面试官:Redis新版本开始引入多线程,谈谈你的看法?
互联网架构师后台回复 2T 有特别礼包
void delCommand(client *c) {delGenericCommand(c,server.lazyfree_lazy_user_del);}/* This command implements DEL and LAZYDEL. */void delGenericCommand(client *c, int lazy) {int numdel = 0, j;for (j = 1; j < c->argc; j++) {expireIfNeeded(c->db,c->argv[j]);// 根据配置确定DEL在执行时是否以lazy形式执行int deleted = lazy ? dbAsyncDelete(c->db,c->argv[j]) :dbSyncDelete(c->db,c->argv[j]);if (deleted) {signalModifiedKey(c,c->db,c->argv[j]);notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_GENERIC,"del",c->argv[j],c->db->id);server.dirty++;numdel++;}}addReplyLongLong(c,numdel);}
/* Delete a key, value, and associated expiration entry if any, from the DB.* If there are enough allocations to free the value object may be put into* a lazy free list instead of being freed synchronously. The lazy free list* will be reclaimed in a different bio.c thread. */#define LAZYFREE_THRESHOLD 64int dbAsyncDelete(redisDb *db, robj *key) {/* Deleting an entry from the expires dict will not free the sds of* the key, because it is shared with the main dictionary. */if (dictSize(db->expires) > 0) dictDelete(db->expires,key->ptr);/* If the value is composed of a few allocations, to free in a lazy way* is actually just slower... So under a certain limit we just free* the object synchronously. */dictEntry *de = dictUnlink(db->dict,key->ptr);if (de) {robj *val = dictGetVal(de);// 计算value的回收收益size_t free_effort = lazyfreeGetFreeEffort(val);/* If releasing the object is too much work, do it in the background* by adding the object to the lazy free list.* Note that if the object is shared, to reclaim it now it is not* possible. This rarely happens, however sometimes the implementation* of parts of the Redis core may call incrRefCount() to protect* objects, and then call dbDelete(). In this case we'll fall* through and reach the dictFreeUnlinkedEntry() call, that will be* equivalent to just calling decrRefCount(). */// 只有回收收益超过一定值,才会执行异步删除,否则还是会退化到同步删除if (free_effort > LAZYFREE_THRESHOLD && val->refcount == 1) {atomicIncr(lazyfree_objects,1);bioCreateBackgroundJob(BIO_LAZY_FREE,val,NULL,NULL);dictSetVal(db->dict,de,NULL);}}/* Release the key-val pair, or just the key if we set the val* field to NULL in order to lazy free it later. */if (de) {dictFreeUnlinkedEntry(db->dict,de);if (server.cluster_enabled) slotToKeyDel(key->ptr);return 1;} else {return 0;}}
// 3.2.5版本ZSet节点实现,value定义robj *obj/* ZSETs use a specialized version of Skiplists */typedef struct zskiplistNode {robj *obj;double score;struct zskiplistNode *backward;struct zskiplistLevel {struct zskiplistNode *forward;unsigned int span;} level[];} zskiplistNode;// 6.0.10版本ZSet节点实现,value定义为sds ele/* ZSETs use a specialized version of Skiplists */typedef struct zskiplistNode {sds ele;double score;struct zskiplistNode *backward;struct zskiplistLevel {struct zskiplistNode *forward;unsigned long span;} level[];} zskiplistNode;
多线程I/O及其局限性
实现原理

int handleClientsWithPendingReadsUsingThreads(void) {.../* Distribute the clients across N different lists. */listIter li;listNode *ln;listRewind(server.clients_pending_read,&li);int item_id = 0;// 将等待处理的客户端分配给I/O线程while((ln = listNext(&li))) {client *c = listNodeValue(ln);int target_id = item_id % server.io_threads_num;listAddNodeTail(io_threads_list[target_id],c);item_id++;}.../* Wait for all the other threads to end their work. */// 轮训等待所有I/O线程处理完while(1) {unsigned long pending = 0;for (int j = 1; j < server.io_threads_num; j++)pending += io_threads_pending[j];if (pending == 0) break;}...return processed;}
void *IOThreadMain(void *myid) {...while(1) {...// I/O线程执行读写操作while((ln = listNext(&li))) {client *c = listNodeValue(ln);// io_threads_op判断是读还是写事件if (io_threads_op == IO_THREADS_OP_WRITE) {writeToClient(c,0);} else if (io_threads_op == IO_THREADS_OP_READ) {readQueryFromClient(c->conn);} else {serverPanic("io_threads_op value is unknown");}}listEmpty(io_threads_list[id]);io_threads_pending[id] = 0;if (tio_debug) printf("[%ld] Done\n", id);}}
局限性
Tair多线程实现原理
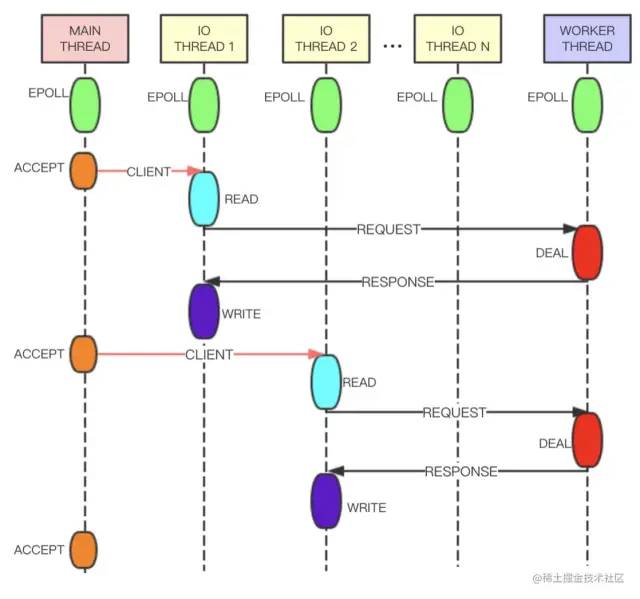
相较于6.0版本的多线程,Tair的多线程实现更加优雅。如下图,Tair的Main Thread负责客户端连接建立等,IO Thread负责请求读取、响应发送、命令解析等,Worker Thread线程专门用于事件处理。IO Thread读取用户的请求并进行解析,之后将解析结果以命令的形式放在队列中发送给Worker Thread处理。Worker Thread将命令处理完成后生成响应,通过另一条队列发送给IO Thread。为了提高线程的并行度,IO Thread和Worker Thread之间采用无锁队列和管道进行数据交换,整体性能会更好。
正文结束
1.心态崩了!税前2万4,到手1万4,年终奖扣税方式1月1日起施行~

评论
