跨平台播放器开发 (七) ffplay 解封装、解码、音视频同步原理分析
简介
该篇主要介绍 「ffplay」 如何实现的解封装,解码和音视频同步的能力,下一篇文章会根据 「ffplay」 已提供的能力,会把一些基础能力给独立出来,以便于后续的扩展。
解封装
解封装,顾名思义其实就是将封装的包裹进行拆解,拿到对应音频、视频的压缩数据。下面我们来看下解封装的主要架构图
下面借用「雷神」绘制的 ffplay 架构图,我提取了对应的解封装:
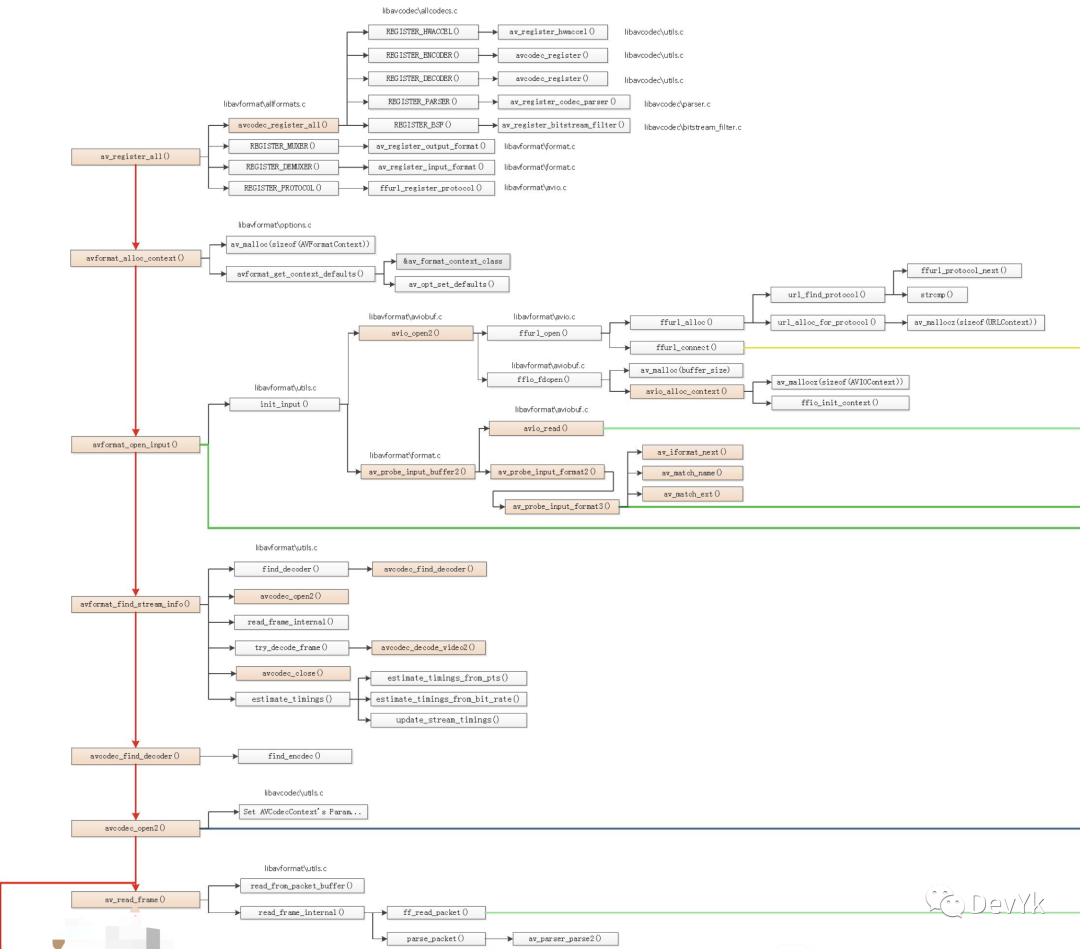
「av_register_all」
如下代码所示,其实在高版本中,可以不需要调用 av_register_all.
/* register all codecs, demux and protocols */
#if CONFIG_AVDEVICE
avdevice_register_all();
#endif
「avformat_open_input」
int avformat_open_input(AVFormatContext **ps, const char *url, ff_const59 AVInputFormat *fmt, AVDictionary **options);
avformat_open_input 的含义就是打开一个输入流并读取封装 header。最后必须使用 avformat_close_input() 关闭流。
「avformat_find_stream_info」
int avformat_find_stream_info(AVFormatContext *ic, AVDictionary **options);
avformat_find_stream_info 函数,主要是探测音频,视频流的基本信息,内部会打开解码,进行解码探测。
「av_read_frame」
int av_read_frame(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt);
av_read_frame 该函数主要是将解封装后的音频、视频、字幕数据读取出来。在 ffplay 源码中有一处需要注意,代码如下:
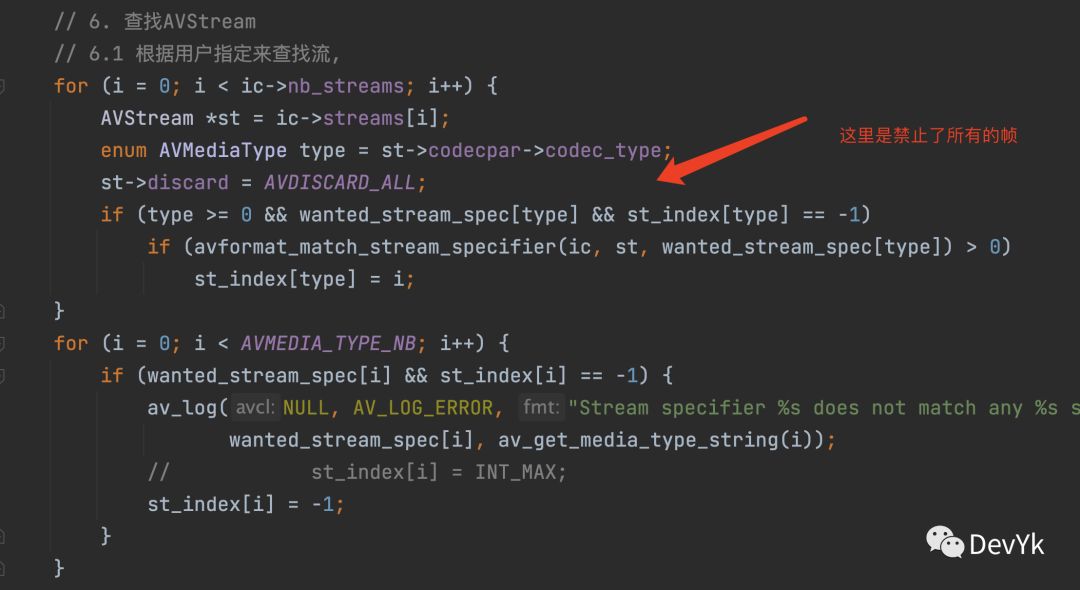
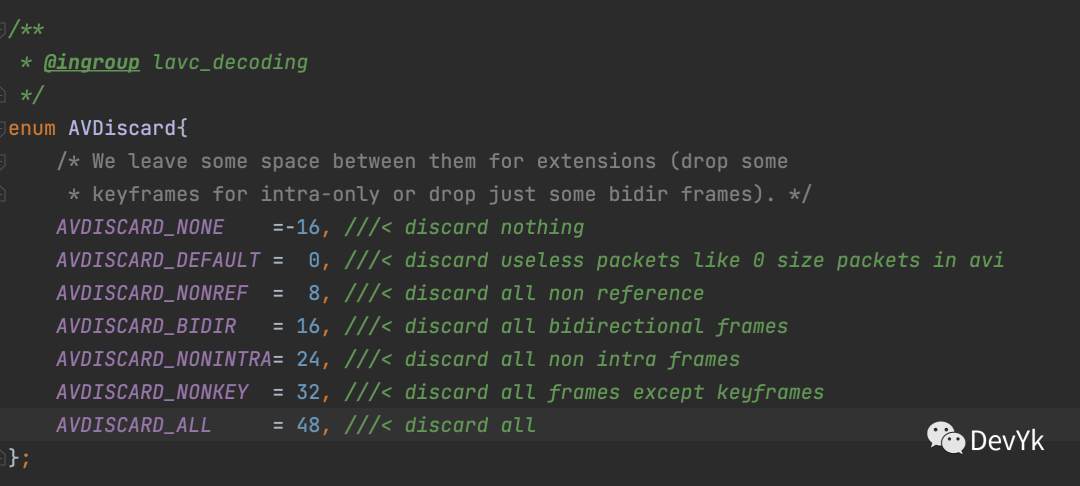
根据源码中的提示,ffplay 将 discard 设置为了禁止「所有帧的读取」 。因为我在解耦 ffplay 代码的时候,没有注意该函数,导致在测试解封装,读取数据失败。
ffplay 中的 av_read_fream 函数,会一直在 read_thread线层中进行死循环读取。
解码
ffplay 中的音频、视频、字幕解码分别创建了独立的线程,在 stream_component_open函数中, 主要代码如下:
static int stream_component_open(VideoState *is, int stream_index) {
...
/* 根据codec_id查找解码器 */
codec = avcodec_find_decoder(avctx->codec_id);
...
//打开解码器
if ((ret = avcodec_open2(avctx, codec, &opts)) < 0) {
goto fail;
}
//在这里对流信息设置了默认,默认我的理解就是可以读取所有的帧
ic->streams[stream_index]->discard = AVDISCARD_DEFAULT;
switch (avctx->codec_type) {
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO:
...
/* prepare audio output 准备音频输出*/
//调用audio_open打开sdl音频输出,实际打开的设备参数保存在audio_tgt,返回值表示输出设备的缓冲区大小
if ((ret = audio_open(is, channel_layout, nb_channels, sample_rate, &is->audio_tgt)) < 0)
goto fail;
...
// 初始化ffplay封装的音频解码器
decoder_init(&is->auddec, avctx, &is->audioq, is->continue_read_thread);
...
// 启动音频解码线程
if ((ret = decoder_start(&is->auddec, audio_thread, "audio_decoder", is)) < 0)
goto out;
SDL_PauseAudioDevice(audio_dev, 0);
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO:
...
// 初始化ffplay封装的视频解码器
decoder_init(&is->viddec, avctx, &is->videoq, is->continue_read_thread);
// 启动视频频解码线程
if ((ret = decoder_start(&is->viddec, video_thread, "video_decoder", is)) < 0)
goto out;
is->queue_attachments_req = 1; // 使能请求mp3、aac等音频文件的封面
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_SUBTITLE: // 视频是类似逻辑处理
...
decoder_init(&is->subdec, avctx, &is->subtitleq, is->continue_read_thread);
if ((ret = decoder_start(&is->subdec, subtitle_thread, "subtitle_decoder", is)) < 0)
goto out;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
根据上面简略代码,可以看出,音频、视频、字幕,分别在 audio_thread、video_thread、subtitle_thread 线程中进行解码。
解码的核心 api 如下:
读取解码后的 AVFrame 原始数据
avcodec_receive_frame(d->avctx, frame);
将压缩数据发送到解码缓冲队列中
avcodec_send_packet(d->avctx, &pkt);
自此,再配合 packet queue, 只要队列中有数据,那么就会调用解码函数,解码成功就会存入对应的 frame queue 中。
音视频同步
何为音视频同步,其实它的作用就是保证音频播放的时间与视频播放的时间要在一条时间线上。所以这里就产生出了,如何保证在一条时间线上,这个时候就需要一个参考,在 ffplay 中默认使用了视频参考音频的方式,
其一,视频以音频为基准(推荐,用的最多):
- 视频播放时间以音频播放时间为准,如果视频比音频快,那么将等待其实就是定帧,如果视频比音频慢,就需要进行丢帧处理了。
其二,音频以视频 pts 为基准
其三,以外部时钟为基准
如果视频向音频同步,那么首先是需要音频播放的时候,将音频播放的 pts 给存储起来,在 ffplay 源码中,是这样进行操作的,主要是在 sdl_audio_callback 代码中,我这里为了便于理解,直接上伪代码吧。
「音频播放 pts 设置」
static void sdl_audio_callback() {
//拿到回调开始时间
long audio_callback_time = av_gettime_relative(); // while 可能产生延迟,最后时间需要算上中间处理的时间
//PCM 音频采样 1024 * 2 通道 * 16/2 byte * 缓存 2 帧 = 8192;
int sdl_audio_buf_size = 8192;
int audio_pts = 0;
int ret = sdl_audio_buf_size;
while (ret > 0)//循环读取,直到读取到足够的数据
{
//1、拿到解码的数据
uint8_t *data_ = NULL;
//2. 拿到解码后的 PCM 数据
int size = get_audio_frame(&data_);
//3、将 pcm 数据,copy 到 sdl 缓冲区中
copy_to_sdl(data_);
ret -= size;
audio_pts+=size/audio_sample_rate;
}
//4、设置音频时钟
//这里的含义就是为了更加准确的计算出当前实际播放了多少音频数据
set_audio_clock(audio_pts-(实际写入到缓存区的音频数据/(sample_rate*2*2)),audio_callback_time);
}
ffplay 主要设置时钟的代码,我给简化成了伪代码,这样看起来或许会更好理解一点。
「视频播放同步设置」
这里我还是以伪代码进行同步
static void video_refresh()
{
//拿到当前时间
int time = av_gettime_relative() / 1000000.0;
//1、计算当前帧显示的持续时长
int last_duration = 当前视频帧pts - 上一帧pts;
double delay = last_duration;
//2、拿到真正需要 delay 时间
double diff = 当前视频帧pts - 获取音频播放的pts;
//拿到最大的一个同步范围,ffplay 最小是0.04s ,最大是 0.1s
double sync_threshold = FFMAX(0.04,
FFMIN(0.1, delay));
if (diff <= -sync_threshold) { // 视频已经落后了
delay = FFMAX(0, delay + diff); // 上一帧持续的时间往小的方向去调整
} else if (diff >= sync_threshold && delay > AV_SYNC_FRAMEDUP_THRESHOLD) {// 视频超前
delay = delay + diff; // 上一帧持续时间往大的方向去调整
} else if (diff >= sync_threshold) {
// 上一帧持续时间往大的方向去调整
delay = 2 * delay;
}
//设置最后一帧显示的时间
frame_timer += delay;
if (frame_timer <= 0)//如果是第一帧,那么直接设置当前系统时间
frame_timer = time;
//判断是否丢帧,如果已经大于显示的一帧数据,那么进行丢帧
double next_duration = get_next_frame().pts - get_last_frame().pts;
if (time > frame_timer + next_duration){
drop_frame();
return;
}
//显示视频帧
display();
//其实就是显示多久
sleep(delay);
}
上面伪代码的注释都比较清晰,相信大家能看得懂,或者你可以直接看 ffplay 源码部分
SDL 预览
SDL预览部分,我这里就不必在分析了,因为代码都是一样的。
总结
该篇简略的分析了 ffplay 实现原理,个人觉得 ffplay 内部最不容易理解的其实是音视频同步,其它都还是比较容易看的懂。建议还是自己读一下 ffplay 源码,这样才会对 ffplay 的理解更加深入。
参考
- ffplay4.2.1
