下载文件时,浏览器是怎么知道文件名称的?
当你在浏览器里下载一个文件时,浏览器是如何知道你所下载的文件的名称的呢?这或许是你从未考虑过的事情,但浏览器必须知道,否则,它就不知道如何保存文件。
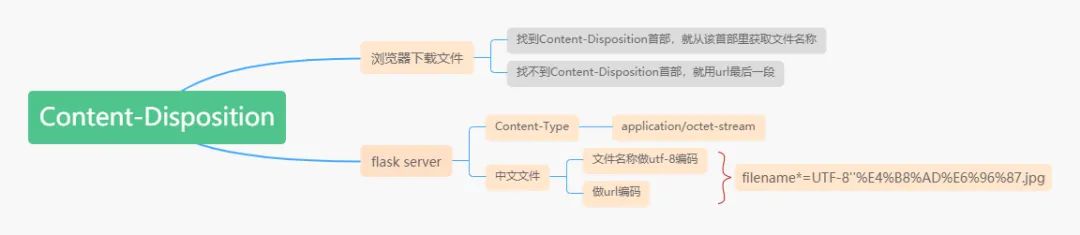
1. Content-Disposition 首部
如果能在在http 响应头中找到一个content-disposition 首部,那么就根据这个首部里的内容来确定所下载文件的名称,通常它的格式是这样的
Content-Disposition: attachment; filename=filename.jpg
attachment表示附件,filename 就是服务端希望你使用的文件名称。
如果在http 响应头中找不到content-disposition, 就会默认用url里的最后一段作为保存文件时的名称。
2. flask 实现文件下载
我编写一个简单点flask web 服务,来验证上面的观点,首先,我不设置Content-Disposition首部
from flask import Flask,send_file
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/download')
def download():
res = send_file('./t.jpg')
res.headers['Content-Type'] = 'application/octet-stream'
return res
app.run(debug=True)
在浏览器里访问 http://127.0.0.1:5000/download, 下载的文件自动被保存为download,文件的原始名称不会作为信息传递给客户端。
如果加上Content-Disposition首部,情况就不一样了
res.headers['Content-Disposition'] = 'attachment; filename=test.jpg'
下载后的文件自动被保存为test.jpg,浏览器通过响应头里的Content-Disposition首部确定了附件的文件名称。
3. flask 下载名称包含中文的文件
最后来看一下中文名称会不会受到影响
res.headers['Content-Disposition'] = 'attachment; filename=中文.jpg'
在浏览器里下载,程序报错了
UnicodeEncodeError: 'latin-1' codec can't encode characters in position 43-44: ordinal not in range(256)
一定是编码问题了,怎么解决呢,将包含中文的字符串进行utf-8编码同时进行url编码,最后以设置成特定的格式
filename = '中文.jpg'
context = "attachment; filename*=UTF-8''{utf_filename}".format(utf_filename=quote(filename.encode('utf-8')))
res.headers['Content-Disposition'] = context
这样,就可以下载成包含中文的文件了。
评论
