使用 Curator 操作 ZooKeeper
Curator是Netflix公司开源的一个ZooKeeper client library,用于简化ZooKeeper客户端编程。它包含如下模块:
Framework:Framework是ZooKeeper API的High-Level的封装,它让访问ZooKeeper更加简单。它基于ZooKeeper添加了一些新的特性,同时屏蔽了访问ZooKeeper集群在管理连接和重试操作方面的复杂度。
Recipes:在Framework的基础上,实现了一些通用的功能,称之为“菜单”。
Utilities:访问ZooKeeper时候的一些公用方法。
Client:一个Low-Level的ZooKeeper客户端,并有一些公用方法。
Errors:Curator的异常处理,包括连接问题,异常恢复等等。
Extensions:
连接ZooKeeper
RetryPolicy retryPolicy = new ExponentialBackoffRetry(1000, 3);
CuratorFramework _client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.newClient("10.23.22.237:2181", retryPolicy);
_client.start();
Curator通过CuratorFrameworkFactory来创建客户端。new出来的客户端可以保存并且重用。在使用之前需要start一下,绝大部分Curator的操作都必须先start。
在new函数中需要传入RetryPolicy接口,重连的策略。当和ZooKeeper发生连接异常或者操作异常的时候,就会使用重连策略。ExponentialBackoffRetry是其中一种重连策略。Curator支持很多种重连策略:RetryNTimes(重连N次策略)、RetryForever(永远重试策略)、ExponentialBackoffRetry(基于backoff的重连策略)、BoundedExponentialBackoffRetry(有边界的基于backoff的重连策略,即,设定最大sleep时间)等等。
下面是官方例子中,ExponentialBackoffRetry的代码片段。
long sleepMs = baseSleepTimeMs * Math.max(1, random.nextInt(1 << (retryCount + 1)));
if ( sleepMs > maxSleepMs )
{
log.warn(String.format("Sleep extension too large (%d). Pinning to %d", sleepMs, maxSleepMs));
sleepMs = maxSleepMs;
}
return sleepMs;
可以看出ExponentialBackoffRetry 重连的时间间隔一般是随着重试的次数递增的,如果时间间隔计算出来大于默认的最大sleep时间的话,则去最大sleep时间。ExponentialBackoffRetry 除了时间的限制以外,还有最大重连次数的限制。而BoundedExponentialBackoffRetry策略只是让用户设置最大sleep时间而已。默认的最大时间是Integer.MAX_VALUE毫秒。
ZooKeeper节点操作
ZooKeeper 节点优点像文件系统的文件夹,每个节点都可以包含数据。但是ZooKeeper的节点是有生命周期的,这取决于节点的类型。在 ZooKeeper 中,节点类型可以分为持久节点(PERSISTENT )、临时节点(EPHEMERAL),以及时序节点(SEQUENTIAL ),具体在节点创建过程中,一般是组合使用,可以生成以下 4 种节点类型。不同的组合可以应用到不同的业务场景中。
1. 持久化节点
持久化节点创建后,就一直存在,除非有删除操作主动来删除这个节点,持久化节点不会因为创建该节点的客户端会话失效而消失。如果重复创建,客户端会抛出NodeExistsException异常。
byte[] data = { 1, 2, 3 };
_client.create().withMode(CreateMode.PERSISTENT).forPath("/zktest/p1", data);
2. 临时节点
创建临时节点后,如果客户端会话失效,那么这个节点会自动被ZooKeeper删除。这里是客户端失效,并不是客户端断开连接。因为ZooKeeper服务端和客户端是用心跳维持状态,会话留一点时间,这个时间是在创建连接的时候可以设置sessionTimeoutMs参数:
CuratorFrameworkFactory.newClient(connectString, sessionTimeoutMs, connectionTimeoutMs, retryPolicy);
创建临时节点的代码如下:
_client.create().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL).forPath("/zktest/e1", data);
3. 持久化时序节点
_client.create().withMode(CreateMode.PERSISTENT_SEQUENTIAL).forPath("/zktest/ps1", data);上述代码执行两次,你会发现客户端不会报NodeExistsException异常,ZooKeeper会为你创建2个节点,ZooKeeper在每个父节点会为他的第一级子节点维护一份时序,会记录每个子节点创建的先后顺序。在创建子节点的时候,可以设置这个属性,那么在创建节点过程中,ZooKeeper会自动为给定节点名加上一个数字后缀,作为新的节点名。
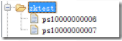
4. 临时时序节点
持久化时序节点不同的就是节点会在会话失效的时候回消失。
_client.create().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL).forPath("/zktest/es1", data);
5. 设置和获取节点数据
//设置节点数据
_client.setData().forPath("/zktest/ps1", data);
//获取节点数据
byte[] data2 = _client.getData().forPath("/zktest/ps1");
分布式锁
使用数据库、Redis、文件系统都可以实现分布式锁,同样ZooKeeper也可以用来实现分布式锁。Curator提供了InterProcessMutex类来帮助我们实现分布式锁,其内部就是使用的EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL类型节点。
public void test() throws Exception {
RetryPolicy retryPolicy = new ExponentialBackoffRetry(3000, 3);
_client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.newClient("10.23.22.237:2181", retryPolicy);
_client.start();
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
fixedThreadPool.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
dowork();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
}
}
private void dowork() throws Exception {
InterProcessMutex ipm = new InterProcessMutex(_client, "/zktest/distributed_lock");
try {
ipm.acquire();
_logger.info("Thread ID:" + Thread.currentThread().getId() + " acquire the lock");
Thread.sleep(1000);
_logger.info("Thread ID:" + Thread.currentThread().getId() + " release the lock");
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
ipm.release();
}
}
执行结果如下图:
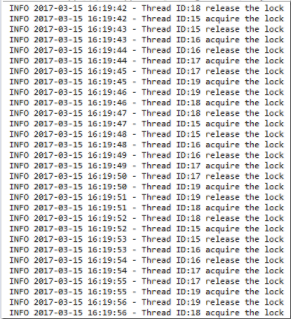
acquire()方法,会在给定的路径下面创建临时时序节点的时序节点。然后它会和父节点下面的其他节点比较时序。如果客户端创建的临时时序节点的数字后缀最小的话,则获得该锁,函数成功返回。如果没有获得到,即,创建的临时节点数字后缀不是最小的,则启动一个watch监听上一个(排在前面一个的节点)。主线程使用object.wait()进行等待,等待watch触发的线程notifyAll(),一旦上一个节点有事件产生马上再次出发时序最小节点的判断。
release()方法就是释放锁,内部实现就是删除创建的EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL节点。
Leader选举
选举可以用来实现Master-Slave模式,也可以用来实现主备切换等功能。Curator提供两种方式实现选举:LeaderSelector 和 LeaderLatch。两种方法都可以使用,LeaderLatch语法较为简单一点,LeaderSelector控制度更高一些。
使用LeaderSelector:
public void test() {
RetryPolicy retryPolicy = new ExponentialBackoffRetry(3000, 3);
_client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.newClient("10.23.22.237:2181", retryPolicy);
_client.start();
dowork();
}
private void dowork() {
LeaderSelectorListener listener = new
LeaderSelectorListenerAdapter() {
public void takeLeadership(CuratorFramework client) throws Exception {
logger.info("Take the lead.");
Thread.sleep(10000);
logger.info("Relinquish the lead.");
}
};
LeaderSelector selector = new LeaderSelector(_client, "/zktest/leader", listener);
selector.autoRequeue();
selector.start();
}
LeaderSelector的内部使用分布式锁InterProcessMutex实现, 并且在LeaderSelector中添加一个Listener,当获取到锁的时候执行回调函数takeLeadership。函数执行完成之后就调用InterProcessMutex.release()释放锁,也就是放弃Leader的角色。
使用LeaderLatch:
public void test() {
RetryPolicy retryPolicy = new ExponentialBackoffRetry(3000, 3);
_client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.newClient("10.23.22.237:2181", retryPolicy);
_client.start();
dowork();
}
private void dowork() {
LeaderLatch leader = new LeaderLatch(_client, "/zktest/leader");
leader.addListener(new LeaderLatchListener() {
@Override
public void isLeader() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
logger.info("Take the lead.");
try {
Thread.sleep(10000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
logger.info("Relinquish the lead.");
}
@Override
public void notLeader() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
logger.info("I am not Leader");
}
});
try {
leader.start();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
同样是实现Leader选举的LeaderLatch并没有通过InterProcessMutex实现,它使用了原生的创建EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL节点的功能再次实现了一遍。同样的在isLeader方法中需要实现Leader的业务需求,但是一旦isLeader方法返回,就相当于Leader角色放弃了,重新进入选举过程。
作者:nick hao
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/haoxinyue/p/6561896.html
本文转自博客园网,版权归原作者所有。
