BufferedInputStream类方法,使用BufferedInputStream类读取文本文件内容
后台回复“Java”即可获赠Java学习资料
大家好,我是Java进阶者。
前言
本文主要学习BufferedInputStream类方法,使用BufferedInputStream类读取文本文件内容、BufferedOutputStream类向文件中写入内容和它的常用方法,接下来小编带大家一起来学习!
一、BufferedInputStream类方法
1.BufferedInputStream是缓冲输入流,可以减少访问磁盘的次数,提高文件的读取性能,它是FilterInputStream类的子类。
2.BufferedInputStream类方法有:
(1)int available()方法:用于返回输入流中可用的未读字节数,而不会由于下一次为此InputStream的方法的调用而阻塞。
(2)void close()方法:关闭此输入流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源。
(3)void mark(int readlimit)方法:输入流的当前位置做个标记,readlimit参数是输入流在标记位置失效前允许读取的字节数。
(4)boolean markSupported()方法:测试输入流是否支持mark和reset方法。
(5)int read()方法:读取一个字节。
(6)int read(byte[] b, int off, int len)方法:读取多个字节到字节数组b中,参数off是数组偏移量,参数len是读取数据的长度。
(7)void reset()方法:重置流的当前位置到前面标记的位置。
(8)long skip(long n)方法:略过流中的数据。若数据不够时,跳过仅有的字节,返回跳过的字节数。
二、BufferedInputStream类read(byte[] b, int off, int len)方法
1.public int read(byte[] b, int off, int len)方法:读取多个字节到字节数组b中,参数off是数组偏移量,参数len是读取数据的长度。
2.read(byte[] b, int off, int len)方法例子的实现:
(1)在text文件夹下创建一个test.txt文件并写入"helloworld,java!"内容。
(2)建立输入流BufferedInputStream, 缓冲区大小为8,读取字节流的前5个字节的代码的实现。
public class P09 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// TODO Auto-generated method stub//创建一个带有缓冲区的输入流BufferedInputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("text/test"), 8);//从字节流中读取5个字节byte temp[]=new byte[5];//read(byte[] b, int off, int len)方法in.read(temp,0,5);System.out.println("字节流的前5个字节是:"+new String(temp));}}
运行的结果如下图所示:

三、BufferedInputStream类mark()和reset()方法
1.void mark(int readlimit)方法:输入流的当前位置做个标记,readlimit参数是输入流在标记位置失效前允许读取的字节数。
2.void reset()方法:重置流的当前位置到前面标记的位置。
3.例子的实现:
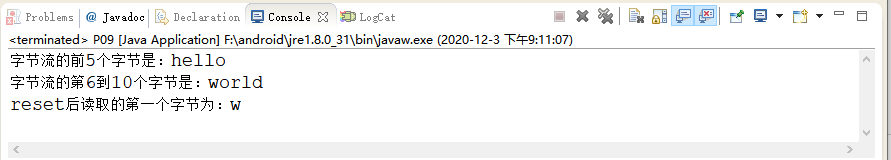
import java.io.*;public class P09 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// TODO Auto-generated method stub//创建一个带有缓冲区的输入流BufferedInputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("text/test"), 8);//从字节流中读取5个字节byte temp[]=new byte[5];//read(byte[] b, int off, int len)方法in.read(temp,0,5);System.out.println("字节流的前5个字节是:"+new String(temp));//标记测试in.mark(6);in.read(temp,0,5);System.out.println("字节流的第6到10个字节是:"+new String(temp));//reset()方法in.reset();System.out.printf("reset后读取的第一个字节为:%c", in.read());}}
运行的结果如下图所示:
四、BufferedOutputStream类
1.BufferedOutputStream类是字节缓冲输出流,它是FilterOutputStream类的子类。
2.BufferedOutputStream类常用的方法有以下所示:
(1)void write(int b)方法:一次写一个字节。
(2)void write(byte[] b,int off,int len)方法:从指定数组b中的从偏移量off开始len个字节写入文件输出流中。off参数表示数组偏移量,len表示要写入的字节数。
(3)void flush()方法:刷新此缓冲的输出流。这迫使所有缓冲的输出字节被写出到底层输出流中。
(4)void close()方法:关闭此输入流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源。
3.BufferedOutputStream方法的实现例子:
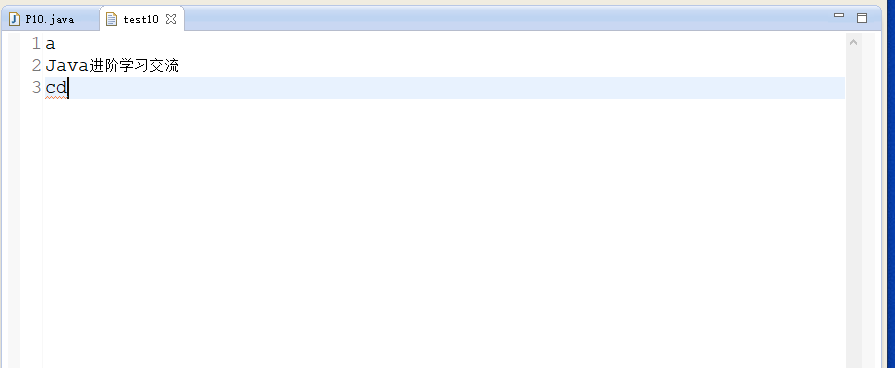
import java.io.*;public class P10 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// TODO Auto-generated method stub//创建一个带缓冲流的输出流BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("text/test10"));//在文本文件中写入小写a字母bos.write(97);//在文本文件中写入"Java进阶学习交流"bos.write("\nJava进阶学习交流\n".getBytes());//创建一个字节数组byte[] bytes = {97,98,99,100,101};//从偏移量2位置开始就是c,获取写入2个字节数bos.write(bytes,2,2);//刷新缓冲流bos.flush();//关闭流bos.close();}}
运行的结果如下所示:
五、总结
本文主要介绍了BufferedInputStream类方法、BufferedOutputStream类。介绍了BufferedInputStream的read(byte[] b, int off, int len)方法、mark()和reset()方法通过例子理解这些方法用法,使用BufferedInputStream来读取文本的内容。BufferedOutputStream类是字节缓冲输出流,它是FilterOutputStream类的子类。BufferedOutputStream来写入文本的内容。希望大家通过本文的学习,对你有所帮助!
我是Java进阶者,希望大家通过本文的学习,对你有所帮助!欢迎大家加我微信,有问题可以随时帮大家解决噢,交个朋友也好哇~
------------------- End -------------------
往期精彩文章推荐:
欢迎大家点赞,留言,转发,转载,感谢大家的相伴与支持
想加入Java学习群请在后台回复【入群】
万水千山总是情,点个【在看】行不行
