项目实践 | 从零开始边缘部署轻量化人脸检测模型——EAIDK310部署篇



继续上一章的话题,前面我们主要聊到关于人脸检测模型UltraFace的训练任务,本文将和大家讨论在开发板上如何部署UltraFace模型,并进行实时视频人脸检测,或者图片流人脸检测。
1Tengine简介
Tengine 由 OPEN AI LAB 主导开发,该项目实现了深度学习神经网络模型在嵌入式设备上的快速、高效部署需求。为实现在众多 AIoT 应用中的跨平台部署,本项目基于原有 Tengine 项目使用 C 语言进行重构,针对嵌入式设备资源有限的特点进行了深度框架裁剪。同时采用了完全分离的前后端设计,有利于 CPU、GPU、NPU 等异构计算单元的快速移植和部署,同时降低评估和迁移成本。
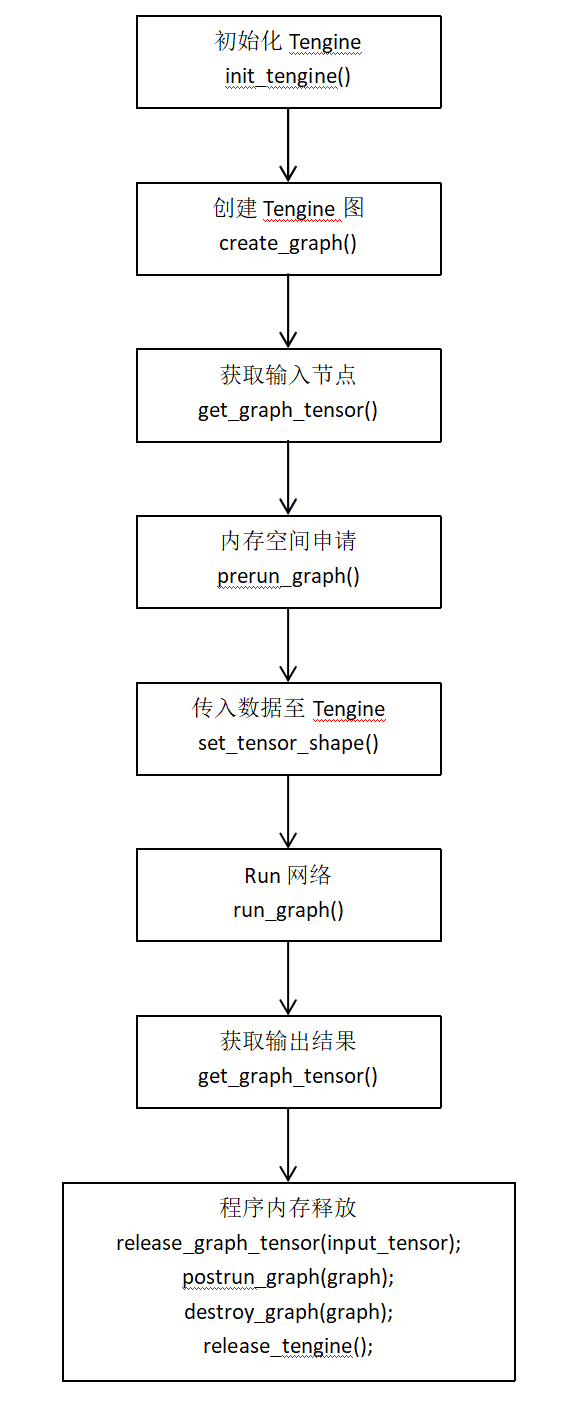
Tengine推理流程
依照顺序调用Tengine核心API如下:
2模块实现
1 模型转换
第1步:转换到onnx模型
model_path = "models/pretrained/version-RFB-320.pth"
net = create_Mb_Tiny_RFB_fd(len(class_names), is_test=True)
net.load(model_path)
net.eval()
net.to("cuda")
model_name = model_path.split("/")[-1].split(".")[0]
model_path = f"models/onnx/{model_name}.onnx"
dummy_input = torch.randn(1, 3, 240, 320).to("cuda")
torch.onnx.export(net, dummy_input, model_path, verbose=False, input_names=['input'], output_names=['scores', 'boxes'])
第2步:编译Tengine模型转换工具
依赖库安装
sudo apt install libprotobuf-dev protobuf-compiler
源码编译
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
make -j`nproc` && make install
编译完成后,生成的可行性文件tm_convert_tool存放在 ./build/install/bin/ 目录下。
第3步:转换onnx模型为tmfile模型
./tm_convert_tool -m xxx.onnx -o xxx.tmfile
-m 为*.caffemodel, *.params, *.weight, *.pb, *.onnx, *.tflite等模型;
-o 为output fp32 tmfile
2 NMS计算
伪代码:
1 将各组box按照score降序排列;
2 从score最大值开始,置为当前box,保存idex,然后依次遍历后面的box,计算与当前box的IOU值,若大于阈值,则抑制,不会输出;
3 完成一轮遍历后,继续选择下一个非抑制的box作为当前box,重复步骤2;
4 返回没有被抑制的index即符合条件的box;
python版本
def NMS(dects,threshhold):
"""
detcs:二维数组(n_samples,5)
5列:x1,y1,x2,y2,score
threshhold: IOU阈值
"""
x1=dects[:,0]
y1=dects[:,1]
x2=dects[:,2]
y2=dects[:,3]
score=dects[:,4]
ndects=dects.shape[0]#box的数量
area=(x2-x1+1)*(y2-y1+1)
order=score.argsort()[::-1] #score从大到小排列的indexs,一维数组
keep=[] #保存符合条件的index
suppressed=np.array([0]*ndects) #初始化为0,若大于threshhold,变为1,表示被抑制
for _i in range(ndects):
i=order[_i] #从得分最高的开始遍历
if suppressed[i]==1:
continue
keep.append(i)
for _j in range(i+1,ndects):
j=order[_j]
if suppressed[j]==1: #若已经被抑制,跳过
continue
xx1=np.max(x1[i],x1[j])#求两个box的交集面积interface
yy1=np.max(y1[i],y1j])
xx2=np.min(x2[i],x2[j])
yy2=np.min(y2[i],y2[j])
w=np.max(0,xx2-xx1+1)
h=np.max(0,yy2-yy1+1)
interface=w*h
overlap=interface/(area[i]+area[j]-interface) #计算IOU(交/并)
if overlap>=threshhold:#IOU若大于阈值,则抑制
suppressed[j]=1
return keep
C++版本
void UltraFace::nms(std::vector<FaceInfo> &input, std::vector<FaceInfo> &output, int type) {
//根据score对候选框进行 sort 排序操作
std::sort(input.begin(), input.end(), [](const FaceInfo &a, const FaceInfo &b) { return a.score > b.score; });
int box_num = input.size();
std::vector<int> merged(box_num, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < box_num; i++) {
if (merged[i])
continue;
std::vector<FaceInfo> buf;
buf.push_back(input[i]);
merged[i] = 1;
float h0 = input[i].y2 - input[i].y1 + 1;
float w0 = input[i].x2 - input[i].x1 + 1;
float area0 = h0 * w0;
for (int j = i + 1; j < box_num; j++) {
if (merged[j])
continue;
//确立每个候选框的坐标以及宽高
float inner_x0 = input[i].x1 > input[j].x1 ? input[i].x1 : input[j].x1;
float inner_y0 = input[i].y1 > input[j].y1 ? input[i].y1 : input[j].y1;
float inner_x1 = input[i].x2 < input[j].x2 ? input[i].x2 : input[j].x2;
float inner_y1 = input[i].y2 < input[j].y2 ? input[i].y2 : input[j].y2;
float inner_h = inner_y1 - inner_y0 + 1;
float inner_w = inner_x1 - inner_x0 + 1;
if (inner_h <= 0 || inner_w <= 0)
continue;
float inner_area = inner_h * inner_w;
float h1 = input[j].y2 - input[j].y1 + 1;
float w1 = input[j].x2 - input[j].x1 + 1;
float area1 = h1 * w1;
float score;
//计算IOU
score = inner_area / (area0 + area1 - inner_area);
//根据阈值进行极大值抑制的筛选
if (score > iou_threshold) {
merged[j] = 1;
buf.push_back(input[j]);
}
}
}
}
2.3 获取候选框
//获取候选框
void UltraFace::generateBBox(std::vector<FaceInfo> &bbox_collection, tensor_t scores, tensor_t boxes) {
float* scores_blob = ( float* )get_tensor_buffer(scores);
float* boxes_blob = ( float* )get_tensor_buffer(boxes);
for (int i = 0; i < num_anchors; i++) {
if (scores_blob[i * 2 + 1] > score_threshold) {
FaceInfo rects;
//确定坐标中心以及box的宽高
float x_center = boxes_blob[i * 4] * center_variance * priors[i][2] + priors[i][0];
float y_center = boxes_blob[i * 4 + 1] * center_variance * priors[i][3] + priors[i][1];
float w = exp(boxes_blob[i * 4 + 2] * size_variance) * priors[i][2];
float h = exp(boxes_blob[i * 4 + 3] * size_variance) * priors[i][3];
//截取坐标结果
rects.x1 = clip(x_center - w / 2.0, 1) * image_w;
rects.y1 = clip(y_center - h / 2.0, 1) * image_h;
rects.x2 = clip(x_center + w / 2.0, 1) * image_w;
rects.y2 = clip(y_center + h / 2.0, 1) * image_h;
rects.score = clip(scores_blob[i * 2 + 1], 1);
bbox_collection.push_back(rects);
}
}
}
2.4 模型检测函数
//模型检测函数
int UltraFace::detect(cv::Mat &raw_image, std::vector<FaceInfo> &face_list) {
if (raw_image.empty()) {
std::cout << "image is empty ,please check!" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
image_h = raw_image.rows;
image_w = raw_image.cols;
int img_size = in_w * in_h * 3;
float* input_data = ( float* )malloc(img_size * sizeof(float));
// 获取来自opencv读取的图片或者视频数据,并返回一个适应模型输入的结果
get_input_data_cv(raw_image, input_data, in_w, in_h, mean_vals, norm_vals, 0);
if (set_tensor_buffer(input_tensor, input_data, (in_w * in_h * 3) * 4) < 0)
{
printf("Set input tensor buffer failed\n");
return -1;
}
//开始计时⏲
auto start = chrono::steady_clock::now();
// 6、Run网络
if (run_graph(graph, 1) < 0)
{
printf("Run graph failed\n");
return -1;
}
// 获取输出结果
string scores = "scores";
string boxes = "boxes";
//7.1、获取分类得分结果
tensor_t tensor_scores = get_graph_tensor(graph, scores.c_str());
//7.2、获取检测框坐标结果
tensor_t tensor_boxes = get_graph_tensor(graph, boxes.c_str());
std::vector<FaceInfo> bbox_collection;
//结束计时,然后计算推理时间
auto end = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> elapsed = end - start;
cout << "inference time:" << elapsed.count() << " s" << endl;
//后处理操作,主要是获取BBox以及NMS操作
generateBBox(bbox_collection, tensor_scores, tensor_boxes);
nms(bbox_collection, face_list);
free(input_data);
return 0;
}
2.5 主函数
#include "UltraFace.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string tengine_path = "/home/chaucer/Tengine_Tutorial/2_FaceDetector/models/version-RFB-320_simplified.tmfile";
UltraFace ultraface(tengine_path, 320, 240, 4, 0.65); // config model input
cv::Mat frame;
//cv::VideoCapture capture(0);
cv::VideoCapture capture("/home/chaucer/face_detect/test_1.mp4");
//cv::Mat frame = cv::imread(image_file);
while(1)
{
capture >> frame;
auto start = chrono::steady_clock::now();
vector<FaceInfo> face_info;
ultraface.detect(frame, face_info);
cout << "face_info " << face_info.size() << endl;
for (auto face : face_info) {
cv::Point pt1(face.x1, face.y1);
cv::Point pt2(face.x2, face.y2);
cv::rectangle(frame, pt1, pt2, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2);
}
auto end = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> elapsed = end - start;
cout << "all time: " << elapsed.count() << " s" << endl;
cv::imshow("UltraFace", frame);
cv::waitKey(1);
string result_name = "result" + to_string(2) + ".jpg";
cv::imwrite(result_name, frame);
}
return 0;
}
3输出结果
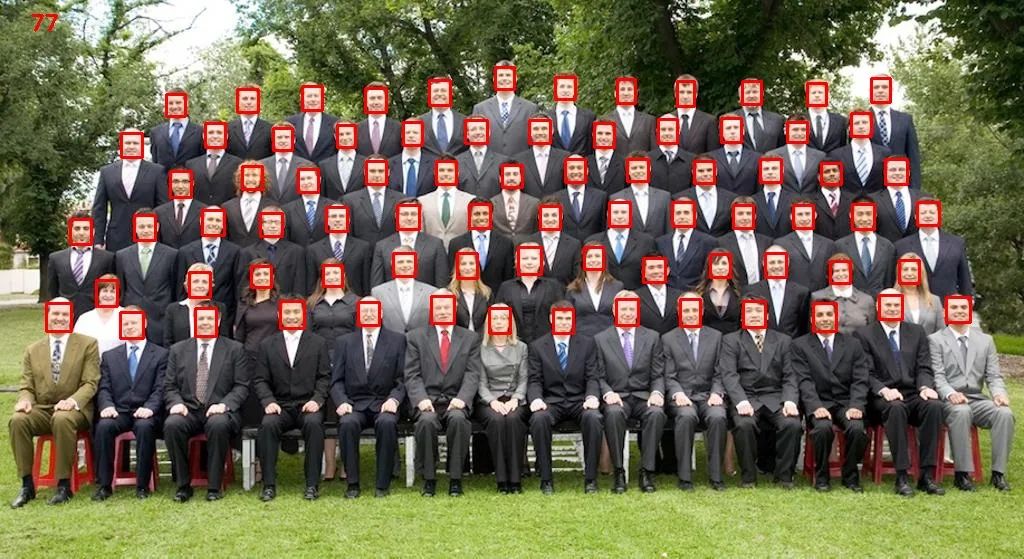
3.1 图片检测结果

3.2 视频检测结果
4参考
[1].https://github.com/Linzaer/Ultra-Light-Fast-Generic-Face-Detector-1MB
[2].https://github.com/OAID/Tengine
[3].https://github.com/jiangzhongbo/Tengine_Tutorial
5推荐阅读

Google新作 | 详细解读 Transformer那些有趣的特性(建议全文背诵)

极品Trick | 在ResNet与Transformer均适用的Skip Connection解读

Transformer又一城 | Swin-Unet:首个纯Transformer的医学图像分割模型解读
轻量化卷积:TBC,不仅仅是参数共享组卷积,更具备跨通道建模
最快ViT | FaceBook提出LeViT,0.077ms的单图处理速度却拥有ResNet50的精度(文末附论文与源码)
本文论文原文获取方式,扫描下方二维码
回复【UltraFaceC】即可获取项目代码
长按扫描下方二维码添加小助手并加入交流群,群里博士大佬云集,每日讨论话题有目标检测、语义分割、超分辨率、模型部署、数学基础知识、算法面试题分享的等等内容,当然也少不了搬砖人的扯犊子
长按扫描下方二维码添加小助手。
可以一起讨论遇到的问题
声明:转载请说明出处
扫描下方二维码关注【集智书童】公众号,获取更多实践项目源码和论文解读,非常期待你我的相遇,让我们以梦为马,砥砺前行!

