Node.js + typescript 写一个命令批处理辅助工具
(给全栈前端精选加星标,提升前端技能)
转自:掘金 - 用户名还没想好
https://juejin.cn/post/6930565860348461063
1.背景
工作中遇到这样一些场景:在php混合html的老项目中写css,但是css写着不太好用,然后就想使用预编译语言来处理,或者写上ts。然后问题来了: 每次写完以后都要手动执行一次命令行把文件编译成css文件,然后又要再输入一行命令把css压缩添加前缀;或者把ts编译成js,然后js压缩混淆。
那么有没有办法不用手动输入命令行呢?如果只是为了不手动输入的话,那么可以在vscode上安装compile hero插件,或者在webstorm上开启file watch功能。可惜的是这些工具或功能只能对当前文件做处理,处理编译后的文件又要手动去执行命令,不能连续监听或监听一次执行多个命令,比如webstorm的file watch监听了sass文件变化, 那么它不能再监听css变化去压缩代码,否则会无限编译下去。
那么为什么不使用webpack或者rollup之类的打包工具呢?首先是这些打包工具太重了不够灵活,毕竟原项目没到重构的时候, 要想使用新一点的技术,那么只能写一点手动编译一点了。
好在这些预编译语言都提供cli工具可在控制台输入命令行编译,那么完全可以把它们的命令关联起来,做一个批量执行的工具。其实shell脚本也可以完成这些功能, 但是其一:shell在windows上的话只能在git bash里运行,在cmd控制台上不能运行,需要专门打开一个git bash,少了一点便利性;其二:在windows上不能监听文件变化。那么既然nodejs能够胜任,那么用前端熟悉的js做那是再好不过了。
2.目标
基础功能 通过控制台输入指令启动:获取控制台输入的命令 运行命令 运行多个命令 通过指定配置文件执行 进阶功能 前后生命周期 遍历文件夹查找匹配运行 - url模板替换 - 执行配置中的命令 - 执行配置中的js 监听文件改动 可通过指令显示隐藏log 可通过指令显示隐藏运行时间 npm全局一次安装,随处执行 额外功能 搜索文件或文件夹 - 忽略大小写 - 忽略文件夹 帮助功能 打开文件 - 直接运行文件 - 在打开资源管理器并选中目标文件 - 在cmd控制台打开对应的路径 配置 依次执行多个命令; 生命周期回调 忽略文件夹 匹配规则 - 匹配成功 - 执行相应命令;- 执行相应js;
ok,那么接下来进入正文吧(源码见底部github链接)。
3.基本功能
1.获取控制台输入的命令
首先是获取到控制台输入的命令,这里抽取出来做为一个工具函数。格式为以"="隔开的键值对,键名以"-"开头,值为空时设置该值为true,变量之间用空格隔开。
// util.ts
/**
* 获取命令行的参数
* @param prefix 前缀
*/
export function getParams(prefix = "-"): { [k: string]: string | true } {
return process.argv.slice(2).reduce((obj, it) => {
const sp = it.split("=");
const key = sp[0].replace(prefix, "");
obj[key] = sp[1] || true;
return obj;
}, {} as ReturnType<typeof getParams>);
}
调用
console.log(getParams());
运行结果

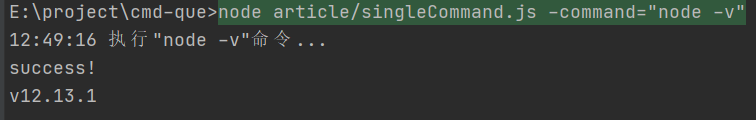
2.运行单个命令
能获取到命令行参数那就好办了,接下来实现执行命令功能。
先实现一个简单的执行命令函数,这要用到child_process模块里的exec函数。
const util = require("util");
const childProcess = require('child_process');
const exec = util.promisify(childProcess.exec); // 这里把exec promisify
需要知道执行状态,所以把它封装一下,不能try catch,出错就直接reject掉,避免后面的命令继续执行。
async function execute(cmd: string): Promise<string> {
console.log('执行"' + cmd + '"命令...');
const {stdout} = await exec(cmd);
console.log('success!');
console.log(stdout);
return stdout;
}
设定命令参数为-command,且必须用”” ““包起来,多个则用“,”隔开
在工具中通过-command/-cmd=启用
调用
const args = getParams();
execute(args.command as string);
运行
3.运行多个命令
现在运行单个命令是没问题的,但是运行多个命令呢?
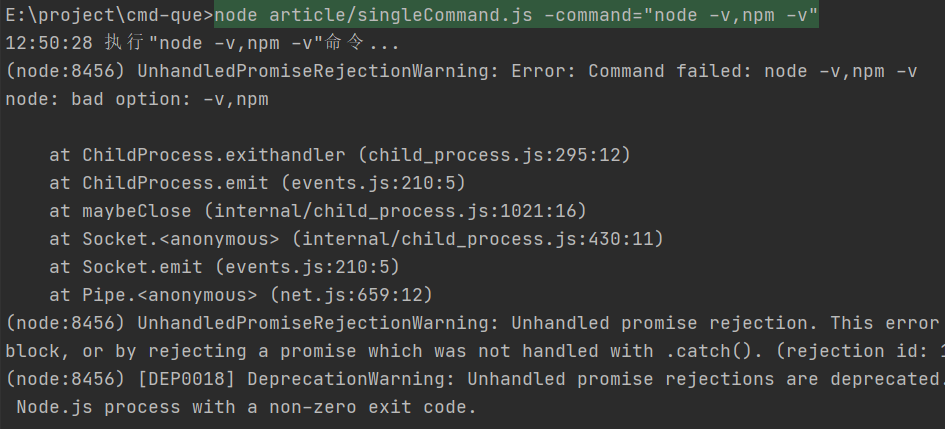
看结果可以发现:结果马上就报错了,把它改成顺序执行
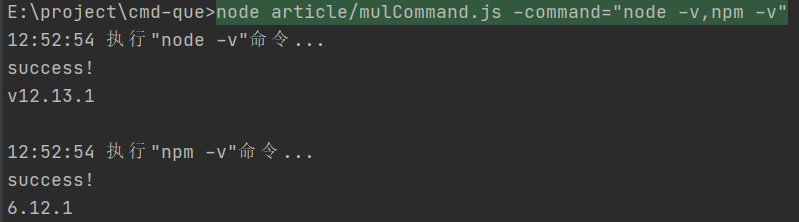
async function mulExec(command: string[]) {
for (const cmd of command) {
await execute(cmd);
}
}
运行
mulExec((args.command as string).split(","));
4.通过指定配置文件运行命令
在工具中通过-config/-c=设置配置的路径
这样通过命令行命令,执行相应的功能就完成了,但是可能会有情况下是要运行很多条命令的,每次都输入一长串命令就不那么好了,所以要添加一个通过配置文件执行的功能。
首先是定义配置文件格式。先来个最简单的
export interface ExecCmdConfig{
command: string[]; // 直接执行命令列表
}
定义一下命令行配置文件变量名为-config
-config= 配置的路径
例如:cmd-que -config="test/cmd.config.js"
配置文件 test/cmd.config.js
module.exports = {
command: [
"stylus E:\\project\\cmd-que\\test\\test.styl",
"stylus test/test1.styl",
]
};
加载配置文件
const Path = require("path");
const configPath = Path.resolve(process.cwd(), args.config);
try {
const config = require(configPath);
mulExec(config.command);
} catch (e) {
console.error("加载配置文件出错", process.cwd(), configPath);
}
运行
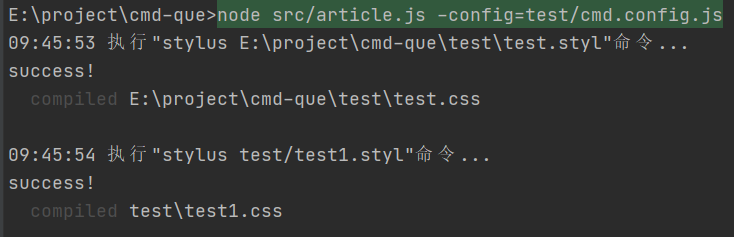
搞定
4.进阶功能
到这里,一个简单的命令批量执行工具代码就已经基本完成了。但是需求总是会变的。
1.前后生命周期
为什么要添加生命周期?因为编译pug文件总是需要在编译完js、css之后,不可能总是需要手动给pug编译命令加上debounce,所以加上结束的回调就很有必要了。
生命周期回调函数类型:
type execFn = (command: string) => Promise<string>;
export interface Config {
beforeStart: (exec: execFn) => Promise<unknown> | unknown;
beforeEnd: (exec: execFn) => Promise<unknown> | unknown;
}
代码
const Path = require("path");
const configPath = Path.resolve(process.cwd(), args.config);
try {
const config = require(configPath);
// beforeStart调用
if (config.beforeStart) await config.beforeStart(execute);
await mulExec(config.command);
// beforeEnd调用
config.beforeEnd && config.beforeEnd(execute);
} catch (e) {
console.error("加载配置文件出错", process.cwd(), configPath);
}
配置文件
cmd.config.js
module.exports = {
beforeStart() {
console.time("time");
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("start");
resolve();
}, 1000);
});
},
beforeEnd() {
console.log("end");
console.timeEnd("time");
},
command: [
// "stylus D:\\project\\cmd-que\\test\\test.styl",
"stylus E:\\project\\cmd-que\\test\\test.styl",
"stylus test/test1.styl",
]
};
运行
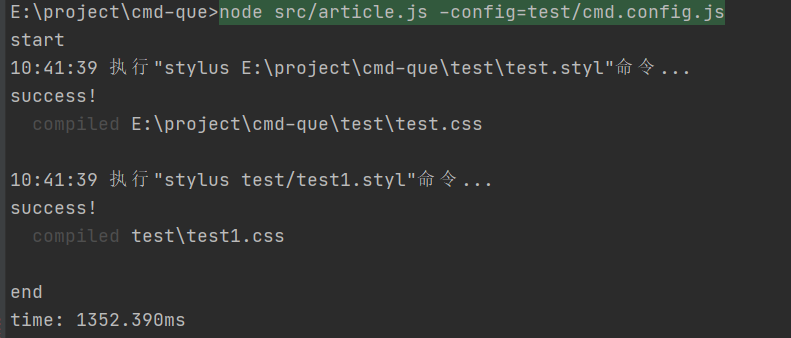
2. 遍历文件夹查找匹配运行
到现在,如果只是执行确定的命令,那么已经完全没问题了,但是有时候需要编译的文件会有很多,像stylus、pug这些可以直接编译整个文件夹的还好, 像ts的话就只能一个文件写一条命令,那也太麻烦了。
所以得增加一个需求:遍历文件夹查找目标文件, 然后执行命令的功能。
写一个遍历文件夹的函数:
// util.ts
const fs = require("fs");
const Path = require("path");
/**
* 遍历文件夹
* @param path
* @param exclude
* @param cb
* @param showLog
*/
export async function forEachDir(
path: string,
exclude: RegExp[] = [],
cb?: (path: string, basename: string, isDir: boolean) => true | void | Promise<true | unknown>,
showLog = false,
) {
showLog && console.log("遍历", path);
try {
const stats = fs.statSync(path);
const isDir = stats.isDirectory();
const basename = Path.basename(path);
const isExclude = () => {
const raw = String.raw`${path}`;
return exclude.some((item) => item.test(raw));
};
if (isDir && isExclude()) return;
const callback = cb || ((path, isDir) => undefined);
const isStop = await callback(path, basename, isDir);
if (!isDir || isStop === true) {
return;
}
const dir = fs.readdirSync(path);
for (const d of dir) {
const p = Path.resolve(path, d);
await forEachDir(p, exclude, cb, showLog);
}
} catch (e) {
showLog && console.log("forEachDir error", path, e);
// 不能抛出异常,否则遍历到System Volume Information文件夹报错会中断遍历
// return Promise.reject(e);
}
}
然后正则验证文件名,如果符合就执行命令
forEachDir("../test", [], (path, basename, isDir) => {
if (isDir) return;
const test = /\.styl$/;
if (!test.test(basename)) return;
return execute("stylus " + path);
});
运行
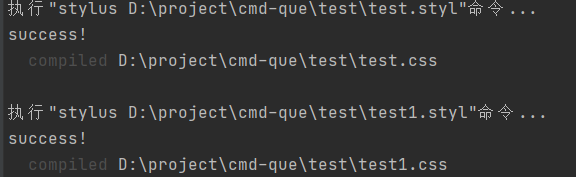
3.通过配置遍历文件夹
url模板替换
看上面的执行情况可以看出,执行的每一条命令路径都是具体的,但是如果我们要遍历文件夹执行命令的话那么这样就不够用了。因为命令都是字符形式的无法根据情况改变,那么有两种方法解决这样的情况:
1.使用字符串模板替换掉对应的字符
2.使用js执行,根据传回的字符来替换掉对应的字符,再执行命令
现在实现一个模板替换的功能(模板来源于webstorm上的file watcher功能,有所增减)
export function executeTemplate(command: string, path = "") {
const cwd = process.cwd();
path = path || cwd;
const basename = Path.basename(path);
const map: { [k: string]: string } = {
"\\$FilePath\\$": path, // 文件完整路径
"\\$FileName\\$": basename, // 文件名
"\\$FileNameWithoutExtension\\$": basename.split(".").slice(0, -1).join("."), // 不含文件后缀的路径
"\\$FileNameWithoutAllExtensions\\$": basename.split(".")[0], // 不含任何文件后缀的路径
"\\$FileDir\\$": Path.dirname(path), // 不含文件名的路径
"\\$Cwd\\$": cwd, // 启动命令所在路径
"\\$SourceFileDir\\$": __dirname, // 代码所在路径
};
const mapKeys = Object.keys(map);
command = mapKeys.reduce((c, k) => c.replace(new RegExp(k, "g"), map[k]), String.raw`${command}`);
return execute(command);
}
配置文件格式最终版如下:
type execFn = (command: string) => Promise<string>;
/**
* @param eventName watch模式下触发的事件名
* @param path 触发改动事件的路径
* @param ext 触发改动事件的文件后缀
* @param exec 执行命令函数
*/
type onFn = (eventName: string, path: string, ext: string, exec: execFn) => Promise<void>
type Rule = {
test: RegExp,
on: onFn,
command: string[];
};
export type RuleOn = Omit<Rule, "command">;
type RuleCmd = Omit<Rule, "on">;
export type Rules = Array<RuleOn | RuleCmd>;
export interface Config {
beforeStart: (exec: execFn) => Promise<unknown> | unknown;
beforeEnd: (exec: execFn) => Promise<unknown> | unknown;
}
export interface ExecCmdConfig extends Config {
command: string[]; // 直接执行命令列表 占位符会被替换
}
export interface WatchConfig extends Config {
exclude?: RegExp[]; // 遍历时忽略的文件夹
include?: string[] | string; // 要遍历/监听的文件夹路径 // 默认为当前文件夹
rules: Rules
}
export function isRuleOn(rule: RuleOn | RuleCmd): rule is RuleOn {
return (rule as RuleOn).on !== undefined;
}
实现
import {getParams, mulExec, forEachDir, executeTemplate} from "../src/utils";
import {isRuleOn, Rules} from "../src/configFileTypes";
(async function () {
// 获取命令行参数
const args = getParams();
// 匹配正则
async function test(eventName: string, path: string, basename: string, rules: Rules = []) {
for (const rule of rules) {
if (!rule.test.test(basename)) continue;
if (isRuleOn(rule)) {
await rule.on(
eventName,
path,
Path.extname(path).substr(1),
(cmd: string) => executeTemplate(cmd, path),
);
} else {
await mulExec(rule.command, path);
}
}
}
// 遍历文件夹
function foreach(
path: string,
exclude: RegExp[] = [],
cb: (path: string, basename: string, isDir: boolean) => true | void | Promise<true | void>,
) {
return forEachDir(path, exclude, (path: string, basename: string, isDir: boolean) => {
return cb(path, basename, isDir);
});
}
const Path = require("path");
const configPath = Path.resolve(process.cwd(), args.config);
try {
const config = require(configPath);
// beforeStart调用
if (config.beforeStart) await config.beforeStart(executeTemplate);
const include = config.include;
// 设置默认路径为命令启动所在路径
const includes = include ? (Array.isArray(include) ? include : [include]) : ["./"];
const rules = config.rules;
for (const path of includes) {
await foreach(path, config.exclude, (path, basename) => {
return test("", path, basename, rules);
});
}
// beforeEnd调用
config.beforeEnd && config.beforeEnd(executeTemplate);
} catch (e) {
console.error("加载配置文件出错", process.cwd(), configPath);
}
})();
执行配置中的命令
配置文件如下:
// test-cmd.config.js
module.exports = {
exclude: [
/node_modules/,
/\.git/,
/\.idea/,
],
rules: [
{
test: /\.styl$/,
command: [
"stylus <$FilePath$> $FileDir$\\$FileNameWithoutAllExtensions$.wxss",
"node -v"
]
}
]
};
运行结果
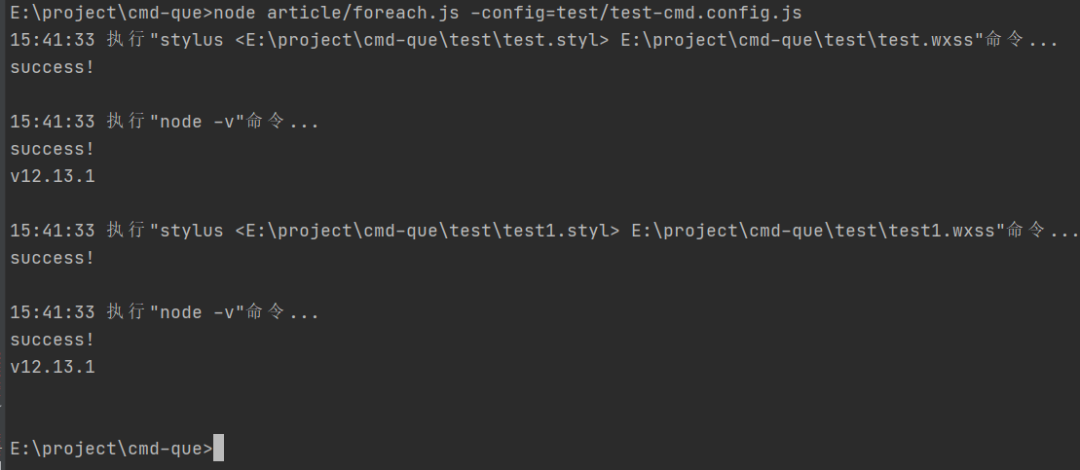
执行配置中的js
module.exports = {
beforeEnd(exec) {
return exec("pug $Cwd$")
},
exclude: [
/node_modules/,
/\.git/,
/\.idea/,
/src/,
/bin/,
],
include: ["./test"],
rules: [
{
test: /\.styl$/,
on: async (eventName, path, ext, exec) => {
if (eventName === "delete") return;
const result = await exec("stylus $FilePath$");
console.log("on", result);
}
},
{
test: /\.ts$/,
on: (eventName, path, ext, exec) => {
if (eventName === "delete") return;
return exec("tsc $FilePath$");
}
},
]
};
运行结果
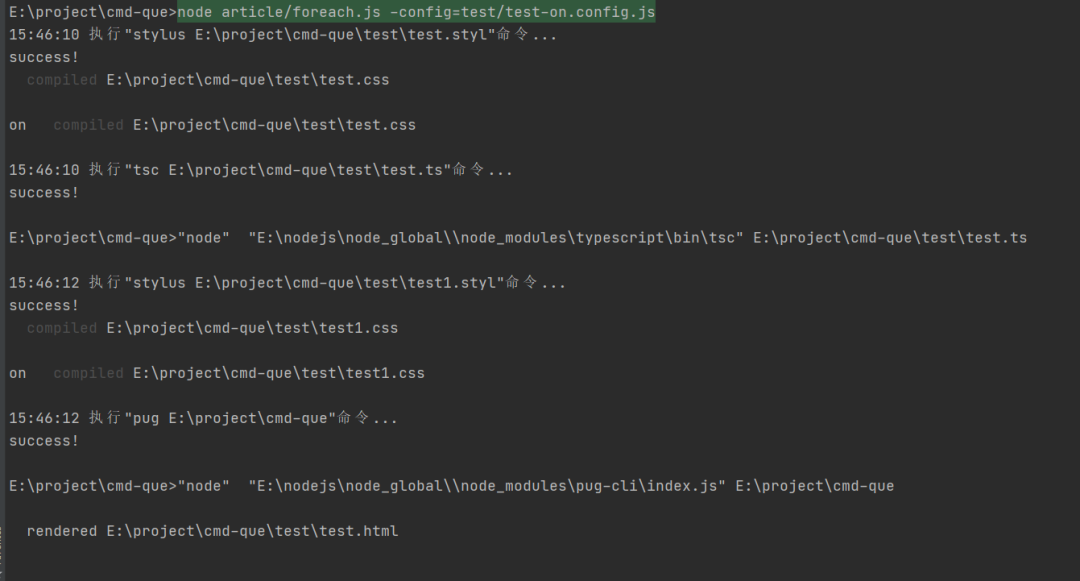
4.监听文件变动
在工具中通过-watch/-w开启 需要与-config搭配使用
监听文件变动nodejs提供了两个函数可供调用:
fs.watch(filename[, options][, listener])
filename <string> | <Buffer> | <URL> options <string> | <Object> - persistent <boolean> 指示如果文件已正被监视,进程是否应继续运行。默认值: true。- recursive <boolean> 指示应该监视所有子目录,还是仅监视当前目录。这适用于监视目录时,并且仅适用于受支持的平台(参见注意事项)。默认值: false。- encoding <string> 指定用于传给监听器的文件名的字符编码。默认值: 'utf8'。 listener <Function> | <undefined> 默认值: undefined。- eventType <string> - filename <string> | <Buffer> 返回: <fs.FSWatcher>
监视 filename 的更改,其中 filename 是文件或目录。
2. fs.watchFile(filename[, options], listener)
filename <string> | <Buffer> | <URL> options <Object>
bigint <boolean> 默认值: false。 persistent <boolean> 默认值: true。 interval <integer> 默认值: 5007。 listener <Function>
current <fs.Stats> previous <fs.Stats> Returns: <fs.StatWatcher>
监视 filename 的更改。每当访问文件时都会调用 listener 回调。
因为watchFile必须监听每个文件,所以选watch函数
文档显示options的recursive参数为true时 监视所有子目录
但是文档又说
仅在 macOS 和 Windows 上支持 recursive 选项。当在不支持该选项的平台上使用该选项时,则会抛出 ERR_FEATURE_UNAVAILABLE_ON_PLATFORM 异常。
在 Windows 上,如果监视的目录被移动或重命名,则不会触发任何事件。当监视的目录被删除时,则报告 EPERM 错误。
所以我这里在判断子文件是否文件夹后,需要手动添加监听子文件夹
import {getParams, mulExec, forEachDir, executeTemplate, debouncePromise} from "../src/utils";
import {isRuleOn, RuleOn, Rules, WatchConfig} from "../src/configFileTypes";
(async function () {
// 获取命令行参数
const args = getParams();
/**
* @param config 配置
* @param watchedList watch列表用于遍历文件夹时判断是否已经watch过的文件夹
*/
async function watch(config: WatchConfig, watchedList: string[]) {
if (!config.rules) throw new TypeError("rules required");
// 编辑器修改保存时会触发多次change事件
config.rules.forEach(item => {
// 可能会有机器会慢一点 如果有再把间隔调大一点
(item as RuleOn).on = debouncePromise(isRuleOn(item) ? item.on : (e, p) => {
return mulExec(item.command, p);
}, 1);
});
const FS = require("fs");
const HandleForeach = (path: string) => {
if (watchedList.indexOf(path) > -1) return;
console.log("对" + path + "文件夹添加监听\n");
const watchCB = async (eventType: string, filename: string) => {
if (!filename) throw new Error("文件名未提供");
const filePath = Path.resolve(path, filename);
console.log(eventType, filePath);
// 判断是否需要监听的文件类型
try {
const exist = FS.existsSync(filePath);
await test(exist ? eventType : "delete", filePath, filename);
if (!exist) {
console.log(filePath, "已删除!");
// 删除过的需要在watchArr里面去掉,否则重新建一个相同名称的目录不会添加监听
const index = watchedList.indexOf(filePath);
if (index > -1) {
watchedList.splice(index, 1);
}
return;
}
// 如果是新增的目录,必须添加监听否则不能监听到该目录的文件变化
const stat = FS.statSync(filePath);
if (stat.isDirectory()) {
foreach(filePath, config.exclude, HandleForeach);
}
} catch (e) {
console.log("watch try catch", e, filePath);
}
};
const watcher = FS.watch(path, null, watchCB);
watchedList.push(path); // 记录已watch的
watcher.addListener("error", function (e: any) {
console.log("addListener error", e);
});
};
const include = config.include;
const includes = include ? (Array.isArray(include) ? include : [include]) : ["./"];
for (const path of includes) {
await foreach(path, config.exclude, (path, basename, isDir) => {
if (isDir) HandleForeach(path);
});
}
}
// 匹配正则
async function test(eventName: string, path: string, basename: string, rules: Rules = []) {
for (const rule of rules) {
if (!rule.test.test(basename)) continue;
if (isRuleOn(rule)) {
await rule.on(
eventName,
path,
Path.extname(path).substr(1),
(cmd: string) => executeTemplate(cmd, path),
);
} else {
await mulExec(rule.command, path);
}
}
}
// 遍历文件夹
function foreach(
path: string,
exclude: RegExp[] = [],
cb: (path: string, basename: string, isDir: boolean) => true | void | Promise<true | void>,
) {
return forEachDir(path, exclude, (path: string, basename: string, isDir: boolean) => {
return cb(path, basename, isDir);
});
}
const Path = require("path");
const configPath = Path.resolve(process.cwd(), args.config);
try {
const config = require(configPath);
// beforeStart调用
if (config.beforeStart) await config.beforeStart(executeTemplate);
await watch(config, []);
// beforeEnd调用
config.beforeEnd && config.beforeEnd(executeTemplate);
} catch (e) {
console.error("加载配置文件出错", process.cwd(), configPath);
}
})();
配置文件
// watch-cmd.config.js
module.exports = {
beforeEnd() {
console.log("end")
},
rules: [
{
test: /\.styl$/,
command: [
"stylus $FilePath$",
"node -v"
]
},
],
exclude: [
/node_modules/,
/\.git/,
/\.idea/,
/src/,
/bin/,
],
include: ["./test"],
};
运行
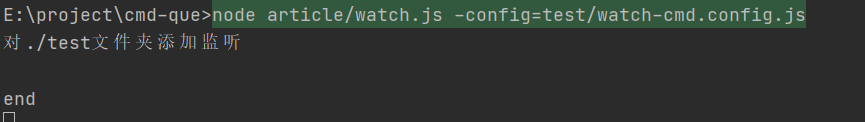
当我改动文件时
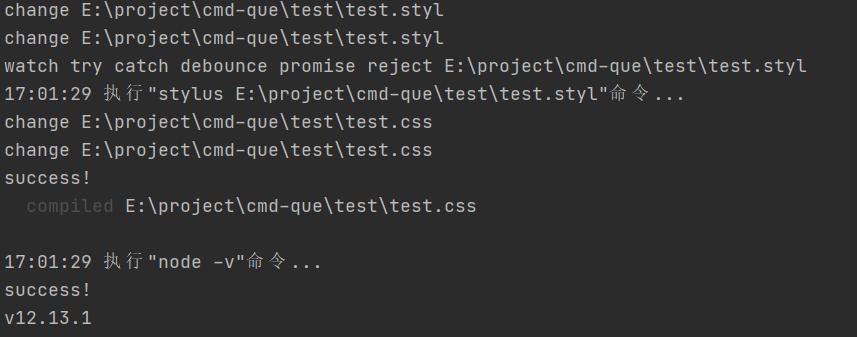
从结果可以看出,文件watch回调触发了多次。其实我们不用编辑器改动文件的话,回调只会触发一次,这是编辑器的问题。
那么细心的读者可能会想到为什么命令不会执行多次呢?
是因为我用debouncePromise把rule.on包裹了一层。
普通的防抖函数是这样的
export function debounce<CB extends (...args: any[]) => void>(callback: CB, delay: number): CB {
let timer: any = null;
return function (...args: any[]) {
if (timer) {
clearTimeout(timer);
timer = null;
}
timer = setTimeout(() => {
timer = null;
callback.apply(this, args);
}, delay);
} as CB;
}
但是这种没办法处理原函数返回promise的情况,也没办法await
所以要改造一下,让它可以处理promise:每次在间隔内执行的时候,都把上一次的promise reject掉
export function debouncePromise<T, CB extends (...args: any[]) => Promise<T>>(callback: CB, delay: number): CB {
let timer: any = null;
let rej: Function;
return function (this: unknown, ...args: any[]) {
return new Promise<T>((resolve, reject) => {
if (timer) {
clearTimeout(timer);
timer = null;
rej("debounce promise reject");
}
rej = reject;
timer = setTimeout(async () => {
timer = null;
const result = await callback.apply(this, args);
resolve(result);
}, delay);
});
} as CB;
}
加到逻辑上
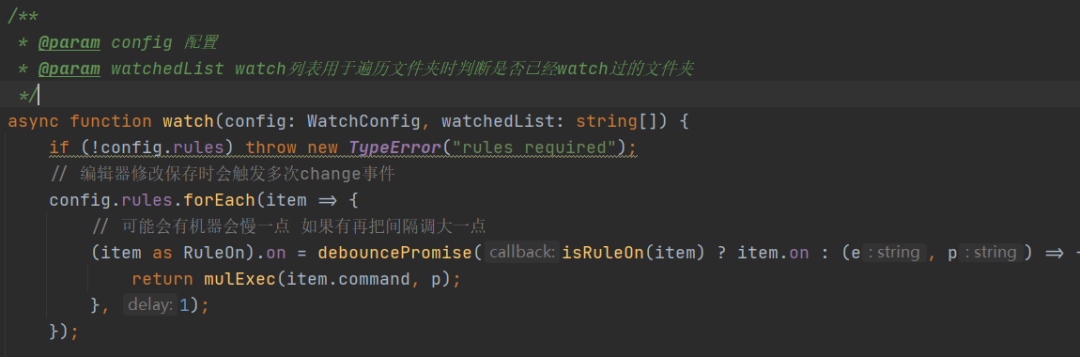
为什么不加到watch的回调上,则是因为部分浏览器最后保存的是目标文件的副本,如果加到watch回调上的话,那就会漏掉目标文件变动了
这样就虽然还是会触发多次监听回调,但只执行最后一次回调。
5.额外功能
1.帮助功能
在工具中通过-help/-h启动
console.log(`
-config/-c= 配置的路径
-help/-h 帮助
-search/-s= 搜索文件或文件夹
-search-flag/-sf= 搜索文件或文件夹 /\\w+/flag
-search-exclude/-se= 搜索文件或文件夹 忽略文件夹 多个用逗号(,)隔开
-open/-o= 打开资源管理器并选中文件或文件夹
-open-type/-ot= 打开资源管理器并选中文件或文件夹
-watch/-w 监听文件改变 与-config搭配使用
-log 遍历文件夹时是否显示遍历log
-time/t 显示执行代码所花费的时间
-command/-cmd= 通过命令行执行命令 多个则用逗号(,)隔开 必须要用引号引起来
`);
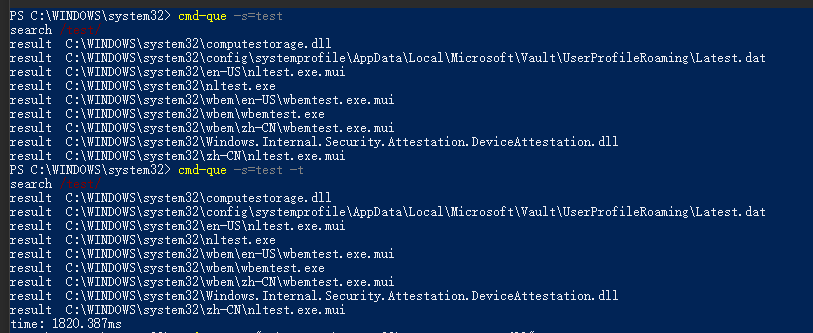
2.搜索文件或文件夹
在工具中通过-search/-s启动
其实这功能和我这工具相关性不大,为什么会加上这样的功能呢?是因为windows上搜索文件,经常目标文件存在都搜索不到,而且这工具遍历文件夹已经很方便了,所以就把搜索文件功能集成到这个工具上了
实现
import {getParams, forEachDir} from "../src/utils";
const args = getParams()
const search = args.search;
const flag = args["search-flag"];
const se = args["search-exclude"];
if (search === true || search === undefined || flag === true || se === true) {
throw new TypeError();
}
const reg = new RegExp(search, flag);
console.log("search", reg);
const exclude = se?.split(",").filter(i => i).map(i => new RegExp(i));
forEachDir("./", exclude, (path, basename) => {
if (reg.test(basename)) console.log("result ", path);
});
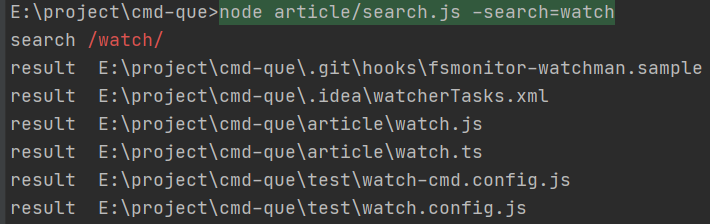
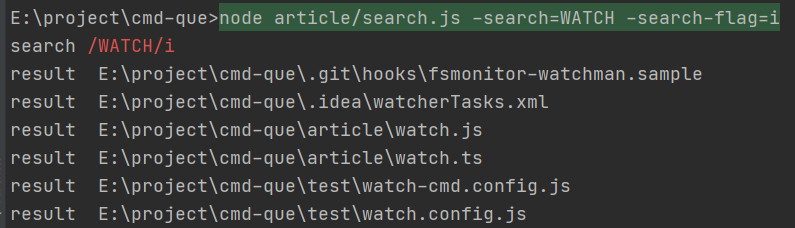
忽略大小写
在工具中-search-flag/-sf=
未忽略大小写
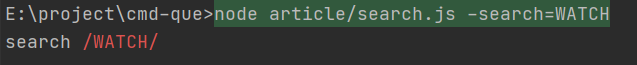
忽略大小写
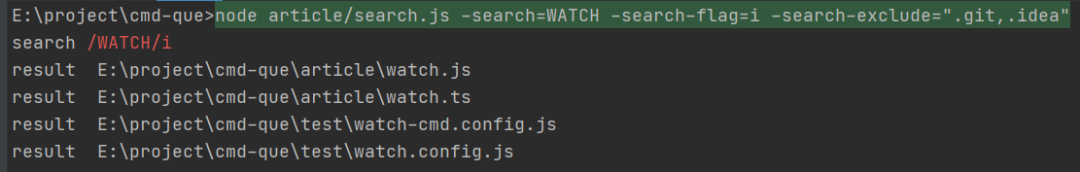
忽略文件夹
在工具中-search-exclude/-se=
3.打开文件功能
搜索到文件之后,自然是要打开文件了(只支持windows)
工具中通过-open/o=打开对应的文件
代码
import {getParams} from "../src/utils";
const Path = require("path")
enum OpenTypes {
select = "select",
cmd = "cmd",
run = "run",
}
type ExecParams = [string, string[]];
const args = getParams();
const open = args.open;
const path = Path.resolve(process.cwd(), open === true ? "./" : open);
const stat = require("fs").statSync(path);
const isDir = stat.isDirectory();
const ot = args["open-type"];
const type: string = !ot || ot === true ? OpenTypes.select : ot;
const spawnSync = require('child_process').spawnSync;
const match: { [k in OpenTypes]: ExecParams } = {
// 运行一次就会打开一个资源管理器,不能只打开一个相同的
[OpenTypes.select]: ["explorer", [`/select,"${path}"`]],
[OpenTypes.run]: ['start', [path]],
[OpenTypes.cmd]: ["start", ["cmd", "/k", `"cd ${isDir ? path : Path.dirname(path)}"`]],
};
const exec = ([command, path]: ExecParams) => spawnSync(command, path, {shell: true});
console.log(path);
exec(match[type as OpenTypes] || match[OpenTypes.select]);
打开资源管理器并且选中文件
命令

结果
在cmd中打开
命令

结果
用默认app打开
命令

结果
上传到npm
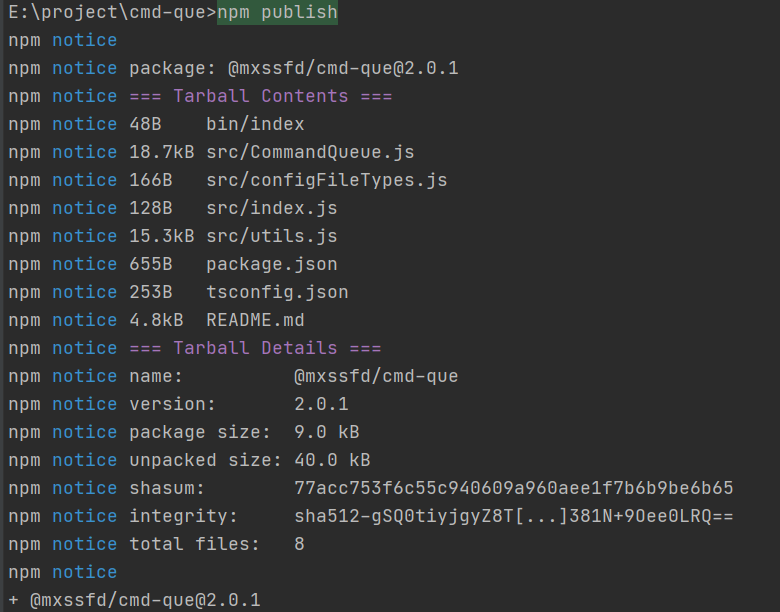
接下来就把它发布到npm上,到时候全局安装后就可以在任意路径上运行了
发布
安装
npm i -g @mxssfd/cmd-que
测试
配合webstorm file watcher自动编译less并postcss编译
首先安装cmd-que
开启file watcher
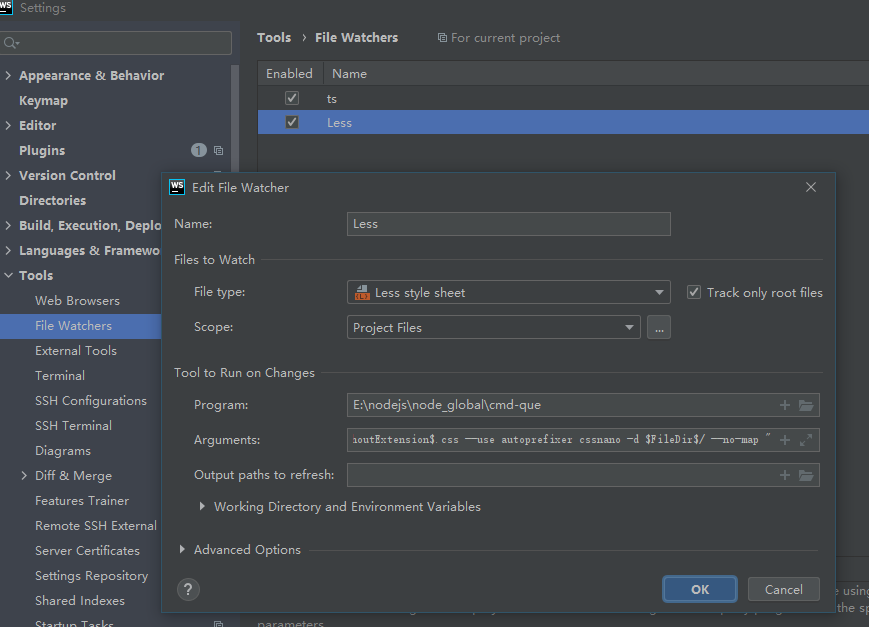
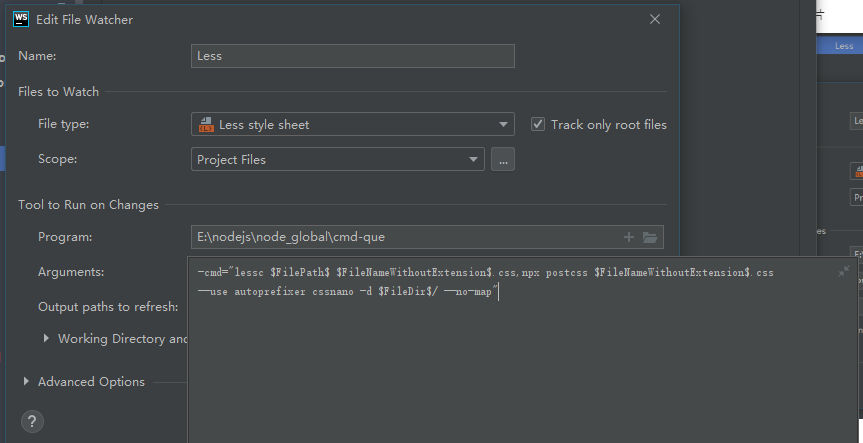
新建less文件

修改less文件
结果

这样配置好以后,每次修改文件就不用手动开启命令而是会自动执行编译命令了
最后
写到这里,功能总算完成了,其实再叫做命令队列执行工具已经有点超纲了,不过常用功能还是用于执行命令的
git地址
https://github.com/mengxinssfd/cmd-que
