作为面试官,为什么我推荐组件库作为前端面试的亮点?
大厂面试的时候,我也看到很多候选人写了
xx组件的封装,很少见过二次组件库的封装或者维护开源组件库,其实这些都是项目上的亮点,一般面试官如果看到,都会详细考察
本文将会以antd Element vant等等组件库为例子,会进行分析对比
为什么需要二次封装组件库?
实际工作中,我们在项目中需要自定义
主题色,更改按钮样式,自定义图标,自定义table组件等等,这些都可以基于antd组件库进行二次封装,减少重复工作,提升开发效率。
所以我们在封装的时候按照下面这四个原则进行思考就行了,另外本身封装组件库对于项目来说也是没有任何风险,因为一开始我们把PropsType直接进行转发,内部再进行增加业务的功能,这样就是达到完全的解耦
-
统一风格:在一个大的项目或者多个相关的项目中,保持一致的界面风格和交互方式是非常重要的。通过二次封装,我们可以定义统一的样式和行为,减少不一致性。
-
降低维护成本:当底层的组件库更新时,我们可能需要在项目的多个地方进行修改。但是如果我们有了自己的封装,只需要在封装层面进行更新即可,这大大降低了维护成本。
-
增加定制功能:有些时候,我们需要在原有组件库的基础上增加一些特定的功能,如特定的验证、错误处理等。二次封装提供了这样的可能。
-
提高开发效率:在一些常用的功能(如表单验证、全局提示等)上,二次封装可以提供更方便的API,提高开发效率。
请结合一个组件库设计的过程,谈谈前端工程化的思想
当我们结合一个组件库设计的过程来谈论前端工程化的思想时,需要理清这些要点:
1. 使用 Lerna 进行多包管理:通过 Lerna 来管理多个包(组件),实现组件级别的解耦、独立版本控制、按需加载等特性。
# 安装 Lerna
npm install -g lerna
# 初始化一个 Lerna 仓库
lerna init
# 创建 "Button" 组件包
lerna create button --yes
2. 规范化提交:使用规范化的提交信息可以提高 Git 日志的可读性,并且可以通过 conventional commits 自动生成 CHANGELOG。可以使用 commitizen、commitlint 等工具来配置。
# 安装相关工具
npm install commitizen cz-conventional-changelog --save-dev
// package.json
{
"scripts": {
"commit": "git-cz"
},
"config": {
"commitizen": {
"path": "cz-conventional-changelog"
}
}
}
3. 代码规范化:通过 ESLint、Prettier 等工具实现代码规范化和格式化,并封装为自己的规范预设。
# 安装相关工具
npm install eslint prettier eslint-plugin-prettier eslint-config-prettier --save-dev
// .eslintrc.js
module.exports = {
extends: ['eslint:recommended', 'plugin:prettier/recommended'],
};
// .prettierrc.js
module.exports = {
singleQuote: true,
trailingComma: 'es5',
};
4. 组件开发调试:需要考虑热更新编译、软链接引用等问题,以方便在开发过程中进行组件的调试。
// packages/button/src/Button.js
import React from 'react';
const Button = ({ type = 'primary', onClick, children }) => {
return (
<button className={`button ${type}`} onClick={onClick}>
{children}
</button>
);
};
export default Button;
5. 文档站点:可以基于 dumi 搭建文档站点,并实现 CDN 加速、增量发布等优化。可以使用 surge 实现 PR 预览。
<!-- packages/button/docs/index.md -->
# Button
A simple button component.
## Usage
import { Button } from 'button-library';
const MyComponent = () => {
return <Button onClick={() => alert('Button clicked!')}>Click Me</Button>;
};
### Props
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
| -------- | ---------------------- | ------- | ----------------------------- |
| type | `primary` \| `secondary` | `primary` | The type of the button. |
| onClick | `function` | | Event handler for click event. |
6. 单元测试:需要考虑 jest、enzyme 等工具的配合使用,生成测试覆盖率报告。
# 安装相关工具
npm install jest enzyme enzyme-adapter-react-16 react-test-renderer --save-dev
// packages/button/src/Button.test.js
import React from 'react';
import { mount } from 'enzyme';
import Button from './Button';
describe('Button', () => {
it('renders without crashing', () => {
const wrapper = mount(<Button>Click Me</Button>);
expect(wrapper.exists()).toBe(true);
});
it('calls onClick function when clicked', () => {
const onClickMock = jest.fn();
const wrapper = mount(<Button onClick={onClickMock}>Click Me</Button>);
wrapper.find('button').simulate('click');
expect(onClickMock).toHaveBeenCalledTimes(1);
});
});
7. 按需加载:需要配合 babel-plugin-import 实现按需加载,即在编译时修改导入路径来实现组件的按需加载。
# 安装相关工具
npm install babel-plugin-import --save-dev
// .babelrc
{
"plugins": [
[
"import",
{
"libraryName": "button-library",
"style": "css"
}
]
]
}
8. 组件设计:需要考虑响应式、主题、国际化、TypeScript 支持等问题,以保证组件的灵活性和可扩展性。
// packages/button/src/Button.js
import React from 'react';
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
const Button = ({ type = 'primary', onClick, children }) => {
return (
<button className={`button ${type}`} onClick={onClick}>
{children}
</button>
);
};
Button.propTypes = {
type: PropTypes.oneOf(['primary', 'secondary']),
onClick: PropTypes.func,
children: PropTypes.node.isRequired,
};
export default Button;
9. 发布前的自动化脚本:需要编写自动化脚本来规范发布流程,确保发布的一致性和可靠性。
// package.json
{
"scripts": {
"prepublish": "npm run lint && npm run test",
"lint": "eslint .",
"test": "jest"
}
}
10. 发布后的处理:考虑补丁升级、文档站点同步发布等问题,以便及时修复问题并提供最新的文档。
11. 制定 Contributing 文档:制定 Contributing 文档可以降低开源社区贡献的门槛,并确保社区成员了解如何参与项目。处理 issues 和 PR 需要有专人负责。
如何对一个组件库进行测试?
首先需要明确,组件库的测试大致可以分为两类:一类是针对组件本身的功能和性能的测试(例如,单元测试、性能测试),另一类是针对组件在集成环境下的行为和性能的测试(例如,集成测试、系统测试)。
1. 功能测试(单元测试)
通常来说,组件的功能测试可以通过单元测试来完成。单元测试的目的是验证组件的单个功能是否按照预期工作。这通常可以通过编写测试用例来完成,每个测试用例针对一个特定的功能。
import { Button } from '../src/Button';
test('Button should do something', () => {
const component = new YourComponent();
// your test logic here
expect(component.doSomething()).toBe('expected result');
});
2. 边界测试
边界测试是一种特殊的功能测试,用于检查组件在输入或输出达到极限或边界条件时的行为。
test('Button should handle boundary condition', () => {
const component = new YourComponent();
// test with boundary value
expect(component.handleBoundaryCondition('boundary value')).toBe('expected result');
});
3. 响应测试
响应测试通常涉及到 UI 组件在不同的设备或屏幕尺寸下的行为。这可能需要使用端到端(E2E)测试工具,如 Puppeteer、Cypress 等。
import { test } from '@playwright/test';
test('Button should be responsive', async ({ page }) => {
await page.goto('http://localhost:3000/your-component');
const component = await page.$('#your-component-id');
expect(await component.isVisible()).toBe(true);
// Simulate a mobile device
await page.setViewportSize({ width: 375, height: 812 });
// Check the component under this condition
// your test logic here
});
4. 交互测试
交互测试也可以通过端到端(E2E)测试工具来完成。
test('Button should handle interactions', async ({ page }) => {
await page.goto('http://localhost:3000/your-component');
const component = await page.$('#your-component-id');
// Simulate a click event
await component.click();
// Check the result of the interaction
// your test logic here
});
5. 异常测试
异常测试用于验证组件在遇到错误或非法输入时能否正确处理。这通常可以通过在测试用例中模拟错误条件来完成。
test('Button should handle errors', () => {
const component = new YourComponent();
// Test with illegal argument
expect(() => {
component.doSomething('illegal argument');
}).toThrow('Expected error message');
});
6. 性能测试
性能测试用于验证组件的性能,例如,加载速度、内存消耗等。
import { performance } from 'perf_hooks';
test('Button should have good performance', () => {
const start = performance.now();
const component = new YourComponent();
component.doSomething();
const end = performance.now();
const duration = end - start;
expect(duration).toBeLessThan(50); // Expect the operation to finish within 50 ms
});
7. 自动化测试
单元测试、集成测试和系统测试都可以通过自动化测试工具进行。例如,Jest 和 Mocha 可以用于自动化运行 JavaScript 单元测试,Puppeteer 和 Selenium 可以用于自动化运行端到端测试。
module.exports = {
roots: ['<rootDir>/src'],
testMatch: ['**/__tests__/**/*.+(ts|tsx|js)', '**/?(*.)+(spec|test).+(ts|tsx|js)'],
transform: {
'^.+\\.(ts|tsx)$': 'ts-jest'
}
};
Element-UI 的多语言方案是怎么设计的?
Element UI 使用了 Vue 的插件
vue-i18n实现多语言支持,具体的设计和实现过程如下:
1. 定义语言包
首先,Element UI 定义了一个 JavaScript 对象作为语言包。每种语言都有一个对应的语言包,例如:
export default {
el: {
colorpicker: {
confirm: 'OK',
clear: 'Clear'
},
// ...other components
}
};
2. 加载语言包
Element UI 提供了一个 i18n 方法用于加载语言包。
import ElementUI from 'element-ui';
import locale from 'element-ui/lib/locale/lang/en';
Vue.use(ElementUI, { locale });
3. 使用语言包
Element UI 的组件会使用 $t 方法获取语言包中的文本。例如:
<template>
<el-button>{{ $t('el.button.confirm') }}</el-button>
</template>
在这个例子中,按钮的文本会根据当前的语言包来显示。
4. 集成 vue-i18n
如果你的项目中已经使用了 vue-i18n,Element UI 会优先使用 vue-i18n 提供的 $t 方法。你可以这样配置:
import Vue from 'vue';
import VueI18n from 'vue-i18n';
import ElementUI from 'element-ui';
import enLocale from 'element-ui/lib/locale/lang/en';
import zhLocale from 'element-ui/lib/locale/lang/zh-CN';
Vue.use(VueI18n);
const messages = {
en: {
message: 'hello',
...enLocale // 或者用 Object.assign({ message: 'hello' }, enLocale)
},
zh: {
message: '你好',
...zhLocale // 或者用 Object.assign({ message: '你好' }, zhLocale)
}
};
const i18n = new VueI18n({
locale: 'zh', // set locale
messages, // set locale messages
});
Vue.use(ElementUI, {
i18n: (key, value) => i18n.t(key, value)
});
在这个例子中,我们先加载了 vue-i18n,然后定义了两种语言的语言包(英文和中文)。最后,我们配置了 Element UI 使用 vue-i18n 的 $t 方法。
这样,Element UI 的组件就能够根据 vue-i18n 的语言设置显示对应的文本。
组件库如何实现在线主题定制的?
1. 使用 CSS 变量定义样式
将组件的样式使用 CSS 变量定义,这样可以通过改变 CSS 变量的值来修改样式。
:root {
--primary-color: #1890ff;
}
.btn {
background: var(--primary-color);
}
2. 提供主题文件进行配置
让用户可以通过导入自定义的主题文件来覆盖默认样式。
// theme.js
export default {
'--primary-color': '#409eff'
}
3. 在线主题编辑器
提供一个在线工具,用户可以在工具中配置主题,生成主题文件。
工具会提交主题配置,服务器端接收后动态编译生成新的样式,并返回给前端。
4. 前端应用新样式
前端通过加载服务器返回的 CSS 文件来应用新的主题样式,实现样式更新而无需重新打包。
// 请求主题文件
fetchTheme(theme).then(css => {
// 动态创建style标签,插入css
const style = document.createElement('style');
style.innerHTML = css;
document.head.appendChild(style);
})
5. 持久化主题配置
将用户主题配置持久化本地存储,这样每次访问都可以应用上次选定的主题。
组件库的类型定义应该怎样设计?
组件库的类型定义设计取决于很多因素,包括库的大小、复杂度、可能的使用场景等。
1. 定义全局类型 versus 定义组件Props类型
在组件库中,我们经常需要定义一些可以在多个组件之间共享的全局类型,以及针对特定组件的props类型。例如:
// 全局类型
export interface Size {
width: number;
height: number;
}
// 组件Props类型
export interface ButtonProps {
size?: Size;
label: string;
onClick?: () => void;
}
2. 类型导出应该集中还是分散?
是否集中导出类型取决于组件库的大小和复杂度。对于小型库,可以在一个单独的文件中集中导出所有类型;对于大型库,可能需要将类型定义分散在各个组件文件中,然后在一个单独的文件中重新导出它们。例如:
// 在各个组件文件中定义和导出类型
// button.ts
export interface ButtonProps { /*...*/ }
// 在一个单独的文件中重新导出所有类型
// types.ts
export type { ButtonProps } from './button';
3. 如何设计类型层级关系?类型复用?
在设计类型时,应尽可能地利用 TypeScript 的类型系统来构建类型层级关系,并复用类型。例如,你可以使用类型交叉(&)和类型联合(|)来复用类型:
type SmallSize = { width: number; height: number };
type LargeSize = SmallSize & { depth: number };
type Size = SmallSize | LargeSize;
4. 类型定义要充分还是精简?
类型定义应尽可能精简,同时提供足够的信息来描述类型的形状和行为。避免使用 any 或 unknown 类型,除非有特别的理由。例如:
// 不好的类型定义
interface ButtonProps {
[key: string]: any; // 这不提供任何有关props的信息
}
// 好的类型定义
interface ButtonProps {
size?: Size;
label: string;
onClick?: () => void;
}
总的来说,设计好的类型定义可以提高代码的可读性和可维护性,同时减少运行时错误。
组件库的渐进升级策略应该怎么设计?
组件库的渐进升级策略通常会涉及到版本控制、向下兼容性、废弃通知以及旧版本的兼容性等多个方面。这种策略的主要目的是在保持库的稳定性和功能性的同时,尽可能地减少对用户的影响。
1. 版本控制策略
组件库通常遵循语义化版本 (SemVer) 规范进行版本控制。在语义化版本中,每个版本号都由三部分组成:主版本号、次版本号和补丁版本号。
例如,版本号为 1.2.3 表示主版本号为 1,次版本号为 2,补丁版本号为 3。
-
主版本号(Major): 当你做了不兼容的 API 修改 -
次版本号(Minor): 当你做了向下兼容的功能性新增 -
补丁版本号(Patch): 当你做了向下兼容的问题修复
2. 向下兼容处理
向下兼容性是指在升级组件库时,保证新版本不会破坏旧版本的功能。例如,如果新版本的一个组件删除了一个属性,而这个属性在旧版本中是必需的,那么这个变化就不是向下兼容的。
在进行不向下兼容的变化时,应在主版本号上进行增加,以警告用户可能需要修改他们的代码。
3. 功能被废弃怎么通知用户升级?
当一个功能或者组件被废弃时,应在库的文档、更新日志以及相关的 API 文档中明确注明。在代码中,可以通过添加警告或者错误信息来提醒用户:
function deprecatedFunction() {
console.warn('Warning: deprecatedFunction is deprecated and will be removed in the next major version.');
// 功能的原始实现
}
4. 兼容旧版本的方案
兼容旧版本的策略取决于特定的需求和资源。一种常见的策略是在主版本升级后,继续维护旧版本的一个分支,以便在必要时进行修复和改进。例如,如果当前版本是 2.x.x,那么可以维护一个 1.x.x 的分支。
在实践中,以上的策略和方法可能需要根据具体的情况进行调整。一个好的渐进升级策略应能够平衡新功能的引入、旧功能的废弃以及向下兼容性的维护。
组件库的按需加载实现中存在哪些潜在问题,如何解决?
按需加载(也称为代码拆分)是现代前端开发中常见的一种优化手段,可以有效地减少应用的初始加载时间。对于组件库来说,它使用户只加载和使用他们真正需要的组件,而不是加载整个库。
babel-plugin-import
Babel 插件: 使用如 babel-plugin-import 的 Babel 插件可以在编译时将导入整个库的语句转换为仅导入使用的组件。
```javascript
import { Button } from 'your-ui-lib';
// 在编译时,babel-plugin-import 将上面的语句转换为以下语句:
// import Button from 'your-ui-lib/button';
```
tree-shaking
Webpack、Rollup 等工具都已经支持了 Tree shaking。在项目的配置中开启 Tree shaking,然后使用 ES Modules 的导入导出语法,即可实现按需加载。
但是在使用 Tree shaking 的时候,有一个需要特别注意的地方,就是“副作用(side effects)”。
有些模块的代码可能会在导入时执行一些副作用,例如改变全局变量、改变导入模块的状态等。这种情况下,即使模块中的部分导出没有被使用,由于其副作用,也不能被 Tree shaking 移除。否则,可能会导致程序运行出错。
例如,在 CSS in JS 的库中,可能存在这样的代码:
import './styles.css'; // 有副作用,改变了全局的样式
在这种情况下,你需要在 package.json 中显式地指定模块的副作用,以防止它们被错误地移除:
{
"name": "your-library",
"sideEffects": [
"./src/styles.css"
]
}
如果你的库没有任何副作用,你可以将 sideEffects 设置为 false:
{
"name": "your-library",
"sideEffects": false
}
样式如何实现真正的按需加载?避免样式重复打包?
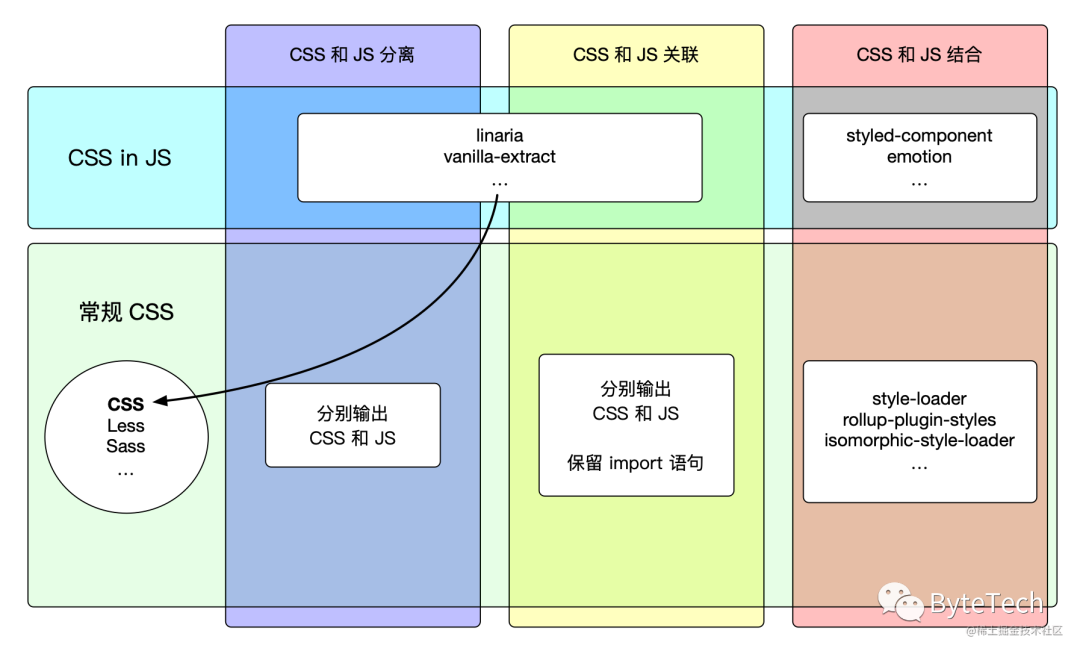
| 样式和逻辑分离 | 样式和逻辑结合 | 样式和逻辑关联 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 开发打包流程 | 中等 | 简单 | 复杂 |
| 输出文件 | JS 文件和 CSS 文件 | JS 文件 | JS 文件和 CSS 文件 |
| 使用方法 | 分别引入 JS 和 CSS | 只引入 JS | 只引入 JS |
| 按需加载 | 需要额外支持 | 支持 | 支持 |
| 性能影响 | 无 | 带额外 runtime,可能有影响 | 无 |
| SSR | 支持 | 需要额外支持(部分方案不支持) | 支持(可能需要使用者调整配置) |
| 支持写法 | 常规 CSS / 零运行时 CSS in JS | 常规 CSS / CSS in JS | 常规 CSS / 零运行时 CSS in JS |
| 关键样式提取 | 自行处理 | 支持 | 自行处理 |
样式和逻辑分离
这种方案中,组件的CSS和JS在代码层面上是分离的,开发时写在不同的文件里。在打包时生成独立的逻辑文件和样式文件。
优点:
-
适用面广,可以支持不同的框架和技术栈。 -
支持SSR,样式处理留给使用者。 -
可以直接提供源码,便于主题定制。
缺点:
-
使用时需要分别引入逻辑和样式,按需加载实现复杂,需要借助`babel-plugin-import`[1]、`unplugin-vue-components`[2]等。 -
样式文件打包可能存在冗余。
适合需要高适用性和灵活性的组件库。
样式和逻辑结合
这种方案将CSS和JS打包在一起,输出单一的JS文件。主要有两种实现形式:
-
CSS in JS:样式以对象或字符串形式存在在JS中。 -
将CSS打包进JS:通过构建工具,将CSS文件内容注入到JS中。
优点:
-
使用简单,只需要引入JS即可。 -
天然支持按需加载。
缺点:
-
需要额外的runtime,可能影响性能。 -
难以利用浏览器缓存。 -
SSR需要框架额外支持。
样式和逻辑关联
这种方案下,虽然CSS和JS在源码层分离,但组件内会直接引用样式,且输出文件中保留import语句。
优点:
-
使用简单,只引入JS即可。 -
支持按需加载。
缺点:
-
对构建和SSR都有一定要求。 -
样式编译复杂。
设计一个组件库的 CI/CD 和发布流程。
可以参考antd
当你设计一个组件库的 CI/CD 和发布流程时,可以考虑以下步骤:
1. 分支管理:
开发者在开发新特性或修复 bug 时,应该在新的分支(通常称为 feature 分支)上进行开发。完成开发后,提交一个 pull request 到 main 或 master 分支,并进行代码审查。
git checkout -b feature/new-component
# 开发过程...
git add .
git commit -m "Add new component"
git push origin feature/new-component
2. 代码检查:
使用如 ESLint、Stylelint 等工具进行代码检查,使用 Jest 等工具进行单元测试和覆盖率检查。这些步骤可以在提交代码时或者 pull request 的过程中自动进行。
例如,可以在 package.json 中添加如下 scripts:
{
"scripts": {
"lint": "eslint --ext .js,.jsx,.ts,.tsx src",
"test": "jest"
}
}
并在 CI/CD 工具中(如 GitHub Actions、Jenkins 等)配置相应的任务:
# .github/workflows/ci.yml
name: CI
on: [push, pull_request]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Check out code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Use Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v2
with:
node-version: '14'
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm ci
- name: Run lint
run: npm run lint
- name: Run tests
run: npm run test
3. 版本管理:
在合并代码并发布新版本前,需要确认新的版本号,并生成相应的 changelog。可以使用如 standard-version 这样的工具自动化这个过程。
npx standard-version
4. 构建:
使用如 Webpack、Rollup 等工具进行构建,生成可以在不同环境(如浏览器、Node.js)下使用的代码。
npm run build
5. 发布:
将构建好的代码发布到 npm,同时更新文档网站。
npm publish
6. 部署:
部署到github pages或者自建服务
如何实现button按钮
jcode
import React, { CSSProperties, FC, MouseEvent, ReactNode } from 'react';
interface ButtonProps {
lock?: boolean;
classNames?: Record<string, string>;
danger?: boolean;
disabled?: boolean;
ghost?: boolean;
href?: string;
htmlType?: 'button' | 'submit' | 'reset';
icon?: ReactNode;
loading?: boolean | { delay: number };
shape?: 'default' | 'circle' | 'round';
size?: 'large' | 'middle' | 'small';
styles?: Record<string, CSSProperties>;
target?: string;
type?: 'primary' | 'dashed' | 'link' | 'text' | 'default';
onClick?: (event: MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement | HTMLAnchorElement>) => void;
children?: ReactNode;
}
const Button: FC<ButtonProps> = ({
lock,
classNames,
danger,
disabled,
ghost,
href,
htmlType = 'button',
icon,
loading,
shape,
size,
styles,
target,
type = 'default',
onClick,
children
}) => {
const baseClassName = 'button';
const className = [
baseClassName,
type && `${baseClassName}--${type}`,
size && `${baseClassName}--${size}`,
shape && `${baseClassName}--${shape}`,
disabled && `${baseClassName}--disabled`,
danger && `${baseClassName}--danger`,
ghost && `${baseClassName}--ghost`,
loading && `${baseClassName}--loading`,
lock && `${baseClassName}--lock`,
].filter(Boolean).join(' ');
const handleClick = (e: MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement | HTMLAnchorElement>) => {
if (disabled) {
e.preventDefault();
} else if (onClick) {
onClick(e);
}
};
return href ? (
<a
className={className}
href={href}
target={target}
onClick={handleClick}
>
{children}
</a>
) : (
<button
className={className}
type={htmlType}
disabled={disabled}
onClick={handleClick}
>
{children}
</button>
);
};
export default Button;
如何实现modal组件
jcode
interface IModalProps {
afterClose?: () => void;
bodyStyle?: CSSProperties;
cancelButtonProps?: React.ButtonHTMLAttributes<HTMLButtonElement>;
cancelText?: ReactNode;
centered?: boolean;
closeIcon?: boolean | ReactNode;
confirmLoading?: boolean;
destroyOnClose?: boolean;
focusTriggerAfterClose?: boolean;
footer?: ReactNode;
forceRender?: boolean;
getContainer?: HTMLElement | (() => HTMLElement) | string | false;
keyboard?: boolean;
mask?: boolean;
maskClosable?: boolean;
maskStyle?: CSSProperties;
modalRender?: (node: ReactNode) => ReactNode;
okButtonProps?: React.ButtonHTMLAttributes<HTMLButtonElement>;
okText?: ReactNode;
okType?: string;
style?: CSSProperties;
title?: ReactNode;
open?: boolean;
width?: string | number;
wrapClassName?: string;
zIndex?: number;
onCancel?: (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement>) => void;
onOk?: (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement>) => void;
afterOpenChange?: (open: boolean) => void;
}
const Modal: React.FC<IModalProps> = ({
children,
title = '',
onCancel,
onOk,
open = false,
mask = true,
}) => {
return (
<>
{mask && <div className="modal-mask" style={{display: open ? 'block' : 'none'}}></div>}
{open && (
<div className="modal" style={{display: 'block'}}>
<h2 className="modal-title">{title}</h2>
<div className="modal-body">{children}</div>
<div className="modal-footer">
<button className="modal-footer-cancel" onClick={onCancel}>
Cancel
</button>
<button className="modal-footer-ok" onClick={onOk}>
OK
</button>
</div>
</div>
)}
</>
);
};
Modal.info = function(props: IModalProps) {
const div = document.createElement('div');
document.body.appendChild(div);
function remove() {
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(div);
document.body.removeChild(div);
}
function onCancel(e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement>) {
if (props.onCancel) {
props.onCancel(e);
}
remove();
}
function onOk(e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement>) {
if (props.onOk) {
props.onOk(e);
}
remove();
}
ReactDOM.render(
<Modal {...props} onCancel={onCancel} onOk={onOk} open={true} />,
div
);
};
如何实现高性能Tree组件
实现Tree组件的核心思路是什么?
Tree组件的核心思路是将原始的嵌套children数据结构平铺成一维数组,然后通过计算每个节点的深度(deep)、层级关系等信息,在渲染时动态计算缩进宽度、连接线等,从而实现树形结构的可视化。
Tree组件如何实现高性能大数据渲染?
-
将原始树形数据平铺为一维数组,便于后续计算 -
计算出实际需要渲染的节点数据,过滤隐藏的节点 -
利用虚拟列表技术只渲染可视区域的数据,实现大数据量的高效渲染
function flattenTreeData(treeData = [], parent = null) {
const nodes = [];
treeData.forEach((node) => {
const newNode = {
...node,
parent,
};
nodes.push(newNode);
if (newNode.children) {
nodes.push(...flattenTreeData(newNode.children, newNode));
}
});
return nodes;
}
如何计算Tree组件中节点的各种状态(展开/折叠、选中等)?
-
展开/折叠状态根据ExpandedKeys计算 -
复选框选中状态需要考虑受控/非受控,严格受控模式,及父子节点关联 -
需要递归计算父节点和子节点的状态 -
利用平铺后的索引进行相关节点查询
function flattenTreeData(treeData = [], parent = null) {
const nodes = [];
treeData.forEach((node) => {
const newNode = {
...node,
parent,
};
nodes.push(newNode);
if (newNode.children) {
nodes.push(...flattenTreeData(newNode.children, newNode));
}
});
return nodes;
}
Tree组件的交互如何实现?点击节点展开折叠,复选框状态切换等
-
点击展开折叠通过更新节点自身状态、可视状态及ExpandedKeys实现 -
点击复选框需要递归更新父子节点的状态,及相关keys -
计算并保存实时状态,通过回调函数通知外部
function toggleExpanded(nodes, node) {
return nodes.map((currentNode) => {
if (currentNode === node) {
return {
...currentNode,
expanded: !currentNode.expanded,
};
}
return currentNode;
});
}
// 在渲染时计算缩进:
function renderNode(node) {
const indentLevel = getIndentLevel(node);
const style = {
paddingLeft: `${indentLevel * 16}px`,
};
return (
<div style={style} onClick={() => handleNodeClick(node)}>
{node.label}
</div>
);
}
如何实现高性能表格Table组件?
可参考ali-react-table:高性能 React 表格组件
表格组件的性能瓶颈主要在哪里?
-
渲染大量 DOM; -
频繁的更新渲染,如选中行状态改变引起整个表格重新渲染。
如何优化表格组件的渲染性能?
-
只渲染必要的列:
const columnsToRender = columns.filter(column => column.shouldRender);
return (
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
{columnsToRender.map(column => (
<th key={column.key}>{column.title}</th>
))}
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{data.map(row => (
<tr key={row.id}>
{columnsToRender.map(column => (
<td key={column.key}>{row[column.key]}</td>
))}
</tr>
))}
</tbody>
</table>
);
-
细粒度更新,只更新变化行/列。在React中,可以使用 React.memo或者shouldComponentUpdate来避免不必要的重渲染:
function Row({ data, columns }) {
return (
<tr>
{columns.map(column => (
<Cell key={column.key} data={data[column.key]} />
))}
</tr>
);
}
const areEqual = (prevProps, nextProps) => {
return prevProps.data === nextProps.data && prevProps.columns === nextProps.columns;
};
export default React.memo(Row, areEqual);
-
采用虚拟化技术,只渲染可视区的行。可以使用第三方库如 react-window或者react-virtualized来实现:
import { FixedSizeList as List } from "react-window";
function Table({ data, columns }) {
const Row = ({ index, style }) => (
<div style={style}>
{columns.map(column => (
<Cell key={column.key} data={data[index][column.key]} />
))}
</div>
);
return (
<List
height={500}
itemCount={data.length}
itemSize={35}
>
{Row}
</List>
);
}
-
使用Web Workers来处理数据处理或计算密集型任务:
// 创建一个新的 worker
const worker = new Worker('worker.js');
// 向 worker 发送数据
worker.postMessage(data);
// 监听 worker 的消息
worker.addEventListener('message', (event) => {
// 更新表格数据
updateTable(event.data);
});
在worker.js中:
self.addEventListener('message', (event) => {
// 处理数据
const processedData = processData(event.data);
// 发送处理后的数据
self.postMessage(processedData);
})参考资料
https://github.com/umijs/babel-plugin-import: https://link.juejin.cn/?target=https%3A%2F%2Fgithub.com%2Fumijs%2Fbabel-plugin-import
[2]https://github.com/antfu/unplugin-vue-components: https://link.juejin.cn/?target=https%3A%2F%2Fgithub.com%2Fantfu%2Funplugin-vue-components
最后
如果你觉得这篇内容对你挺有启发,我想邀请你帮我个小忙:
点个「喜欢」或「在看」,让更多的人也能看到这篇内容
我组建了个氛围非常好的前端群,里面有很多前端小伙伴,欢迎加我微信「sherlocked_93」拉你加群,一起交流和学习
关注公众号「前端下午茶」,持续为你推送精选好文,也可以加我为好友,随时聊骚。