JDK 源码解析:深入浅出异步任务 FutureTask
作者:Sumkor
来源:SegmentFault 思否社区
前言
在 Java 中,Runnable 接口表示一个没有返回结果的任务,而 Callable 接口表示具有返回结果的任务。
在并发编程中,异步执行任务,再获取任务结果,可以提高系统的吞吐量。Future 接口应运而生,它表示异步任务的执行结果,并提供了检查任务是否执行完、取消任务、获取任务执行结果等功能。FutureTask 是 Future 接口的基本实现,常与线程池实现类 ThreadPoolExecutor 配合使用。
| 本文基于 jdk1.8.0_91
1. 继承体系
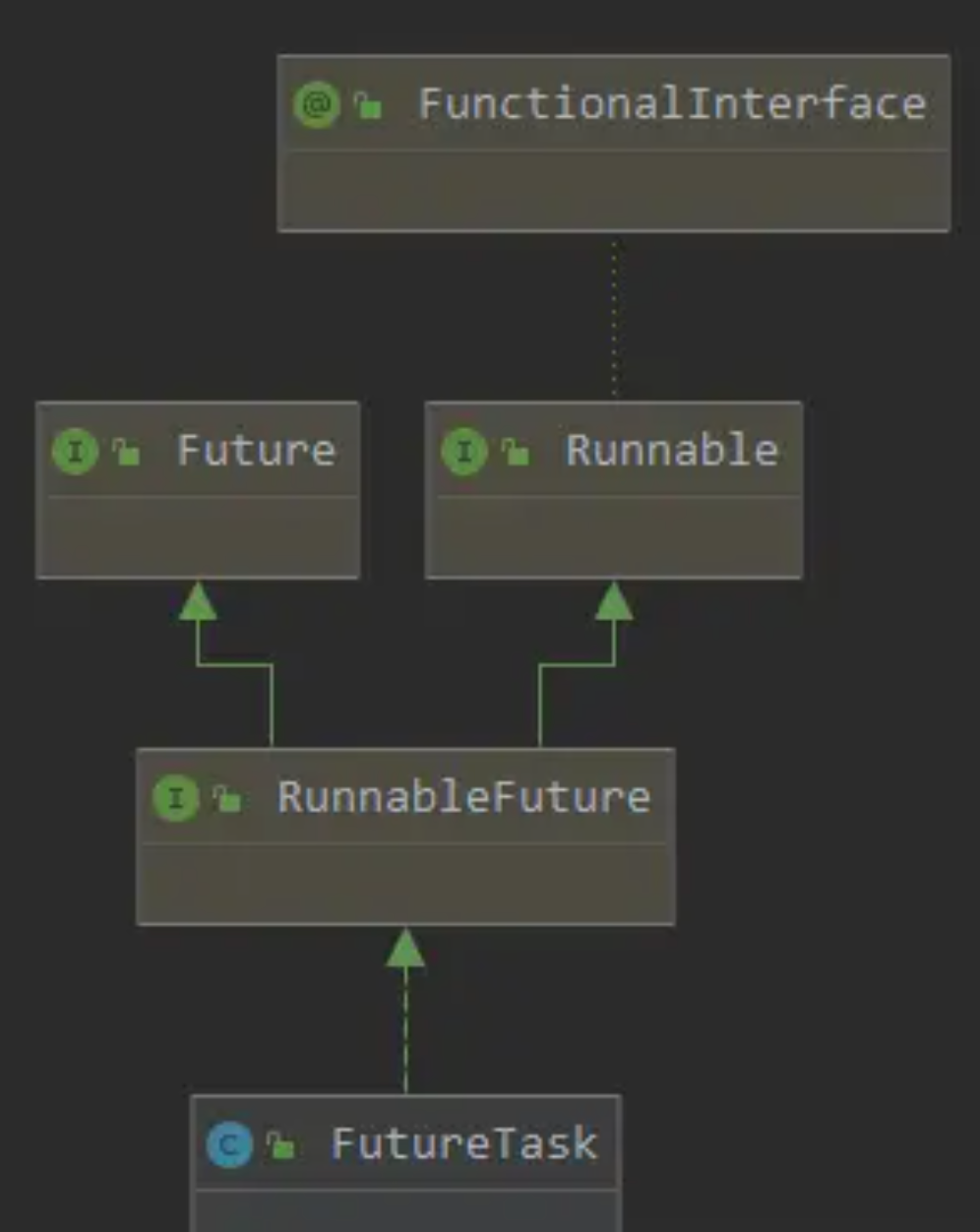
RunnableFuture 接口同时实现了 Runnable 接口和 Future 接口,是一种冗余设计。
java.util.concurrent.RunnableFuture
/*** A {@link Future} that is {@link Runnable}. Successful execution of* the {@code run} method causes completion of the {@code Future}* and allows access to its results.** @see FutureTask* @see Executor* @since 1.6* @author Doug Lea* @param <V> The result type returned by this Future's {@code get} method*/public interface RunnableFuture<V> extends Runnable, Future<V> {/*** Sets this Future to the result of its computation* unless it has been cancelled.*/void run();}
FutureTask 是一个可取消的异步任务,是对 Future 接口的基本实现,具有以下功能:
启动或中断的任务的执行;
判断任务是否执行完成;
获取任务执行完成后的结果。
同时,FutureTask 可以用于包装 Callable 或 Runnable 对象。
由于它实现了 Runnable 接口,可以提交给 Executor 执行。
/*** A cancellable asynchronous computation.** @since 1.5* @author Doug Lea* @param <V> The result type returned by this FutureTask's {@code get} methods*/public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V>
java.util.concurrent.Executor
/*** An object that executes submitted {@link Runnable} tasks.** @since 1.5* @author Doug Lea*/public interface Executor {void execute(Runnable command);}
2. 属性
java.util.concurrent.FutureTask
// The run state of this task, initially NEW.// 任务的执行状态,初始为 NEW。private volatile int state;/** The underlying callable; nulled out after running */// 需要执行的任务,任务执行完后为空private Callable<V> callable;/** The result to return or exception to throw from get() */// 任务的执行结果,或者任务抛出的异常private Object outcome; // non-volatile, protected by state reads/writes/** The thread running the callable; CASed during run() */// 执行任务的线程private volatile Thread runner;/** Treiber stack of waiting threads */// 指向栈顶的指针,栈结构用于存储等待任务执行结果的线程private volatile WaitNode waiters;
其中 state、runner、waiters 三个属性在并发时存在争用,采用 CAS 维护其准确性。
// Unsafe mechanicsprivate static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;private static final long stateOffset;private static final long runnerOffset;private static final long waitersOffset;static {try {UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();Class<?> k = FutureTask.class;stateOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("state"));runnerOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("runner"));waitersOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("waiters"));} catch (Exception e) {throw new Error(e);}}
2.1 状态定义
/*** The run state of this task, initially NEW. The run state* transitions to a terminal state only in methods set,* setException, and cancel. During completion, state may take on* transient values of COMPLETING (while outcome is being set) or* INTERRUPTING (only while interrupting the runner to satisfy a* cancel(true)). Transitions from these intermediate to final* states use cheaper ordered/lazy writes because values are unique* and cannot be further modified.** Possible state transitions:* NEW -> COMPLETING -> NORMAL* NEW -> COMPLETING -> EXCEPTIONAL* NEW -> CANCELLED* NEW -> INTERRUPTING -> INTERRUPTED*/private volatile int state;private static final int NEW = 0;private static final int COMPLETING = 1;private static final int NORMAL = 2;private static final int EXCEPTIONAL = 3;private static final int CANCELLED = 4;private static final int INTERRUPTING = 5;private static final int INTERRUPTED = 6;
FutureTask 中使用 state 代表任务在运行过程中的状态。随着任务的执行,状态将不断地进行转变。
状态的说明:
NEW:新建状态,任务都从该状态开始。
COMPLETING:任务正在执行中。
NORMAL:任务正常执行完成。
EXCEPTIONAL:任务执行过程中抛出了异常。
CANCELLED:任务被取消(不响应中断)。
INTERRUPTING:任务正在被中断。
INTERRUPTED:任务已经中断。
状态转移过程:
NEW -> COMPLETING -> NORMALNEW -> COMPLETING -> EXCEPTIONALNEW -> CANCELLEDNEW -> INTERRUPTING -> INTERRUPTED
状态的分类:
任务的初始状态:NEW
任务的中间状态:COMPLETING、INTERRUPTING
任务的终止状态:NORMAL、EXCEPTIONAL、CANCELLED、INTERRUPTED
2.1 状态使用
FutureTask 中判断任务是否已取消、是否已完成,是根据 state 来判断的。
public boolean isCancelled() {return state >= CANCELLED; // CANCELLED、INTERRUPTING、INTERRUPTED}public boolean isDone() {return state != NEW;}
可以看到:
被取消或被中断的任务(CANCELLED、INTERRUPTING、INTERRUPTED),都视为已取消。
当任务离开了初始状态 NEW,就视为任务已结束。任务的中间态很短暂,并不代表任务正在执行,而是任务已经执行完了,正在设置最终的返回结果。
根据状态值,FutureTask 可以保证已经完成的任务不会被再次运行或者被取消。
中间状态虽然是一个瞬时状态,在 FutureTask 中用于线程间的通讯。
例如:
在 FutureTask#run 中检测到状态 >= INTERRUPTING,说明其他线程发起了取消操作,当前线程需等待对方完成中断。
在 FutureTask#get 中检测到状态 <= COMPLETING,说明执行任务的线程尚未处理完,当前线程需等待对方完成任务。
2.2 栈(Treiber stack)
/** Treiber stack of waiting threads */private volatile WaitNode waiters; // 栈顶指针/*** Simple linked list nodes to record waiting threads in a Treiber* stack. See other classes such as Phaser and SynchronousQueue* for more detailed explanation.*/static final class WaitNode {volatile Thread thread; // 等待任务执行结果的线程volatile WaitNode next; // 栈的下一个节点WaitNode() { thread = Thread.currentThread(); }}
FutureTask 使用链表来构造栈(Treiber stack,使用 CAS 保证栈操作的线程安全,参考 java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue.TransferStack)。
其中 waiters 是链表的头节点,代表栈顶的指针。
栈的作用:
FutureTask 实现了 Future 接口,如果获取结果时,任务还没有执行完毕,那么获取结果的线程就在栈中挂起,直到任务执行完毕被唤醒。
3. 构造函数
赋值任务,设置任务的初始状态。
/*** Creates a {@code FutureTask} that will, upon running, execute the* given {@code Callable}.** @param callable the callable task* @throws NullPointerException if the callable is null*/public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) {if (callable == null)throw new NullPointerException();this.callable = callable;this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable}/*** Creates a {@code FutureTask} that will, upon running, execute the* given {@code Runnable}, and arrange that {@code get} will return the* given result on successful completion.** @param runnable the runnable task* @param result the result to return on successful completion. If* you don't need a particular result, consider using* constructions of the form:* {@code Future<?> f = new FutureTask<Void>(runnable, null)}* @throws NullPointerException if the runnable is null*/public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) {this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result);this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable}
值得注意的两个地方:
FutureTask 创建的时候,状态为 NEW。
由于 FutureTask 使用 Callable 表示任务,需用 Executors#callable 方法将 Runnable 转换为 Callable。
测试:
public void executors() throws Exception {Callable<String> callable = Executors.callable(new Runnable() {public void run() {System.out.println("run!");}}, "haha");String call = callable.call();System.out.println("call = " + call);}
执行结果:
run!call = haha
更多原文内容提前看:
Runnable 实现
FutureTask#run
FutureTask#set
FutureTask#setException
FutureTask#finishCompletion
FutureTask#handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt
FutureTask#runAndReset
Future 实现
Future#get
FutureTask#awaitDone
FutureTask#report
Future#get(timeout, unit)
Future#cancel
实例
总结