三款主流的 JSON 解析库性能大比拼,到底谁最牛?
点击“开发者技术前线”,选择“星标🔝”
让一部分开发者看到未来

来自github中文社区
这期我们来聊聊Java中解析JSON的三个主流类库:
FastJSON、Gson和Jackson。
先来看下这三货在Github上的基本数据:
码友们对这三货各方面也一直争议不断,大多关心的,还是性能以及稳定性。本文主测性能;对于这三个库的简介以及用法,就不去废话了,一个简单明了的测评,直接上!
主要对这三个类库在JSON序列化和反序列化在速度方面的表现做一些测评,为了防止由于内存导致测试结果出现偏差,测试中对JVM内存配置-Xmx4g -Xms4g。
测试代码已经贴到了文章末尾。

JSON序列化(Object => JSON)
测试样本数量为100000个,为了保证每个类库在测试中都能处理同一个样本,先把样本Java对象保存在文件中。每个类库测试5次,每次循环测试10遍,去掉最快速度和最慢速度,对剩下的8遍求平均值作为最终的速度,取5次测试中最好的平均速度作为最终的测试数据。
测试结果:
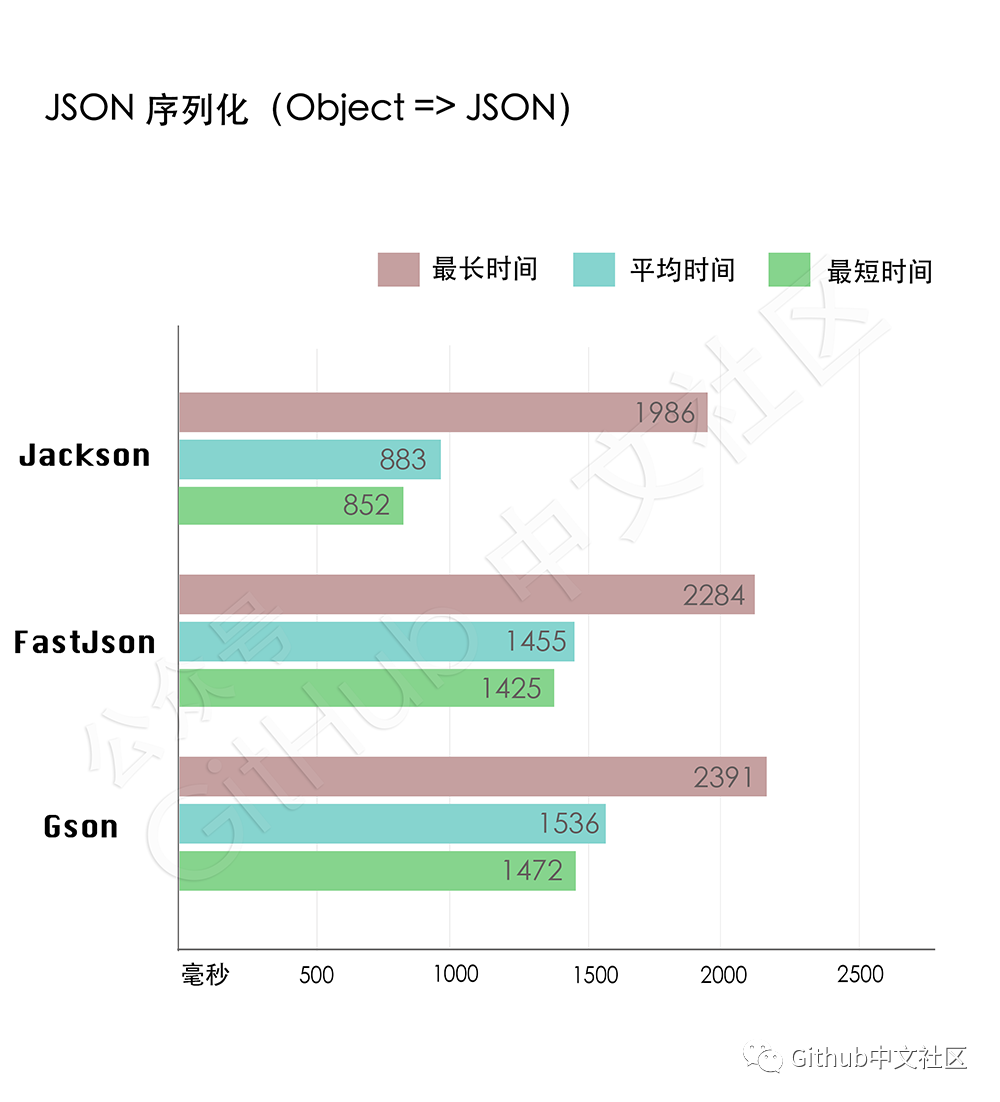
从测试数据可以看出,Jackson是最快的(耗时比Gson少了大约700毫秒),Gson耗时最久。

JSON反序列化(JSON => Object)
同样,测试样本数量为100000个,为了保证每个类库在测试中都能处理同一个样本,先把样本JSON对象保存在文件中。每个类库测试5次,每次循环测试10遍,去掉最快速度和最慢速度,对剩下的8遍求平均值作为最终的速,取5次测试中最好的平均速度作为最终的测试数据。
测试结果:
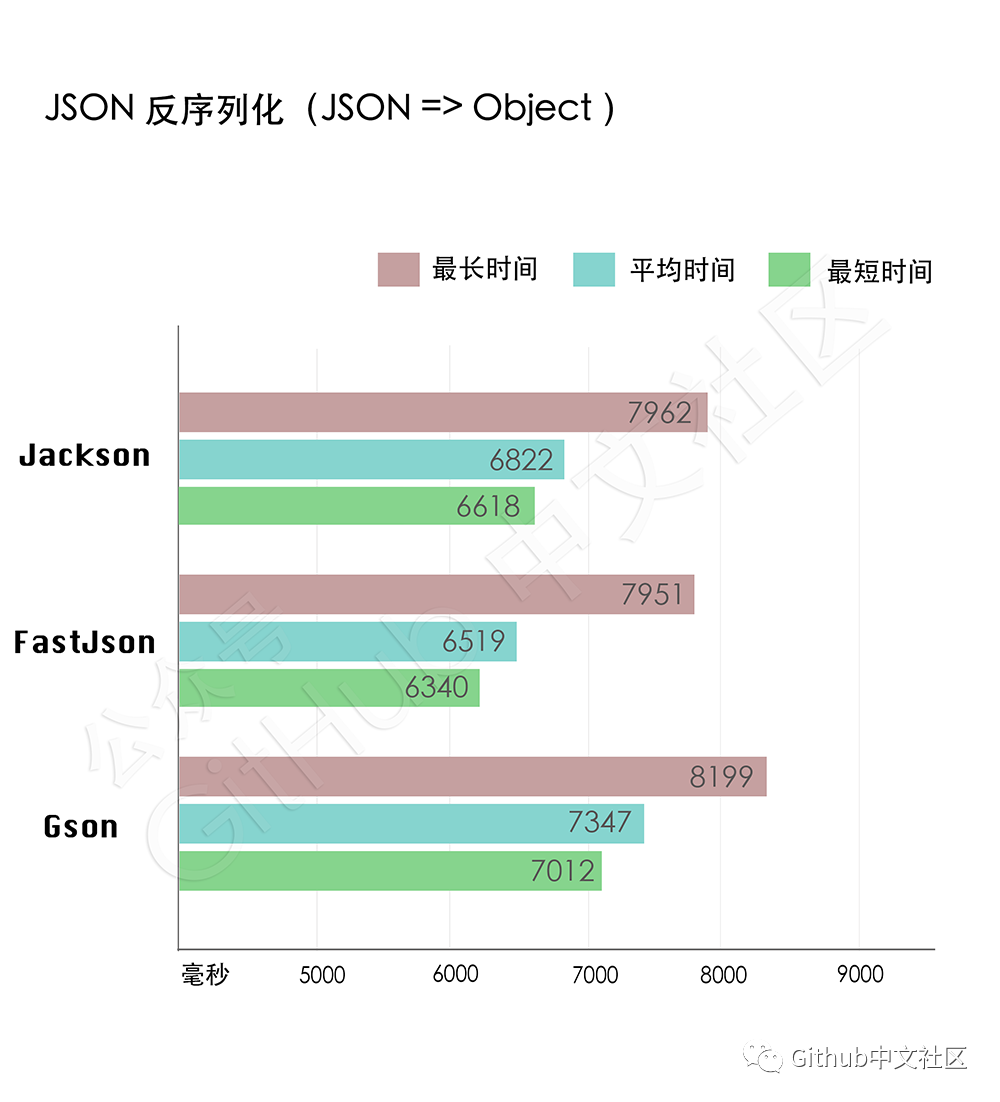
从测试数据可以看出,在反序列化上性能 FastJson最快,不过与Jackson差距并不明显,Gson耗时最久

可见,不管是序列化还是反序列化,速度方面首先阵亡的,是Gson!

那还剩下FastJson和Jackson
FastJson在某些方面确实快一些,但是和Jackson 的差距不大,优势并没有太明显。Jackson还可以加上AfterBurner来使用byte generation,这样和FastJson的差距就更小了。
除了在反序列化的速度胜出外,FastJson相比较 Jackson 有不少短板,我们可以从以下3方面对比:
1. 可定制性
Jackson有灵活的API,可以很容易进行扩展和定制,而且很多时候需要的模块都已经有人提供了。比如guava中定义的数据类型,比如kotlin语言Immutable的类型等,比如java8 引入的新日期时间类型和Optional都已经有支持的模块。
FastJson只有一个(简陋)的SerializeFilter机制用来定制序列化,ParseProcess机制用来定制反序列化,每次调用序列化/反序列化的的时候都要自己传filter或者Process这个参数过去,Jackson和 Gson都是直接注册模块就可以了,Jackson还可以使用SPI来自动发现和注册模块。
2. 代码质量
公司有一些项目使用了Fastjson,在使用Fastjson的项目里面曾碰到过的两个低级bug:
1. 碰到在128~255 的字符直接异常,这些主要是西欧语言的字符,因为他用一个数组来记录 转义后的字符表示,但是数组长度只有128...
2. 内存占用过多。Fastjson为了性能,在ThreadLocal中缓存了char[] buffer,这样避免分配内存和gc的开销。但是如果碰到了大的json(比如10M这样的),就会占用大量的内存,而且以后都是处理小JSON了内存占用也回不来。
这些问题虽然后来的版本都修复了,但是也反映出Fastjson代码质量上要求不够严格。而Jackson这么多年来使用上还没有碰到过这样的Bug.
3. 文档
相比Jackson, Fastjson英文文档就显得比较欠缺,已有的也不规范,这样就更没法指望老外用了,相对还是国内开发者占大多数
这么来看,最终结果很明显了:
观点
JSON从发明到现在之所以流行,并不是因为json快的原因(比json快且小巧的格式和类库一大把),而是因为json和web结合的时候更易于使用,对开发人员易于理解。很多人拿FastJson和Jackson比,就像拿非智能机和iphone比待机时间,其功能性不一样,Jackson的很多功能FastJson并没有实现,所以这种对比也不客观。FastJson之所以没在国际上流行起来,最主要的原因应该是开发者的思路全放到“快”上去了,而偏离了“标准”及功能性,质量也不够好,有点“舍本逐末”的味道。
当然在目前的环境下,国产软件能踏实的心态做好开源的不多,FastJson团队能这么快的反馈并修正问题,这种精神还是值得称赞的。希望国内的技术从业者能更重视“技术的原始需求”。
测试代码:
样本对象包括Boolean、Int、Long、Double、Date、String、List和Map字段,其中List长度和Map的Key数量可以根据需要改变。
/*** 样本数据工厂 提供各类元数据样本*/public class DataFactory {private static final String[] chars = new String[] { "0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "a", "b","c", "d", "e", "f", "g", "h", "i", "j", "k", "l", "m", "n", "o", "p", "q", "r", "s", "t", "u", "v", "w","x", "y", "z", "A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G", "H", "I", "J", "K", "L", "M", "N", "O", "P", "Q", "R","S", "T", "U", "V", "W", "X", "Y", "Z" };// 配置各项长度/数量private static final int charNum = 62;private static final int maxStrLength = 120;private static final int defaultStrLength = 50;private static final int maxListSize = 120;private static final int defaultListSize = 20;private static final int maxMapSize = 120;private static final int defaultMapSize = 20;private static final String[] types = new String[] { "string", "int", "long", "double", "boolean", "date"};private static final int typeNum = 6;private static final Random random = new Random();/*** 生成随机长度的字符串* @return 字符串*/public static String randomString(){return randomString(random.nextInt(maxStrLength));}/*** 生成指定长度字符串* @param len 字符串长度*/public static String randomString(int len) {if (len < 1 || len > maxStrLength) {len = defaultStrLength;}StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(len);for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {sb.append(chars[random.nextInt(charNum)]);}return sb.toString();}/*** 生成List,元素的数量随机* @return*/public static List<String> randomStringList() {return randomStringList(random.nextInt(maxListSize));}/*** 生成List样本* @param size 元素的数量* @return*/public static List<String> randomStringList(int size) {if (size < 1 || size > maxListSize) {size = defaultListSize;}List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {list.add(randomString(random.nextInt(maxStrLength)));}return list;}/*** 生成随机Map样本,key的数量随机* @return*/public static Map<String, Object> randomMap() {return randomMap(random.nextInt(maxMapSize));}/*** 生成随机Map样本* @param size key的数量* @return*/public static Map<String, Object> randomMap(int size) {if (size < 1 || size > maxMapSize) {size = defaultMapSize;}Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {String type = types[random.nextInt(typeNum)];if ("boolean".equals(type)) {map.put("key" + i, random.nextBoolean());} else if ("int".equals(type)) {map.put("key" + i, random.nextInt());} else if ("long".equals(type)) {map.put("key" + i, random.nextLong());} else if ("double".equals(type)) {map.put("key" + i, random.nextDouble());} else if ("date".equals(type)) {map.put("key" + i, new Date());} else if ("string".equals(type)) {map.put("key" + i, randomString(random.nextInt(maxStrLength)));}}return map;}}/*** 样本对象*/public class TestEntity implements Serializable {private Double dataDouble;private Date dataDate;private String dataStr;private Boolean dataBoolean;private Integer dataInt;private Long dataLong;private List<String> dataList;private Map<String, Object> dataMap;public TestEntity() {Random random = new Random();dataBoolean = random.nextBoolean();dataInt = random.nextInt();dataLong = random.nextLong();dataDouble = random.nextDouble();dataDate = new Date();dataStr = DataFactory.randomString();dataList = DataFactory.randomStringList(defaultListSize);dataMap = DataFactory.randomMap(mapKeyNum);}/*** 指定元素数量的样本*/public TestEntity(int listSize, int mapKeyNum) {Random random = new Random();dataBoolean = random.nextBoolean();dataInt = random.nextInt();dataLong = random.nextLong();dataDouble = random.nextDouble();dataDate = new Date();dataStr = DataFactory.randomString();dataList = DataFactory.randomStringList(listSize);dataMap = DataFactory.randomMap(defaultMapSize);}// get and set// ......}/*** 测试入口*/public class TestBuilder {public static void main(String[] args) {int testSize = 100000;String jsonDataPath = "d:\\test_json.dat";String objectDataPath = "d:\\test_object.dat";buildJson(testSize, 10, 10, jsonDataPath);buildObject(testSize, 10, 10, objectDataPath);}public static List<String> loadJSON(String filePath) {List<String> list = new LinkedList<String>();File file = new File(filePath);if (!file.exists()) {return list;}BufferedReader br = null;try {br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));String line = br.readLine();while(line != null){list.add(line);line = br.readLine();}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {if (null != br) {try {br.close();} catch (IOException e) {}}}return list;}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static List<TestEntity> loadTests(String filePath) {List<TestEntity> list = new LinkedList<TestEntity>();File file = new File(filePath);if (!file.exists()) {return list;}ObjectInputStream ois = null;try {ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));list = (List<TestEntity>) ois.readObject();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {if (null != ois) {try {ois.close();} catch (IOException e) {}}}return list;}/*** 创建样本** @param testSize 样本数量* @param listSize 样本List长度* @param mapKeyNum 样本Map的Key数量* @return 样本List*/public static List<TestEntity> buildTest(int testSize, int listSize, int mapKeyNum) {List<TestEntity> list = new LinkedList<TestEntity>();for (int i = 0; i < testSize; i++) {list.add(new TestEntity(listSize, mapKeyNum));}return list;}/*** 创建默认样本*/public static List<TestEntity> buildTest(int testSize) {List<TestEntity> list = new LinkedList<TestEntity>();for (int i = 0; i < testSize; i++) {list.add(new TestEntity());}return list;}/*** 创建样本,并把样本JSON序列化,保存到文件中。** @param testSize 样本数量* @param listSize 样本List长度* @param mapKeyNum 样本Map中Key的数量* @param filePath 样本输出的文件路径*/public static void buildJson(int testSize, int listSize, int mapKeyNum, String filePath) {File file = new File(filePath);File parent = file.getParentFile();if (!parent.exists()) {parent.mkdirs();}if (file.exists()) {file.delete();}List<TestEntity> list = buildTest(testSize, listSize, mapKeyNum);StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();for (TestEntity item : list) {sb.append(JSON.toJSONString(item));sb.append("\n");}BufferedWriter bw = null;try {file.createNewFile();bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));bw.write(sb.toString());bw.flush();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {if (null != bw) {try {bw.close();} catch (IOException e) {}}}}public static void buildJson(int testSize, String filePath) {File file = new File(filePath);File parent = file.getParentFile();if (!parent.exists()) {parent.mkdirs();}if (file.exists()) {file.delete();}List<TestEntity> list = buildTest(testSize);StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();for (TestEntity item : list) {sb.append(JSON.toJSONString(item));sb.append("\n");}BufferedWriter bw = null;try {file.createNewFile();bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));bw.write(sb.toString());bw.flush();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {if (null != bw) {try {bw.close();} catch (IOException e) {}TestEntity}}}public static void buildObject(int testSize, String filePath) {List<TestEntity> list = buildTest(testSize);File file = new File(filePath);File parent = file.getParentFile();if (!parent.exists()) {parent.mkdirs();}if (file.exists()) {file.delete();}ObjectOutputStream oos = null;try {file.createNewFile();oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));oos.writeObject(list);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {if (null != oos) {try {oos.close();} catch (IOException e) {}}}}/*** 生成样本对象,并保存到指定文件** @param testSize 样本大小* @param listSize 样本中List字段长度* @param mapKeyNum 样本中Map对象Key数量* @param filePath 样本输出的路径*/public static void buildObject(int testSize, int listSize, int mapKeyNum, String filePath) {List<TestEntity> list = buildTest(testSize, listSize, mapKeyNum);File file = new File(filePath);File parent = file.getParentFile();if (!parent.exists()) {parent.mkdirs();}if (file.exists()) {file.delete();}ObjectOutputStream oos = null;try {file.createNewFile();oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));oos.writeObject(list);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {if (null != oos) {try {oos.close();} catch (IOException e) {}}}}}
开发者技术前线 ,汇集技术前线快讯和关注行业趋势,大厂干货,是开发者经历和成长的优秀指南。