当初男票就是用 canvas 画一场流星雨把我追到手的
开始
妹子都喜欢流星,如果她说不喜欢,那她一定是一个假妹子。
现在就一起来做一场流星雨,用程序员的野路子浪漫一下。
要画一场流星雨,首先,自然我们要会画一颗流星。
玩过 canvas 的同学,你画圆画方画线条这么 6,如果说叫你画下面这个玩意儿,你会不会觉得你用的是假 canvas?canvas 没有画一个带尾巴玩意儿的 api 啊。

画一颗流星
是的,的却是没这个 api,但是不代表我们画不出来。流星就是一个小石头,然后因为速度过快产生大量的热量带动周围的空气发光发热,所以经飞过的地方看起来就像是流星的尾巴,我们先研究一下流星这个图像,整个流星处于他自己的运动轨迹之中,当前的位置最亮,轮廓最清晰,而之前划过的地方离当前位置轨迹距离越远就越暗淡越模糊。
上面的分析结果很关键, canvas 上是每一帧就重绘一次,每一帧之间的时间间隔很短。流星经过的地方会越来越模糊最后消失不见,那有没有可以让画布画的图像每过一帧就变模糊一点而不是全部清除的办法?如果可以这样,就可以把每一帧用线段画一小段流星的运动轨迹,最后画出流星的效果。

骗纸!你也许会说,这那里像流星了???
别急,让我多画几段给你看看。

什么?还是不像?我们把它画小点,这下总该像了把?

上面几幅图我是在 ps 上模拟的,本质上 ps 也是在画布上绘画,我们马上在 canvas 上试试。
那,直接代码实现一下。
// 坐标
class Crood {
constructor(x=0, y=0) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
setCrood(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
copy() {
return new Crood(this.x, this.y);
}
}
// 流星
class ShootingStar {
constructor(init=new Crood, final=new Crood, size=3, speed=200, onDistory=null) {
this.init = init; // 初始位置
this.final = final; // 最终位置
this.size = size; // 大小
this.speed = speed; // 速度:像素/s
// 飞行总时间
this.dur = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(this.final.x-this.init.x, 2) + Math.pow(this.final.y-this.init.y, 2)) * 1000 / this.speed;
this.pass = 0; // 已过去的时间
this.prev = this.init.copy(); // 上一帧位置
this.now = this.init.copy(); // 当前位置
this.onDistory = onDistory;
}
draw(ctx, delta) {
this.pass += delta;
this.pass = Math.min(this.pass, this.dur);
let percent = this.pass / this.dur;
this.now.setCrood(
this.init.x + (this.final.x - this.init.x) * percent,
this.init.y + (this.final.y - this.init.y) * percent
);
// canvas
ctx.strokeStyle = '#fff';
ctx.lineCap = 'round';
ctx.lineWidth = this.size;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(this.now.x, this.now.y);
ctx.lineTo(this.prev.x, this.prev.y);
ctx.stroke();
this.prev.setCrood(this.now.x, this.now.y);
if (this.pass === this.dur) {
this.distory();
}
}
distory() {
this.onDistory && this.onDistory();
}
}
// effet
let cvs = document.querySelector('canvas');
let ctx = cvs.getContext('2d');
let T;
let shootingStar = new ShootingStar(
new Crood(100, 100),
new Crood(400, 400),
3,
200,
()=>{cancelAnimationFrame(T)}
);
let tick = (function() {
let now = (new Date()).getTime();
let last = now;
let delta;
return function() {
delta = now - last;
delta = delta > 500 ? 30 : (delta < 16? 16 : delta);
last = now;
// console.log(delta);
T = requestAnimationFrame(tick);
ctx.save();
ctx.fillStyle = 'rgba(0,0,0,0.2)'; // 每一帧用 “半透明” 的背景色清除画布
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, cvs.width, cvs.height);
ctx.restore();
shootingStar.draw(ctx, delta);
}
})();
tick();
效果:一颗流星

sogoyi 快看,一颗活泼不做作的流星!!! 是不是感觉动起来更加逼真一点?
流星雨
我们再加一个流星雨 MeteorShower 类,生成多一些随机位置的流星,做出流星雨。
// 坐标
class Crood {
constructor(x=0, y=0) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
setCrood(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
copy() {
return new Crood(this.x, this.y);
}
}
// 流星
class ShootingStar {
constructor(init=new Crood, final=new Crood, size=3, speed=200, onDistory=null) {
this.init = init; // 初始位置
this.final = final; // 最终位置
this.size = size; // 大小
this.speed = speed; // 速度:像素/s
// 飞行总时间
this.dur = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(this.final.x-this.init.x, 2) + Math.pow(this.final.y-this.init.y, 2)) * 1000 / this.speed;
this.pass = 0; // 已过去的时间
this.prev = this.init.copy(); // 上一帧位置
this.now = this.init.copy(); // 当前位置
this.onDistory = onDistory;
}
draw(ctx, delta) {
this.pass += delta;
this.pass = Math.min(this.pass, this.dur);
let percent = this.pass / this.dur;
this.now.setCrood(
this.init.x + (this.final.x - this.init.x) * percent,
this.init.y + (this.final.y - this.init.y) * percent
);
// canvas
ctx.strokeStyle = '#fff';
ctx.lineCap = 'round';
ctx.lineWidth = this.size;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(this.now.x, this.now.y);
ctx.lineTo(this.prev.x, this.prev.y);
ctx.stroke();
this.prev.setCrood(this.now.x, this.now.y);
if (this.pass === this.dur) {
this.distory();
}
}
distory() {
this.onDistory && this.onDistory();
}
}
class MeteorShower {
constructor(cvs, ctx) {
this.cvs = cvs;
this.ctx = ctx;
this.stars = [];
this.T;
this.stop = false;
this.playing = false;
}
createStar() {
let angle = Math.PI / 3;
let distance = Math.random() * 400;
let init = new Crood(Math.random() * this.cvs.width|0, Math.random() * 100|0);
let final = new Crood(init.x + distance * Math.cos(angle), init.y + distance * Math.sin(angle));
let size = Math.random() * 2;
let speed = Math.random() * 400 + 100;
let star = new ShootingStar(
init, final, size, speed,
()=>{this.remove(star)}
);
return star;
}
remove(star) {
this.stars = this.stars.filter((s)=>{ return s !== star});
}
update(delta) {
if (!this.stop && this.stars.length < 20) {
this.stars.push(this.createStar());
}
this.stars.forEach((star)=>{
star.draw(this.ctx, delta);
});
}
tick() {
if (this.playing) return;
this.playing = true;
let now = (new Date()).getTime();
let last = now;
let delta;
let _tick = ()=>{
if (this.stop && this.stars.length === 0) {
cancelAnimationFrame(this.T);
this.playing = false;
return;
}
delta = now - last;
delta = delta > 500 ? 30 : (delta < 16? 16 : delta);
last = now;
// console.log(delta);
this.T = requestAnimationFrame(_tick);
ctx.save();
ctx.fillStyle = 'rgba(0,0,0,0.2)'; // 每一帧用 “半透明” 的背景色清除画布
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, cvs.width, cvs.height);
ctx.restore();
this.update(delta);
}
_tick();
}
start() {
this.stop = false;
this.tick();
}
stop() {
this.stop = true;
}
}
// effet
let cvs = document.querySelector('canvas');
let ctx = cvs.getContext('2d');
let meteorShower = new MeteorShower(cvs, ctx);
meteorShower.start();
效果:流星雨

透明背景
先不急着激动,这个流星雨有点单调,可以看到上面的代码中,每一帧,我们用了透明度为 0.2 的黑色刷了一遍画布,背景漆黑一片,如果说我们的需求是透明背景呢?
比如,我们要用这个夜景图片做背景,然后在上面加上我们的流星,我们每一帧刷一层背景的小伎俩就用不了啦。因为我们要保证除开流星之外的部分,应该是透明的。

这里就要用到一个冷门的属性了,globalCompositeOperation,全局组合操作?原谅我放荡不羁的翻译。
这个属性其实就是用来定义后绘制的图形与先绘制的图形之间的组合显示效果的。
他可以设置这些值
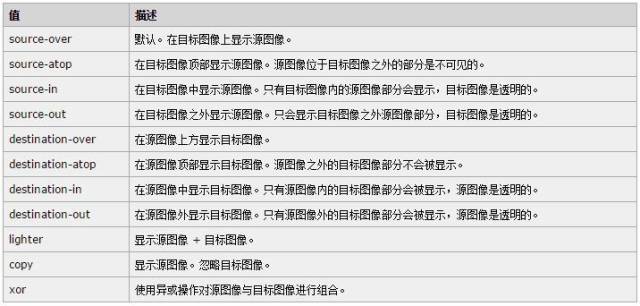
这些属性说明没必要仔细看,更不用记下来,直接看 api 示例 运行效果就很清楚了。示例里,先绘制的是填充正方形,后绘制的是填充圆形。
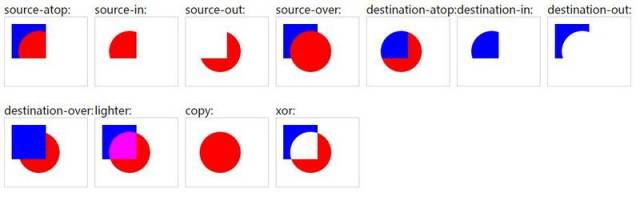
是不是豁然开朗,一目了然?
对于我们来说,原图像是每一帧画完的所有流星,目标图像是画完流星之后半透明覆盖画布的黑色矩形。而我们每一帧要保留的就是,上一帧 0.8 透明度的流星,覆盖画布黑色矩形我们不能显示。
注意这里的 destination-out 和 destination-in,示例中这两个属性最终都只有部分源图像保留了下来,符合我们只要保留流星的需求。我觉得 w3cschool 上描述的不是很正确,我用我自己的理解概括一下。
destination-in :只保留了源图像(矩形)和目标图像(圆)交集区域的源图像
destination-out:只保留了源图像(矩形)减去目标图像(圆)之后区域的源图像
上述示例目标图像的透明度是 1,源图像被减去的部分是完全不见了。而我们想要的是他可以按照目标透明度进行部分擦除。改一下示例里的代码看看是否支持半透明的计算。
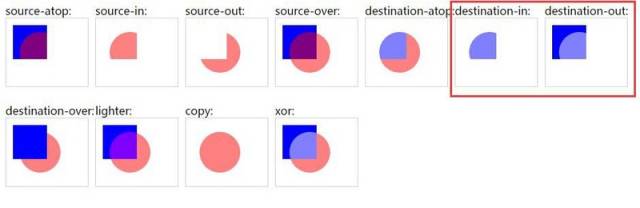
看来这个属性支持半透明的计算。源图像和目标图像交叠的部分以半透明的形式保留了下来。也就是说如果我们要保留 0.8 透明度的流星,可以这样设置 globalCompositeOperation
ctx.fillStyle = 'rgba(0,0,0,0.8)'
globalCompositeOperation = 'destination-in';
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, cvs.width, cvs.height);
// 或者
ctx.fillStyle = 'rgba(0,0,0,0.2)'
globalCompositeOperation = 'destination-out';
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, cvs.width, cvs.height);
最终效果
加上 globalCompositeOperation 之后的效果既最终效果:

快约上你的妹子看流星雨吧。
...
什么?你没有妹子?
源自:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000008664249
声明:文章著作权归作者所有,如有侵权,请联系小编删除
