实现 Promises/A+ api属性源码附带注解详情
简单的 Promises/A+ 实现
博客:webvueblog.github.io/promise/
仓库地址:promise
MiniPromise.js 实现
MiniPromise.resolve()
MiniPromise.reject()
MiniPromise.then()
MiniPromise.all()
MiniPromise.race()
MiniPromise.any()
MiniPromise.allSettled()
通篇讲解promise,学习promise相关内容,熟练使用promise;了解promise可以做什么,不可以做什么。
promise是抽象异步处理对象以及对其进行各种操作的组件。promise最初被提出是在E语言中,它是基于并列/并行处理设计的一编程语言。
我们在 基于JavaScript的异步处理,大都想到使用回调函数。
使用回调函数的异步处理
getAsync("file.txt", function(error, result) { // 取得失败时的处理
if (error) { throw error;
} // 取得成功时的处理});复制代码node.js 规定在 JavaScript 的回调函数的一个参数为 error 对象,这是 Node.js 的一般写法。
promsie 时可以将复杂的异步处理轻松地进行模式化,写法:
var promise = getAsyncPromise('file.txt');
promise.then(function(result) { // 获取文件内容成功时的处理}).catch(function(error) { // 获取文件内容失败时的处理});复制代码ES6 Promise 标准
Constructor
Promise类似于 XMLHttpRequest,从构造函数 Promise 来创建一个新建的 promise 对象作为接口。
要想创建一个 promise 对象,可以使用 new 来调用 promise 的构造器来进行实例化。
var promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) { // 异步处理
// 处理结束后,调用 resolve 或 reject});复制代码Instance Method
通过 new 生成的 promise 对象为了设置其值在 resolve (成功)/ reject(失败) 时调用的回调函数可以使用 promise.then() 实例方法。
promise.then(onFulfilled, onRejected)复制代码resolve(成功)时
onFulfilled 会被调用
reject(失败)时
onRejected 会被调用
onFulfilled, onRejected 两个都是可选参数。
promise.then 成功和失败时都可以使用。对于异常进行处理时可以采用 promise.then(undefined, onRejected) 这种方式,只指定 reject 时的回调函数即可。不过这种情况下请使用 promise.catch(onRejected) 是更好的选择。
promise.catch(onRejected)复制代码Static Method
像 promise 这样的全局对象还拥有一些静态方法。
包括 Promise.all() 还有 Promise.resolve() 等在内,主要都是一些对 Promise 进行操作的辅助方法。
Promise工作流程
promise工作流程代码:
function asyncFunction() { return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { setTimeout(function () {
resolve('Async Hello world');
}, 1000);
});
}复制代码new Promise 构造器之后,会返回一个 promise 对象
asyncFunction().then(function(value) { console.log(value); // => 'Async Hello world'}).catch(function (error) { console.log(error);
});复制代码为promise对象设置 .then 调用返回值时的回调函数。
asyncFunction 这个函数会返回 promise 对象,对于这个 promise 对象,我们调用它的 then 方法来设置 resolve 后的回调函数, catch 方法来设置发生错误时的回调函数。
该promise对象会在setTimeout之后的 1000ms 被 resolve, 这时 then 的调用函数会被调用,并输出 'Async Hello world'。
在这种情况下 catch 的回调函数并不会被执行(因为promise返回了resolve),不过如果运行环境没有提供 setTimeout 函数的话,那么就会产生异常,在 catch 中设置的回调函数就会被执行。
如果不使用catch方法,只使用then方法的话:
只声明 promise.then(onFulfilled, onRejected)
asyncFunction().then(function (value) { console.log(value);
},function (error) { console.log(error);
});复制代码Promise的状态
用 new Promise 实例化的 promise 对象有三种状态:
has-resolution: FulFilled
resolve(成功)时,此时调用 onFulfilled
has-rejection: Rejected
reject(失败)时,此时调用 onRejected
unresolved: Pending
既不是resolve也不是reject的状态。也就是promise对象刚被创建后的初始化状态等
建议使用:Pending,Fulfilled,Rejected 的状态名称进行讲述。
pending -> value -> Fulfilled
pending -> error -> Rejected
状态的改变
promise 对象的状态,从 Pending 转换为 Fulfilled 或 Rejected 之后,这个 promise 对象的状态就不会再发生任何变化。
在 .then 后执行的函数可以肯定地说只会被调用一次。并且 Fulfilled 和 Rejected 这两个中的任一状态都可以表示为 Settled(不变的)。
Settled
resolve(成功) 或 reject(失败)
当 promise 的对象状态发生变化时,用 .then 来定义只会被调用一次的函数。
Promise 代码
创建promise对象的流程:
new Promise(fn) 返回一个 promise 对象
在 fn 中指定异步等处理
处理结果正常的话,调用 resolve(处理结果值)
处理结果错误的话,调用 reject(Error对象)
用 Promise 来通过异步处理方式来获取 XMLHttpRequest(XHR)的数据:
来创建XHR的promise对象
// 运行示例var URL = "http://xxx.org/get";
getURL(URL).then(function onFulfilled(value){console.log(value);
}).catch(function onRejected(error){console.error(error);
});function getURL(URL) { return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { var req = new XMLHttpRequest();
req.open('GET', URL, true);
req.onload = function () { if (req.status === 200) {
resolve(req.responseText);
} else {
reject(new Error(req.statusText));
}
};
req.onerror = function () {
reject(new Error(req.statusText));
};
req.send();
});
}复制代码为promise对象添加处理方法主要有以下两种
promise对象被 resolve 时的处理(onFulfilled)
promise对象被 reject 时的处理(onRejected)
此时所谓的 通信成功 , 指的就是在被resolve后, promise对象变为FulFilled状态 。
被resolve后的处理,可以在 .then 方法中传入想要调用的函数。
用 new Promise 方法创建promise对象
用 .then 或 .catch 添加promise对象的处理函数
Promise.resolve
静态方法 Promise.resolve(value) 可以认为是 new Promise() 方法的快捷方式。
Promise.resolve(18); 等同于 可以认为是以下代码的语法糖:
new Promise(function(resolve){
resolve(18);
});复制代码方法 Promise.resolve(value); 的返回值也是一个promise对象
Promise.resolve(18).then(function(value){ console.log(value);
})复制代码Promise.resolve 方法另一个作用就是将 thenable 对象转换为promise对象。
Promise.resolve 方法另一个作用就是将 thenable 对象转换为promise对象。
ES6 Promises里提到了Thenable这个概念,简单来说它就是一个非常类似promise的东西。
就像我们有时称具有 .length 方法的非数组对象为Array like一样,thenable指的是一个具有 .then 方法的对象。
这种将thenable对象转换为promise对象的机制要求thenable对象所拥有的 then 方法应该和Promise所拥有的 then 方法具有同样的功能和处理过程,在将thenable对象转换为promise对象的时候,还会巧妙的利用thenable对象原来具有的 then 方法。
到底什么样的对象能算是thenable的呢,最简单的例子就是 jQuery.ajax(),它的返回值就是thenable的。
$.ajax('/json/comment.json');// => 拥有 `.then` 方法的对象复制代码这个thenable的对象可以使用 Promise.resolve 来转换为一个promise对象。
将thenable对象转换promise对象
var promise = Promise.resolve($.ajax('/json/comment.json'));// => promise对象promise.then(function(value){ console.log(value);
});复制代码Promise.resolve 方法可以认为它的作用就是将传递给它的参数填充(Fulfilled)到promise对象后并返回这个promise对象。
Promise.reject
Promise.reject(error) 是 new Promise() 方法的快捷方式。
比如 Promise.reject(new Error("出错了")) 就是下面代码的语法糖形式。
new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
reject(new Error("出错了"));
});复制代码这段代码的功能是调用该promise对象通过then指定的 onRejected 函数,并将错误(Error)对象传递给这个 onRejected 函数。
Promise.reject(new Error("BOOM!")).catch(function(error){ console.error(error);
});复制代码.then 中指定的方法调用是异步进行的
var promise = new Promise(function (resolve){ console.log("inner promise"); // 1
resolve(18);
});
promise.then(function(value){ console.log(value); // 3});console.log("outer promise"); // 2复制代码function onReady(fn) { var readyState = document.readyState; if (readyState === 'interactive' || readySate === 'complete') {
fn();
} else { window.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', fn);
}
}
onReady(function () { console.log('DOM fully loaded and parsed');
});复制代码then
promise可以写成方法链的形式
aPromise.then(function taskA(value){ // task A}).then(function taskB(vaue){ // task B}).catch(function onRejected(error){ console.log(error);
});复制代码promise chain
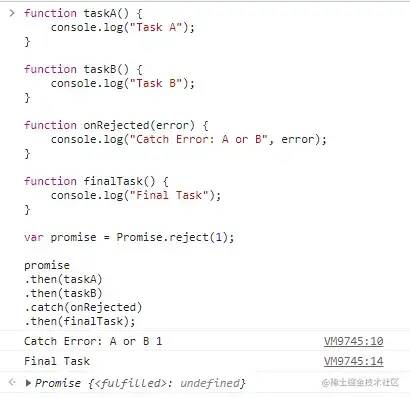
promise-then-catch-flow.js
function taskA() { console.log("Task A");
}function taskB() { console.log("Task B");
}function onRejected(error) { console.log("Catch Error: A or B", error);
}function finalTask() { console.log("Final Task");
}var promise = Promise.resolve();
promise
.then(taskA)
.then(taskB)
.catch(onRejected)
.then(finalTask);复制代码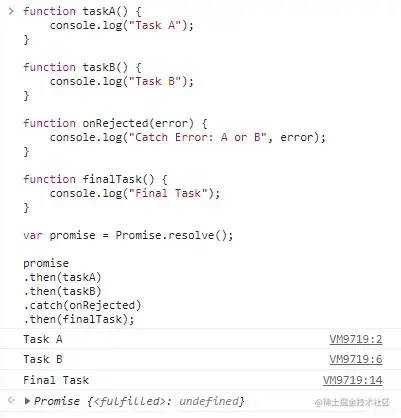
then
注册 onFulfilled 时的回调函数
catch
注册 onRejected 时的回调函数
promise chain 中如何传递参数
return 返回值
每个方法中 return 的值不仅只局限于字符串或者数值类型,也可以是对象或者promise对象等复杂类型
return的值会由 Promise.resolve(return的返回值); 进行相应的包装处理,因此不管回调函数中会返回一个什么样的值,最终 then 的结果都是返回一个新创建的promise对象
Promise.then 不仅仅是注册一个回调函数那么简单,它还会将回调函数的返回值进行转换,创建并返回一个 promise 对象。
catch
Promise.cath 只是 promise.then(undefined, onRejected); 方法的一个别名而已。这个方法用来注册当promise对象状态变为Rejected时的回调函数。
var promise = Promise.reject(new Error("message"));
promise.catch(function (error) { console.error(error);
});复制代码解决Promise.catch标识符冲突问题
var promise = Promise.reject(new Error("message"));
promise["catch"](function (error) { console.error(error);
});var promise = Promise.reject(new Error("message"));
promise.then(undefined, function (error) { console.error(error);
});复制代码每次调用then都会返回一个新创建的promise对象
不管是 then 还是 catch 方法调用,都返回了一个新的promise对象。
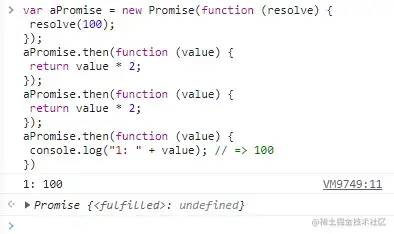
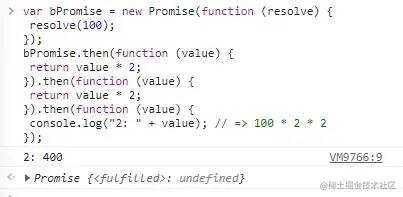
var aPromise = new Promise(function (resolve) {
resolve(100);
});var thenPromise = aPromise.then(function (value) { console.log(value);
});var catchPromise = thenPromise.catch(function (error) { console.error(error);
});console.log(aPromise !== thenPromise); // => trueconsole.log(thenPromise !== catchPromise);// => true复制代码then 和 catch 都返回了和调用者不同的promise对象。
promise object -> then(promise object)(value -> onFulfilled; error -> onRejected) -> catch(error -> onRejected)
then 的使用方式上的差别
Promise.all
Promise.all 接收一个 promise对象的数组作为参数,当这个数组里的所有promise对象全部变为resolve或reject状态的时候,它才会去调用 .then 方法。
使用一个计时器来计算一下程序执行时间
// `delay`毫秒后执行resolvefunction timerPromisefy(delay) { return new Promise(function (resolve) { setTimeout(function () {
resolve(delay);
}, delay);
});
}var startDate = Date.now();// 所有promise变为resolve后程序退出Promise.all([
timerPromisefy(1),
timerPromisefy(32),
timerPromisefy(64),
timerPromisefy(128)
]).then(function (values) { console.log(Date.now() - startDate + 'ms'); // 約128ms
console.log(values); // [1,32,64,128]});复制代码Promise.race
Promise.race 方法 ,接收一个promise对象数组为参数。
Promise.all 在接收到的所有的对象promise都变为 FulFilled 或者 Rejected 状态之后才会继续进行后面的处理, 与之相对的是 Promise.race 只要有一个promise对象进入FulFilled 或者 Rejected 状态的话,就会继续进行后面的处理。
then 与 catch 比较
使用 promise.then(onFulfilled, onRejected) 的话
在 onFulfilled 中发生异常的话,在 onRejected 中是捕获不到这个异常的。
在 promise.then(onFulfilled).catch(onRejected) 的情况下
then 中产生的异常能在 .catch 中捕获
.then 和 .catch 在本质上是没有区别的
需要分场合使用。
由于 .catch 方法是 .then 的别名,我们使用 .then 也能完成同样的工作。只不过使用 .catch 的话意图更明确,更容易理解
练习
then
promise.then(onFulfilled, onRejected);
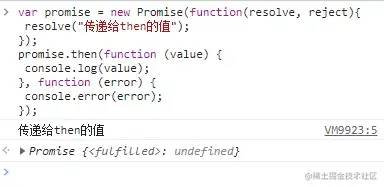
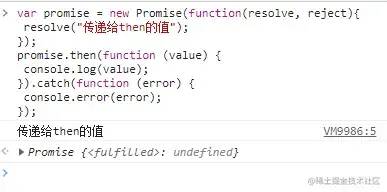
catch
promise.catch(onRejected);
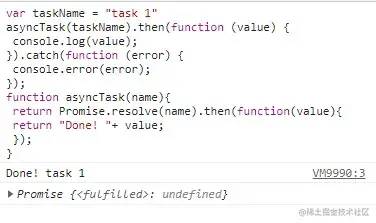
resolve
Promise.resolve(promise);
Promise.resolve(thenable);
Promise.resolve(object);
接收到promise对象参数的时候
返回的还是接收到的promise对象
接收到thenable类型的对象的时候
返回一个新的promise对象,这个对象具有一个 then 方法
接收的参数为其他类型的时候(包括JavaScript对或null等)
返回一个将该对象作为值的新promise对象
reject
Promise.reject(object)
和 Promise.resolve不同的是,即使Promise.reject接收到的参数是一个promise对象,该函数也还是会返回一个全新的promise对象。
all
Promise.all(promiseArray);
生成并返回一个新的promise对象。
参数传递promise数组中所有的promise对象都变为resolve的时候,该方法才会返回, 新创建的promise则会使用这些promise的值。
如果参数中的任何一个promise为reject的话,则整个Promise.all调用会立即终止,并返回一个reject的新的promise对象。
由于参数数组中的每个元素都是由 Promise.resolve 包装(wrap)的,所以Paomise.all可以处理不同类型的promose对象。
race
Promise.race(promiseArray)
生成并返回一个新的promise对象。
参数 promise 数组中的任何一个promise对象如果变为resolve或者reject的话, 该函数就会返回,并使用这个promise对象的值进行resolve或者reject。
