自己动手写一个持久层框架
1. JDBC问题分析
我们来看一段JDBC的代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
//1. 加载数据库驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Drive");
//2. 通过驱动管理类获取数据库链接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://hocalhost:3306/mybatis?characterEncoding=utf-8",
"root","root");
//3. 定义SQL语句 ?表示占位符
String sql = "SELECT * FROM user WHERE username = ?";
//4. 获取预处理对象Statement
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//5. 设置参数,第一个参数为SQL语句中参数的序号(从1开始),第二个参数为设置的参数值
preparedStatement.setString(1,"tom");
//6. 向数据库发出SQL执行查询,查询出结果集
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//7. 遍历查询结果集
while (resultSet.next()){
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String userName = resultSet.getString("username");
//封装User
user.setId(id);
user.setUserName(userName);
}
System.out.println(user);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
可以看到,直接使用JDBC开发是存在一些问题的,我们来分析下:
问题分析:
数据库配置信息存在硬编码问题 频繁创建、释放数据库链接
//1. 加载数据库驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Drive");
//2. 通过驱动管理类获取数据库链接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://hocalhost:3306/mybatis?characterEncoding=utf-8","root","root");
sql语句、设置参数、获取结果集均存在硬编码问题
//3. 定义SQL语句 ?表示占位符
String sql = "SELECT * FROM user WHERE username = ?";
//4. 获取预处理对象Statement
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//5. 设置参数,第一个参数为SQL语句中参数的序号(从1开始),第二个参数为设置的参数值
preparedStatement.setString(1,"tom");
//6. 向数据库发出SQL执行查询,查询出结果集
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String userName = resultSet.getString("username");
手动封装返回结果集 较为繁琐
//7. 遍历查询结果集
while (resultSet.next()){
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String userName = resultSet.getString("username");
//封装User
user.setId(id);
user.setUserName(userName);
}
System.out.println(user);
解决思路:
写在配置文件中 连接池(c3p0、dbcp、德鲁伊...) 配置文件 (和1放一起吗?No,经常变动和不经常变动的不要放在一起) 反射、内省
下面根据这个解决思路,自己动手写一个持久层框架,写框架之前分析这个框架需要做什么
2. 自定义框架思路分析
使用端(项目):
引入自定义持久层框架的jar包 提供两部分配置信息:
数据库配置信息 SQL配置信息(SQL语句)
使用配置文件来提供这些信息: sqlMapConfig.xml :存放数据库的配置信息 mapper.xml :存放SQL配置信息
自定义持久层框架(工程):
持久层框架的本质就是对JDBC代码进行了封装
加载配置文件:根据配置文件的路径加载配置文件成字节输入流,存储内存中
“
Q:getResourceAsStearm方法需要执行两次分别加载sqlMapConfig额和mapper吗?
A:可以但没必要,我们可以在sqlMapConfig.xml中写入mapper.xml的全路径即可
”创建Resources类 方法:getResourceAsStream(String path) 创建两个javaBean:(容器对象):存放的就是配置文件解析出来的内容
Configuration:核心配置类:存放sqlMapConfig.xml解析出来的内容 MappedStatement:映射配置类:存放mapper.xml解析出来的内容 解析配置文件:使用dom4j
创建类:SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 方法:build(InputStream in) 这个流就是刚才存在内存中的 使用dom4j解析配置文件,将解析出来的内容封装到容器对象中 创建SqlSessionFactory对象;生产sqlSession:会话对象(工厂模式 降低耦合,根据不同需求生产不同状态的对象) 创建sqlSessionFactory接口及实现类DefaultSqlSessionFactory
openSession(); 生产sqlSession 创建SqlSession接口及实现类DefaultSession
selectList() selectOne() update() delete() ... 定义对数据库的CRUD操作,例如: 创建Executor接口及实现类SimpleExecutor实现类
query(Configuration con,MappedStatement ms,Object ...param);执行JDBC代码, Object ...param具体的参数值,可变参;
3. 创建表并编写测试类
SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for user
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`;
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(50) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 4 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of user
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `user` VALUES (1, 'lucy');
INSERT INTO `user` VALUES (2, 'tom');
INSERT INTO `user` VALUES (3, 'jack');
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
1. 创建一个Maven项目—— Ipersistence_test
2. 在resource中创建sqlMapConfig.xml 和 UserMapper.xml
UserMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="user">
<select id="selectList" resultType="com.dxh.pojo.User">
select * from user
select>
<select id="selectOne" resultType="com.dxh.pojo.User" paramterType="com.dxh.pojo.User">
select * from user where id = #{id} and username = #{userName}
select>
mapper>
“Q:为什么要有namespace和id ?A:当一个
”*Mapper.xml中有多条sql时,无法区分具体是哪一条所以增加 id
如果有UserMapper.xml和ProductMapper.xml,假设他们的查询的id都为”selectList“,那么将无法区分具体是查询user还是查询product的。所以增加 namespacenamespace.id 组成sql的唯一标识,也称为statementId
sqlMapConfig.xml
<configuration>
<dataSource>
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver">property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql:///zdy_mybatis">property>
<property name="username" value="root">property>
<property name="password" value="root">property>
dataSource>
<mapper resource="UserMapper.xml">mapper>
configuration>
4. 开始编写持久层框架
自定义持久层框架(工程):
“本质就是对JDBC代码进行了封装
”
加载配置文件:根据配置文件的路径加载配置文件成字节输入流,存储内存中
创建Resources类 方法:getResourceAsStream(String path) 创建两个javaBean:(容器对象):存放的就是配置文件解析出来的内容
Configuration:核心配置类:存放sqlMapConfig.xml解析出来的内容 MappedStatement:映射配置类:存放mapper.xml解析出来的内容 解析配置文件:使用dom4j
创建类:SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 方法:build(InputStream in) 这个流就是刚才存在内存中的 使用dom4j解析配置文件,将解析出来的内容封装到容器对象中 创建SqlSessionFactory对象;生产sqlSession:会话对象(工厂模式 降低耦合,根据不同需求生产不同状态的对象) 创建sqlSessionFactory接口及实现类DefaultSqlSessionFactory
openSession(); 生产sqlSession 创建SqlSession接口及实现类DefaultSession
定义对数据库的CRUD操作 创建Executor接口及实现类SimpleExecutor实现类
query(Configuration con,MappedStatement ms,Object ...param);执行JDBC代码, Object ...param具体的参数值,可变参;
我们之前已经对持久层框架进行了分析,需要做6部分组成,如下:
1. 加载配置文件
我们要把用户端的配置文件成字节输入流并存到内存中:
新建Resource类,提供一个static InputStream getResourceAsStream(String path)方法,并返回inputstream
package com.dxh.io;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class Resource {
//根据配置文件的路径,将配置文件加载成字节输入流,存储在内存中
public static InputStream getResourceAsStream(String path){
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resource.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(path);
return resourceAsStream;
}
}
2. 创建JavaBean(容器对象)
之前我们说到,要把解析出来的配置文件封装成对象。
MappedStatement (存放SQL信息) Configuration (存放数据库配置信息)
// MappedStatement,我们存放SQL的信息
package com.dxh.pojo;
public class MappedStatement {
// id标识
private String id;
//返回值类型
private String resultType;
//参数值类型
private String paramterType;
//sql语句
private String sql;
getset省略...
}
这里我们把封装好的MappedStatement对象也放在Configuration中,同时我们不存放数据库的url、username...了,直接存放DataSource
package com.dxh.pojo;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Configuration {
private DataSource dataSource;
/**
* key statementId (就是namespace.id)
* value:封装好的MappedStatement对象
*/
Map mappedStatementMap = new HashMap<>();
getset省略...
}
3.解析xml文件
这一步我们解析两个xml文件sqlMapConfig.xml、mapper.xml
我们首先把解析的过程封装起来:新建XMLConfigBuild.java
package com.dxh.config;
import com.dxh.io.Resource;
import com.dxh.pojo.Configuration;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import java.beans.PropertyVetoException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
public class XMLConfigBuild {
private Configuration configuration;
public XMLConfigBuild() {
this.configuration = new Configuration();
}
/**
* 该方法就是将配置文件进行解析(dom4j),封装Configuration
*/
public Configuration parseConfig(InputStream inputStream) throws DocumentException, PropertyVetoException {
Document document = new SAXReader().read(inputStream);
//
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement();
List list = rootElement.selectNodes("//property");
Properties properties = new Properties();
for (Element element : list) {
String name = element.attributeValue("name");
String value = element.attributeValue("value");
properties.setProperty(name,value);
}
//C3P0连接池
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
comboPooledDataSource.setDriverClass(properties.getProperty("driverClass"));
comboPooledDataSource.setJdbcUrl(properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl"));
comboPooledDataSource.setUser(properties.getProperty("username"));
comboPooledDataSource.setPassword(properties.getProperty("password"));
configuration.setDataSource(comboPooledDataSource);
//mapper.xml解析 :拿到路径--字节输入流---dom4j解析
List mapperList = rootElement.selectNodes("//mapper");
for (Element element : mapperList) {
//拿到路径
String mapperPath = element.attributeValue("resource");
//字节输入流
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resource.getResourceAsStream(mapperPath);
//dom4j解析
// 因为解析完成后的MappedStatement要放在Configuration里,所以传入一个configuration进去
XMLMapperBuild xmlMapperBuild = new XMLMapperBuild(configuration);
xmlMapperBuild.parse(resourceAsStream);
}
return configuration;
}
}
3.1 解析Mapper.xml文件:
package com.dxh.config;
import com.dxh.pojo.Configuration;
import com.dxh.pojo.MappedStatement;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
public class XMLMapperBuild {
private Configuration configuration;
public XMLMapperBuild(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
public void parse(InputStream inputStream) throws DocumentException {
Document document = new SAXReader().read(inputStream);
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement();
String namespace = rootElement.attributeValue("namespace");
List list = rootElement.selectNodes("//select");
for (Element element : list) {
String id = element.attributeValue("id");
String resultType = element.attributeValue("resultType");
String paramterType = element.attributeValue("paramterType");
String sqlText = element.getTextTrim();
MappedStatement mappedStatement = new MappedStatement();
mappedStatement.setId(id);
mappedStatement.setParamterType(paramterType);
mappedStatement.setResultType(resultType);
mappedStatement.setSql(sqlText);
String key = namespace+"."+id;
configuration.getMappedStatementMap().put(key,mappedStatement);
}
}
}
很容易理解,因为我们解析后要返回Configuration对象,所以我们需要声明一个Configuration 并初始化。
我们把加载文件后的流传入,通过dom4j解析,并通过ComboPooledDataSource(C3P0连接池)生成我们需要的DataSource,并存入Configuration对象中。
Mapper.xml解析方式同理。
3.2 创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder类:有了上述两个解析方法后,我们创建一个类,用来调用这个方法,同时这个类返回SqlSessionFacetory
SqlSessionFacetory:用来生产sqlSession:sqlSession就是会话对象(工厂模式 降低耦合,根据不同需求生产不同状态的对象)
package com.dxh.sqlSession;
import com.dxh.config.XMLConfigBuild;
import com.dxh.pojo.Configuration;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import java.beans.PropertyVetoException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class SqlSessionFacetoryBuild {
public SqlSessionFacetory build(InputStream in) throws DocumentException, PropertyVetoException {
//1. 使用dom4j解析配置文件,将解析出来的内容封装到configuration中
XMLConfigBuild xmlConfigBuild = new XMLConfigBuild();
Configuration configuration = xmlConfigBuild.parseConfig(in);
//2. 创建sqlSessionFactory对象 工厂类:生产sqlSession:会话对象,与数据库交互的增删改查都封装在sqlSession中
DefaultSqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFacetory = new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(configuration);
return sqlSessionFacetory;
}
}
4. 创建SqlSessionFacetory接口和实现类
基于开闭原则我们创建SqlSessionFacetory接口和实现类DefaultSqlSessionFactory
接口中我们定义openSession()方法,用于生产SqlSession
package com.dxh.sqlSession;
public interface SqlSessionFacetory {
public SqlSession openSession();
}
package com.dxh.sqlSession;
import com.dxh.pojo.Configuration;
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFacetory{
private Configuration configuration;
public DefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration);
}
}
同样我们在DefaultSqlSessionFactory中传入Configuration,Configuration需要我们一直往下传递
5.创建SqlSession接口以及它的实现类
在接口中,我定义两个方法:
因为参数类型和个数我们都不知道,所以我们使用泛型,同时,传入statementId(namespace、. 、id 组成)
package com.dxh.sqlSession;
import java.util.List;
public interface SqlSession {
//查询多条
public List selectList(String statementId,Object... params) throws Exception ;
//根据条件查询单个
public T selectOne(String statementId,Object... params) throws Exception;
}
package com.dxh.sqlSession;
import com.dxh.pojo.Configuration;
import java.util.List;
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private Configuration configuration;
public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
@Override
public List selectList(String statementId, Object... params) throws Exception {
//将要完成对simpleExecutor里的query方法调用
SimpleExecutor simpleExecutor = new SimpleExecutor();
List 这里selectOne方法和selectList方法的参数结构都是一样的,所以我们可以通过selectList.get(0)的方式得到一个返回结果。而selectList中则是重点,我们需要创建一个对象SimpleExecutor并在其中执行SQL
6.创建Executor接口及实现类SimpleExecutor实现类
package com.dxh.sqlSession;
import com.dxh.pojo.Configuration;
import com.dxh.pojo.MappedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
public interface Executor {
/**
*
* @param configuration 数据库配置信息
* @param mappedStatement SQL配置信息
* @param params 可变参
* @return
*/
public List query(Configuration configuration, MappedStatement mappedStatement,Object... params) throws SQLException, Exception ;
}
package com.dxh.sqlSession;
import com.dxh.config.BoundSql;
import com.dxh.pojo.Configuration;
import com.dxh.pojo.MappedStatement;
import com.dxh.utils.GenericTokenParser;
import com.dxh.utils.ParameterMapping;
import com.dxh.utils.ParameterMappingTokenHandler;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author https://github.com/CoderXiaohui
* @Description
* @Date 2020-11-07 22:27
*/
public class SimpleExecutor implements Executor{
/**
* 就是在执行JDBC的代码
*/
@Override
public List query(Configuration configuration, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object... params) throws Exception {
//1. 注册驱动,获取链接
Connection connection = configuration.getDataSource().getConnection();
//2. 获取SQL语句
//假设获取的SQL是 : select * from user where id = #{id} and username = #{userName} JDBC是无法识别的,
// 所以要转换sql :select * from user where id = ?and username = ? ,转换过程中还需要对#{}中的值进行解析存储
String sql = mappedStatement.getSql();
BoundSql boundSql = getBoundSql(sql);
//3. 获取预处理对象:preparedStatement
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(boundSql.getSqlText());
//4. 设置参数
//获取到参数的全路径
String paramterType = mappedStatement.getParamterType();
Class paramterTypeClass = getClassType(paramterType);
List parameterMappingList = boundSql.getParameterMappingList();
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappingList.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappingList.get(i);
String content = parameterMapping.getContent();
//反射
Field declaredField = paramterTypeClass.getDeclaredField(content);
//暴力访问,防止它是私有的
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
Object o = declaredField.get(params[0]);
//下标从1开始
preparedStatement.setObject(i+1,o);
}
//5. 执行sql
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
String resultType = mappedStatement.getResultType();
Class resultTypeClass = getClassType(resultType);
ArrayList objects = new ArrayList<>();
//6. 封装返回结果集
while (resultSet.next()){
Object o = resultTypeClass.newInstance();
//元数据
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
//metaData.getColumnCount() :查询结果的总列数
for (int i = 1; i <= metaData.getColumnCount(); i++) {
//字段名
String columnName = metaData.getColumnName(i);
//字段的值
Object value = resultSet.getObject(columnName);
//使用反射或者内省,根据数据库表和实体的对应关系,完成封装
//PropertyDescriptor 内省库中的一个类,就是把resultTypeClass中的columnName属性来生产读写方法
PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor = new PropertyDescriptor(columnName, resultTypeClass);
Method writeMethod = propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod();
//把具体的值封装到o这个对象中
writeMethod.invoke(o,value);
}
objects.add(o);
}
return (List) objects;
}
private Class getClassType(String paramterType) throws ClassNotFoundException {
if (paramterType!=null){
Class aClass = Class.forName(paramterType);
return aClass;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 完成对#{}解析工作:
* 1. 将#{}使用?进行替换
* 2. 解析出#{}里面的值进行存储
* @param sql
* @return
*/
private BoundSql getBoundSql(String sql) {
//标记处理类:配置标记解析器来完成对占位符的处理工作
ParameterMappingTokenHandler parameterMappingTokenHandler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler();
GenericTokenParser genericTokenParser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", parameterMappingTokenHandler);
//返回解析后的sql
String parseSql = genericTokenParser.parse(sql);
//#{}里面解析出来的参数名称
List parameterMappings = parameterMappingTokenHandler.getParameterMappings();
BoundSql boundSql = new BoundSql(parseSql,parameterMappings);
return boundSql;
}
}
package com.dxh.config;
import com.dxh.utils.ParameterMapping;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 该方法的作用下面讲解
*/
public class BoundSql {
private String sqlText;//解析后的sql
private List parameterMappingList = new ArrayList<>();
public BoundSql(String sqlText, List parameterMappingList) {
this.sqlText = sqlText;
this.parameterMappingList = parameterMappingList;
}
}
这里的实现大致可分为6部分:
注册驱动,获取链接:通过传入的configuration得到datasource,然后调用 getConnection()得到链接获取SQL语句
我们mapper.xml的SQL语句是这样的select * from user where id = #{id} and username = #{username},需要转换为select * from user where id = ? and username =?这样JDBC才能认。同时我们需要把#{}中的参数赋值到?这个占位符处。这里我们定义了一个getBoundSql方法,通过标记处理类(配置标记解析器来完成对占位符的处理工作)解析成带有?的sql,同时把#{}里面的内容传入ParameterMapping中。通过 connection.prepareStatement(boundSql.getSqlText())得到预处理对象设置参数,我们在mapper.xml文件中已经写了 paramterType,有了入参类型的全路径我们可以通过反射获取其对象。根据ParameterMapping中存入的的#{}中的内容,通过反射获取其值,然后与下标绑定。执行SQL 封装返回结果集 这里使用内省 返回 (List) objects
7.结束
此时我们框架中的代码已经写完了。
8.测试类
package com.dxh.test;
import com.dxh.io.Resource;
import com.dxh.pojo.User;
import com.dxh.sqlSession.SqlSession;
import com.dxh.sqlSession.SqlSessionFacetory;
import com.dxh.sqlSession.SqlSessionFacetoryBuild;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.beans.PropertyVetoException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
public class IPersistenceTest {
@Test
public void test() throws Exception {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resource.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFacetory sqlSessionFacetory = new SqlSessionFacetoryBuild().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFacetory.openSession();
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setUsername("lucy");
User user2 = sqlSession.selectOne("user.selectOne",user);
System.out.println(user2.toString());
// List userList = sqlSession.selectList("user.selectList");
// for (User user1 : userList) {
// System.out.println(user1);
// }
}
}
执行结果:
User{id=1, username='lucy'}
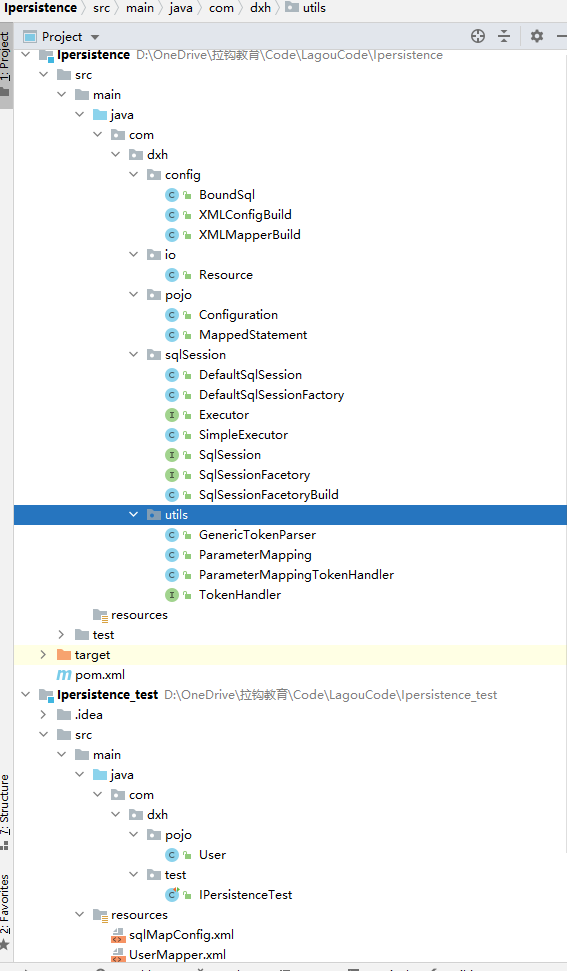
最终的目录结构:
5. 自定义持久层框架的优化
我们的自定义持久层框架已经完成了,下面我们分析下这个框架,看看还有没有明显的弊端。
首先,我们先模仿正常的项目,创建一个Dao层
package com.dxh.dao;
import com.dxh.pojo.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface IUserDao {
//查询所有用户
public List findAll() throws Exception ;
//根据条件进行查询
public User findByCondition(User user) throws Exception;
}
package com.dxh.dao;
import com.dxh.io.Resource;
import com.dxh.pojo.User;
import com.dxh.sqlSession.SqlSession;
import com.dxh.sqlSession.SqlSessionFacetory;
import com.dxh.sqlSession.SqlSessionFacetoryBuild;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
public class IUserDaoImpl implements IUserDao {
@Override
public List findAll() throws Exception {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resource.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFacetory sqlSessionFacetory = new SqlSessionFacetoryBuild().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFacetory.openSession();
List userList = sqlSession.selectList("user.selectList");
return userList;
}
@Override
public User findByCondition(User user) throws Exception {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resource.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFacetory sqlSessionFacetory = new SqlSessionFacetoryBuild().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFacetory.openSession();
User user2 = sqlSession.selectOne("user.selectOne",user);
return user2;
}
}
问题分析:
很明显存在代码重复的问题,他们的前三句话都一样(加载配置文件、创建SqlSessionFacetory、生产SqlSeesion)
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resource.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFacetory sqlSessionFacetory = new SqlSessionFacetoryBuild().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFacetory.openSession();statementId存在硬编码问题ListuserList = sqlSession.selectList("user.selectList");
User user2 = sqlSession.selectOne("user.selectOne",user);
解决思路:
使用代理模式生成Dao层代理实现类。
在SqlSession接口中增加一个方法并实现:
//为Dao接口生产代理实现类
public T getMapper(Class mapperClass);
@Override
public T getMapper(Class mapperClass) {
//使用JDK动态代理来为Dao接口生成代理对象,并返回
Object o = Proxy.newProxyInstance(DefaultSqlSession.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{mapperClass}, new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
return null;
}
});
return (T) o;
}
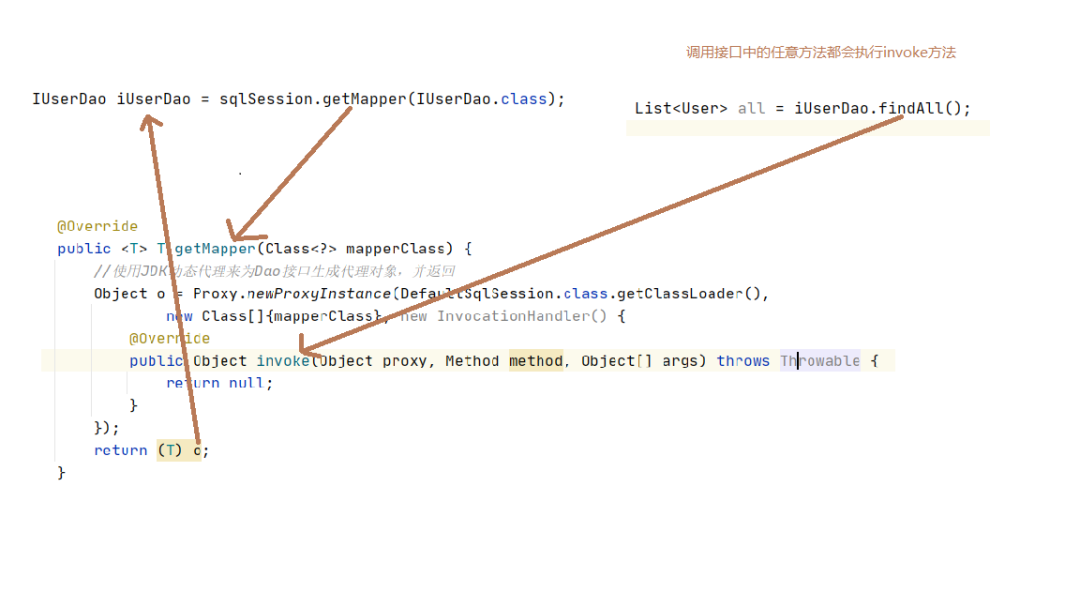
我们使用Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h)方法来生产代理对象。一会我们再来实现invoke方法。
那么此时我们如果再想执行方法应该这样做:
IUserDao iUserDao = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
List all = iUserDao.findAll();
通过 sqlSession.getMapper()方法获得代理对象通过代理对象调用 findAll()方法执行invoke方法
我们来看看invoke方法:
Object proxy :当前代理对象的引用 Method method :当前被调用方法的引用
比如我们当前的代理对象iUserDao调用的是findAll()方法,而method就是findAll方法的引用Object[] args :传递的参数,比如我们想要根据条件查询
编写invoke()方法:
我们要首先明确一点,不论如何封装,底层都还是执行JDBC代码,那么我们就要根据不同情况 调用selectList或者selectOne。
此时就有一个疑问了:selectList和selectOne都需要一个参数——statementId,而此时我们是拿不到statementId的。
但是我们可以根据method对象得到方法名,和方法所在类的全类名。
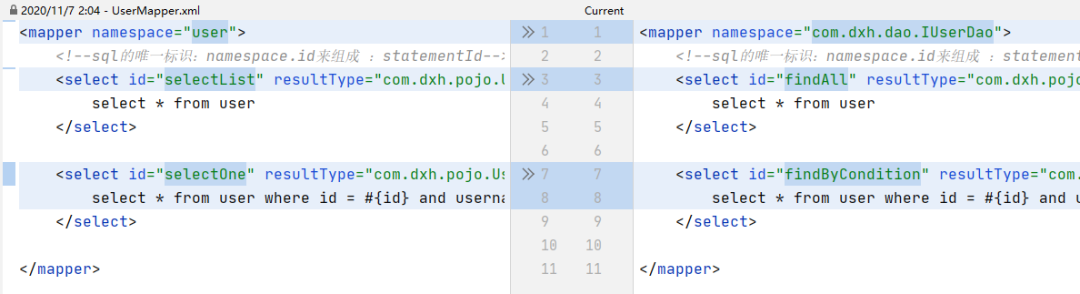
因此我们需要规范下statementId的组成:
“statementId = namespace.id = 方法所在类的全类名.方法名
”
修改UserMapper.xml
@Override
public T getMapper(Class mapperClass) {
//使用JDK动态代理来为Dao接口生成代理对象,并返回
Object o = Proxy.newProxyInstance(DefaultSqlSession.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{mapperClass}, new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//底层都还是执行JDBC代码 //根据不同情况 调用selectList或者selectOne
//准备参数:1. statementId
/**
* **此时就有一个疑问了:`selectList`和`selectOne`都需要一个参数——`statementId`,
* 而此时我们是拿不到`statementId`的。
* 但是我们可以根据`method`对象得到方法名,和方法所在类的全类名。
* 因此我们需要规范下statementId的组成:
* **statementId = namespace.id = 方法所在类的全类名.方法名
*/
String methodName = method.getName();
String className = method.getDeclaringClass().getName();
String statementId = className+"."+methodName;
//准备参数:2. args
//获取被调用方法的返回值类型
Type genericReturnType = method.getGenericReturnType();
//判断是否进行了泛型类型参数化 就是判断当前的返回值类型是否有泛型
if (genericReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType){
List selectList = selectList(statementId, args);
return selectList;
}
return selectOne(statementId,args);
}
});
return (T) o;
}
测试:
package com.dxh.test;
import com.dxh.dao.IUserDao;
import com.dxh.io.Resource;
import com.dxh.pojo.User;
import com.dxh.sqlSession.SqlSession;
import com.dxh.sqlSession.SqlSessionFacetory;
import com.dxh.sqlSession.SqlSessionFacetoryBuild;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.beans.PropertyVetoException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
public class IPersistenceTest {
@Test
public void test() throws Exception {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resource.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFacetory sqlSessionFacetory = new SqlSessionFacetoryBuild().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFacetory.openSession();
IUserDao iUserDao = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
List all = iUserDao.findAll();
System.out.println(all);
//打印结果:[User{id=1, username='lucy'}, User{id=2, username='李四'}, User{id=3, username='null'}]
User user1 = iUserDao.findByCondition(user);
System.out.println(user1);
//User{id=1, username='lucy'}
}
}
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/isdxh/p/13953368.html
作者:DXH's Blog
最近熬夜给大家准备了515套Java代码,有一些是业务类的小项目,比如Java博客项目,也有脚手架、也有平时用一些的工具类、21套小程序代码,也有一些游戏类的项目。
扫以下二维码并回复“828”即可获取
或者在本公众号对话框回复【828】马上获取