API 网关 gRPC-Gateway V2 初探
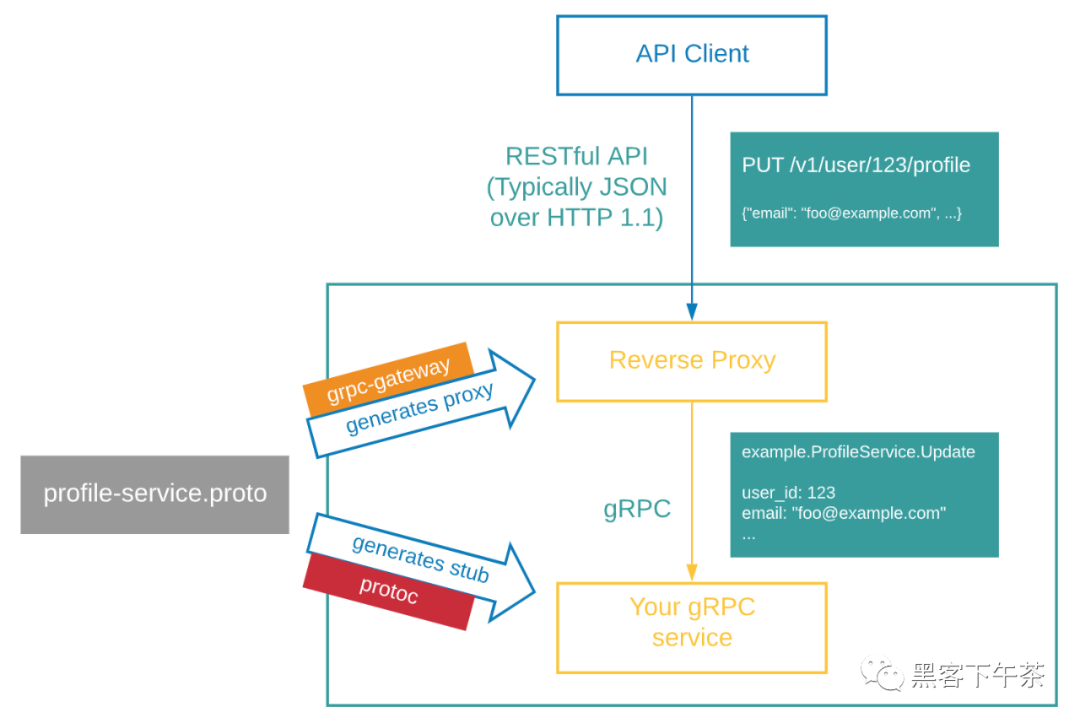
gRPC-Gateway 简介
我们都知道 gRPC 并不是万能的工具。在某些情况下,我们仍然想提供传统的 HTTP/JSON API。原因可能从保持向后兼容性到支持编程语言或 gRPC 无法很好地支持的客户端。但是仅仅为了公开 HTTP/JSON API 而编写另一个服务是一项非常耗时且乏味的任务。
那么,有什么方法可以只编写一次代码,却可以同时在 gRPC 和 HTTP/JSON 中提供 API?
答案是 Yes。
gRPC-Gateway 是 Google protocol buffers compiler protoc 的插件。它读取 protobuf service 定义并生成反向代理服务器( reverse-proxy server) ,该服务器将 RESTful HTTP API 转换为 gRPC。该服务器是根据服务定义中的 google.api.http 批注(annotations)生成的。
这有助于你同时提供 gRPC 和 HTTP/JSON 格式的 API。
开始之前
在开始编码之前,我们必须安装一些工具。
在示例中,我们将使用 Go gRPC Server,因此请首先从 https://golang.org/dl/ 安装 Go。
安装 Go 之后,请使用 go get 下载以下软件包:
$ go get github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/v2/protoc-gen-grpc-gateway
$ go get google.golang.org/protobuf/cmd/protoc-gen-go
$ go get google.golang.org/grpc/cmd/protoc-gen-go-grpc
这将安装我们生成存根所需的协议生成器插件。确保将 $GOPATH/bin 添加到 $PATH 中,以便通过 go get 安装的可执行文件在 $PATH 中可用。
我们将在本教程的新模块中进行工作,因此,请立即在您选择的文件夹中创建该模块:
创建 go.mod 文件
使用 go mod init 命令启动你的 module 以创建 go.mod 文件。
运行 go mod init 命令,给它代码所在 module 的路径。在这里,使用 github.com/myuser/myrepo 作为 module 路径—在生产代码中,这将是可以从其中下载 module 的 URL。
$ go mod init github.com/myuser/myrepo
go: creating new go.mod: module github.com/myuser/myrepo
go mod init 命令创建一个 go.mod 文件,该文件将您的代码标识为可以从其他代码中使用的 module。您刚创建的文件仅包含模块名称和代码支持的 Go 版本。但是,当您添加依赖项(即其他模块的软件包)时,go.mod 文件将列出要使用的特定 module 版本。这样可以使构建具有可复制性,并使您可以直接控制要使用的 module 版本。
用 gRPC 创建一个简单的 hello world
为了了解 gRPC-Gateway,我们首先要制作一个 hello world gRPC 服务。
使用 protocol buffers 定义 gRPC service
在创建 gRPC 服务之前,我们应该创建一个 proto 文件来定义我们需要的东西,这里我们在 proto/helloworld/ 目录下创建了一个名为 hello_world.proto 的文件。
gRPC service 使用 Google Protocol Buffers 定义的。这里定义如下:
syntax = "proto3";
package helloworld;
// The greeting service definition
service Greeter {
// Sends a greeting
rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply) {}
}
// The request message containing the user's name
message HelloRequest {
string name = 1;
}
// The response message containing the greetings
message HelloReply {
string message = 1;
}
使用 buf 生成 stubs
Buf 是一个工具,它提供了各种 protobuf 实用程序,如 linting, breaking change detection 和 generation。请在 https://docs.buf.build/installation/ 上找到安装说明。
它是通过 buf.yaml 文件配置的,应将其检入你存储库的根目录中。如果存在,Buf 将自动读取此文件。也可以通过命令行标志 --config 提供配置,该标志接受 .json 或 .yaml 文件的路径,或是直接 JSON 或 YAML 数据。
所有使用本地 .proto 文件作为输入的 Buf 操作都依赖于有效的构建配置。这个配置告诉 Buf 在哪里搜索 .proto 文件,以及如何处理导入。与 protoc(所有 .proto 文件都是在命令行上手动指定的)不同,buf 的操作方式是递归地发现配置下的所有 .proto 文件并构建它们。
下面是一个有效配置的示例,假设您的 .proto 文件根位于相对于存储库根的 proto 文件夹中。
version: v1beta1
name: buf.build/myuser/myrepo
build:
roots:
- proto
要为 Go 生成 type 和 gRPC stubs,请在存储库的根目录下创建文件 buf.gen.yaml:
version: v1beta1
plugins:
- name: go
out: proto
opt: paths=source_relative
- name: go-grpc
out: proto
opt: paths=source_relative
我们使用 go 和 go-grpc 插件生成 Go types 和 gRPC service 定义。我们正在输出相对于 proto 文件夹的生成文件,并使用 path=source_relative 选项,这意味着生成的文件将与源 .proto 文件显示在同一目录中。
然后运行:
$ buf generate
这将为我们的 proto 文件层次结构中的每个 protobuf 软件包生成一个 *.pb.go 和 *_grpc.pb.go 文件。
使用 protoc 生成 stubs
这是一个 protoc 命令可能会生成 Go stubs 的示例,假设您位于存储库的根目录,并且您的 proto 文件位于一个名为 proto 的目录中:
$ protoc -I ./proto \
--go_out ./proto --go_opt paths=source_relative \
--go-grpc_out ./proto --go-grpc_opt paths=source_relative \
./proto/helloworld/hello_world.proto
我们使用 go 和 go-grpc 插件生成 Go types 和 gRPC service 定义。我们正在输出相对于 proto 文件夹的生成文件,并使用 path=source_relative 选项,这意味着生成的文件将与源 .proto 文件显示在同一目录中。
这将为 proto/helloworld/hello_world.proto 生成一个 *.pb.go 和 *_grpc.pb.go 文件。
创建 main.go
在创建 main.go 文件之前,我们假设用户已经创建了一个名为 github.com/myuser/myrepo 的 go.mod。此处的 import 使用的是相对于存储库根目录的 proto/helloworld 中生成的文件的路径。
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"net"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
helloworldpb "github.com/myuser/myrepo/proto/helloworld"
)
type server struct{}
func NewServer() *server {
return &server{}
}
func (s *server) SayHello(ctx context.Context, in *helloworldpb.HelloRequest) (*helloworldpb.HelloReply, error) {
return &helloworldpb.HelloReply{Message: in.Name + " world"}, nil
}
func main() {
// Create a listener on TCP port
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":8080")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Failed to listen:", err)
}
// Create a gRPC server object
s := grpc.NewServer()
// Attach the Greeter service to the server
helloworldpb.RegisterGreeterServer(s, &server{})
// Serve gRPC Server
log.Println("Serving gRPC on 0.0.0.0:8080")
log.Fatal(s.Serve(lis))
}
将 gRPC-Gateway 批注添加到现有的 proto 文件中
现在,我们已经可以使用 Go gRPC 服务器,我们需要添加 gRPC-Gateway 批注。
批注定义了 gRPC 服务如何映射到 JSON 请求和响应。使用 protocol buffers 时,每个 RPC 必须使用 google.api.http 批注定义 HTTP 方法和路径。
因此,我们需要将 google/api/http.proto 导入添加到 proto 文件中。我们还需要添加所需的 HTTP->gRPC 映射。在这种情况下,我们会将 POST /v1/example/echo 映射到我们的 SayHello RPC。
syntax = "proto3";
package helloworld;
import "google/api/annotations.proto";
// Here is the overall greeting service definition where we define all our endpoints
service Greeter {
// Sends a greeting
rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply) {
option (google.api.http) = {
post: "/v1/example/echo"
body: "*"
};
}
}
// The request message containing the user's name
message HelloRequest {
string name = 1;
}
// The response message containing the greetings
message HelloReply {
string message = 1;
}
生成 gRPC-Gateway stubs
现在我们已经将 gRPC-Gateway 批注添加到了 proto 文件中,我们需要使用 gRPC-Gateway 生成器来生成存根(stubs)。
使用 buf
我们需要将 gRPC-Gateway 生成器添加到生成配置中:
version: v1beta1
plugins:
- name: go
out: proto
opt: paths=source_relative
- name: go-grpc
out: proto
opt: paths=source_relative,require_unimplemented_servers=false
- name: grpc-gateway
out: proto
opt: paths=source_relative
我们还需要将 googleapis 依赖项添加到我们的 buf.yaml 文件中:
version: v1beta1
name: buf.build/myuser/myrepo
deps:
- buf.build/beta/googleapis
build:
roots:
- proto
然后,我们需要运行 buf beta mod update 以选择要使用的依赖项版本。
就是这样!现在,如果您运行:
$ buf generate
它应该产生一个 *.gw.pb.go 文件。
使用 protoc
在使用 protoc 生成 stubs 之前,我们需要将一些依赖项复制到我们的 proto 文件结构中。将一部分 googleapis 从官方存储库复制到您本地的原始文件结构中。之后看起来应该像这样:
proto
├── google
│ └── api
│ ├── annotations.proto
│ └── http.proto
└── helloworld
└── hello_world.proto
现在我们需要将 gRPC-Gateway 生成器添加到 protoc 调用中:
$ protoc -I ./proto \
--go_out ./proto --go_opt paths=source_relative \
--go-grpc_out ./proto --go-grpc_opt paths=source_relative \
--grpc-gateway_out ./proto --grpc-gateway_opt paths=source_relative \
./proto/helloworld/hello_world.proto
这将生成一个 *.gw.pb.go 文件。
我们还需要在 main.go 文件中添加 gRPC-Gateway 多路复用器(mux)并为其提供服务。
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"net"
"net/http"
"github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/v2/runtime"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
helloworldpb "github.com/myuser/myrepo/proto/helloworld"
)
type server struct{
helloworldpb.UnimplementedGreeterServer
}
func NewServer() *server {
return &server{}
}
func (s *server) SayHello(ctx context.Context, in *helloworldpb.HelloRequest) (*helloworldpb.HelloReply, error) {
return &helloworldpb.HelloReply{Message: in.Name + " world"}, nil
}
func main() {
// Create a listener on TCP port
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":8080")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Failed to listen:", err)
}
// Create a gRPC server object
s := grpc.NewServer()
// Attach the Greeter service to the server
helloworldpb.RegisterGreeterServer(s, &server{})
// Serve gRPC server
log.Println("Serving gRPC on 0.0.0.0:8080")
go func() {
log.Fatalln(s.Serve(lis))
}()
// Create a client connection to the gRPC server we just started
// This is where the gRPC-Gateway proxies the requests
conn, err := grpc.DialContext(
context.Background(),
"0.0.0.0:8080",
grpc.WithBlock(),
grpc.WithInsecure(),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Failed to dial server:", err)
}
gwmux := runtime.NewServeMux()
// Register Greeter
err = helloworldpb.RegisterGreeterHandler(context.Background(), gwmux, conn)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Failed to register gateway:", err)
}
gwServer := &http.Server{
Addr: ":8090",
Handler: gwmux,
}
log.Println("Serving gRPC-Gateway on http://0.0.0.0:8090")
log.Fatalln(gwServer.ListenAndServe())
}
测试 gRPC-Gateway
现在我们可以启动服务器了:
$ go run main.go
然后,我们使用 cURL 发送 HTTP 请求:
$ curl -X POST -k http://localhost:8090/v1/example/echo -d '{"name": " hello"}'
{"message":"hello world"}
Refs
https://github.com/iamrajiv/helloworld-grpc-gateway
https://grpc-ecosystem.github.io/grpc-gateway/docs/tutorials/introduction/
