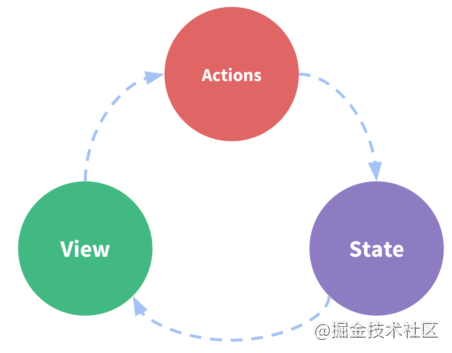
示意图说明:
State:驱动应用的数据源(单向数据流) View:以声明方式将 state 映射到视图(静态显示出来的数据源) Actions:处理用户在view上面操作而导致的状态变化(数据源变化追踪)
一个简单的demo案例:
<template>
<div>
<!-- view -->
<div>{{ count }}</div>
<button @click="increment">increment</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// state
data () {
return {
count: 0
}
},
// actions
methods: {
increment () {
this.count++
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
vuex解决的问题
多个视图组件,包括父子组件,兄弟组件之间的状态共享 不同视图组件的行为需要变更同一个状态
vuex使用场景
中大型单页应用,需要考虑如何更好地在组件外部管理状态,简单应用不建议使用
vuex与全局变量的区别
响应式:vuex的状态存储是响应式的,当Vue组件从store中读取状态的时候,若store中的状态发生变化,那么相应的组件也会得到高效更新 不能直接改变store:不能直接改变store的变化,改变store中状态的唯一途径是commit mutation,方便于跟踪每一个状态的变化
vuex核心流程
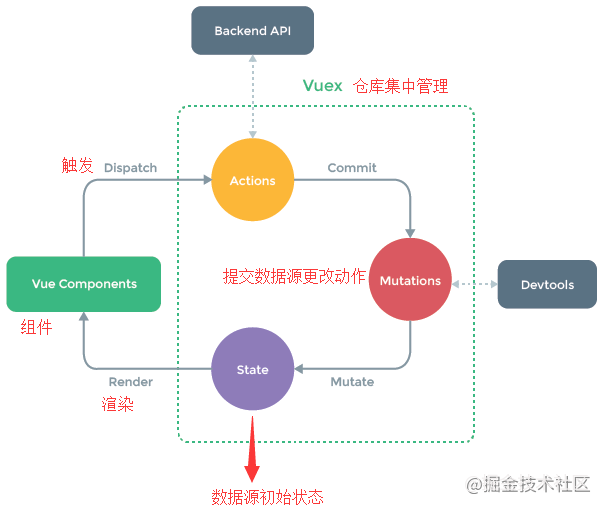
示意图说明:
Vue Components:Vue组件。HTML页面上,负责接收用户操作等交互行为,执行dispatch方法触发对应action进行回应 Dispatch:操作行为触发方法,是唯一能执行action的方法 Actions:操作行为处理模块。负责处理Vue Components接收到的所有交互行为。包含同步/异步操作,支持多个同名方法,按照注册的顺序依次触发。向后台API请求的操作就在这个模块中进行,包括触发其他action以及提交mutation的操作。该模块提供了Promise的封装,以支持action的链式触发 Commit:状态改变提交操作方法。对mutation进行提交,是唯一能执行mutation的方法 Mutations:状态改变操作方法。是Vuex修改state的唯一推荐方法,其他修改方式在严格模式下将会报错。该方法只能进行同步操作,且方法名只能全局唯一。操作之中会有一些hook暴露出来,以进行state的监控等 State:页面状态管理容器对象。集中存储Vue components中data对象的零散数据,全局唯一,以进行统一的状态管理。页面显示所需的数据从该对象中进行读取,利用Vue的细粒度数据响应机制来进行高效的状态更新 Getters:state对象读取方法。图中没有单独列出该模块,应该被包含在了render中,Vue Components通过该方法读取全局state对象
总结说明:
Vue组件接收交互行为,调用dispatch方法触发action相关处理,若页面状态需要改变,则调用commit方法提交mutation修改state,通过getters获取到state新值,重新渲染Vue Components,界面随之更新
安装
npm install vuex --save
简单示例
(1)src/vuex/store.js中写入以下代码:
// 引入vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 使用vuex
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 1、state:创建初始化状态
const state = {
// 放置初始状态
count: 1
}
// 2、mutations:创建改变状态的方法
const mutations = {
// 状态变更函数-一般大写
ADD (state, n) {
state.count += n;
}
}
// 3、getters:提供外部获取state
const getters = {
count: function(state){
return state.count;
}
}
// 4、actions:创建驱动方法改变mutations
const actions ={
// 触发mutations中相应的方法-一般小写
add ({commit}, data) {
commit('ADD', data)
}
}
// 5、全部注入Store中
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations,
getters,
actions
});
// 6、输出store
export default store;
代码说明:
state - mutations - getters - actions - store,以上写法基本固定。 小型项目用上面的简单管理状态即可。
(2)src/main.js代码中
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
// 引入store
import store from './vuex/store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store, // 全局注入
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})
(3)src/compontent/Count.vue页面组件中代码如下:
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h1>{{ msg }}</h1>
<h2>{{count}}</h2>
<button @click="clickAdd">新增</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {
msg: 'Vuex test!'
}
},
computed: {
// 获取state值
count() {
return this.$store.state.count;
}
},
methods: {
clickAdd() {
//分发action中的add方法
this.$store.dispatch('add', 1);
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
状态对象的获取方法
在组件的template中直接使用
<h2>{{ $store.state.count }}</h2>
在计算属性computed中直接赋值
// 方式1:直接获取
computed: {
count() {
// this指的是main.js中的vue实例对象
return this.$store.state.count;
}
}
通过mapState的对象来赋值
// 方式2:利用mapState
computed: mapState({
// es5写法
count: function (state) {
return state.count;
},
// es6写法
count: state => state.count
})
通过mapState的数组来赋值
// 方式3:数组获取
computed: mapState(['count'])
通过mapState的JSON来赋值
// 方式4:JSON获取
computed: mapState({
count: 'count'
})
mutations-getters-actions异步
mutations(修改状态)
(1)template中直接使用$store.commit( )触发
// template
<button @click="$store.commit('ADD')">+</button>
// src/vuex/store.js
const mutations = {
// 状态变更函数
ADD (state) {
state.count++;
}
}
(2)利用mapMutations引入触发
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h1>{{ msg }}</h1>
<h2>{{count}}</h2>
<!-- 3、、直接调用相应的方法 -->
<button @click="ADD">+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 1、引入mapMutations
import {mapState, mapMutations} from 'vuex'
export default {
data () {
return {
msg: 'Vuex test!'
}
},
// 通过mapState的JSON来赋值
computed: mapState({
count: 'count'
}),
// 2、methods中加入mapMutations
methods: mapMutations([
'ADD'
])
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
getters(获取state和过滤)
(1)基本用法
// src/vuex/store.js
const getters = {
count: function(state){
// 返回加上100
return state.count + 100;
}
}
(2)常规获取值
computed: {
// 获取getters
count(){
return this.$store.getters.count;
}
}
(3)mapGetters获取值
// 1、引入mapMutations
import {mapState, mapMutations, mapGetters} from 'vuex'
// 2、使用
computed: {
// 获取getters
...mapGetters(["count"])
}
actions(异步状态修改)
actions和mutations功能基本一样,不同点是,actions是异步的改变state状态,而mutations是同步改变状态。不过实际项目中一般都是通过actions改变mutations中的值。
(1)store.js中增加异步代码
// src/vuex/store.js
const actions ={
// 触发mutations中相应的方法
add ({commit}) {
// 增加异步
setTimeout(()=>{
commit('ADD')
},3000);
console.log('我比reduce提前执行');
}
}
(2)常规使用
// template
<button @click="add">+</button>
// script
methods: {
add() {
//分发action
this.$store.dispatch('add');
}
}
(3)mapActions的使用
// template
<button @click="add">+</button>
// script
// 引入mapActions
import {mapState, mapActions} from 'vuex'
// 使用mapActions
methods: {
...mapActions(['add'])
}
传递参数
只需要在mutations和actions相应的地方加上参数,然后调用的时候传入即可。
(1)src/vuex/store.js中
// actions中传递参数
const mutations = {
ADD (state, n) {
state.count += n;
}
}
// actions中传递参数
const actions ={
// 触发mutations中相应的方法
add ({commit}, n) {
// 增加异步
setTimeout(()=>{
commit('ADD', n);
},3000);
console.log('我比reduce提前执行');
}
}
(2)页面组件常规调用传递
// template
<button @click="add">+</button>
// script
methods: {
add() {
// 分发action
this.$store.dispatch('add', 99);
}
}
(3)页面组件使用mapActions调用传递
// template
<button @click="add(99)">+</button>
// script
methods: {
...mapActions(['add'])
}
module-模块组
当应用非常复杂,状态非常多的时候,需要将store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块,从上至下进行同样方式的分割。
大致的结构
// 模块A
const moduleA = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
// 模块B
const moduleB = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
// 组装
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
})
// 取值
store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态
store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态
实际开发中建议把module分开编写。
(1)src/vuex/module1.js
// 模块1
const module1 = {
// 初始化状态
state: {
module1: {
name: '模块1'
}
},
// 编写动作
mutations: {
CHANGE1 (state, data) {
state.module1 = data;
}
},
// 取值
getters: {
module1: function(state){
return state.module1;
}
},
// 创建驱动,可异步
actions: {
change1 ({commit}, data) {
commit('CHANGE1', data)
}
}
}
export default module1;
(2)src/vuex/module2.js
// 模块1
const module2 = {
// 初始化状态
state: {
module2: {
name: '模块2'
}
},
// 编写动作
mutations: {
CHANGE2 (state, data) {
state.module2 = data;
}
},
// 取值
getters: {
module2: function(state){
return state.module2;
}
},
// 创建驱动,可异步
actions: {
change2 ({commit}, data) {
commit('CHANGE2', data)
}
}
}
export default module2;
(3)src/vuex/store.js
// 引入vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 引入module1
import module1 from '@/vuex/module1'
// 引入module2
import module2 from '@/vuex/module2'
// 使用vuex
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 模块注入
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: module1,
b: module2
}
})
// 输出store
export default store;
(4)组件中使用,src/compontent/one.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<!-- module1 -->
<h2>{{ module1.name }}</h2>
<button @click="change1({'name': 'change1'})">module1改变</button>
<!-- module2 -->
<h2>{{ module2.name }}</h2>
<button @click="change2({'name': 'change2'})">module2改变</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 引入快捷方法
import {mapState, mapGetters, mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'app',
data () {
return {
}
},
computed:{
// mapState取值
// ...mapState({
// module1: state => state.a.module1.name,
// module2: state => state.b.module2.name
// })
// mapGetter取值
...mapGetters(['module1', 'module2'])
},
methods: {
// mapAction取方法
...mapActions([
'change1',
'change2'
])
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
PS:module中命名要唯一,不然获取值和改变值的时候会冲突,目前亲测mapGetters只能获取对象。
vue-router
Vue Router 是 Vue.js 官方的路由管理器。它和 Vue.js 的核心深度集成,让构建单页面应用变得易如反掌。
包含的功能有:
嵌套的路由/视图表 模块化的、基于组件的路由配置 路由参数、查询、通配符 基于 Vue.js 过渡系统的视图过渡效果 细粒度的导航控制 带有自动激活的 CSS class 的链接 HTML5 历史模式或 hash 模式,在 IE9 中自动降级 自定义的滚动条行为
安装
使用命令安装:
npm install vue-router --save
在src/router/index.js文件中
// 引入vue框架
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入vue-router路由依赖
import Router from 'vue-router'
// 引入页面组件,命名为HelloWorld
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld'
// Vue全局使用Router
Vue.use(Router)
// 定义路由配置
export default new Router({
routes: [ //配置路由,这里是个数组
{ //每一个链接都是一个对象
path: '/', //链接路径
name: 'HelloWorld', //路由名称,
component: HelloWorld //对应的组件模板
}
]
})
在系统入口文件main.js中注入router,代码如下:
// 引入vue框架
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入根组件
import App from './App'
// 引入路由配置
import router from './router'
// 关闭生产模式下给出的提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 定义实例
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router, // 注入框架中
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})
页面跳转
router-link标签跳转
在html标签内使用router-link跳转,相应于超链接a标签,使用方式如下:
<router-link to="/">[显示字段]</router-link>
to:导航路径
使用示例如下:
<p>导航 :
<router-link to="/">首页</router-link>
<router-link to="/hello">hello</router-link>
</p>
编程式导航-JS代码内部跳转
实际项目中,很多时候都是通过在JS代码内部进行导航的跳转,使用方式如下:
this.$router.push('/xxx')
具体的简单用法:
(1)先编写一个按钮,在按钮上绑定goHome( )方法。
<button @click="goHome">回到首页</button>
(2)在<script>模块里加入goHome方法,并用this.$router.push(‘/’)导航到首页
export default {
name: 'app',
methods: {
goHome(){
this.$router.push('/home');
}
}
}
其他常用方法
// 后退一步记录,等同于 history.back()
this.$router.go(-1)
// 在浏览器记录中前进一步,等同于 history.forward()
this.$router.go(1)
子路由-路由嵌套
子路由,也叫路由嵌套,采用在children后跟路由数组来实现,数组里和其他配置路由基本相同,需要配置path和component,然后在相应部分添加
src/components/Home.vue(父页面)
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h1>{{ msg }}</h1>
<!-- 添加子路由导航 -->
<p>导航 :
<router-link to="/home">首页</router-link> |
<router-link to="/home/one">-子页面1</router-link> |
<router-link to="/home/two">-子页面2</router-link>
</p>
<!-- 子页面展示部分 -->
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Home',
data () {
return {
msg: 'Home Page!'
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
src/components/One.vue(子页面1)
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h1>{{ msg }}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'One',
data () {
return {
msg: 'Hi, I am One Page!'
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
src/components/Two.vue(子页面2)
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h1>{{ msg }}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Two',
data () {
return {
msg: 'Hi, I am Two Page!'
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
src/router/index.js(路由配置)
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import Home from '@/components/Home'
import One from '@/components/One'
import Two from '@/components/Two'
Vue.use(Router)
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/', // 默认页面重定向到主页
redirect: '/home'
},
{
path: '/home', // 主页路由
name: 'Home',
component: Home,
children:[ // 嵌套子路由
{
path:'one', // 子页面1
component:One
},
{
path:'two', // 子页面2
component:Two
},
]
}
]
})
路由传递参数
通过<router-link> 标签中的to传参
基本语法:
<router-link :to="{name:xxx, params: {key:value}}">valueString</router-link>
PS:上面to前边是带冒号,后边跟的是一个对象形势的字符串
name:在路由配置文件中起的name值。叫做命名路由。 params:要传的参数,它是对象形式,在对象里可以传递多个值。
具体实例如下:
(1)在src/components/Home.vue里面导航中添加如下代码:
<router-link :to="{name: 'one', params:{username:'test123'}}">子页面1</router-link>
(2)在src/router/indes.js中添加如下代码,重点是name:
{
path:'one', // 子页面1
name: 'one', // 路由名称-命名路由
component:One
}
(3)在src/components/One.vue里面接受参数,代码如下:
<h2>{{$route.params.username}}</h2>
url中传递参数
(1)在路由中以冒号传递,在src/router/index.js中加入如下代码:
{
path:'/home/two/:id/:name', // 子页面2
component:Two
},
(2)接受参数,在src/components/Two.vuez中加入如下代码:
<p>ID:{{ $route.params.id}}</p>
<p>名称:{{ $route.params.name}}</p>
(3)路由跳转,在src/components/Home.vue中加入如下代码:
<router-link to="/home/two/1/张三">子页面2</router-link>
PS:to前没有冒号为字符串路由,必须全部匹配。
(4)如果路由参数需要有特定的规则,就需要加入正则表达式了,示例如下:
{
path:'/home/two/:id(\d+)/:name', // 子页面2
component:Two
}
编程式导航-params传递参数
(1)在src/router/index.js页面加入如下代码:
{
path:'/home/three', // 子页面3
name: 'three',
component:Three
}
(2)在src/components/Three.vue页面加入如下代码:
<p>ID:{{ $route.params.id}}</p>
<p>名称:{{ $route.params.name}}</p>
(3)在src/components/Home.vue中加入如下代码:
// template
<button @click="toThreePage">页面3-params传参</button>
// script
methods: {
toThreePage() {
this.$router.push({name: 'three', params: {id: 1, name: 'zhangsan'}})
}
}
说明:
A、动态路由使用params传递参数,在this.$router.push() 方法中path不能和params一起使用,否则params将无效。需要用name来指定页面。
B、以上方式参数不会显示到浏览器的地址栏中,如果刷新一次页面,就获取不到参数了,改进方式将第一部中的代码改成如下:
{
path:'/home/three/:id/:name', // 子页面3
name: 'three',
component:Three
}
编程式导航-query传递参数
(1)在src/router/index.js页面加入如下代码:
{
path:'/home/three', // 子页面3
name: 'three',
component:Three
}
(2)在src/components/Three.vue页面加入如下代码:
<p>ID:{{ $route.query.id}}</p>
<p>名称:{{ $route.query.name}}</p>
(3)在src/components/Home.vue中加入如下代码:
// template
<button @click="toThreePage">页面3-params传参</button>
// script
methods: {
toThreePage() {
this.$router.push({path: '/home/three', query: {id: 1, name: 'zhangsan'}})
}
}
PS:动态路由使用query传递参数,会显示到浏览器地址栏中,以上链接为
/home/three?id=1&name=zhangsan
命名路由-命名视图-重定向-别名
命名路由
给一个路由命一个唯一的名称,然后跳转调用这个名称即可。
(1)在src/router/index.js中加一个带name的路由,代码如下:
{
path: 'one', // 子页面1
name: 'one', // 路由名称-命名路由
component: One // 页面组件
}
(2)在src/component/Home.vue页面中调用,代码如下:
// template跳转调用
<router-link :to="{name: 'one'}">子页面1</router-link>
// router.push函数跳转调用
router.push({ name: 'user'}})
命名视图
在同一个页面展示多个视图,如果不用嵌套,只能采用命名视图来实现了,代码如下:
(1)在src/router/index.js中,代码如下:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
// 创建页面组件
const Header = { template: '<div>Header</div>' }
const Left = { template: '<div>Left</div>' }
const Right = { template: '<div>Right</div>' }
Vue.use(Router)
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/', // 主页路由
components: {
default: Header,
a: Left,
b: Right
}
}
]
})
(2)在src/App.vue中,代码如下:
<template>
<div id="app">
<router-view />
<router-view name="a" class="left" />
<router-view name="b" class="right" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App'
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
width: 500px;
border: 1px solid red;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.left,.right{
float: left;
width:48%;
text-align: center;
border:1px solid red
}
</style>
PS:经过实践,命名视图只能放在最顶级的页面中,即第一步中的代码不能放在其他页面中。
重定向
重定向是通过route的配置中关键词redirect来实现的,具体代码如下:
(1)在src/router/index.js中,代码如下:
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/', // 默认页面重定向到主页
redirect: '/home' // 重定向
},
{
path: '/home', // 主页路由
component: Home,
children:[ // 嵌套子路由
{
path:'/home/two/:id/:name', // 子页面2
component:Two
},
{
path:'/home/three/:id/:name', // 子页面3
name: 'three', // 路由名称-命名路由
redirect: '/home/two/:id/:name' // 重定向-传递参数
},
]
}
]
})
(2)在src/components/Home.vue中,代码如下:
<router-link to="/">首页</router-link> |
<router-link to="/home/two/1/lisi">子页面2</router-link> |
<router-link :to="{name: 'three', params: {id: 1, name: 'zhangsan'}}">子页面3</router-link>
说明1-不带参数的重定向:
redirect: '/home' // 重定向-不带参数
说明2-带参数的重定向:
redirect: '/home/two/:id/:name' // 重定向-传递参数
别名
重定向是通过route的配置中关键词alias来实现的,具体代码如下:
(1)在src/router/index.js中,代码如下:
{
path:'/one', // 子页面1
component:One,
alias: '/oneother'
}
(2)在src/components/Home.vue中,代码如下:
<router-link to="/oneother">子页面1</router-link>
说明1:redirect和alias的区别
redirect:直接改变了url的值,把url变成了真实的path路径。\ alias:url路径没有别改变,这种更友好,让用户知道自己访问的路径,只是改变了 <router-view>中的内容。
说明2:
别名请不要用在path为’/’中,如下代码的别名是不起作用的。
{
path: '/',
component: Hello,
alias:'/home'
}
过渡动画
代码示例
(1)在<router-view>标签的外部添加<transition>标签,标签还需要一个name属性,代码如下:
<transition name="fade" mode="out-in">
<router-view />
</transition>
(2)加入CSS,一共4个CSS类名,四个类名与transition的name属性有关,比如name=”fade”,相应的css如下:
/*页面切换动画*/
/*进入过渡的结束状态,元素被插入时就生效,在过渡过程完成后移除*/
.fade-enter-active {
transition: opacity .5s;
}
/*进入过渡的开始状态,元素被插入时生效,只应用一帧后立刻删除*/
.fade-enter {
opacity: 0;
}
/*离开过渡的开始状态,元素被删除时触发,只应用一帧后立刻删除*/
.fade-leave {
opacity: 1;
}
/*离开过渡的结束状态,元素被删除时生效,离开过渡完成后被删除*/
.fade-leave-active {
opacity:0;
transition: opacity .5s;
}
过渡模式mode
in-out:新元素先进入过渡,完成之后当前元素过渡离开,默认模式。 out-in:当前元素先进行过渡离开,离开完成后新元素过渡进入。
mode与404
mode模式
代码示例:
export default new Router({
mode: 'history', //mode模式
routes: [...]
})
mode取值说明:
(1)histroy:URL就像正常的 url,示例:http://localhost:8080/home
(2)hash:默认值,会多一个“#”,示例:http://localhost:8080/#/home
404页面设置
如果访问的路由不存在,或者用户输入错误时,会有一个404友好的提示页面,配置如下:
(1)在/src/router/index.js中加入如下代码:
// 404
{
path: '*',
component: () => import('@/components/404')
}
(2)在src/components/404.vue中编写如下代码:
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h1>404 not found</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
路由钩子
路由钩子,即导航钩子,其实就是路由拦截器,vue-router一共有三类:
全局钩子:最常用 路由单独钩子 组件内钩子
全局钩子
在src/router/index.js中使用,代码如下:
// 定义路由配置
const router = new VueRouter({ ... })
// 全局路由拦截-进入页面前执行
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
// 这里可以加入全局登陆判断
// 继续执行
next();
});
// 全局后置钩子-常用于结束动画等
router.afterEach(() => {
//不接受next
});
export default router;
每个钩子方法接收三个参数:
to: Route : 即将要进入的目标 [路由对象]
from: Route : 当前导航正要离开的路由
next: Function : 继续执行函数
next():继续执行 next(false):中断当前的导航。 next(‘/‘) 或 next({ path: ‘/‘ }):跳转新页面,常用于登陆失效跳转登陆
路由单独钩子
使用:在路由配置中单独加入钩子,在src/router/index.js中使用,代码如下:
{
path:'/home/one', // 子页面1
component: One,
// 路由内钩子
beforeEnter: (to, from, next) => {
console.log('进入前执行');
next();
}
}
组件内钩子
使用:在路由组件内定义钩子函数:
beforeRouteEnter:进入页面前调用 beforeRouteUpdate (2.2 新增):页面路由改变时调用,一般需要带参数 beforeRouteLeave:离开页面调用
任意找一页面,编写如下代码:
<script>
export default {
name: 'Two',
data () {
return {
msg: 'Hi, I am Two Page!'
}
},
// 进入页面前调用
beforeRouteEnter(to, from, next) {
console.log('进入enter路由钩子')
next()
},
// 离开页面调用
beforeRouteLeave(to,from, next){
console.log('进入leave路由钩子')
next()
},
// 页面路由改变时调用
beforeRouteUpdate(to, from, next) {
console.log('进入update路由钩子')
console.log(to.params.id)
next()
}
}
</script>
路由懒加载
路由正常模式:
// 1、先引入页面组件
import Home from '@/components/Home'
// 2、使用组件
{
path: '/home',
component: Home
}
懒加载模式
大项目中,为了提高初始化页面的效率,路由一般使用懒加载模式,一共三种实现方式。
(1)第一种写法:
component: (resolve) => require(['@/components/One'], resolve)
(2)第二种写法:
component: () => import('@/components/Two')
(3)第三种写法:
components: r => require.ensure([], () => r(require('@/components/Three')), 'group-home')
PS:
一般常用第二种简写 第三种中,’group-home’是把组件按组分块打包, 可以将多个组件放入这个组中,在打包的时候Webpack会将相同 chunk 下的所有异步模块打包到一个异步块里面。
vue-cli
vue-cli是vue官方出品的快速构建单页应用的脚手架,里面集成了webpack,npm,nodejs,babel,vue,vue-router等.
全局安装vue-cli,命令行:
npm install vue-cli -g
初始化项目
在实际开发中,一般都会使用webpack这个模板,命令使用如下:
vue init webpack my-vue-demo
运行项目
npm run dev
以上命令为开发模式下运行项目
npm run build
以上命令为项目发布打包

main.js(入口文件)
// 引入vue框架
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入根组件
import App from './App'
// 引入路由配置
import router from './router'
// 关闭生产模式下给出的提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 定义实例
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})
router(路由配置)
// 引入vue框架
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入vue-router路由依赖
import Router from 'vue-router'
// 引入页面组件,命名为HelloWorld
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld'
// 使用路由依赖
Vue.use(Router)
// 定义路由配置
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
name: 'HelloWorld',
component: HelloWorld
}
]
})
模板
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Vue入门之组件</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- template标签模板 -->
<template id="demo2">
<h2 style="color:red">我是template标签模板</h2>
</template>
</div>
<!-- script标签模板 -->
<script type="x-template" id="demo3">
<h2 style="color:red">我是script标签模板</h2>
</script>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 实例化
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'hello'
},
// 选项模板
//template:`<h1 style="color:red">我是选项模板</h1>`
//template:'#demo2'
template:'#demo3'
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
组件注册
(1)全局注册
// script
Vue.component('button-counter', {
data: function () {
return {
count: 0
}
},
template: '<button v-on:click="count++">全局组件显示: {{ count }}</button>'
});
new Vue({
el: '#app'
});
// html使用
<button-counter></button-counter>
(2)局部注册
// script
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components:{
"button-inner":{
data: function() {
return {
inner: 0
}
},
template: '<button v-on:click="inner++">局部组件显示: {{ inner }}</button>'
}
}
});
// html使用
<button-inner></button-inner>
自定义指令
vue中的自定义指令通过Vue.directive来实现
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Vue入门之自定义指令</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div v-test="color">
{{num}}
</div>
</div>
<button onclick="unbindApp()">解绑</button>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 解绑
function unbindApp() {
app.$destroy();
}
// 自定义指令
Vue.directive("test",{
//1-被绑定
bind:function (el, binding, vnode) {
console.log("1-bind 被绑定");
console.log("el:",el);
console.log("binding:",binding);
console.log("vnode:",vnode);
el.style.color = binding.value;
},
//2-被插入
inserted:function (el, binding, vnode) {
console.log("2-inserted 被插入");
},
//3-更新
update:function (el, binding, vnode) {
console.log("3-update 更新");
},
//4-更新完成
componentUpdated:function (el, binding, vnode) {
console.log("4-componentUpdated 更新完成");
},
//5-解绑
unbind:function (el, binding, vnode) {
console.log("5-unbind 解绑");
}
});
var app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
num: 123,
color:'red'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
参数说明
el:指令所绑定的元素,可以用来直接操作DOM binding:一个对象,包含指令的很多信息 vnode::Vue编译生成的虚拟节点
$on(在构造器外部添加事件)
$on接收两个参数,第一个参数是调用时的事件名称,第二个参数是一个匿名方法
app.$on('reduce',function(){
console.log('执行了reduce()');
this.count--;
});
$once(执行一次的事件)
app.$once('reduceOnce',function(){
console.log('只执行一次的方法');
this.count--;
});
$off(关闭事件)
function off(){
console.log('关闭事件');
app.$off('reduce');
}
extends
扩展:对构造器进行扩展
// 扩展
var extendObj ={
created: function(){
console.log("我是被扩展出来的");
}
}
// 实例化vue
var app = new Vue({
// 挂载实例
el:'#app',
// 页面数据初始化,字符,对象、数组
data:{
},
// 扩展
extends: extendObj
})

📚掘金文章
前端日常总结 一份不可多得的TypeScript系统入门整理 JS葵花宝典秘籍笔记,为你保驾护航金三银四 TypeScript趁早学习提高职场竞争力 前端模拟面试字数过23477万内容 JavaScript数据结构之链表 | 技术点评 JavaScript的数据结构-集合 |技术点评 这是我的第一次JavaScript初级技巧 一个合格的初级前端工程师需要掌握的模块笔记 【初级】个人分享Vue前端开发教程笔记 localStorage和sessionStorage本地存储 HTML5中的拖放功能 挑战前端知识点HTTP/ECMAScript 前端170面试题+答案学习整理(良心制作)
❤️关注+点赞+收藏+评论+转发❤️
点赞、收藏和评论
我是Jeskson(达达前端),感谢各位人才的:点赞、收藏和评论,我们下期见!(如本文内容有地方讲解有误,欢迎指出☞谢谢,一起学习了)
我们下期见!
文章持续更新,可以微信搜一搜「 程序员哆啦A梦 」第一时间阅读,回复【资料】有我准备的一线大厂资料,本文 https://www.1024bibi.com 已经收录
github收录,欢迎Star:https://github.com/webVueBlog/WebFamily
