步履不停:TensorFlow 2.4 新功能一览!
文 / Goldie Gadde 和 Nikita Namjoshi,TensorFlow
TensorFlow 2.4 正式发布!随着对分布式训练和混合精度提供更多支持,加入新的 Numpy 前端及用于监控和诊断性能瓶颈的工具,这个版本的亮点在于推出新功能,以及对性能和扩展方面的增强。
tf.distribute 的新增功能
参数服务器策略
在版本 2.4 中,实验性引入了 tf.distribute 模块的支持,可通过 ParameterServerStrategy 和自定义训练循环对 Keras 模型进行异步训练。与 MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy 一样,ParameterServerStrategy 是一种多工作器数据并行策略;但其梯度更新方式为异步执行。
ParameterServerStrategy
https://tensorflow.google.cn/api_docs/python/tf/distribute/experimental/ParameterServerStrategy
参数服务器训练集群包含工作节点和参数服务器。系统会在参数服务器上创建变量,然后工作节点会在每个步骤中进行读取和更新。变量的读取和更新会在各工作节点上独立进行,同时无需采取任何同步操作。由于工作节点互不依赖,因此该策略具有工作器容错的优势,并会在使用抢占式服务器时有所助益。
如要开始使用此策略,请查阅参数服务器训练教程。此教程介绍了如何设置 ParameterServerStrategy,并说明了如何使用 ClusterCoordinator 类来创建资源、调度函数和处理任务失败。
参数服务器训练教程
https://tensorflow.google.cn/tutorials/distribute/parameter_server_trainingClusterCoordinator
https://tensorflow.google.cn/api_docs/python/tf/distribute/experimental/coordinator/ClusterCoordinator
多工作节点镜像策略
MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy 多工作节点镜像策略 已顺利度过实验阶段,现已成为稳定 API 的组成部分。与单个工作节点副本 MirroredStrategy 一样,MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy 通过同步数据并行化实现分布式训练。但利用 MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy,您可以在多台机器上进行训练,且每台机器可以都搭载多个 GPU。
MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy
https://tensorflow.google.cn/api_docs/python/tf/distribute/MultiWorkerMirroredStrategyMirroredStrategy
https://tensorflow.google.cn/api_docs/python/tf/distribute/MirroredStrategy
在同步训练中,每个工作节点会在输入数据的不同片段上计算正向和反向传递次数,并且在每个步骤结束时汇总梯度。对于这种称为 All Reduce 的汇总, MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy 会使用集合运算保持变量同步。集合运算是 TensorFlow 图表中的单个算子,可以根据硬件、网络拓扑和张量大小在 TensorFlow 运行时中自动选择 All Reduce 算法。集合运算还可实现其他集合运算,例如广播和 All Gather。
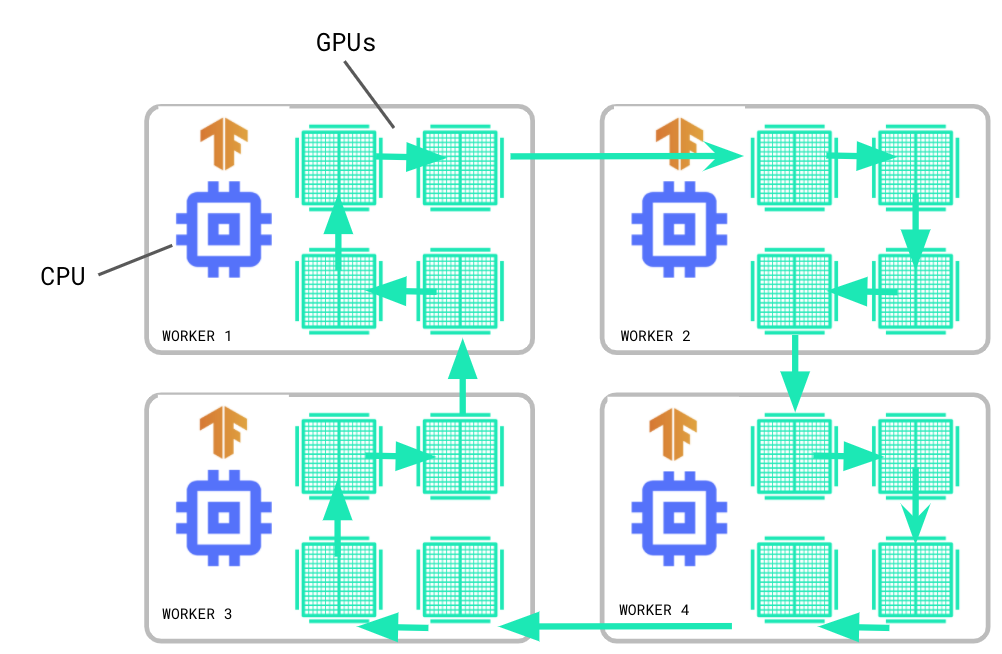
集合运算
https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/ops/collective_ops.py
如要开始使用 MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy,请查阅使用 Keras 进行多工作器训练教程,该教程已更新了有关数据集分片、保存/加载使用分布策略训练的模型,以及使用 BackupAndRestore 回调进行故障恢复的详细信息。
使用 Keras 进行多工作器训练
https://tensorflow.google.cn/tutorials/distribute/multi_worker_with_kerasBackupAndRestore
https://tensorflow.google.cn/api_docs/python/tf/keras/callbacks/experimental/BackupAndRestore
如果您不熟悉分布式训练,并希望了解入门方法,或者有兴趣在 Google 云端平台 (GCP) 上进行分布式训练,请参阅本博文,以获取关于关键概念和步骤的介绍。
Keras 的相关更新
混合精度
在 TensorFlow 2.4 中,Keras 混合精度 API 已顺利度过实验阶段,现已成为稳定的 API。大多数 TensorFlow 模型使用的是 float32 dtype;但也存在使用更少内存的低精度类型(如 float16)。混合精度指在同一模型中通过使用 16 位和 32 位浮点类型,以加快训练速度。该 API 可使模型在 GPU 上性能提高 3 倍,在 TPU 上提高 60%。
Keras 混合精度 API
https://tensorflow.google.cn/api_docs/python/tf/keras/mixed_precision
如要使用混合精度 API,您必须使用 Keras 层和优化工具,但无需使用其他 Keras 类,例如模型或损失。如果您对如何利用此 API 实现性能优化颇有兴趣,请查阅混合精度教程。
混合精度教程
https://tensorflow.google.cn/guide/mixed_precision
优化工具
此版本支持重构 tf.keras.optimizers.Optimizer 类,使 model.fit 或自定义训练循环的用户能够编写任何适用于优化工具的训练代码。现所有内置的 tf.keras.optimizer.Optimizer 子类均可支持使用 gradient_transformers 和 gradient_aggregator 参数,您可借此轻松定义自定义梯度转换。
tf.keras.optimizers.Optimizer
https://tensorflow.google.cn/api_docs/python/tf/keras/optimizers/Optimizer
通过重构,您现在可以在编写自定义训练循环时将损失张量直接传递给 Optimizer.minimize:
tape = tf.GradientTape()
with tape:
y_pred = model(x, training=True)
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y_true)
# 如下所示,在使用损失“张量”时,您可以在“tf.GradientTape”中进行传递。
optimizer.minimize(loss, model.trainable_variables, tape=tape)
此类更改旨在使 Model.fit 和自定义训练循环都能摆脱优化工具细节的限制,从而使您无需修改,即可编写任何适用于优化工具的训练代码。
函数式 API 模型构建的内部改进
最后,在 Keras 中,TensorFlow 2.4 可支持对 Keras Functional API 内部主要结构的重构,从而可降低函数式模型构建的内存消耗并简化触发逻辑。开展此类重构操作还能够确保 TensorFlowOpLayers 行为可预测,并可与 CompositeTensor 类型的签名一起使用。
隆重推出 tf.experimental.numpy
TensorFlow 2.4 以 tf.experimental.numpy 形式,实验性引入了对 NumPy API 子集的支持。您可借此模块,运行由 TensorFlow 加速的 NumPy 代码。由于此 API 基于 TensorFlow 构建而成,因此可支持访问所有 TensorFlow API,与 TensorFlow 实现无缝互操作,并会通过编译和自动矢量化开展优化。例如,TensorFlow ND 数组可以与 NumPy 函数进行交互,同样地,TensorFlow NumPy 函数也可以接受包括 tf.Tensor 和 np.ndarray 在内的不同类型的输入。
import tensorflow.experimental.numpy as tnp ```
# 在输入流水线中使用 NumPy 代码
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(
tnp.random.randn(1000, 1024)).map(
lambda z: z.clip(-1,1)).batch(100)
# 通过 NumPy 代码计算梯度
def grad(x, wt):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch(wt)
output = tnp.dot(x, wt)
output = tf.sigmoid(output)
return tape.gradient(tnp.sum(output), wt)
tf.experimental.numpy
https://tensorflow.google.cn/api_docs/python/tf/experimental/numpyNumPy API 实验性支持
https://github.com/tensorflow/community/blob/master/governance/api-reviews.md#experimental-apis
您可以查阅 TensorFlow 指南上的 NumPy API,了解更多关于使用此 API 的信息。
TensorFlow 指南上的 NumPy API
https://tensorflow.google.cn/guide/tf_numpy
全新性能分析器工具
TensorFlow Profiler 中的多工作器支持
TensorFlow Profiler 是一套用于评估 TensorFlow 模型训练性能和资源消耗情况的工具。TensorFlow Profiler 可帮助您了解模型中算子的硬件资源消耗、诊断瓶颈并最终加快训练速度。
TensorFlow Profiler
https://tensorflow.google.cn/guide/profiler
之前版本的TensorFlow Profiler 支持监控多 GPU、单主机训练作业。在现在 2.4 版本中,您可以分析 MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy 训练作业的性能。例如,您可以使用采样模型 API 来执行按需分析,并连接到 MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy 工作节点上正在使用的同一服务器端口:
# 在模型运行之前启动性能分析器服务器。
tf.profiler.experimental.server.start(6009)
# 在此处插入模型代码……
# 例如,您的工作器 IP 地址是 10.0.0.2、10.0.0.3、10.0.0.4,然后您
# 希望执行 2 秒钟的性能分析。性能分析数据将
# 保存至 Google Cloud Storage 路径“your_tb_logdir”。
tf.profiler.experimental.client.trace(
'grpc://10.0.0.2:6009,grpc://10.0.0.3:6009,grpc://10.0.0.4:6009',
'gs://your_tb_logdir',
2000)
采样模型
https://tensorflow.google.cn/guide/profiler#sampling_mode
或者,您可以通过向 Capture Profile(捕获分析结果)工具提供工作节点地址来使用 TensorBoard 配置文件插件。
分析完成后,您可以使用新的 Pod Viewer 工具选择一个训练步骤,并查阅所有工作节点的分步时间类别细分。
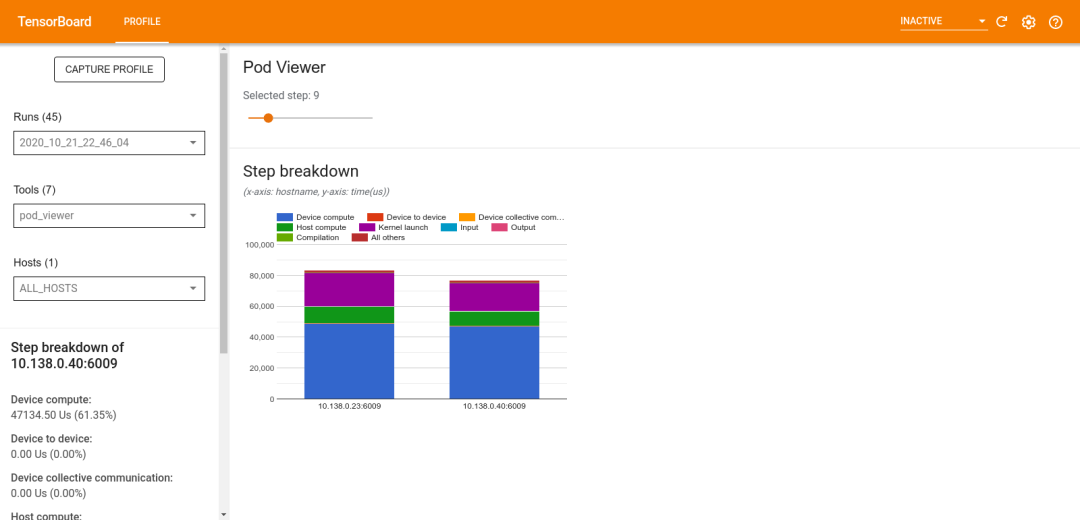
Pod Viewer 工具
https://tensorflow.google.cn/guide/profiler#pod_viewer
有关如何使用 TensorFlow Profiler 的更多信息,请查阅新发布的 GPU 性能指南。此指南介绍了您在对模型训练作业进行性能分析时可能遇到的常见情况,并提供了调试工作流程来帮助您优化性能,无论您是使用单个 GPU、多个 GPU 还是使用多台机器进行训练,均可从中受益。
GPU 性能指南
https://tensorflow.google.cn/guide/gpu_performance_analysis
TFLite Profiler
在 2.4 版本中,您亦可在 Android 中启用对 TFLite 内部结构的跟踪。现在,您可以使用 Android 版 TFLite Profiler 来识别性能瓶颈。TFLite 性能评估指南介绍了如何使用 Android Studio CPU 性能分析器和系统跟踪应用添加跟踪事件,启用 TFLite 跟踪以及捕获跟踪。
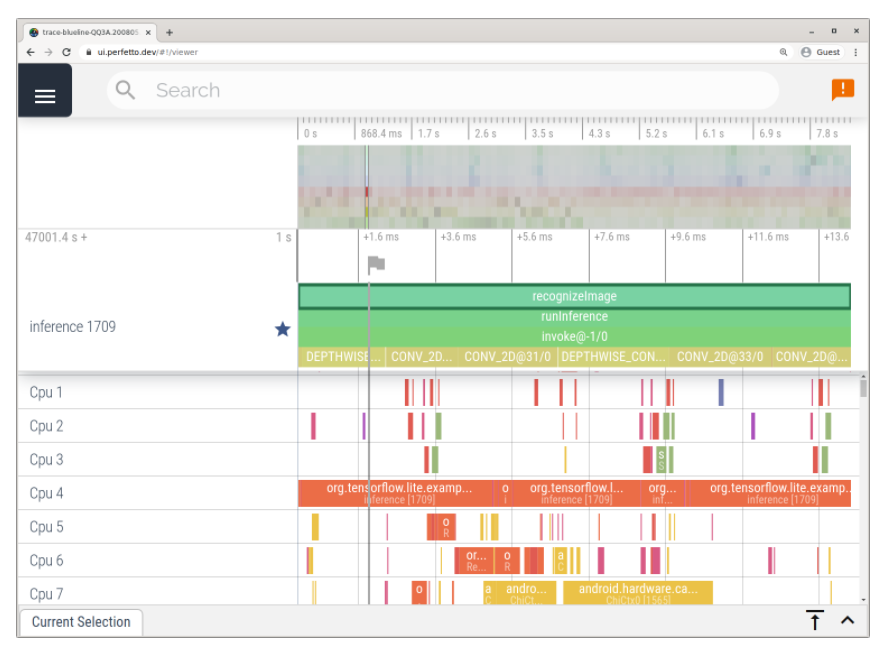
使用 Android 系统跟踪应用进行跟踪的示例
TFLite 性能评估指南
https://tensorflow.google.cn/lite/performance/measurement#trace_tensorflow_lite_internals_in_android
提供 GPU 支持的新功能
TensorFlow 2.4 可与 CUDA 11 和 cuDNN 8 一起运行,以支持最新上市的 NVIDIA Ampere GPU 架构。如需了解 CUDA 11 功能的更多信息,请查阅此 NVIDIA 开发者博客。
NVIDIA 开发者博客
https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/cuda-11-features-revealed/
此外,我们亦会默认在搭载 Ampere 的 GPU 上启用对 TensorFloat-32 的支持。TensorFloat-32(简称为“TF32”)是 NVIDIA Ampere GPU 的一种数学模式,可加快令某些 float32 算子(例如矩阵乘法和卷积)在 Ampere GPU 上的运行速度,但精度降低。如需了解更多信息,请查阅 tf.config.experimental.enable_tensor_float_32_execution 文档。
tf.config.experimental.enable_tensor_float_32_execution
https://tensorflow.google.cn/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/enable_tensor_float_32_execution
后续步骤
请参阅版本说明了解更多信息。如需获取最新消息,敬请阅读 TensorFlow 公众号(TensorFlow_official),或订阅 B 站 Google 中国 (space.bilibili.com/64169458)。如欲分享您的构建成果,请通过 Community Spotlight 计划 (goo.gle/TFCS) 向我们提交您的作品。如需提供反馈,请在 GitHub上提交问题。谢谢!
版本说明
https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/releasesGitHub
https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues
推荐阅读
CondInst:性能和速度均超越Mask RCNN的实例分割模型
mmdetection最小复刻版(十一):概率Anchor分配机制PAA深入分析
MMDetection新版本V2.7发布,支持DETR,还有YOLOV4在路上!
无需tricks,知识蒸馏提升ResNet50在ImageNet上准确度至80%+
不妨试试MoCo,来替换ImageNet上pretrain模型!
mmdetection最小复刻版(七):anchor-base和anchor-free差异分析
mmdetection最小复刻版(四):独家yolo转化内幕
机器学习算法工程师
一个用心的公众号

