快收藏!我整理了100个Python小技巧!

导读:目前Python可以说是非常流行,在目前的编程语言中,Python的抽象程度是最高的,是最接近自然语言的,很容易上手。

numbers = [2, 4, 6, 8, 1]
for number in numbers:
if number % 2 == 1:
print(number)
break
else:
print("No odd numbers")
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
one, two, three, four, five = my_list
import heapq
scores = [51, 33, 64, 87, 91, 75, 15, 49, 33, 82]
print(heapq.nlargest(3, scores)) # [91, 87, 82]
print(heapq.nsmallest(5, scores)) # [15, 33, 33, 49, 51]
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4]
print(my_list) # [1, 2, 3, 4]
print(*my_list) # 1 2 3 4def sum_of_elements(*arg):
total = 0
for i in arg:
total += i
return total
result = sum_of_elements(*[1, 2, 3, 4])
print(result) # 10_, *elements_in_the_middle, _ = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
print(elements_in_the_middle) # [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
one, two, three, four = 1, 2, 3, 4
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
squared_numbers = [num * num for num in numbers]
print(squared_numbers) # [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]dictionary = {'a': 4, 'b': 5}
squared_dictionary = {key: num * num for (key, num) in dictionary.items()}
print(squared_dictionary) # {'a': 16, 'b': 25}
from enum import Enum
class Status(Enum):
NO_STATUS = -1
NOT_STARTED = 0
IN_PROGRESS = 1
COMPLETED = 2
print(Status.IN_PROGRESS.name) # IN_PROGRESS
print(Status.COMPLETED.value) # 2
name = "Banana"
print(name * 4) # BananaBananaBananaBanana
1 < x < 10x = 3
print(1 < x < 10) # True
print(1 < x and x < 10) # True
first_dictionary = {'name': 'Fan', 'location': 'Guangzhou'}
second_dictionary = {'name': 'Fan', 'surname': 'Xiao', 'location': 'Guangdong, Guangzhou'}
result = first_dictionary | second_dictionary
print(result)
# {'name': 'Fan', 'location': 'Guangdong, Guangzhou', 'surname': 'Xiao'}
books = ('Atomic habits', 'Ego is the enemy', 'Outliers', 'Mastery')
print(books.index('Mastery')) # 3input = "[1,2,3]"
import ast
def string_to_list(string):
return ast.literal_eval(string)
string = "[1, 2, 3]"
my_list = string_to_list(string)
print(my_list) # [1, 2, 3]
string = "[[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6]]"
my_list = string_to_list(string)
print(my_list) # [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
def subtract(a, b):
return a - b
print((subtract(1, 3))) # -2
print((subtract(3, 1))) # 2def subtract(a, b):
return a - b
print((subtract(a=1, b=3))) # -2
print((subtract(b=3, a=1))) # -2
print(1, 2, 3, "a", "z", "this is here", "here is something else")
print("Hello", end="")
print("World") # HelloWorld
print("Hello", end=" ")
print("World") # Hello World
print('words', 'with', 'commas', 'in', 'between', sep=', ')
# words, with, commas, in, between
print("29", "01", "2022", sep="/") # 29/01/2022
print("name", "domain.com", sep="@") # name@domain.com
four_letters = "abcd" # this works
4_letters = "abcd" # this doesn’t work+variable = "abcd" # this doesn’t work
number = 0110 # this doesn't worka______b = "abcd" # this works
_a_b_c_d = "abcd" # this also worksprint(1_000_000_000) # 1000000000
print(1_234_567) # 1234567my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
my_list.reverse()
print(my_list) # ['d', 'c', 'b', 'a']
my_string = "This is just a sentence"
print(my_string[0:5]) # This
# Take three steps forward
print(my_string[0:10:3]) # Tsse
my_string = "This is just a sentence"
print(my_string[10:0:-1]) # suj si sih
# Take two steps forward
print(my_string[10:0:-2]) # sjs i
my_string = "This is just a sentence"
print(my_string[4:]) # is just a sentence
print(my_string[:3]) # Thi
print(3/2) # 1.5
print(3//2) # 1
is:检查两个变量是否指向同一对象内存中
==:比较两个对象的值
first_list = [1, 2, 3]
second_list = [1, 2, 3]
# 比较两个值
print(first_list == second_list) # True
# 是否指向同一内存
print(first_list is second_list)
# False
third_list = first_list
print(third_list is first_list)
# True
dictionary_one = {"a": 1, "b": 2}
dictionary_two = {"c": 3, "d": 4}
merged = {**dictionary_one, **dictionary_two}
print(merged) # {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3, 'd': 4}
first = "abc"
second = "def"
print(first < second) # True
second = "ab"
print(first < second) # False
my_string = "abcdef"
print(my_string.startswith("b")) # False
print(id(1)) # 4325776624
print(id(2)) # 4325776656
print(id("string")) # 4327978288
number = 1
print(id(number)) # 4325215472
print(id(1)) # 4325215472
number = 3
print(id(number)) # 4325215536
print(id(1)) # 4325215472
name = "Fatos"
print(id(name)) # 4422282544
name = "fatos"
print(id(name)) # 4422346608
cities = ["Beijing", "Guangzhou", "chengdu"]
print(id(cities)) # 4482699712
cities.append("Beijing")
print(id(cities)) # 4482699712my_set = {1, 2, 3, 4}
print(id(my_set)) # 4352726176
my_set.add(5)
print(id(my_set)) # 4352726176
my_set = frozenset(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])
my_set.add("a")def check_number(number):
if number > 0:
return "Positive"
elif number == 0:
return "Zero"
return "Negative"
print(check_number(1)) # Positive
def check_if_anagram(first_word, second_word):
first_word = first_word.lower()
second_word = second_word.lower()
return sorted(first_word) == sorted(second_word)
print(check_if_anagram("testinG", "Testing")) # True
print(check_if_anagram("Here", "Rehe")) # True
print(check_if_anagram("Know", "Now")) # False
print(ord("A")) # 65
print(ord("B")) # 66
print(ord("C")) # 66
print(ord("a")) # 97
dictionary = {"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": 3}
keys = dictionary.keys()
print(list(keys)) # ['a', 'b', 'c']
dictionary = {"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": 3}
values = dictionary.values()
print(list(values)) # [1, 2, 3]
dictionary = {"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": 3}
reversed_dictionary = {j: i for i, j in dictionary.items()}
print(reversed) # {1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c'}
print(int(False)) # 0
print(float(True)) # 1.0x = 10
y = 12
result = (x - False)/(y * True)
print(result) # 0.8333333333333334print(bool(.0)) # False
print(bool(3)) # True
print(bool("-")) # True
print(bool("string")) # True
print(bool(" ")) # Trueprint(complex(10, 2)) # (10+2j)print(hex(11)) # 0xbmy_list = [3, 4, 5]
my_list.append(6)
my_list.insert(0, 2)
print(my_list) # [2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
comparison = lambda x: if x > 3:
print("x > 3")
else:
print("x is not greater than 3")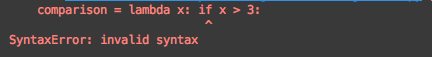
comparison = lambda x: "x > 3" if x > 3
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4]
odd = filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 1, my_list)
print(list(odd)) # [1, 3]
print(my_list) # [1, 2, 3, 4]my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4]
squared = map(lambda x: x ** 2, my_list)
print(list(squared)) # [1, 4, 9, 16]
print(my_list) # [1, 2, 3, 4]
for number in range(1, 10, 3):
print(number, end=" ")
# 1 4 7
def range_with_zero(number):
for i in range(0, number):
print(i, end=' ')
def range_with_no_zero(number):
for i in range(number):
print(i, end=' ')
range_with_zero(3) # 0 1 2
range_with_no_zero(3) # 0 1 2
def get_element_with_comparison(my_list):
if len(my_list) > 0:
return my_list[0]
def get_first_element(my_list):
if len(my_list):
return my_list[0]
elements = [1, 2, 3, 4]
first_result = get_element_with_comparison(elements)
second_result = get_element_with_comparison(elements)
print(first_result == second_result) # True
def get_address():
return "First address"
def get_address():
return "Second address"
def get_address():
return "Third address"
print(get_address()) # Third addressclass Engineer:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
self.__starting_salary = 62000
dain = Engineer('Dain')
print(dain._Engineer__starting_salary) # 62000
import sys
print(sys.getsizeof("bitcoin")) # 56
def get_sum(*arguments):
result = 0
for i in arguments:
result += i
return result
print(get_sum(1, 2, 3)) # 6
print(get_sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)) # 15
print(get_sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7)) # 28class Parent:
def __init__(self, city, address):
self.city = city
self.address = address
class Child(Parent):
def __init__(self, city, address, university):
super().__init__(city, address)
self.university = university
child = Child('Peking University', 'Fudan University', 'Tsinghua University')
print(child.university) # Tsinghua University
class Parent:
def __init__(self, city, address):
self.city = city
self.address = address
class Child(Parent):
def __init__(self, city, address, university):
Parent.__init__(self, city, address)
self.university = university
child = Child('Peking University', 'Fudan University', 'Tsinghua University')
print(child.university) # Tsinghua Universityprint(10 + 1) # 两数相加
print('first' + 'second') # 字符串相加
class Expenses:
def __init__(self, rent, groceries):
self.rent = rent
self.groceries = groceries
def __add__(self, other):
return Expenses(self.rent + other.rent,
self.groceries + other.groceries)
april_expenses = Expenses(1000, 200)
may_expenses = Expenses(1000, 300)
total_expenses = april_expenses + may_expenses
print(total_expenses.rent) # 2000
print(total_expenses.groceries) # 500class Game:
def __init__(self, score):
self.score = score
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.score < other.score
first = Game(1)
second = Game(2)
print(first < second) # Trueclass Journey:
def __init__(self, location, destination, duration):
self.location = location
self.destination = destination
self.duration = duration
def __eq__(self, other):
return ((self.location == other.location) and
(self.destination == other.destination) and
(self.duration == other.duration))
first = Journey('Location A', 'Destination A', '30min')
second = Journey('Location B', 'Destination B', '30min')
print(first == second)
__sub__() for -
__mul__() for *
__truediv__() for /
__ne__() for !=
__ge__() for >=
__gt__() for >
class Rectangle:
def __init__(self, a, b):
self.a = a
self.b = b
def __repr__(self):
return repr('Rectangle with area=' + str(self.a * self.b))
print(Rectangle(3, 4)) # 'Rectangle with area=12'
string = "This is just a sentence."
result = string.swapcase()
print(result) # tHIS IS JUST A SENTENCE.
string = " "
result = string.isspace()
print(result) # Truename = "Password"
print(name.isalnum()) # True
name = "Secure Password "
print(name.isalnum()) # False
name = "S3cur3P4ssw0rd"
print(name.isalnum()) # True
name = "133"
print(name.isalnum()) # True
string = "Name"
print(string.isalpha()) # True
string = "Firstname Lastname"
print(string.isalpha()) # False
string = "P4ssw0rd"
print(string.isalpha()) # False
string = "This is a sentence with "
print(string.rstrip()) # "This is a sentence with"
string = "this here is a sentence…..,,,,aaaaasd"
print(string.rstrip(".,dsa")) # "this here is a sentence"string = "ffffffffFirst"
print(string.lstrip("f")) # First
string = "seven"
print(string.isdigit()) # False
string = "1337"
print(string.isdigit()) # True
string = "5a"
print(string.isdigit()) # False
string = "2**5"
print(string.isdigit()) # False
# 42673
string = "四二六七三"
print(string.isdigit()) # False
print(string.isnumeric()) # Truestring = "This is a sentence"
print(string.istitle()) # False
string = "10 Python Tips"
print(string.istitle()) # True
string = "How to Print A String in Python"
# False
print(string.istitle())
string = "PYTHON"
print(string.istitle()) # False
numbers = (1, 2, 3, 4)
print(numbers[-1]) # 4
print(numbers[-4]) # 1
mixed_tuple = (("a"*10, 3, 4), ['first', 'second', 'third'])
print(mixed_tuple[1]) # ['first', 'second', 'third']
print(mixed_tuple[0]) # ('aaaaaaaaaa', 3, 4)
names = ["Besim", "Albert", "Besim", "Fisnik", "Meriton"]
print(names.count("Besim")) # 2
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
slicing = slice(-4, None)
print(my_list[slicing]) # [4, 5, 6]
print(my_list[-3]) # 4string = "Data Science"
slice_object = slice(5, None)
print(string[slice_object]) # Sciencemy_tuple = ('a', 1, 'f', 'a', 5, 'a')
print(my_tuple.count('a')) # 3
my_tuple = ('a', 1, 'f', 'a', 5, 'a')
print(my_tuple.index('f')) # 2
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)
print(my_tuple[::3]) # (1, 4, 7, 10)
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)
print(my_tuple[3:]) # (4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4]
my_list.clear()
print(my_list) # []
my_set = {1, 2, 3}
my_set.clear()
print(my_set) # set()
my_dict = {"a": 1, "b": 2}
my_dict.clear()
print(my_dict) # {}
first_set = {4, 5, 6}
second_set = {1, 2, 3}
print(first_set.union(second_set)) # {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}first_set = {4, 5, 6}
second_set = {1, 2, 3}
first_set.update(second_set)
print(first_set) # {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
def is_positive(number):
print("Positive" if number > 0 else "Negative") # Positive
is_positive(-3)
math_points = 51
biology_points = 78
physics_points = 56
history_points = 72
my_conditions = [math_points > 50, biology_points > 50,
physics_points > 50, history_points > 50]
if all(my_conditions):
print("Congratulations! You have passed all of the exams.")
else:
print("I am sorry, but it seems that you have to repeat at least one exam.")
# Congratulations! You have passed all of the exams.
math_points = 40
biology_points = 78
physics_points = 56
history_points = 72
my_conditions = [math_points > 50, biology_points > 50,
physics_points > 50, history_points > 50]
if any(my_conditions):
print("Congratulations! You have passed all of the exams.")
else:
print("I am sorry, but it seems that you have to repeat at least one exam.")
# Congratulations! You have passed all of the exams.print(bool("Non empty")) # True
print(bool("")) # False
print(bool([])) # False
print(bool(set([]))) # False
print(bool({})) # False
print(bool({"a": 1})) # True
print(bool(False)) # False
print(bool(None)) # False
print(bool(0)) # False
string = "string"
def do_nothing():
string = "inside a method"
do_nothing()
print(string) # stringstring = "string"
def do_nothing():
global string
string = "inside a method"
do_nothing()
print(string) # inside a methodfrom collections import Counter
result = Counter("Banana")
print(result) # Counter({'a': 3, 'n': 2, 'B': 1})
result = Counter([1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 1, 6])
print(result) # Counter({1: 5, 2: 1, 3: 1, 4: 1, 5: 1, 6: 1})
from collections import Counter
def check_if_anagram(first_string, second_string):
first_string = first_string.lower()
second_string = second_string.lower()
return Counter(first_string) == Counter(second_string)
print(check_if_anagram('testinG', 'Testing')) # True
print(check_if_anagram('Here', 'Rehe')) # True
print(check_if_anagram('Know', 'Now')) # Falsedef check_if_anagram(first_word, second_word):
first_word = first_word.lower()
second_word = second_word.lower()
return sorted(first_word) == sorted(second_word)
print(check_if_anagram("testinG", "Testing")) # True
print(check_if_anagram("Here", "Rehe")) # True
print(check_if_anagram("Know", "Now")) # False
from itertools import count
my_vowels = ['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u', 'A', 'E', 'I', 'O', 'U']
current_counter = count()
string = "This is just a sentence."
for i in string:
if i in my_vowels:
print(f"Current vowel: {i}")
print(f"Number of vowels found so far: {next(current_counter)}")
Current vowel: i
Number of vowels found so far: 0
Current vowel: i
Number of vowels found so far: 1
Current vowel: u
Number of vowels found so far: 2
Current vowel: a
Number of vowels found so far: 3
Current vowel: e
Number of vowels found so far: 4
Current vowel: e
Number of vowels found so far: 5
Current vowel: e
Number of vowels found so far: 6
from collections import Counter
result = Counter([1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 2, 2])
print(result) # Counter({2: 5, 1: 1, 3: 1})
print(result.most_common()) # [(2, 5), (1, 1), (3, 1)]
my_list = ['1', 1, 0, 'a', 'b', 2, 'a', 'c', 'a']
print(max(set(my_list), key=my_list.count)) # a浅拷贝: 拷贝父对象,但是不会拷贝对象的内部的子对象。
深拷贝: 拷贝父对象,以及其内部的子对象。
first_list = [[1, 2, 3], ['a', 'b', 'c']]
second_list = first_list.copy()
first_list[0][2] = 831
print(first_list) # [[1, 2, 831], ['a', 'b', 'c']]
print(second_list) # [[1, 2, 831], ['a', 'b', 'c']]
import copy
first_list = [[1, 2, 3], ['a', 'b', 'c']]
second_list = copy.deepcopy(first_list)
first_list[0][2] = 831
print(first_list) # [[1, 2, 831], ['a', 'b', 'c']]
print(second_list) # [[1, 2, 3], ['a', 'b', 'c']]my_dictonary = {"name": "Name", "surname": "Surname"}
print(my_dictonary["age"]) KeyError: 'age'from collections import defaultdict
my_dictonary = defaultdict(str)
my_dictonary['name'] = "Name"
my_dictonary['surname'] = "Surname"
print(my_dictonary["age"]) class OddNumbers:
def __iter__(self):
self.a = 1
return self
def __next__(self):
x = self.a
self.a += 2
return x
odd_numbers_object = OddNumbers()
iterator = iter(odd_numbers_object)
print(next(iterator)) # 1
print(next(iterator)) # 3
print(next(iterator)) # 5
my_set = set([1, 2, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(list(my_set)) # [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]import pandas
print(pandas) # <module 'torch' from '/Users/...'odd_numbers = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
even_numbers = []
for i in range(9):
if i not in odd_numbers:
even_numbers.append(i)
print(even_numbers) # [0, 2, 4, 6, 8]sort():对原始列表进行排序
sorted():返回一个新的排序列表
groceries = ['milk', 'bread', 'tea']
new_groceries = sorted(groceries)
# new_groceries = ['bread', 'milk', 'tea']
print(new_groceries)
# groceries = ['milk', 'bread', 'tea']
print(groceries)
groceries.sort()
# groceries = ['bread', 'milk', 'tea']
print(groceries)import uuid
# 根据主机ID、序列号和当前时间生成UUID
print(uuid.uuid1()) # 308490b6-afe4-11eb-95f7-0c4de9a0c5af
# 生成一个随机UUID
print(uuid.uuid4()) # 93bc700b-253e-4081-a358-24b60591076a

评论
