深入理解JDBC设计模式: DriverManager 解析
JDBC 是java中的一个数据连接技术,它提供了统一的 API 允许用户访问任何形式的表格数据,尤其是存储在关系数据库中的数据。
虽然目前JDBC已经基本被隐藏在了许多数据库框架之后,但是其底层原理从未变过。所以,多一点了解JDBC还是有意义的。
JDBC 之所以能提供统一的API,是基于对所有数据库的抽象及合理的定义。但是每个数据库厂家毕竟是不一样的,JDBC自然要屏蔽这种不一样,它是如何做到的呢?这就是本文讨论的 DriverManager, 它是一个桥接模式的完美应用。其调用图可表示为如下:
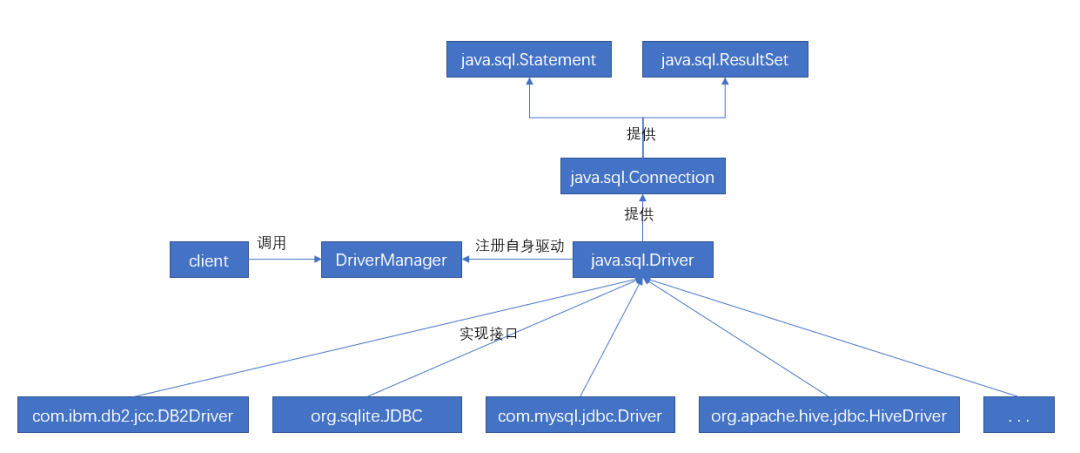
0:JDBC的编程模型
JDBC的编程模式是固定的,也就说操作步骤基本是一定的,如下:
public class JdbcDriverManagerTest {private static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf8";private static final String USER = "root";private static final String PASSWORD = "123456";@Testpublic void testJdbcRaw() throws Exception {//1.加载驱动程序Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");//2. 获得数据库连接Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USER, PASSWORD);//3.操作数据库,实现增删改查, 连接模式有2种: createStatement / prepareStatementStatement stmt = conn.createStatement();// PreparedStatement ptmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //预编译SQL,减少sql执行 //预编译ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT username, age FROM user");//如果有数据,rs.next()返回truewhile(rs.next()){System.out.println(rs.getString("username")+" 年龄:"+rs.getInt("age"));}// 4. 关闭连接conn.close();}}
所以,总体来说,就是4个步骤:
1. 加载驱动程序;
2. 获得数据库连接;
3. 操作数据库,实现增删改查, 连接模式有2种: createStatement / prepareStatement;
4. 关闭数据库连接;
有同学可能要说了,这么简单的事,有什么好分析的?
我们要分析的点:
1. 驱动是如何加载的?
2. 连接是如何获取的?
3. 数据操作是如何传递给数据库的?
4. 连接是如何关闭的?
其实可以看出就是针对每个功能,我们都来问个如何实现就行了。
1. 驱动是如何加载的?
如果我们不考虑统一各数据库的统一性,比如需要创建一个 mysql 的连接,那么我们只需要将mysql 的连接工具类,new一个对象出来就可以了。然而,jdbc却是不可以这么干的,因为它要成为一种标准。实现很简单,直接通过一个反射方法,就可以加载驱动了,那么具体是如何加载的呢?
以mysql 为例,使用反射方法去找到 驱动类 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); 所以,如何驱动起来,也是这个驱动类应该做的事了。
// mysql 的驱动类如下// 重点1: 该驱动类必须实现 java.sql.Driver 接口public class Driver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver {//// Register ourselves with the DriverManager//static {try {// 重点2: 必须在加载时,就将自身注册到 DriverManager 中java.sql.DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());} catch (SQLException E) {throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");}}/*** Construct a new driver and register it with DriverManager** @throws SQLException* if a database error occurs.*/public Driver() throws SQLException {// Required for Class.forName().newInstance()}}// java.sql.DriverManager#registerDriver/*** Registers the given driver with the {@code DriverManager}.* A newly-loaded driver class should call* the method {@code registerDriver} to make itself* known to the {@code DriverManager}. If the driver is currently* registered, no action is taken.** @param driver the new JDBC Driver that is to be registered with the* {@code DriverManager}* @exception SQLException if a database access error occurs* @exception NullPointerException if {@code driver} is null*/public static synchronized void registerDriver(java.sql.Driver driver)throws SQLException {// driverAction 为null, 连接建立后不做任何事, 有的数据库需要进一步的操作registerDriver(driver, null);}/*** Registers the given driver with the {@code DriverManager}.* A newly-loaded driver class should call* the method {@code registerDriver} to make itself* known to the {@code DriverManager}. If the driver is currently* registered, no action is taken.** @param driver the new JDBC Driver that is to be registered with the* {@code DriverManager}* @param da the {@code DriverAction} implementation to be used when* {@code DriverManager#deregisterDriver} is called* @exception SQLException if a database access error occurs* @exception NullPointerException if {@code driver} is null* @since 1.8*/public static synchronized void registerDriver(java.sql.Driver driver,DriverAction da)throws SQLException {/* Register the driver if it has not already been added to our list */if(driver != null) {// CopyOnWriteArrayList<DriverInfo> registeredDrivers// 使用线程安全的容器来存放驱动,对于读多写少的场景,CopyOnWriteArrayList 是比较擅长的// 多次注册不影响结果// 使用 DriverInfo 将 Driver 包装起来registeredDrivers.addIfAbsent(new DriverInfo(driver, da));} else {// This is for compatibility with the original DriverManagerthrow new NullPointerException();}println("registerDriver: " + driver);}
这样,mysql 的驱动就注册到 DriverManager 中了,也就是可以接受 DriverManager 的管理了,需要注意的是,这里的类加载是特别的,它是违背“双亲委托加载模型”的一个案例,使用的是 contextClassLoader 进行加载驱动的。接下来我们要讲的统一的API获取数据库连接。
2. 如何获取数据库连接?
通过注册的方式,我已经将数据库的实例,交给了 DriverManager, 此时再要获取数据库连接,也就只需要问 DriverManager 要就行了。
我们以一个时序图总览全局:
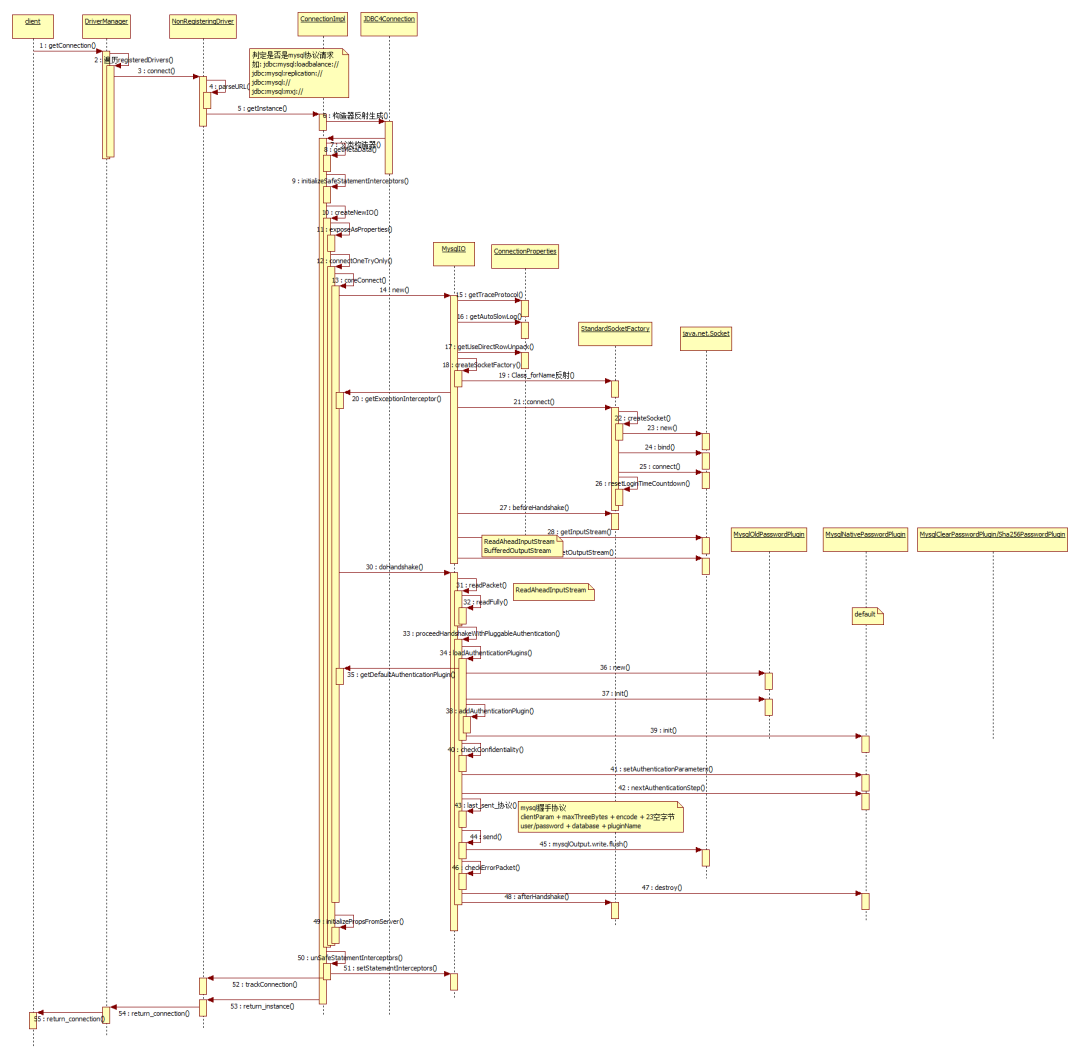
// java.sql.DriverManager#getConnection(java.lang.String, java.lang.String, java.lang.String)/*** Attempts to establish a connection to the given database URL.* The <code>DriverManager</code> attempts to select an appropriate driver from* the set of registered JDBC drivers.*<p>* <B>Note:</B> If the {@code user} or {@code password} property are* also specified as part of the {@code url}, it is* implementation-defined as to which value will take precedence.* For maximum portability, an application should only specify a* property once.** @param url a database url of the form* <code>jdbc:<em>subprotocol</em>:<em>subname</em></code>* @param user the database user on whose behalf the connection is being* made* @param password the user's password* @return a connection to the URL* @exception SQLException if a database access error occurs or the url is* {@code null}* @throws SQLTimeoutException when the driver has determined that the* timeout value specified by the {@code setLoginTimeout} method* has been exceeded and has at least tried to cancel the* current database connection attempt*/// CallerSensitive 是为了避免获取反射获取实例时忽略该调用栈@CallerSensitivepublic static Connection getConnection(String url,String user, String password) throws SQLException {java.util.Properties info = new java.util.Properties();if (user != null) {info.put("user", user);}if (password != null) {info.put("password", password);}// 统一将必要信息封装到 Properties 中,方便各自的驱动按需获取return (getConnection(url, info, Reflection.getCallerClass()));}// Worker method called by the public getConnection() methods.private static Connection getConnection(String url, java.util.Properties info, Class<?> caller) throws SQLException {/** When callerCl is null, we should check the application's* (which is invoking this class indirectly)* classloader, so that the JDBC driver class outside rt.jar* can be loaded from here.*/// callerCL 可能为空,因为加载不到外部调用的类,此处违反了 双亲委派模型ClassLoader callerCL = caller != null ? caller.getClassLoader() : null;synchronized(DriverManager.class) {// synchronize loading of the correct classloader.if (callerCL == null) {// 通过 ContextClassLoader 进行加载callerCL = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();}}if(url == null) {throw new SQLException("The url cannot be null", "08001");}println("DriverManager.getConnection(\"" + url + "\")");// Walk through the loaded registeredDrivers attempting to make a connection.// Remember the first exception that gets raised so we can reraise it.SQLException reason = null;for(DriverInfo aDriver : registeredDrivers) {// If the caller does not have permission to load the driver then// skip it.// 检查 classloader 是否相同,从而确认是否可以进行加载if(isDriverAllowed(aDriver.driver, callerCL)) {try {println(" trying " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());// 其实是一个个驱动地尝试连接,直到找到第1个可用的连接// 其实一般是通过 连接协议来自行判定的,稍后我们以 mysql 的连接示例看一下Connection con = aDriver.driver.connect(url, info);if (con != null) {// Success!println("getConnection returning " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());return (con);}} catch (SQLException ex) {if (reason == null) {reason = ex;}}} else {println(" skipping: " + aDriver.getClass().getName());}}// if we got here nobody could connect.if (reason != null) {println("getConnection failed: " + reason);throw reason;}println("getConnection: no suitable driver found for "+ url);throw new SQLException("No suitable driver found for "+ url, "08001");}// 检查 driver 属于 classLoader 的管理范围private static boolean isDriverAllowed(Driver driver, ClassLoader classLoader) {boolean result = false;if(driver != null) {Class<?> aClass = null;try {aClass = Class.forName(driver.getClass().getName(), true, classLoader);} catch (Exception ex) {result = false;}result = ( aClass == driver.getClass() ) ? true : false;}return result;}
DriverManager 通过遍历所有驱动列表的形式,查找是否是某种类型的数据库操作。虽然看起来好像有点费事,但是毕竟是做通用的框架,这样做可以保证正确性,况且几次调用对性能影响也不大。虽然各驱动可以自行处理或拒绝某协议请求,但是一般都是以url前缀作为判断接受与否的。我们来看下 mysql 如何处理?
// Mysql 的实现中是以 NonRegisteringDriver 作为实现类的// com.mysql.jdbc.NonRegisteringDriver#connect// 根据 url 的和各属性配置信息,创建一个真实的连接到mysql的网络通道// url格式如: jdbc:mysql://host:port/databasepublic java.sql.Connection connect(String url, Properties info) throws SQLException {if (url != null) {// 负载均衡式访问mysql, jdbc:mysql:loadbalance://if (StringUtils.startsWithIgnoreCase(url, LOADBALANCE_URL_PREFIX)) {return connectLoadBalanced(url, info);}// 多副本式访问mysql, jdbc:mysql:replication://else if (StringUtils.startsWithIgnoreCase(url, REPLICATION_URL_PREFIX)) {return connectReplicationConnection(url, info);}}Properties props = null;// 解析各属性,解析不正确,则说明不是标准的mysql协议请求if ((props = parseURL(url, info)) == null) {return null;}// 以下处理只针对一个 mysql-host 的情况处理if (!"1".equals(props.getProperty(NUM_HOSTS_PROPERTY_KEY))) {return connectFailover(url, info);}try {// 这个就是 mysql 的底层的连接的实现了// 大概就是按照mysql的协议,打开一个socket连接之类的,我们可以稍微看看Connection newConn = com.mysql.jdbc.ConnectionImpl.getInstance(host(props), port(props), props, database(props), url);return newConn;} catch (SQLException sqlEx) {// Don't wrap SQLExceptions, throw// them un-changed.throw sqlEx;} catch (Exception ex) {SQLException sqlEx = SQLError.createSQLException(Messages.getString("NonRegisteringDriver.17") + ex.toString() + Messages.getString("NonRegisteringDriver.18"),SQLError.SQL_STATE_UNABLE_TO_CONNECT_TO_DATASOURCE, null);sqlEx.initCause(ex);throw sqlEx;}}// 解析 url 的各项参数,全组装到 urlProps 中返回// 相比于普通的简单前缀判定多了些工作public Properties parseURL(String url, Properties defaults) throws java.sql.SQLException {Properties urlProps = (defaults != null) ? new Properties(defaults) : new Properties();if (url == null) {return null;}// 连接协议验证:if (!StringUtils.startsWithIgnoreCase(url, URL_PREFIX) && !StringUtils.startsWithIgnoreCase(url, MXJ_URL_PREFIX)&& !StringUtils.startsWithIgnoreCase(url, LOADBALANCE_URL_PREFIX) && !StringUtils.startsWithIgnoreCase(url, REPLICATION_URL_PREFIX)) {return null;}// ... 解析各附加参数及配置文件参数 ...return urlProps;}// 创建连接到 mysql-server/*** Creates a connection instance -- We need to provide factory-style methods* so we can support both JDBC3 (and older) and JDBC4 runtimes, otherwise* the class verifier complains when it tries to load JDBC4-only interface* classes that are present in JDBC4 method signatures.*/protected static Connection getInstance(String hostToConnectTo, int portToConnectTo, Properties info, String databaseToConnectTo, String url)throws SQLException {// 此处会检测 java.sql.NClobif (!Util.isJdbc4()) {return new ConnectionImpl(hostToConnectTo, portToConnectTo, info, databaseToConnectTo, url);}// 所以我们分析这个创建方式// 使用 com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection 新建一个实例返回// JDBC_4_CONNECTION_CTOR 是 JDBC4Connection 的构造方法return (Connection) Util.handleNewInstance(JDBC_4_CONNECTION_CTOR, new Object[] { hostToConnectTo, Integer.valueOf(portToConnectTo), info,databaseToConnectTo, url }, null);}// com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection#JDBC4Connectionpublic JDBC4Connection(String hostToConnectTo, int portToConnectTo, Properties info, String databaseToConnectTo, String url) throws SQLException {// 父类将会创建到mysql-server 的连接super(hostToConnectTo, portToConnectTo, info, databaseToConnectTo, url);}
JDBC4Connection 类继承图如下:

ConnectionImpl负责建立连接到mysql-server,它主要处理各种连接准备和异常处理
// com.mysql.jdbc.ConnectionImpl/*** Creates a connection to a MySQL Server.** @param hostToConnectTo* the hostname of the database server* @param portToConnectTo* the port number the server is listening on* @param info* a Properties[] list holding the user and password* @param databaseToConnectTo* the database to connect to* @param url* the URL of the connection* @param d* the Driver instantation of the connection* @exception SQLException* if a database access error occurs*/public ConnectionImpl(String hostToConnectTo, int portToConnectTo, Properties info, String databaseToConnectTo, String url) throws SQLException {this.connectionCreationTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();...try {// 元数据信息初始化this.dbmd = getMetaData(false, false);initializeSafeStatementInterceptors();// 创建io到mysqlcreateNewIO(false);unSafeStatementInterceptors();} catch (SQLException ex) {cleanup(ex);// don't clobber SQL exceptionsthrow ex;} catch (Exception ex) {cleanup(ex);... 封装错误信息 ...throw sqlEx;}NonRegisteringDriver.trackConnection(this);}// com.mysql.jdbc.ConnectionImpl#createNewIO/*** Creates an IO channel to the server** @param isForReconnect* is this request for a re-connect* @return a new MysqlIO instance connected to a server* @throws SQLException* if a database access error occurs* @throws CommunicationsException*/public void createNewIO(boolean isForReconnect) throws SQLException {synchronized (getConnectionMutex()) {// Synchronization Not needed for *new* connections, but defintely for connections going through fail-over, since we might get the new connection up// and running *enough* to start sending cached or still-open server-side prepared statements over to the backend before we get a chance to// re-prepare them...Properties mergedProps = exposeAsProperties(this.props);// 非高可用状态,只连接一次,失败即失败if (!getHighAvailability()) {connectOneTryOnly(isForReconnect, mergedProps);return;}connectWithRetries(isForReconnect, mergedProps);}}// 连接到mysql-server, 不重试private void connectOneTryOnly(boolean isForReconnect, Properties mergedProps) throws SQLException {Exception connectionNotEstablishedBecause = null;try {// 核心连接操作,实例放到 this.io 中coreConnect(mergedProps);this.connectionId = this.io.getThreadId();this.isClosed = false;...this.io.setStatementInterceptors(this.statementInterceptors);// Server properties might be different from previous connection, so initialize again...initializePropsFromServer();...return;} catch (Exception EEE) {... 异常资源处理throw chainedEx;}}// 真正的连接动作,将连接实例体现到 this.io 中private void coreConnect(Properties mergedProps) throws SQLException, IOException {int newPort = 3306;String newHost = "localhost";String protocol = mergedProps.getProperty(NonRegisteringDriver.PROTOCOL_PROPERTY_KEY);// 通常protocol 为空if (protocol != null) {// "new" style URLif ("tcp".equalsIgnoreCase(protocol)) {newHost = normalizeHost(mergedProps.getProperty(NonRegisteringDriver.HOST_PROPERTY_KEY));newPort = parsePortNumber(mergedProps.getProperty(NonRegisteringDriver.PORT_PROPERTY_KEY, "3306"));} else if ("pipe".equalsIgnoreCase(protocol)) {setSocketFactoryClassName(NamedPipeSocketFactory.class.getName());String path = mergedProps.getProperty(NonRegisteringDriver.PATH_PROPERTY_KEY);if (path != null) {mergedProps.setProperty(NamedPipeSocketFactory.NAMED_PIPE_PROP_NAME, path);}} else {// normalize for all unknown protocolsnewHost = normalizeHost(mergedProps.getProperty(NonRegisteringDriver.HOST_PROPERTY_KEY));newPort = parsePortNumber(mergedProps.getProperty(NonRegisteringDriver.PORT_PROPERTY_KEY, "3306"));}} else {String[] parsedHostPortPair = NonRegisteringDriver.parseHostPortPair(this.hostPortPair);newHost = parsedHostPortPair[NonRegisteringDriver.HOST_NAME_INDEX];newHost = normalizeHost(newHost);if (parsedHostPortPair[NonRegisteringDriver.PORT_NUMBER_INDEX] != null) {newPort = parsePortNumber(parsedHostPortPair[NonRegisteringDriver.PORT_NUMBER_INDEX]);}}this.port = newPort;this.host = newHost;// reset max-rows to default valuethis.sessionMaxRows = -1;// MysqlIO 承载连接this.io = new MysqlIO(newHost, newPort, mergedProps, getSocketFactoryClassName(), getProxy(), getSocketTimeout(),this.largeRowSizeThreshold.getValueAsInt());// 连接到数据库,以测试连接的有效性this.io.doHandshake(this.user, this.password, this.database);if (versionMeetsMinimum(5, 5, 0)) {// error messages are returned according to character_set_results which, at this point, is set from the response packetthis.errorMessageEncoding = this.io.getEncodingForHandshake();}}
MysqlIO 类是专门负责与mysql-server 进行网络交互的一个工具类,它基于Socket的长链接进行交互,绑定输入输出流等。其构造方法如下:
/*** Constructor: Connect to the MySQL server and setup a stream connection.** @param host* the hostname to connect to* @param port* the port number that the server is listening on* @param props* the Properties from DriverManager.getConnection()* @param socketFactoryClassName* the socket factory to use* @param conn* the Connection that is creating us* @param socketTimeout* the timeout to set for the socket (0 means no* timeout)** @throws IOException* if an IOException occurs during connect.* @throws SQLException* if a database access error occurs.*/public MysqlIO(String host, int port, Properties props, String socketFactoryClassName, MySQLConnection conn, int socketTimeout,int useBufferRowSizeThreshold) throws IOException, SQLException {// JDBC4Connectionthis.connection = conn;if (this.connection.getEnablePacketDebug()) {this.packetDebugRingBuffer = new LinkedList<StringBuffer>();}this.traceProtocol = this.connection.getTraceProtocol();this.useAutoSlowLog = this.connection.getAutoSlowLog();this.useBufferRowSizeThreshold = useBufferRowSizeThreshold;this.useDirectRowUnpack = this.connection.getUseDirectRowUnpack();this.logSlowQueries = this.connection.getLogSlowQueries();this.reusablePacket = new Buffer(INITIAL_PACKET_SIZE);this.sendPacket = new Buffer(INITIAL_PACKET_SIZE);this.port = port;this.host = host;// com.mysql.jdbc.StandardSocketFactorythis.socketFactoryClassName = socketFactoryClassName;// 创建socketFactory 实例this.socketFactory = createSocketFactory();this.exceptionInterceptor = this.connection.getExceptionInterceptor();try {// 创建真实的socket连接到 mysql-server, 与远程进行网络IO通信this.mysqlConnection = this.socketFactory.connect(this.host, this.port, props);if (socketTimeout != 0) {try {this.mysqlConnection.setSoTimeout(socketTimeout);} catch (Exception ex) {/* Ignore if the platform does not support it */}}this.mysqlConnection = this.socketFactory.beforeHandshake();// 转换输入流到 this.mysqlInput 中if (this.connection.getUseReadAheadInput()) {this.mysqlInput = new ReadAheadInputStream(this.mysqlConnection.getInputStream(), 16384, this.connection.getTraceProtocol(),this.connection.getLog());} else if (this.connection.useUnbufferedInput()) {this.mysqlInput = this.mysqlConnection.getInputStream();} else {this.mysqlInput = new BufferedInputStream(this.mysqlConnection.getInputStream(), 16384);}// 转换输出流到 this.mysqlOutput 中this.mysqlOutput = new BufferedOutputStream(this.mysqlConnection.getOutputStream(), 16384);this.isInteractiveClient = this.connection.getInteractiveClient();this.profileSql = this.connection.getProfileSql();this.autoGenerateTestcaseScript = this.connection.getAutoGenerateTestcaseScript();this.needToGrabQueryFromPacket = (this.profileSql || this.logSlowQueries || this.autoGenerateTestcaseScript);if (this.connection.getUseNanosForElapsedTime() && Util.nanoTimeAvailable()) {this.useNanosForElapsedTime = true;this.queryTimingUnits = Messages.getString("Nanoseconds");} else {this.queryTimingUnits = Messages.getString("Milliseconds");}if (this.connection.getLogSlowQueries()) {calculateSlowQueryThreshold();}} catch (IOException ioEx) {throw SQLError.createCommunicationsException(this.connection, 0, 0, ioEx, getExceptionInterceptor());}}
3. 如何执行sql操作
主要有两种方式, statement 和 prepareStatement. PreparedStatement继承自Statement,两者都是接口。区别是:PreparedStatement是预编译的(mysql提供的能力),比Statement效率高,可以使用占位符,可防止SQL注入。
过程比较冗长,还是以一个时序图来总览下:

//获取预处理对象statement = getConnection().prepareStatement(sql);statement.executeUpdate(sql);// com.mysql.jdbc.ConnectionImpl#prepareStatement(java.lang.String)/*** A SQL statement with or without IN parameters can be pre-compiled and* stored in a PreparedStatement object. This object can then be used to* efficiently execute this statement multiple times.* <p>* <B>Note:</B> This method is optimized for handling parametric SQL statements that benefit from precompilation if the driver supports precompilation. In* this case, the statement is not sent to the database until the PreparedStatement is executed. This has no direct effect on users; however it does affect* which method throws certain java.sql.SQLExceptions* </p>* <p>* MySQL does not support precompilation of statements, so they are handled by the driver.* </p>** @param sql* a SQL statement that may contain one or more '?' IN parameter* placeholders* @return a new PreparedStatement object containing the pre-compiled* statement.* @exception SQLException* if a database access error occurs.*/public java.sql.PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException {return prepareStatement(sql, DEFAULT_RESULT_SET_TYPE, DEFAULT_RESULT_SET_CONCURRENCY);}// com.mysql.jdbc.ConnectionImpl#prepareStatement(java.lang.String, int, int)/*** JDBC 2.0 Same as prepareStatement() above, but allows the default result* set type and result set concurrency type to be overridden.** @param sql* the SQL query containing place holders* @param resultSetType* a result set type, see ResultSet.TYPE_XXX* @param resultSetConcurrency* a concurrency type, see ResultSet.CONCUR_XXX* @return a new PreparedStatement object containing the pre-compiled SQL* statement* @exception SQLException* if a database-access error occurs.*/public java.sql.PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {synchronized (getConnectionMutex()) {// 检查连接是否已关闭checkClosed();//// FIXME: Create warnings if can't create results of the given type or concurrency//PreparedStatement pStmt = null;boolean canServerPrepare = true;// 解析 ? 处理String nativeSql = getProcessEscapeCodesForPrepStmts() ? nativeSQL(sql) : sql;if (this.useServerPreparedStmts && getEmulateUnsupportedPstmts()) {canServerPrepare = canHandleAsServerPreparedStatement(nativeSql);}if (this.useServerPreparedStmts && canServerPrepare) {if (this.getCachePreparedStatements()) {synchronized (this.serverSideStatementCache) {pStmt = (com.mysql.jdbc.ServerPreparedStatement) this.serverSideStatementCache.remove(sql);if (pStmt != null) {((com.mysql.jdbc.ServerPreparedStatement) pStmt).setClosed(false);pStmt.clearParameters();}if (pStmt == null) {try {pStmt = ServerPreparedStatement.getInstance(getLoadBalanceSafeProxy(), nativeSql, this.database, resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);if (sql.length() < getPreparedStatementCacheSqlLimit()) {((com.mysql.jdbc.ServerPreparedStatement) pStmt).isCached = true;}pStmt.setResultSetType(resultSetType);pStmt.setResultSetConcurrency(resultSetConcurrency);} catch (SQLException sqlEx) {// Punt, if necessaryif (getEmulateUnsupportedPstmts()) {pStmt = (PreparedStatement) clientPrepareStatement(nativeSql, resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency, false);if (sql.length() < getPreparedStatementCacheSqlLimit()) {this.serverSideStatementCheckCache.put(sql, Boolean.FALSE);}} else {throw sqlEx;}}}}} else {try {pStmt = ServerPreparedStatement.getInstance(getLoadBalanceSafeProxy(), nativeSql, this.database, resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency);pStmt.setResultSetType(resultSetType);pStmt.setResultSetConcurrency(resultSetConcurrency);} catch (SQLException sqlEx) {// Punt, if necessaryif (getEmulateUnsupportedPstmts()) {pStmt = (PreparedStatement) clientPrepareStatement(nativeSql, resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency, false);} else {throw sqlEx;}}}} else {// 生成 PreparedStatementpStmt = (PreparedStatement) clientPrepareStatement(nativeSql, resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency, false);}return pStmt;}}
执行更新操作,其实就是将statement中的sql与参数,根据协议要求,写入远程即可,如下:
// com.mysql.jdbc.PreparedStatement#executeUpdate()/*** Execute a SQL INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE statement. In addition, SQL* statements that return nothing such as SQL DDL statements can be* executed.** @return either the row count for INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE; or 0 for SQL* statements that return nothing.** @exception SQLException* if a database access error occurs*/public int executeUpdate() throws SQLException {return executeUpdate(true, false);}/** We need this variant, because ServerPreparedStatement calls this for* batched updates, which will end up clobbering the warnings and generated* keys we need to gather for the batch.*/protected int executeUpdate(boolean clearBatchedGeneratedKeysAndWarnings, boolean isBatch) throws SQLException {synchronized (checkClosed().getConnectionMutex()) {if (clearBatchedGeneratedKeysAndWarnings) {clearWarnings();this.batchedGeneratedKeys = null;}// 代入参数执行return executeUpdate(this.parameterValues, this.parameterStreams, this.isStream, this.streamLengths, this.isNull, isBatch);}}// com.mysql.jdbc.PreparedStatement#executeUpdate(byte[][], java.io.InputStream[], boolean[], int[], boolean[], boolean)/*** Added to allow batch-updates** @param batchedParameterStrings* string values used in single statement* @param batchedParameterStreams* stream values used in single statement* @param batchedIsStream* flags for streams used in single statement* @param batchedStreamLengths* lengths of streams to be read.* @param batchedIsNull* flags for parameters that are null** @return the update count** @throws SQLException* if a database error occurs*/protected int executeUpdate(byte[][] batchedParameterStrings, InputStream[] batchedParameterStreams, boolean[] batchedIsStream, int[] batchedStreamLengths,boolean[] batchedIsNull, boolean isReallyBatch) throws SQLException {synchronized (checkClosed().getConnectionMutex()) {MySQLConnection locallyScopedConn = this.connection;if (locallyScopedConn.isReadOnly()) {throw SQLError.createSQLException(Messages.getString("PreparedStatement.34") + Messages.getString("PreparedStatement.35"),SQLError.SQL_STATE_ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT, getExceptionInterceptor());}if ((this.firstCharOfStmt == 'S') && isSelectQuery()) {throw SQLError.createSQLException(Messages.getString("PreparedStatement.37"), "01S03", getExceptionInterceptor());}implicitlyCloseAllOpenResults();ResultSetInternalMethods rs = null;// 转换参数为 Buffer 形式Buffer sendPacket = fillSendPacket(batchedParameterStrings, batchedParameterStreams, batchedIsStream, batchedStreamLengths);String oldCatalog = null;if (!locallyScopedConn.getCatalog().equals(this.currentCatalog)) {oldCatalog = locallyScopedConn.getCatalog();locallyScopedConn.setCatalog(this.currentCatalog);}//// Only apply max_rows to selects//locallyScopedConn.setSessionMaxRows(-1);boolean oldInfoMsgState = false;if (this.retrieveGeneratedKeys) {oldInfoMsgState = locallyScopedConn.isReadInfoMsgEnabled();locallyScopedConn.setReadInfoMsgEnabled(true);}// 执行更新rs = executeInternal(-1, sendPacket, false, false, null, isReallyBatch);if (this.retrieveGeneratedKeys) {locallyScopedConn.setReadInfoMsgEnabled(oldInfoMsgState);rs.setFirstCharOfQuery(this.firstCharOfStmt);}if (oldCatalog != null) {locallyScopedConn.setCatalog(oldCatalog);}this.results = rs;this.updateCount = rs.getUpdateCount();if (containsOnDuplicateKeyUpdateInSQL() && this.compensateForOnDuplicateKeyUpdate) {if (this.updateCount == 2 || this.updateCount == 0) {this.updateCount = 1;}}int truncatedUpdateCount = 0;if (this.updateCount > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {truncatedUpdateCount = Integer.MAX_VALUE;} else {truncatedUpdateCount = (int) this.updateCount;}this.lastInsertId = rs.getUpdateID();return truncatedUpdateCount;}}
4. 如何获取查询结果?
ResultSet 的处理。
// com.mysql.jdbc.StatementImpl#executeQuery/*** Execute a SQL statement that returns a single ResultSet** @param sql* typically a static SQL SELECT statement** @return a ResulSet that contains the data produced by the query** @exception SQLException* if a database access error occurs*/public java.sql.ResultSet executeQuery(String sql) throws SQLException {synchronized (checkClosed().getConnectionMutex()) {MySQLConnection locallyScopedConn = this.connection;this.retrieveGeneratedKeys = false;resetCancelledState();checkNullOrEmptyQuery(sql);boolean doStreaming = createStreamingResultSet();// Adjust net_write_timeout to a higher value if we're streaming result sets. More often than not, someone runs into an issue where they blow// net_write_timeout when using this feature, and if they're willing to hold a result set open for 30 seconds or more, one more round-trip isn't// going to hurt//// This is reset by RowDataDynamic.close().if (doStreaming && this.connection.getNetTimeoutForStreamingResults() > 0) {executeSimpleNonQuery(locallyScopedConn, "SET net_write_timeout=" + this.connection.getNetTimeoutForStreamingResults());}if (this.doEscapeProcessing) {// 避免sql注入Object escapedSqlResult = EscapeProcessor.escapeSQL(sql, locallyScopedConn.serverSupportsConvertFn(), this.connection);if (escapedSqlResult instanceof String) {sql = (String) escapedSqlResult;} else {sql = ((EscapeProcessorResult) escapedSqlResult).escapedSql;}}char firstStatementChar = StringUtils.firstAlphaCharUc(sql, findStartOfStatement(sql));if (sql.charAt(0) == '/') {if (sql.startsWith(PING_MARKER)) {doPingInstead();return this.results;}}checkForDml(sql, firstStatementChar);implicitlyCloseAllOpenResults();CachedResultSetMetaData cachedMetaData = null;if (useServerFetch()) {this.results = createResultSetUsingServerFetch(sql);return this.results;}CancelTask timeoutTask = null;String oldCatalog = null;try {if (locallyScopedConn.getEnableQueryTimeouts() && this.timeoutInMillis != 0 && locallyScopedConn.versionMeetsMinimum(5, 0, 0)) {timeoutTask = new CancelTask(this);locallyScopedConn.getCancelTimer().schedule(timeoutTask, this.timeoutInMillis);}if (!locallyScopedConn.getCatalog().equals(this.currentCatalog)) {oldCatalog = locallyScopedConn.getCatalog();locallyScopedConn.setCatalog(this.currentCatalog);}//// Check if we have cached metadata for this query...//Field[] cachedFields = null;if (locallyScopedConn.getCacheResultSetMetadata()) {cachedMetaData = locallyScopedConn.getCachedMetaData(sql);if (cachedMetaData != null) {cachedFields = cachedMetaData.fields;}}locallyScopedConn.setSessionMaxRows(this.maxRows);statementBegins();this.results = locallyScopedConn.execSQL(this, sql, this.maxRows, null, this.resultSetType, this.resultSetConcurrency, doStreaming,this.currentCatalog, cachedFields);if (timeoutTask != null) {if (timeoutTask.caughtWhileCancelling != null) {throw timeoutTask.caughtWhileCancelling;}timeoutTask.cancel();locallyScopedConn.getCancelTimer().purge();timeoutTask = null;}synchronized (this.cancelTimeoutMutex) {if (this.wasCancelled) {SQLException cause = null;if (this.wasCancelledByTimeout) {cause = new MySQLTimeoutException();} else {cause = new MySQLStatementCancelledException();}resetCancelledState();throw cause;}}} finally {this.statementExecuting.set(false);if (timeoutTask != null) {timeoutTask.cancel();locallyScopedConn.getCancelTimer().purge();}if (oldCatalog != null) {locallyScopedConn.setCatalog(oldCatalog);}}// lastInsertIdthis.lastInsertId = this.results.getUpdateID();if (cachedMetaData != null) {locallyScopedConn.initializeResultsMetadataFromCache(sql, cachedMetaData, this.results);} else {if (this.connection.getCacheResultSetMetadata()) {locallyScopedConn.initializeResultsMetadataFromCache(sql, null /* will be created */, this.results);}}return this.results;}}// 获取结果通过 ResulSet.next()/*** A ResultSet is initially positioned before its first row, the first call* to next makes the first row the current row; the second call makes the* second row the current row, etc.** <p>* If an input stream from the previous row is open, it is implicitly closed. The ResultSet's warning chain is cleared when a new row is read* </p>** @return true if the new current is valid; false if there are no more rows** @exception SQLException* if a database access error occurs*/public boolean next() throws SQLException {synchronized (checkClosed().getConnectionMutex()) {if (this.onInsertRow) {this.onInsertRow = false;}if (this.doingUpdates) {this.doingUpdates = false;}boolean b;// 是否有数据if (!reallyResult()) {throw SQLError.createSQLException(Messages.getString("ResultSet.ResultSet_is_from_UPDATE._No_Data_115"), SQLError.SQL_STATE_GENERAL_ERROR,getExceptionInterceptor());}// 可以在数据不使用前触发 closeOpenStreams()// BufferRow 会处理事务,ByteArrayRow 则会空处理if (this.thisRow != null) {this.thisRow.closeOpenStreams();}if (this.rowData.size() == 0) {b = false;} else {// 通过 RowDataStatic 进行数据迭代this.thisRow = this.rowData.next();// 没有数据了,返回falseif (this.thisRow == null) {b = false;} else {clearWarnings();b = true;}}// 设置位置描述信息setRowPositionValidity();return b;}}// com.mysql.jdbc.RowDataStatic#nextpublic ResultSetRow next() throws SQLException {// 移动到下一个数据点即可this.index++;if (this.index < this.rows.size()) {ResultSetRow row = this.rows.get(this.index);return row.setMetadata(this.metadata);}return null;}
5. 如何关闭数据库连接?
这自然了也对应的数据库驱动实现的东西。
// com.mysql.jdbc.ConnectionImpl#close/*** In some cases, it is desirable to immediately release a Connection's* database and JDBC resources instead of waiting for them to be* automatically released (cant think why off the top of my head) <B>Note:</B>* A Connection is automatically closed when it is garbage collected.* Certain fatal errors also result in a closed connection.** @exception SQLException* if a database access error occurs*/public void close() throws SQLException {synchronized (getConnectionMutex()) {// 关闭前如果有拦截器,先调用拦截器处理if (this.connectionLifecycleInterceptors != null) {new IterateBlock<Extension>(this.connectionLifecycleInterceptors.iterator()) {@Overridevoid forEach(Extension each) throws SQLException {((ConnectionLifecycleInterceptor) each).close();}}.doForAll();}realClose(true, true, false, null);}}// com.mysql.jdbc.ConnectionImpl#realClose/*** Closes connection and frees resources.** @param calledExplicitly* is this being called from close()* @param issueRollback* should a rollback() be issued?* @throws SQLException* if an error occurs*/public void realClose(boolean calledExplicitly, boolean issueRollback, boolean skipLocalTeardown, Throwable reason) throws SQLException {SQLException sqlEx = null;if (this.isClosed()) {return;}this.forceClosedReason = reason;try {if (!skipLocalTeardown) {if (!getAutoCommit() && issueRollback) {try {rollback();} catch (SQLException ex) {sqlEx = ex;}}// 埋点上报reportMetrics();if (getUseUsageAdvisor()) {if (!calledExplicitly) {String message = "Connection implicitly closed by Driver. You should call Connection.close() from your code to free resources more efficiently and avoid resource leaks.";this.eventSink.consumeEvent(new ProfilerEvent(ProfilerEvent.TYPE_WARN, "", this.getCatalog(), this.getId(), -1, -1, System.currentTimeMillis(), 0, Constants.MILLIS_I18N, null, this.pointOfOrigin, message));}long connectionLifeTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - this.connectionCreationTimeMillis;if (connectionLifeTime < 500) {String message = "Connection lifetime of < .5 seconds. You might be un-necessarily creating short-lived connections and should investigate connection pooling to be more efficient.";this.eventSink.consumeEvent(new ProfilerEvent(ProfilerEvent.TYPE_WARN, "", this.getCatalog(), this.getId(), -1, -1, System.currentTimeMillis(), 0, Constants.MILLIS_I18N, null, this.pointOfOrigin, message));}}try {// 关闭所有 statementcloseAllOpenStatements();} catch (SQLException ex) {sqlEx = ex;}if (this.io != null) {try {// 关闭io流,断开与远程的连接this.io.quit();} catch (Exception e) {}}} else {this.io.forceClose();}if (this.statementInterceptors != null) {for (int i = 0; i < this.statementInterceptors.size(); i++) {this.statementInterceptors.get(i).destroy();}}if (this.exceptionInterceptor != null) {this.exceptionInterceptor.destroy();}} finally {this.openStatements = null;if (this.io != null) {this.io.releaseResources();this.io = null;}this.statementInterceptors = null;this.exceptionInterceptor = null;ProfilerEventHandlerFactory.removeInstance(this);synchronized (getConnectionMutex()) {if (this.cancelTimer != null) {this.cancelTimer.cancel();}}this.isClosed = true;}if (sqlEx != null) {throw sqlEx;}}///*** Closes this statement, and frees resources.** @param calledExplicitly* was this called from close()?** @throws SQLException* if an error occurs*/protected void realClose(boolean calledExplicitly, boolean closeOpenResults) throws SQLException {MySQLConnection locallyScopedConn = this.connection;if (locallyScopedConn == null) {return; // already closed}synchronized (locallyScopedConn.getConnectionMutex()) {// additional check in case Statement was closed while current thread was waiting for lockif (this.isClosed) {return;}if (this.useUsageAdvisor) {if (!calledExplicitly) {String message = Messages.getString("Statement.63") + Messages.getString("Statement.64");this.eventSink.consumeEvent(new ProfilerEvent(ProfilerEvent.TYPE_WARN, "", this.currentCatalog, this.connectionId, this.getId(), -1, System.currentTimeMillis(), 0, Constants.MILLIS_I18N, null, this.pointOfOrigin, message));}}if (closeOpenResults) {closeOpenResults = !(this.holdResultsOpenOverClose || this.connection.getDontTrackOpenResources());}if (closeOpenResults) {if (this.results != null) {try {this.results.close();} catch (Exception ex) {}}if (this.generatedKeysResults != null) {try {this.generatedKeysResults.close();} catch (Exception ex) {}}closeAllOpenResults();}if (this.connection != null) {if (!this.connection.getDontTrackOpenResources()) {this.connection.unregisterStatement(this);}}this.isClosed = true;this.results = null;this.generatedKeysResults = null;this.connection = null;this.warningChain = null;this.openResults = null;this.batchedGeneratedKeys = null;this.localInfileInputStream = null;this.pingTarget = null;}}// com.mysql.jdbc.MysqlIO#quit/*** Log-off of the MySQL server and close the socket.** @throws SQLException*/final void quit() throws SQLException {try {// we're not going to read the response, fixes BUG#56979 Improper connection closing logic leads to TIME_WAIT sockets on servertry {if (!this.mysqlConnection.isClosed()) {try {// socket 输入流关闭this.mysqlConnection.shutdownInput();} catch (UnsupportedOperationException ex) {// ignore, some sockets do not support this method}}} catch (IOException ioEx) {this.connection.getLog().logWarn("Caught while disconnecting...", ioEx);}Buffer packet = new Buffer(6);this.packetSequence = -1;this.compressedPacketSequence = -1;packet.writeByte((byte) MysqlDefs.QUIT);// 向远程写入退出标识后send(packet, packet.getPosition());} finally {// 强制关闭本地连接forceClose();}}// com.mysql.jdbc.MysqlIO#forceClose/*** Forcibly closes the underlying socket to MySQL.*/protected final void forceClose() {try {// 将所有socket资源放到 NetworkResources, 统一释放getNetworkResources().forceClose();} finally {this.mysqlConnection = null;this.mysqlInput = null;this.mysqlOutput = null;}}// com.mysql.jdbc.NetworkResources#forceClose/*** Forcibly closes the underlying socket to MySQL.*/protected final void forceClose() {// 依次调用 close() 方法关闭流try {try {if (this.mysqlInput != null) {this.mysqlInput.close();}} finally {if (this.mysqlConnection != null && !this.mysqlConnection.isClosed() && !this.mysqlConnection.isInputShutdown()) {try {this.mysqlConnection.shutdownInput();} catch (UnsupportedOperationException ex) {// ignore, some sockets do not support this method}}}} catch (IOException ioEx) {// we can't do anything constructive about this}try {try {if (this.mysqlOutput != null) {this.mysqlOutput.close();}} finally {if (this.mysqlConnection != null && !this.mysqlConnection.isClosed() && !this.mysqlConnection.isOutputShutdown()) {try {this.mysqlConnection.shutdownOutput();} catch (UnsupportedOperationException ex) {// ignore, some sockets do not support this method}}}} catch (IOException ioEx) {// we can't do anything constructive about this}try {if (this.mysqlConnection != null) {this.mysqlConnection.close();}} catch (IOException ioEx) {// we can't do anything constructive about this}}
6. 其他数据库驱动的注册
sqlite 驱动类: org.sqlite.JDBC,协议前缀: jdbc:sqlite:
public class JDBC implements Driver{public static final String PREFIX = "jdbc:sqlite:";static {try {// 注册驱动DriverManager.registerDriver(new JDBC());}catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 检测是不是sqlite支持的协议,前缀验证即可/*** Validates a URL* @param url* @return true if the URL is valid, false otherwise*/public static boolean isValidURL(String url) {return url != null && url.toLowerCase().startsWith(PREFIX);}/*** @see java.sql.Driver#connect(java.lang.String, java.util.Properties)*/public Connection connect(String url, Properties info) throws SQLException {return createConnection(url, info);}/*** Creates a new database connection to a given URL.* @param url the URL* @param prop the properties* @return a Connection object that represents a connection to the URL* @throws SQLException* @see java.sql.Driver#connect(java.lang.String, java.util.Properties)*/public static Connection createConnection(String url, Properties prop) throws SQLException {if (!isValidURL(url))return null;url = url.trim();return new SQLiteConnection(url, extractAddress(url), prop);}}
Hive 驱动类: org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver,协议前缀: jdbc:hive2://
public class HiveDriver implements Driver {static {try {java.sql.DriverManager.registerDriver(new HiveDriver());} catch (SQLException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}// 验证是否是支持的协议,判断前缀即可/*** Checks whether a given url is in a valid format.** The current uri format is: jdbc:hive://[host[:port]]** jdbc:hive:// - run in embedded mode jdbc:hive://localhost - connect to* localhost default port (10000) jdbc:hive://localhost:5050 - connect to* localhost port 5050** TODO: - write a better regex. - decide on uri format*/public boolean acceptsURL(String url) throws SQLException {return Pattern.matches(Utils.URL_PREFIX + ".*", url);}/** As per JDBC 3.0 Spec (section 9.2)* "If the Driver implementation understands the URL, it will return a Connection object;* otherwise it returns null"*/public Connection connect(String url, Properties info) throws SQLException {return acceptsURL(url) ? new HiveConnection(url, info) : null;}}
DB2 驱动类: com.ibm.db2.jcc.DB2Driver, 协议前缀: jdbc:db2:// ;
Oracle 驱动类: oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver, 协议前缀: jdbc:oracle:thin: ;
7. jdbc 之后
jdbc设计确实是很成功的,定义了使用数据的规范,各厂商只需实现自己的驱动即可接入到java中。
然而,jdbc这样的操作毕竟太过于模板化,如果在每个项目里反复写这些模板代码,那就是太伤了。所以,涌现出大量的orm框架,如: hibernates, mybatis. 将我们从模板代码中解放出来。底层受益出jdbc的设计,高层高效服务于开发人员。

腾讯、阿里、滴滴后台面试题汇总总结 — (含答案)
面试:史上最全多线程面试题 !
最新阿里内推Java后端面试题
JVM难学?那是因为你没认真看完这篇文章

关注作者微信公众号 —《JAVA烂猪皮》
了解更多java后端架构知识以及最新面试宝典

看完本文记得给作者点赞+在看哦~~~大家的支持,是作者源源不断出文的动力
作者:等你归去来
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/yougewe/p/12460685.html
