妙用Java 8中的 Function接口,消灭if...else(非常新颖的写法)
程序员的成长之路
互联网/程序员/技术/资料共享
阅读本文大概需要 3.5 分钟。
来自:juejin.cn/post/7011435192803917831
-
Function函数式接口
-
Supplier供给型函数
-
Consumer消费型函数
-
Runnable无参无返回型函数
-
Function函数的表现形式为接收一个参数,并返回一个值。Supplier、Consumer和Runnable可以看作Function的一种特殊表现形式
-
使用小技巧
-
处理抛出异常的if
-
处理if分支操作
-
如果存在值执行消费操作,否则执行基于空的操作
在开发过程中经常会使用
if...else...进行判断抛出异常、分支处理等操作。这些if...else...充斥在代码中严重影响了代码代码的美观,这时我们可以利用Java 8的Function接口来消灭if...else...。 if (...){
throw new RuntimeException("出现异常了");
}
if (...){
doSomething();
} else {
doOther();
}
Function 函数式接口
使用注解
@FunctionalInterface标识,并且只包含一个抽象方法的接口是函数式接口。函数式接口主要分为Supplier供给型函数、Consumer消费型函数、Runnable无参无返回型函数和Function有参有返回型函数。
Function可以看作转换型函数
Supplier供给型函数
Supplier的表现形式为不接受参数、只返回数据 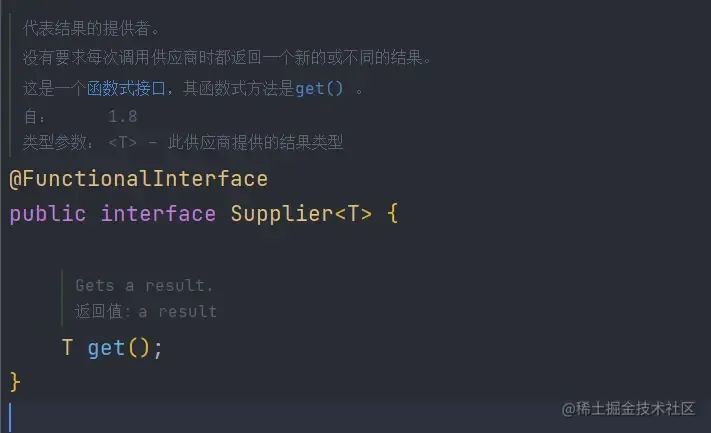
图片
Consumer消费型函数
Consumer消费型函数和Supplier刚好相反。Consumer接收一个参数,没有返回值 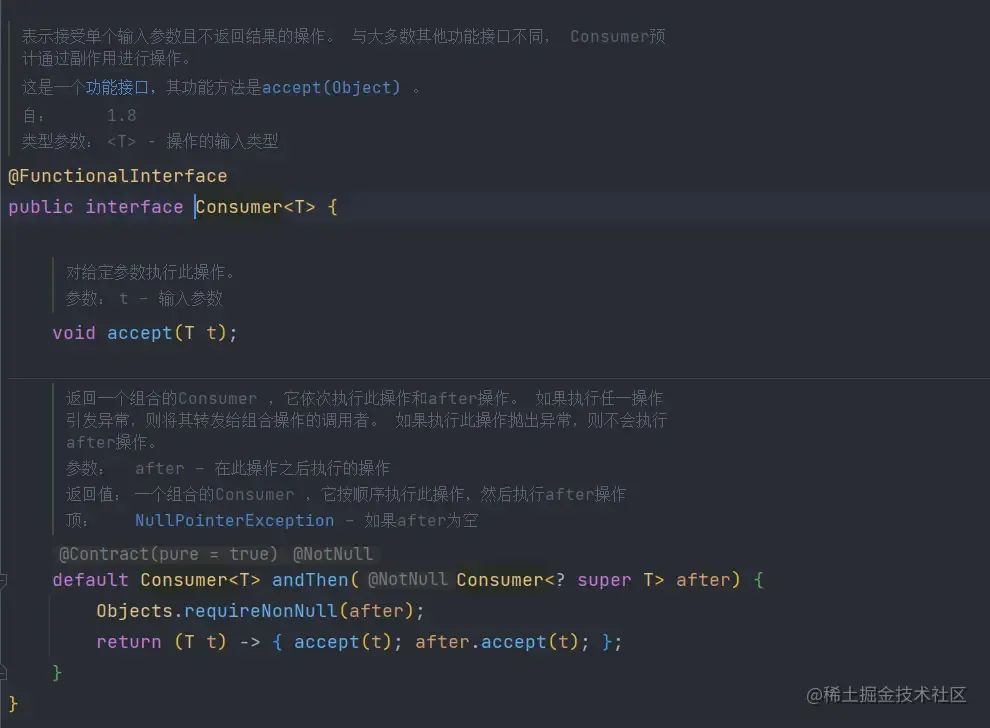
图片
Runnable无参无返回型函数
Runnable的表现形式为即没有参数也没有返回值 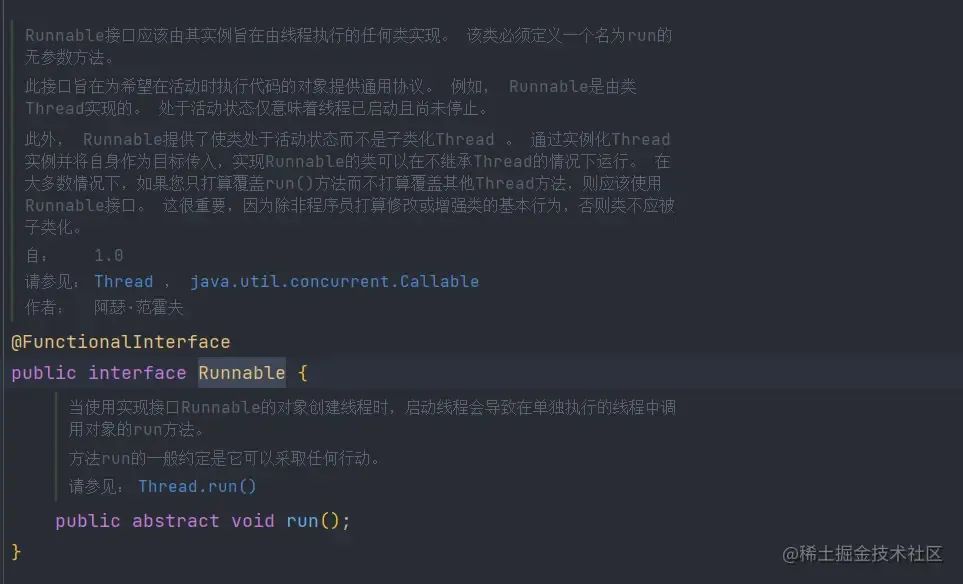
图片
Function函数的表现形式为接收一个参数,并返回一个值。Supplier、Consumer和Runnable可以看作Function的一种特殊表现形式
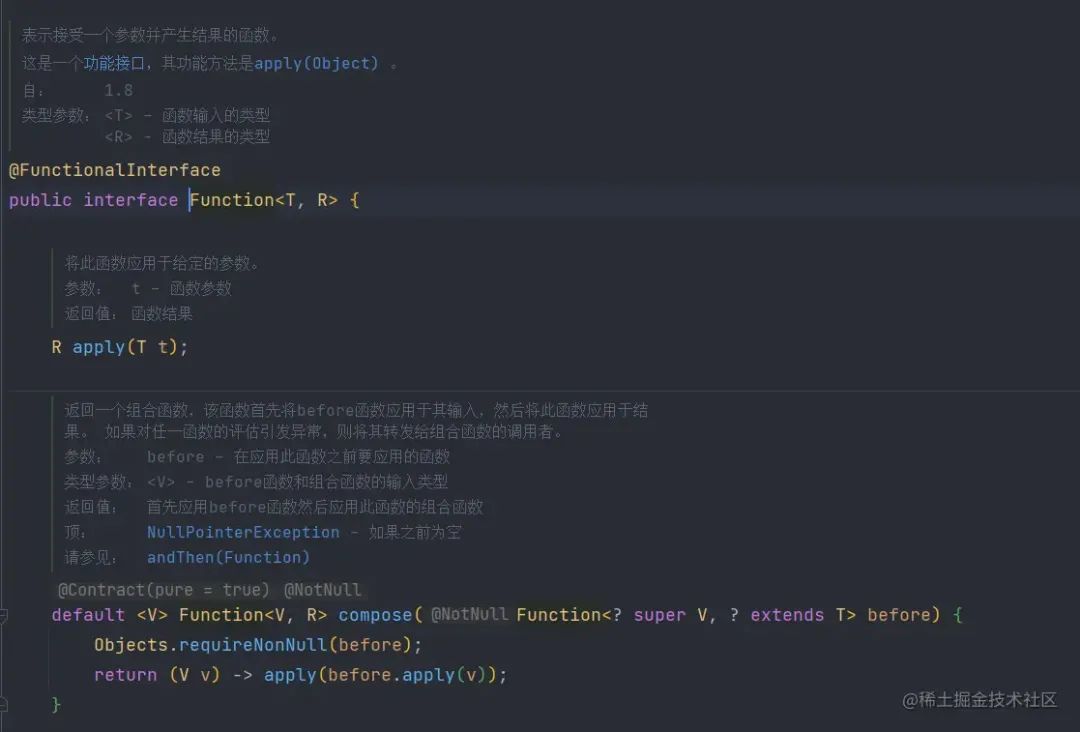
图片
使用小技巧
处理抛出异常的if
-
定义函数
定义一个抛出异常的形式的
函数式接口, 这个接口只有参数没有返回值是个消费型接口 /**
* 抛异常接口
**/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ThrowExceptionFunction {
/**
* 抛出异常信息
*
* @param message 异常信息
* @return void
**/
void throwMessage(String message);
}
-
编写判断方法
创建工具类
VUtils并创建一个isTure方法,方法的返回值为刚才定义的函数式接口-ThrowExceptionFunction。ThrowExceptionFunction的接口实现逻辑为当参数b为true时抛出异常 /**
* 如果参数为true抛出异常
*
* @param b
* @return com.example.demo.func.ThrowExceptionFunction
**/
public static ThrowExceptionFunction isTure(boolean b){
return (errorMessage) -> {
if (b){
throw new RuntimeException(errorMessage);
}
};
}
-
使用方式
调用工具类参数参数后,调用
函数式接口的throwMessage方法传入异常信息。当出入的参数为false时正常执行 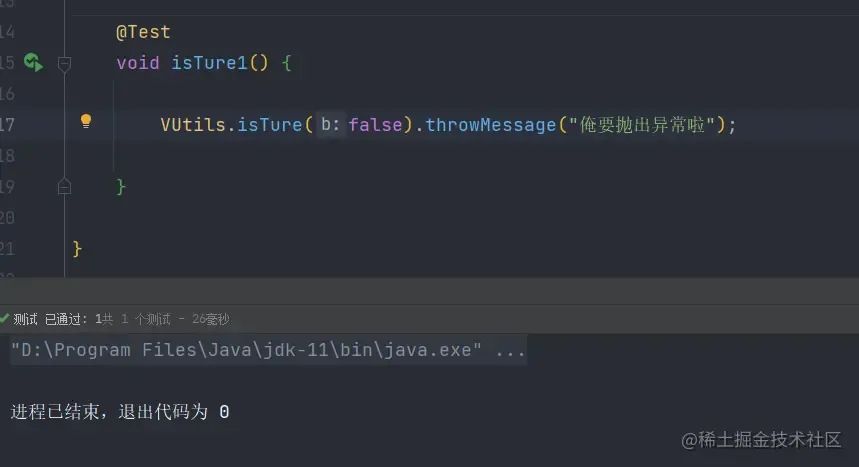
图片
当出入的参数为
true时抛出异常 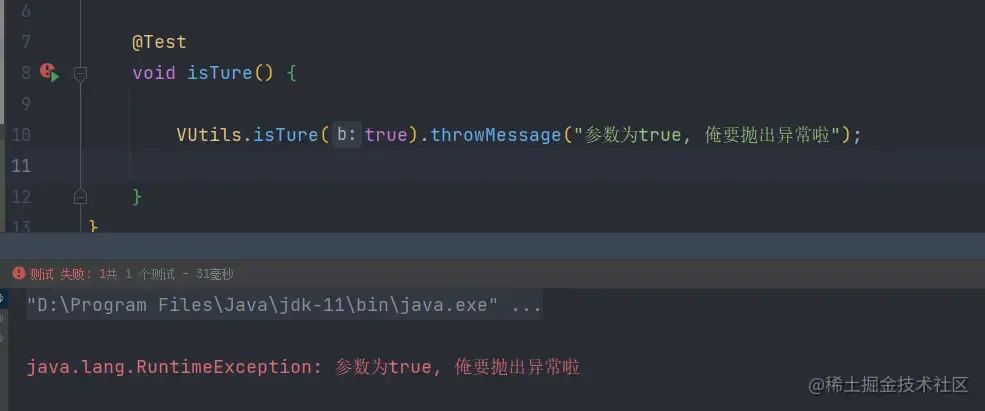
图片
处理if分支操作
-
定义函数式接口
创建一个名为
BranchHandle的函数式接口,接口的参数为两个Runnable接口。这两个两个Runnable接口分别代表了为true或false时要进行的操作 /**
* 分支处理接口
**/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BranchHandle {
/**
* 分支操作
*
* @param trueHandle 为true时要进行的操作
* @param falseHandle 为false时要进行的操作
* @return void
**/
void trueOrFalseHandle(Runnable trueHandle, Runnable falseHandle);
}
-
编写判断方法
创建一个名为
isTureOrFalse的方法,方法的返回值为刚才定义的函数式接口-BranchHandle。 /**
* 参数为true或false时,分别进行不同的操作
*
* @param b
* @return com.example.demo.func.BranchHandle
**/
public static BranchHandle isTureOrFalse(boolean b){
return (trueHandle, falseHandle) -> {
if (b){
trueHandle.run();
} else {
falseHandle.run();
}
};
}
-
使用方式
参数为
true时,执行trueHandle 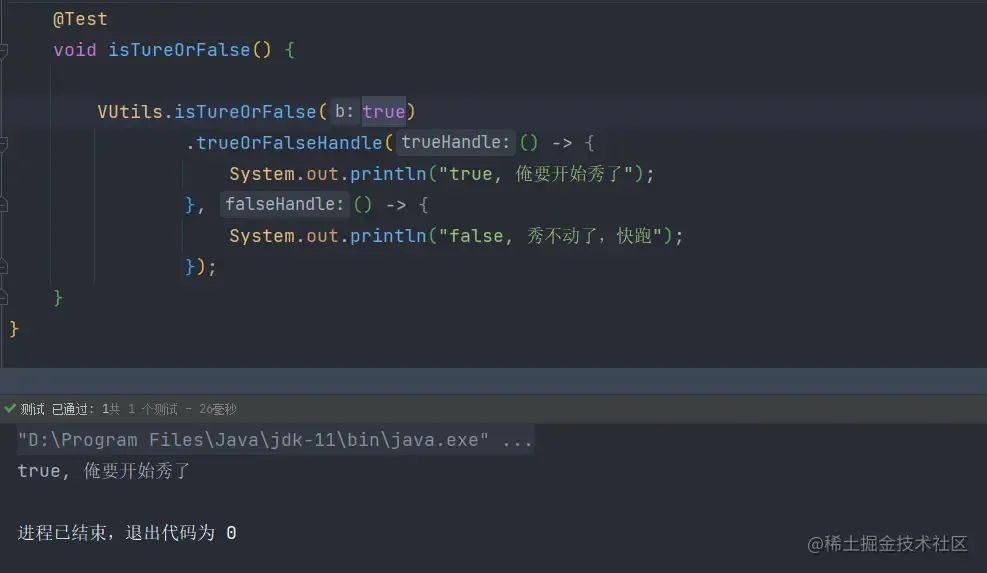
图片
参数为
false时,执行falseHandle 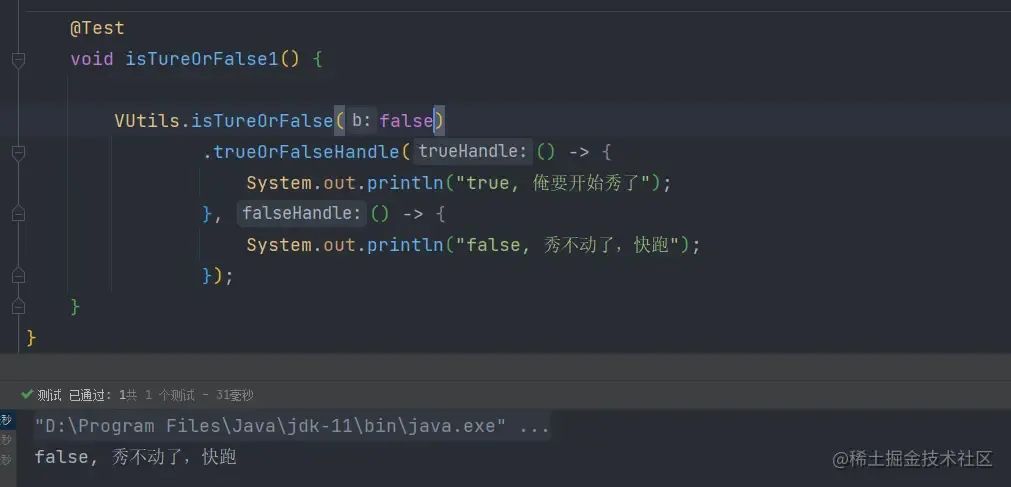
图片
如果存在值执行消费操作,否则执行基于空的操作
-
定义函数
创建一个名为
PresentOrElseHandler的函数式接口,接口的参数一个为Consumer接口。一个为Runnable,分别代表值不为空时执行消费操作和值为空时执行的其他操作 /**
* 空值与非空值分支处理
*/
public interface PresentOrElseHandler<T extends Object> {
/**
* 值不为空时执行消费操作
* 值为空时执行其他的操作
*
* @param action 值不为空时,执行的消费操作
* @param emptyAction 值为空时,执行的操作
* @return void
**/
void presentOrElseHandle(Consumer<? super T> action, Runnable emptyAction);
}
-
编写判断方法
创建一个名为
isBlankOrNoBlank的方法,方法的返回值为刚才定义的函数式接口-PresentOrElseHandler。 /**
* 参数为true或false时,分别进行不同的操作
*
* @param b
* @return com.example.demo.func.BranchHandle
**/
public static PresentOrElseHandler<?> isBlankOrNoBlank(String str){
return (consumer, runnable) -> {
if (str == null || str.length() == 0){
runnable.run();
} else {
consumer.accept(str);
}
};
}
-
使用方式
调用工具类参数参数后,调用
函数式接口的presentOrElseHandle方法传入一个Consumer和Runnable 参数不为空时,打印参数
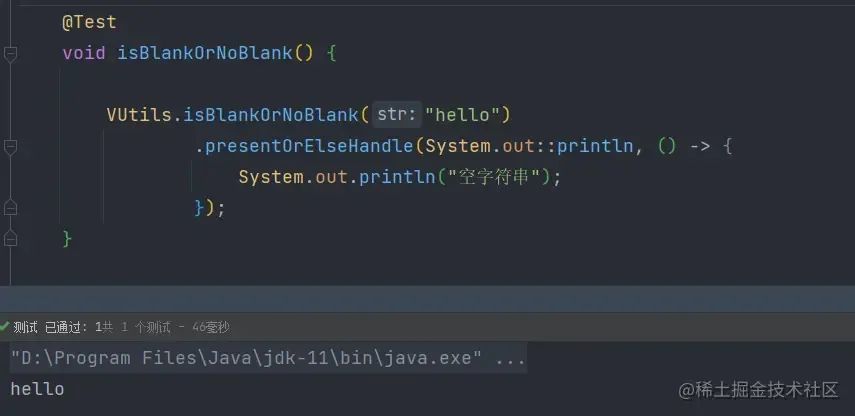
图片
参数不为空时
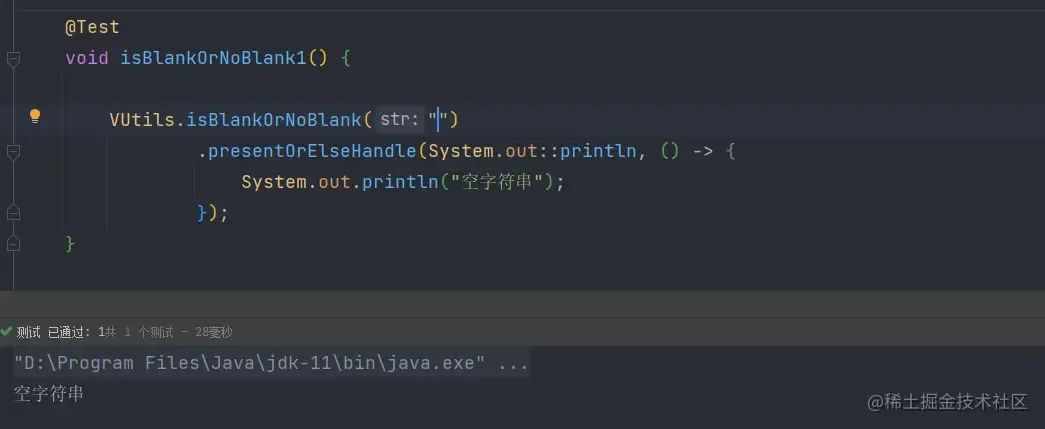
图片
推荐阅读:
我把SpringBoot的banner换成了美女,老板说工作不饱和,建议安排加班...
互联网初中高级大厂面试题(9个G)
内容包含Java基础、JavaWeb、MySQL性能优化、JVM、锁、百万并发、消息队列、高性能缓存、反射、Spring全家桶原理、微服务、Zookeeper......等技术栈!
⬇戳阅读原文领取! 朕已阅