Pytorch基础 | eval()的用法比较
点击上方“机器学习与生成对抗网络”,关注星标
获取有趣、好玩的前沿干货!
01
1.1 model.train()
1.2 model.eval()
1.3 分析原因
# 定义一个网络class Net(nn.Module):def __init__(self, l1=120, l2=84):super(Net, self).__init__()self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 5)self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, l1)self.fc2 = nn.Linear(l1, l2)self.fc3 = nn.Linear(l2, 10)def forward(self, x):x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))x = x.view(-1, 16 * 5 * 5)x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))x = self.fc3(x)return x# 实例化这个网络Model = Net()# 训练模式使用.train()Model.train(mode=True)# 测试模型使用.eval()Model.eval()
def train(model, optimizer, epoch, train_loader, validation_loader):model.train() # ???????????? 错误的位置for batch_idx, (data, target) in experiment.batch_loop(iterable=train_loader):# model.train() # 正确的位置,保证每一个batch都能进入model.train()的模式data, target = Variable(data), Variable(target)# Inferenceoutput = model(data)loss_t = F.nll_loss(output, target)# The iconic grad-back-step triooptimizer.zero_grad()loss_t.backward()optimizer.step()if batch_idx % args.log_interval == 0:train_loss = loss_t.item()train_accuracy = get_correct_count(output, target) * 100.0 / len(target)experiment.add_metric(LOSS_METRIC, train_loss)experiment.add_metric(ACC_METRIC, train_accuracy)print('Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format(epoch, batch_idx, len(train_loader),100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader), train_loss))with experiment.validation():val_loss, val_accuracy = test(model, validation_loader) # ????????????experiment.add_metric(LOSS_METRIC, val_loss)experiment.add_metric(ACC_METRIC, val_accuracy)
def test(model, test_loader):model.eval()# ...
02
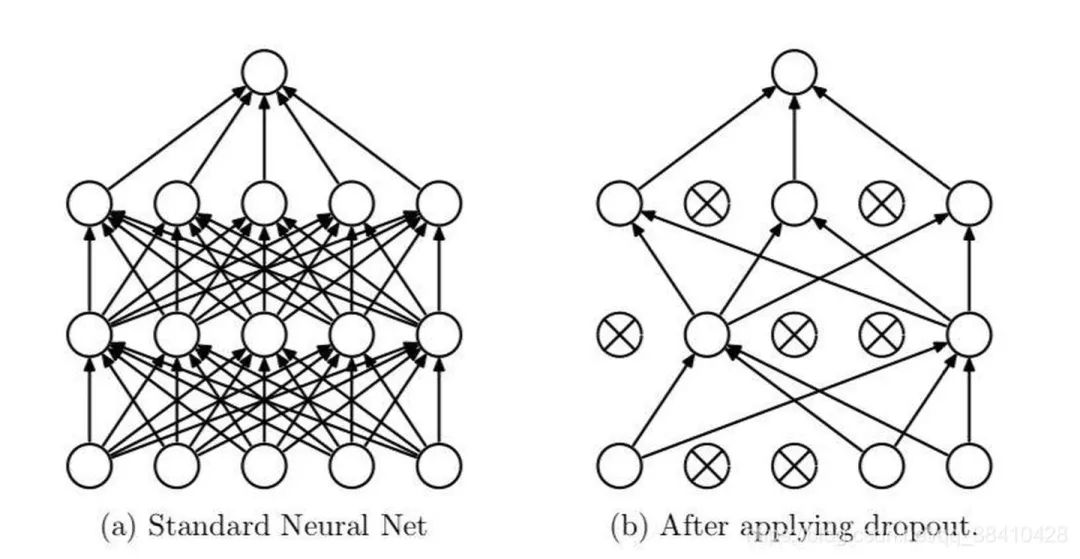
在train模式下,dropout网络层会按照设定的参数p设置保留激活单元的概率(保留概率=p); BN层会继续计算数据的mean和var等参数并更新。
在eval模式下,dropout层会让所有的激活单元都通过,而BN层会停止计算和更新mean和var,直接使用在训练阶段已经学出的mean和var值。
猜您喜欢:
附下载 |《TensorFlow 2.0 深度学习算法实战》
评论
