程序员必须清楚的 10 个高级 SQL 概念!
阅读本文大概需要 6.5 分钟。
1.常见表表达式(CTEs)
SELECT
name,
salary
FROM
People
WHERE
NAME IN ( SELECT DISTINCT NAME FROM population WHERE country = "Canada" AND city = "Toronto" )
AND salary >= (
SELECT
AVG( salary )
FROM
salaries
WHERE
gender = "Female")
with toronto_ppl as (
SELECT DISTINCT name
FROM population
WHERE country = "Canada"
AND city = "Toronto"
)
, avg_female_salary as (
SELECT AVG(salary) as avgSalary
FROM salaries
WHERE gender = "Female"
)
SELECT name
, salary
FROM People
WHERE name in (SELECT DISTINCT FROM toronto_ppl)
AND salary >= (SELECT avgSalary FROM avg_female_salary)
2.递归CTEs.
锚构件:返回CTE的基本结果的初始查询 递归成员:引用CTE的递归查询。这是所有与锚构件的联盟 停止递归构件的终止条件
with org_structure as (
SELECT id
, manager_id
FROM staff_members
WHERE manager_id IS NULL
UNION ALL
SELECT sm.id
, sm.manager_id
FROM staff_members sm
INNER JOIN org_structure os
ON os.id = sm.manager_id
3.临时函数
它允许您将代码的块分解为较小的代码块 它适用于写入清洁代码 它可以防止重复,并允许您重用类似于使用Python中的函数的代码。
SELECT name
, CASE WHEN tenure < 1 THEN "analyst"
WHEN tenure BETWEEN 1 and 3 THEN "associate"
WHEN tenure BETWEEN 3 and 5 THEN "senior"
WHEN tenure > 5 THEN "vp"
ELSE "n/a"
END AS seniority
FROM employees
CREATE TEMPORARY FUNCTION get_seniority(tenure INT64) AS (
CASE WHEN tenure < 1 THEN "analyst"
WHEN tenure BETWEEN 1 and 3 THEN "associate"
WHEN tenure BETWEEN 3 and 5 THEN "senior"
WHEN tenure > 5 THEN "vp"
ELSE "n/a"
END
);
SELECT name
, get_seniority(tenure) as seniority
FROM employees
4.使用CASE WHEN枢转数据
Initial table:
+------+---------+-------+
| id | revenue | month |
+------+---------+-------+
| 1 | 8000 | Jan |
| 2 | 9000 | Jan |
| 3 | 10000 | Feb |
| 1 | 7000 | Feb |
| 1 | 6000 | Mar |
+------+---------+-------+
Result table:
+------+-------------+-------------+-------------+-----+-----------+
| id | Jan_Revenue | Feb_Revenue | Mar_Revenue | ... | Dec_Revenue |
+------+-------------+-------------+-------------+-----+-----------+
| 1 | 8000 | 7000 | 6000 | ... | null |
| 2 | 9000 | null | null | ... | null |
| 3 | null | 10000 | null | ... | null |
+------+-------------+-------------+-------------+-----+-----------+
5.EXCEPT vs NOT IN
6.自联结
+----+-------+--------+-----------+
| Id | Name | Salary | ManagerId |
+----+-------+--------+-----------+
| 1 | Joe | 70000 | 3 |
| 2 | Henry | 80000 | 4 |
| 3 | Sam | 60000 | NULL |
| 4 | Max | 90000 | NULL |
+----+-------+--------+-----------+Answer:
SELECT
a.Name as Employee
FROM
Employee as a
JOIN Employee as b on a.ManagerID = b.Id
WHERE a.Salary > b.Salary
7.Rank vs Dense Rank vs Row Number
按购物,利润等数量排名最高值的客户 排名销售数量的顶级产品 以最大的销售排名顶级国家 排名在观看的分钟数,不同观众的数量等观看的顶级视频。
SELECT Name
, GPA
, ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY GPA desc)
, RANK() OVER (ORDER BY GPA desc)
, DENSE_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY GPA desc)
FROM student_grades

8.计算Delta值
# Comparing each month's sales to last month
SELECT month
, sales
, sales - LAG(sales, 1) OVER (ORDER BY month)
FROM monthly_sales
# Comparing each month's sales to the same month last year
SELECT month
, sales
, sales - LAG(sales, 12) OVER (ORDER BY month)
FROM monthly_sales
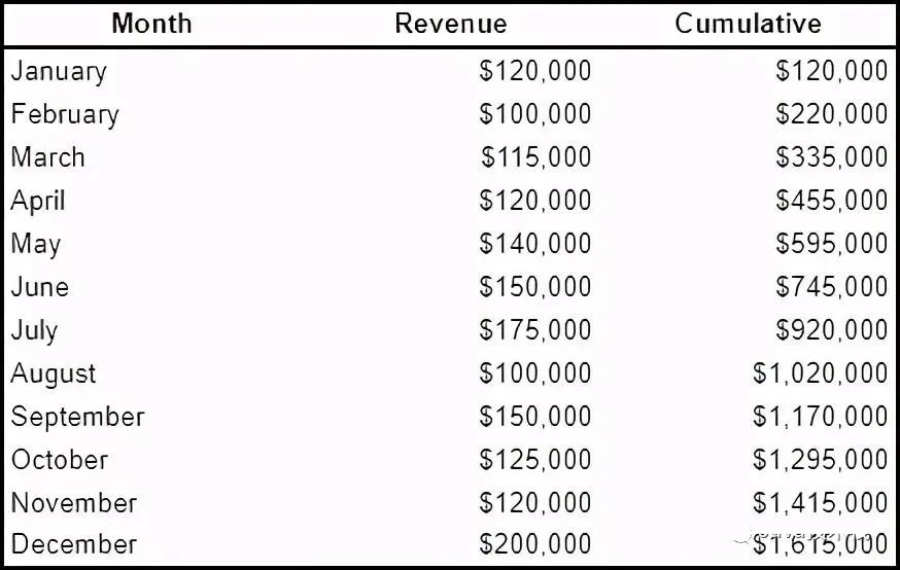
9.计算运行总数
SELECT Month
, Revenue
, SUM(Revenue) OVER (ORDER BY Month) AS Cumulative
FROM monthly_revenue
10.日期时间操纵
提炼 日元 date_add,date_sub. date_trunc.
+---------+------------------+------------------+
| Id(INT) | RecordDate(DATE) | Temperature(INT) |
+---------+------------------+------------------+
| 1 | 2015-01-01 | 10 |
| 2 | 2015-01-02 | 25 |
| 3 | 2015-01-03 | 20 |
| 4 | 2015-01-04 | 30 |
+---------+------------------+------------------+Answer:
SELECT
a.Id
FROM
Weather a,
Weather b
WHERE
a.Temperature > b.Temperature
AND DATEDIFF(a.RecordDate, b.RecordDate) = 1
