总结零散的 MySQL 基础知识
前言
在日常开发中,一些不常用且又比较基础的知识,过了一段时间之后,总是容易忘记或者变得有点模棱两可。本篇主要记录一些关于MySQL数据库比较基础的知识,以便日后快速查看。
SQL命令
SQL命令分可以分为四组:DDL、DML、DCL和TCL。四组中包含的命令分别如下
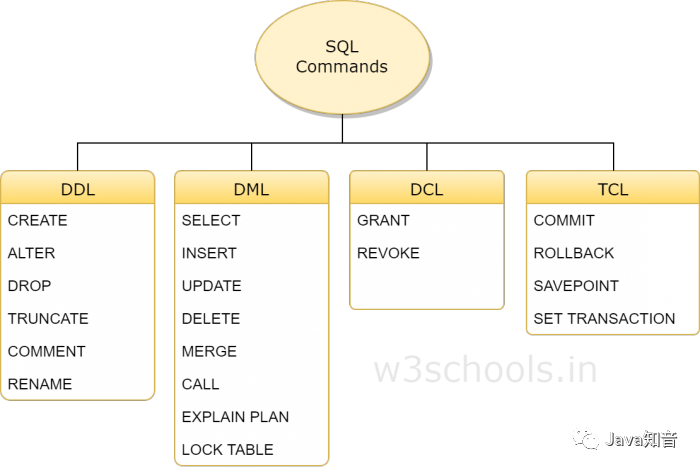 DDL
DDL
DDL是数据定义语言(Data Definition Language)的简称,它处理数据库schemas和描述数据应如何驻留在数据库中。
CREATE:创建数据库及其对象(如表,索引,视图,存储过程,函数和触发器)ALTER:改变现有数据库的结构DROP:从数据库中删除对象TRUNCATE:从表中删除所有记录,包括为记录分配的所有空间都将被删除COMMENT:添加注释RENAME:重命名对象
# 建表
CREATE TABLE sicimike (
id int(4) primary key auto_increment COMMENT '主键ID',
name varchar(10) unique,
age int(3) default 0,
identity_card varchar(18)
# PRIMARY KEY (id) // 也可以通过这种方式设置主键
# UNIQUE KEY (name) // 也可以通过这种方式设置唯一键
# key/index (identity_card, col1...) // 也可以通过这种方式创建索引
) ENGINE = InnoDB;
# 设置主键
alter table sicimike add primary key(id);
# 删除主键
alter table sicimike drop primary key;
# 设置唯一键
alter table sicimike add unique key(column_name);
# 删除唯一键
alter table sicimike drop index column_name;
# 创建索引
alter table sicimike add [unique/fulltext/spatial] index/key index_name (identity_card[(len)] [asc/desc])[using btree/hash]
create [unique/fulltext/spatial] index index_name on sicimike(identity_card[(len)] [asc/desc])[using btree/hash]
example:alter table sicimike add index idx_na(name, age);
# 删除索引
alter table sicimike drop key/index identity_card;
drop index index_name on sicimike;
# 查看索引
show index from sicimike;
# 查看列
desc sicimike;
# 新增列
alter table sicimike add column column_name varchar(30);
# 删除列
alter table sicimike drop column column_name;
# 修改列名
alter table sicimike change column_name new_name varchar(30);
# 修改列属性
alter table sicimike modify column_name varchar(22);
# 查看建表信息
show create table sicimike;
# 添加表注释
alter table sicimike comment '表注释';
# 添加字段注释
alter table sicimike modify column column_name varchar(10) comment '姓名';DML
SELECT,INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE等,它用于存储,修改,检索和删除数据库中的数据。-- 查询从第11条数据开始的连续5条数据
select * from sicimike limit 10, 5group bygroup by)语句,不要求select返回的列,必须是分组的列或者是一个聚合函数。select查询的列不是分组的列,也不是聚合函数,则会返回该分组中第一条记录的数据。对比下面两条SQL语句,第二条SQL语句中,cname既不是分组的列,也不是以聚合函数的形式出现。所以在liming这个分组中,cname取的是第一条数据。mysql> select * from c;
+-----+-------+----------+
| CNO | CNAME | CTEACHER |
+-----+-------+----------+
| 1 | 数学 | liming |
| 2 | 语文 | liming |
| 3 | 历史 | xueyou |
| 4 | 物理 | guorong |
| 5 | 化学 | liming |
+-----+-------+----------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select cteacher, count(cteacher), cname from c group by cteacher;
+----------+-----------------+-------+
| cteacher | count(cteacher) | cname |
+----------+-----------------+-------+
| guorong | 1 | 物理 |
| liming | 3 | 数学 |
| xueyou | 1 | 历史 |
+----------+-----------------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)havinghaving关键字用于对分组后的数据进行筛选,功能相当于分组之前的where,不过要求更严格。过滤条件要么是一个聚合函数( ... having count(x) > 1),要么是出现在select后面的列(select col1, col2 ... group by x having col1 > 1)update tableA a inner join tableB b on a.xxx = b.xxx set a.col1 = xxx, b.col1 = xxx where ...delete a, b from tableA a inner join tableB b on a.xxx = b.xxx where a.col1 = xxx and b.col1 = xxxDCL
GRANT之类的命令,并且主要涉及数据库系统的权限,权限和其他控件。GRANT:允许用户访问数据库的权限REVOKE:撤消用户使用GRANT命令赋予的访问权限
TCL
COMMIT:提交事务ROLLBACK:在发生任何错误的情况下回滚事务
范式
数据库规范化,又称正规化、标准化,是数据库设计的一系列原理和技术,以减少数据库中数据冗余,增进数据的一致性。关系模型的发明者埃德加·科德最早提出这一概念,并于1970年代初定义了第一范式、第二范式和第三范式的概念,还与Raymond F. Boyce于1974年共同定义了第三范式的改进范式——BC范式。
除外还包括针对多值依赖的第四范式,连接依赖的第五范式、DK范式和第六范式。
第一范式

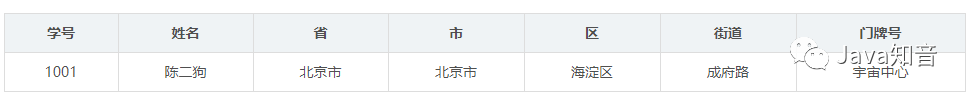
第二范式


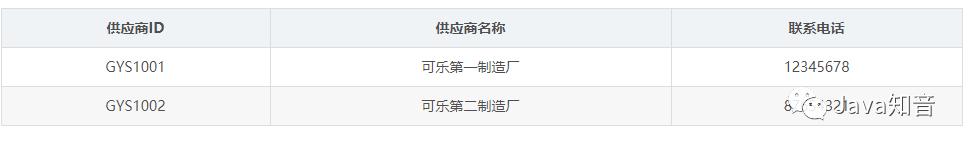
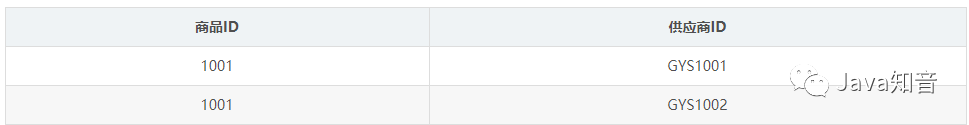
第三范式
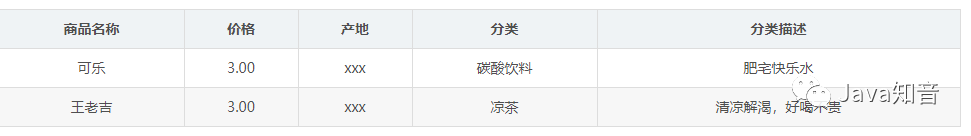
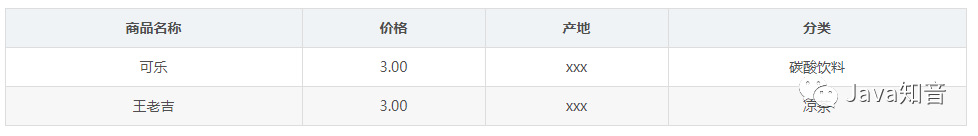
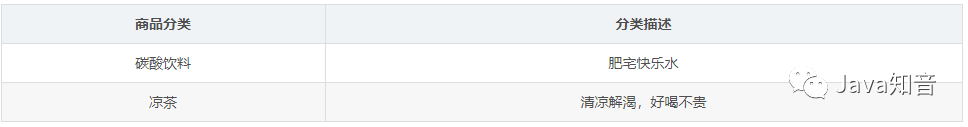
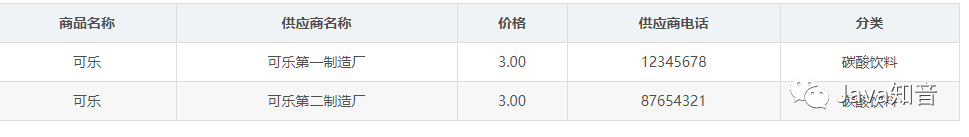
插入异常:如果某个实体随着另一个实体的存在而存在,即缺少某个实体是无法表示这个实体,那么这个表就存在插入异常。 更新异常:如果更改表所对应的某个实体实例的单独属性时,需要将多行更新,那么就说明这个表存在更新异常 删除异常:如果删除表的某一行来表示某实体实例失效时,导致另一个不同实体实例信息丢失,那么这个表就存在删除异常
横表纵表
# 横表
CREATE TABLE `table_h2z` (
`name` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
`chinese` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`math` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`english` int(11) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
/*Data for the table `table_h2z` */
insert into `table_h2z`(`name`,`chinese`,`math`,`english`) values
('mike',45,43,87),
('lily',53,64,88),
('lucy',57,75,75);
# 纵表
CREATE TABLE `table_z2h` (
`name` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
`subject` varchar(8) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`score` int(11) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
/*Data for the table `table_z2h` */
insert into `table_z2h`(`name`,`subject`,`score`) values
('mike','chinese',45),
('lily','chinese',53),
('lucy','chinese',57),
('mike','math',43),
('lily','math',64),
('lucy','math',75),
('mike','english',87),
('lily','english',88),
('lucy','english',75);横表转纵表
SELECT NAME, 'chinese' AS `subject`, chinese AS `score` FROM table_h2z
UNION ALL
SELECT NAME, 'math' AS `subject`, math AS `score` FROM table_h2z
UNION ALL
SELECT NAME, 'english' AS `subject`, english AS `score` FROM table_h2z+------+---------+-------+
| name | subject | score |
+------+---------+-------+
| mike | chinese | 45 |
| lily | chinese | 53 |
| lucy | chinese | 57 |
| mike | math | 43 |
| lily | math | 64 |
| lucy | math | 75 |
| mike | english | 87 |
| lily | english | 88 |
| lucy | english | 75 |
+------+---------+-------+
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)SELECT NAME,
SUM(CASE `subject` WHEN 'chinese' THEN score ELSE 0 END) AS chinese,
SUM(CASE `subject` WHEN 'math' THEN score ELSE 0 END) AS math,
SUM(CASE `subject` WHEN 'english' THEN score ELSE 0 END) AS english
FROM table_z2h
GROUP BY NAME+------+---------+------+---------+
| name | chinese | math | english |
+------+---------+------+---------+
| lily | 53 | 64 | 88 |
| lucy | 57 | 75 | 75 |
| mike | 45 | 43 | 87 |
+------+---------+------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)参考
https://www.w3schools.in/mysql/ddl-dml-dcl/
获得原创整理:《第2版:互联网大厂面试题》
评论
